https://github.com/firefly-cpp/niaarm
A minimalistic framework for Numerical Association Rule Mining
https://github.com/firefly-cpp/niaarm
association-rule-mining association-rules data-mining data-science evolutionary-algorithms swarm-intelligence
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
A minimalistic framework for Numerical Association Rule Mining
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/firefly-cpp/niaarm
- Owner: firefly-cpp
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-11-23T12:11:15.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-21T08:51:26.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-11T12:07:31.108Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: association-rule-mining, association-rules, data-mining, data-science, evolutionary-algorithms, swarm-intelligence
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 44 MB
- Stars: 16
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

NiaARM
A minimalistic framework for Numerical Association Rule Mining
🔍 Detailed insights •
📦 Installation •
🚀 Usage •
📄 Cite us •
📚 References •
📖 See also •
🔑 License •
🫂 Contributors
NiaARM is a framework for Association Rule Mining based on nature-inspired algorithms for optimization. 🌿 The framework is written fully in Python and runs on all platforms. NiaARM allows users to preprocess the data in a transaction database automatically, to search for association rules and provide a pretty output of the rules found. 📊 This framework also supports integral and real-valued types of attributes besides the categorical ones. Mining the association rules is defined as an optimization problem, and solved using the nature-inspired algorithms that come from the related framework called [NiaPy](https://github.com/NiaOrg/NiaPy). 🔗
* **Documentation:** https://niaarm.readthedocs.io/en/latest
* **Tested OS:** Windows, Ubuntu, Fedora, Alpine, Arch, macOS. **However, that does not mean it does not work on others**
## 🔍 Detailed insights
The current version includes (but is not limited to) the following functions:
- loading datasets in CSV format 📁
- preprocessing of data 🧹
- searching for association rules 🔎
- providing output of mined association rules 📋
- generating statistics about mined association rules 📊
- visualization of association rules 📈
- association rule text mining (experimental) 📄
## 📦 Installation
### pip
To install `NiaARM` with pip, use:
```sh
pip install niaarm
```
To install `NiaARM` on Alpine Linux, enable Community repository and use:
```sh
$ apk add py3-niaarm
```
To install `NiaARM` on Arch Linux, use an [AUR helper](https://wiki.archlinux.org/title/AUR_helpers):
```sh
$ yay -Syyu python-niaarm
```
To install `NiaARM` on Fedora, use:
```sh
$ dnf install python3-niaarm
```
To install `NiaARM` on NixOS, use:
```sh
nix-env -iA nixos.python311Packages.niaarm
```
## 🚀 Usage
### Loading data
In NiaARM, data loading is done via the `Dataset` class. There are two options for loading data:
#### Option 1: From a pandas DataFrame (recommended)
```python
import pandas as pd
from niaarm import Dataset
df = pd.read_csv('datasets/Abalone.csv')
# preprocess data...
data = Dataset(df)
print(data) # printing the dataset will generate a feature report
```
#### Option 2: Directly from a CSV file
```python
from niaarm import Dataset
data = Dataset('datasets/Abalone.csv')
print(data)
```
### Preprocessing
#### Data Squashing
Optionally, a preprocessing technique, called data squashing [5], can be applied. This will significantly reduce the number of transactions, while providing similar results to the original dataset.
```python
from niaarm import Dataset, squash
dataset = Dataset('datasets/Abalone.csv')
squashed = squash(dataset, threshold=0.9, similarity='euclidean')
print(squashed)
```
### Mining association rules
#### The easy way (recommended)
Association rule mining can be easily performed using the `get_rules` function:
```python
from niaarm import Dataset, get_rules
from niapy.algorithms.basic import DifferentialEvolution
data = Dataset("datasets/Abalone.csv")
algo = DifferentialEvolution(population_size=50, differential_weight=0.5, crossover_probability=0.9)
metrics = ('support', 'confidence')
rules, run_time = get_rules(data, algo, metrics, max_iters=30, logging=True)
print(rules) # Prints basic stats about the mined rules
print(f'Run Time: {run_time}')
rules.to_csv('output.csv')
```
#### The hard way
The above example can be also be implemented using a more low level interface,
with the `NiaARM` class directly:
```python
from niaarm import NiaARM, Dataset
from niapy.algorithms.basic import DifferentialEvolution
from niapy.task import Task, OptimizationType
data = Dataset("datasets/Abalone.csv")
