https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsf-hmm
Estimation of per-individual inbreeding tracts under a probabilistic framework
https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsf-hmm
genotype-likelihoods hmm inbreeding ngs population-genomics
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
Estimation of per-individual inbreeding tracts under a probabilistic framework
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsf-hmm
- Owner: fgvieira
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2014-03-05T14:42:27.000Z (over 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-08-11T10:32:08.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-10-20T19:49:40.569Z (about 2 years ago)
- Topics: genotype-likelihoods, hmm, inbreeding, ngs, population-genomics
- Language: C++
- Homepage:
- Size: 303 KB
- Stars: 13
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# ngsF-HMM
`ngsF-HMM` is a program to estimate per-individual inbreeding tracts using a two-state Hidden Markov Model (HMM). Furthermore, instead of using called genotypes, it uses a probabilistic framework that takes the uncertainty of genotype's assignation into account; making it specially suited for low-quality or low-coverage datasets.
### Citation
`ngsF-HMM` was published in 2016 at [Bioinformatics](http://bioinformatics.oxfordjournals.org/content/32/14/2096), so please cite it if you use it in your work:
Vieira FG, Albrechtsen A and Nielsen R
Estimating IBD tracts from low coverage NGS data
Bioinformatics (2016) 32: 2096-2102
### Installation
`ngsF-HMM` can be easily installed but has some external dependencies:
* Mandatory:
* `gcc`: >= 4.9.2 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)
* `zlib`: v1.2.7 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)
* `gsl` : v1.15 tested on Debian 7.8 (wheezy)
* Optional (only needed for testing or auxilliary scripts):
* `md5sum`
* `Perl` packages: `Getopt::Long`, and `IO::Zlib`
* `R` packages: `optparse`, and `plyr`
To install the entire package just download the source code:
% git clone https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsF-HMM.git
and run:
% cd ngsF-HMM
% make
To run the tests (only if installed through [ngsTools](https://github.com/mfumagalli/ngsTools)):
% make test
Executables are built into the main directory. If you wish to clean all binaries and intermediate files:
% make clean
### Usage
% ./ngsF-HMM [options] --n_ind INT --n_sites INT --glf glf/in/file --out output/file
#### Parameters
* `--geno FILE`: input file with genotypes, genotype likelihoods or genotype posterior probabilities.
* `--pos` FILE: input file with site coordinates (one per line), where the 1st column stands for the chromosome/contig and the 2nd for the position (bp); remaining columns are ignored.
* `--lkl`: input are genotype likelihoods (BEAGLE format).
* `--loglkl`: input are genotype log-likelihoods.
* `--n_ind INT`: sample size (number of individuals).
* `--n_sites INT`: total number of sites.
* `--call_geno`: call genotypes before running analyses.
* `--freq DOUBLE or CHAR`: initial frequency values. Can be defined by user as a DOUBLE, (r)andom, (e)stimated or read from a FILE.
* `--freq_est INT`: allele frequency estimation method: 0) fixed (no optimizatopn); 1) assuming independence of sites; and 2) through haplotype frequency.
* `--indF DOUBLE-DOUBLE or CHAR`: initial inbreeding and transition parameter values. Can be defined by user as a DOUBLE-DOUBLE, (r)andom, or read from a FILE.
* `--indF_fixed`: inbreeding parameter values are fixed (will not be optimized).
* `--alpha_fixed`: transition parameter values are fixed (will not be optimized).
* `--out CHAR`: prefix for output files.
* `--log INT`: dump LOG file each INT iterations. [0]
* `--log_bin`: dump LOG file in binary.
* `--min_iters INT`: minimum number of EM iterations. [10]
* `--max_iters INT`: maximum number of EM iterations. [100]
* `--min_epsilon FLOAT`: maximum RMSD between iterations to assume convergence. [1e-5]
* `--n_threads INT`: number of threads to use. [1]
* `--verbose INT`: selects verbosity level. [1]
* `--seed INT`: seed for random number generator.
### Input data
As input, `ngsF-HMM` accepts both genotypes, genotype likelihoods (GP) or genotype posterior probabilities (GP). Genotypes must be input as gziped TSV with one row per site and one column per individual 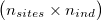 and genotypes coded as [-1, 0, 1, 2]. The file can have a header and an arbitrary number of columns preceeding the actual data (that will all be ignored), much like the Beagle file format ([link](http://faculty.washington.edu/browning/beagle/beagle.html)).
As for GL and GP, `ngsF-HMM` accepts both gzipd TSV and binary formats, but with 3 columns per individual 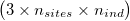 and, in the case of binary, the GL/GP coded as doubles.
### Stopping Criteria
An issue on iterative algorithms is the stopping criteria. `ngsF-HMM` implements a dual condition threshold: relative difference in log-likelihood and estimates RMSD (F and freq). As for which threshold to use, simulations show that 1e-5 seems to be a reasonable value. However, if you're dealing with low coverage data (2x-3x), it might be worth to use lower thresholds (between 1e-6 and 1e-9).
To avoid convergence to local maxima, ngsF-HMM should be run several times from different starting points. To make this task easier, a script (`ngsF-HMM.sh`) is provided that can be called with the exact same parameters as `ngsF-HMM`.
### Output files
`ngsF-HMM` will output several files, some depending on input options:
* `.indF`: file similar to [ngsF](https://github.com/fgvieira/ngsF) output format, where the first line stands for the final log-likelihood, followed by per individual (one per line) inbreeding coefficients (1st column) and transition rate parameters (2nd column) and, finally, the per-site minor allele frequency.
* `.ibd`: file storing IBD tracts results, where the first line stores per-individual log-likelihoods. The following lines (one per individual) contain the most-probable inbreeding tracts coded as an INT per site (0: position is not IBD; 1: position is IBD), followed by the IBD posterior probabilities coded as a FLOAT per site (one line per individual).
* `.geno`: binary file with genotype posterior probabilities (similar to ANGSD `-doGeno 32`).
* `.log.gz`: if option `-log INT` is specified, a gziped log file similar to `.ibd` is printed every `INT` iterations.
* `.pdf`: optionally, the `scripts/ngsF-HMMplot.R` script can be used to plot the IBD tracts.
### Thread pool
The thread pool implementation was adapted from Mathias Brossard's and is freely available from:
https://github.com/mbrossard/threadpool