# Create a problem
# dimension represents the dimension of the problem;
# features represent the list of features, while transactions depicts the list of transactions
# metrics is a sequence of metrics to be taken into account when computing the fitness;
# you can also pass in a dict of the shape {'metric_name': };
# when passing a sequence, the weights default to 1.
problem = NiaARM(data.dimension, data.features, data.transactions, metrics=('support', 'confidence'), logging=True)
# build niapy task
task = Task(problem=problem, max_iters=30, optimization_type=OptimizationType.MAXIMIZATION)
# use Differential Evolution (DE) algorithm from the NiaPy library
# see full list of available algorithms: https://github.com/NiaOrg/NiaPy/blob/master/Algorithms.md
algo = DifferentialEvolution(population_size=50, differential_weight=0.5, crossover_probability=0.9)
# run algorithm
best = algo.run(task=task)
# sort rules
problem.rules.sort()
# export all rules to csv
problem.rules.to_csv('output.csv')
```
#### Interest measures
The framework implements several popular interest measures, which can be used to compute the fitness function value of rules
and for assessing the quality of the mined rules. A full list of the implemented interest measures along with their descriptions
and equations can be found [here](interest_measures.md).
### Visualization
The framework currently supports ([visualizations](visualization.md)):
- hill slopes (presented in [4]),
- scatter plot and
- grouped matrix plot visualization methods.
More visualization methods are planned to be implemented in future releases.
#### Hill Slopes
```python
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from niaarm import Dataset, get_rules
from niaarm.visualize import hill_slopes
dataset = Dataset('datasets/Abalone.csv')
metrics = ('support', 'confidence')
rules, _ = get_rules(dataset, 'DifferentialEvolution', metrics, max_evals=1000, seed=1234)
some_rule = rules[150]
hill_slopes(some_rule, dataset.transactions)
plt.show()
```
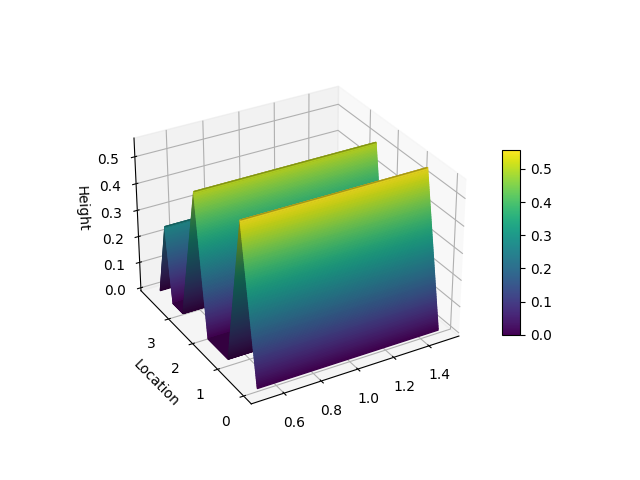
#### Scatter Plot
```python
from examples.visualization_examples.prepare_datasets import get_weather_data
from niaarm import Dataset, get_rules
from niaarm.visualize import scatter_plot
# Get prepared data
arm_df = get_weather_data()
# Prepare Dataset
dataset = Dataset(path_or_df=arm_df,delimiter=",")
# Get rules
metrics = ("support", "confidence")
rules, run_time = get_rules(dataset, "DifferentialEvolution", metrics, max_evals=500)
# Add lift to metrics
metrics = list(metrics)
metrics.append("lift")
metrics = tuple(metrics)
# Visualize scatter plot
fig = scatter_plot(rules=rules, metrics=metrics, interactive=False)
fig.show()
```

#### Grouped Matrix Plot
```python
from examples.visualization_examples.prepare_datasets import get_football_player_data
from niaarm import Dataset, get_rules
from niaarm.visualize import grouped_matrix_plot
# Get prepared data
arm_df = get_football_player_data()
# Prepare Dataset
dataset = Dataset(path_or_df=arm_df, delimiter=",")
# Get rules
metrics = ("support", "confidence")
rules, run_time = get_rules(dataset, "DifferentialEvolution", metrics, max_evals=500)
# Add lift to metrics
metrics = list(metrics)
metrics.append("lift")
metrics = tuple(metrics)
# Visualize grouped matrix plot
fig = grouped_matrix_plot(rules=rules, metrics=metrics, k=5, interactive=False)
fig.show()
```

### Text Mining (Experimental)
An experimental implementation of association rule text mining using nature-inspired algorithms, based on ideas from [5]
is also provided. The `niaarm.text` module contains the `Corpus` and `Document` classes for loading and preprocessing corpora,
a `TextRule` class, representing a text rule, and the `NiaARTM` class, implementing association rule text mining
as a continuous optimization problem. The `get_text_rules` function, equivalent to `get_rules`, but for text mining, was also
added to the `niaarm.mine` module.
```python
import pandas as pd
from niaarm.text import Corpus
from niaarm.mine import get_text_rules
from niapy.algorithms.basic import ParticleSwarmOptimization
df = pd.read_json('datasets/text/artm_test_dataset.json', orient='records')
documents = df['text'].tolist()
corpus = Corpus.from_list(documents)
algorithm = ParticleSwarmOptimization(population_size=200, seed=123)
metrics = ('support', 'confidence', 'aws')
rules, time = get_text_rules(corpus, max_terms=5, algorithm=algorithm, metrics=metrics, max_evals=10000, logging=True)
print(rules)
print(f'Run time: {time:.2f}s')
rules.to_csv('output.csv')
```
**Note:** You may need to download stopwords and the punkt tokenizer from nltk by running `import nltk; nltk.download('stopwords'); nltk.download('punkt')`.
For a full list of examples see the [examples folder](https://github.com/firefly-cpp/NiaARM/tree/main/examples)
in the GitHub repository.
### Command line interface
We provide a simple command line interface, which allows you to easily
mine association rules on any input dataset, output them to a csv file and/or perform
a simple statistical analysis on them. For more details see the [documentation](https://niaarm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/cli.html).
```shell
niaarm -h
```
```
usage: niaarm [-h] [-v] [-c CONFIG] [-i INPUT_FILE] [-o OUTPUT_FILE] [--squashing-similarity {euclidean,cosine}] [--squashing-threshold SQUASHING_THRESHOLD] [-a ALGORITHM] [-s SEED] [--max-evals MAX_EVALS] [--max-iters MAX_ITERS]
[--metrics METRICS [METRICS ...]] [--weights WEIGHTS [WEIGHTS ...]] [--log] [--stats]
Perform ARM, output mined rules as csv, get mined rules' statistics
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
-c CONFIG, --config CONFIG
Path to a TOML config file
-i INPUT_FILE, --input-file INPUT_FILE
Input file containing a csv dataset
-o OUTPUT_FILE, --output-file OUTPUT_FILE
Output file for mined rules
--squashing-similarity {euclidean,cosine}
Similarity measure to use for squashing
--squashing-threshold SQUASHING_THRESHOLD
Threshold to use for squashing
-a ALGORITHM, --algorithm ALGORITHM
Algorithm to use (niapy class name, e.g. DifferentialEvolution)
-s SEED, --seed SEED Seed for the algorithm's random number generator
--max-evals MAX_EVALS
Maximum number of fitness function evaluations
--max-iters MAX_ITERS
Maximum number of iterations
--metrics METRICS [METRICS ...]
Metrics to use in the fitness function.
--weights WEIGHTS [WEIGHTS ...]
Weights in range [0, 1] corresponding to --metrics
--log Enable logging of fitness improvements
--stats Display stats about mined rules
```
Note: The CLI script can also run as a python module (`python -m niaarm ...`)
## 📄 Cite us
Stupan, Ž., & Fister Jr., I. (2022). [NiaARM: A minimalistic framework for Numerical Association Rule Mining](https://www.theoj.org/joss-papers/joss.04448/10.21105.joss.04448.pdf). Journal of Open Source Software, 7(77), 4448.
## 📚 References
Ideas are based on the following research papers:
[1] I. Fister Jr., A. Iglesias, A. Gálvez, J. Del Ser, E. Osaba, I Fister. [Differential evolution for association rule mining using categorical and numerical attributes](http://www.iztok-jr-fister.eu/static/publications/231.pdf) In: Intelligent data engineering and automated learning - IDEAL 2018, pp. 79-88, 2018.
[2] I. Fister Jr., V. Podgorelec, I. Fister. [Improved Nature-Inspired Algorithms for Numeric Association Rule Mining](https://iztok-jr-fister.eu/static/publications/324.pdf). In: Vasant P., Zelinka I., Weber GW. (eds) Intelligent Computing and Optimization. ICO 2020. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 1324. Springer, Cham.
[3] I. Fister Jr., I. Fister [A brief overview of swarm intelligence-based algorithms for numerical association rule mining](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.15524). arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.15524 (2020).
[4] Fister, I. et al. (2020). [Visualization of Numerical Association Rules by Hill Slopes](http://www.iztok-jr-fister.eu/static/publications/280.pdf).
In: Analide, C., Novais, P., Camacho, D., Yin, H. (eds) Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning – IDEAL 2020.
IDEAL 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12489. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-62362-3_10
[5] I. Fister, S. Deb, I. Fister, [Population-based metaheuristics for Association Rule Text Mining](http://www.iztok-jr-fister.eu/static/publications/260.pdf),
In: Proceedings of the 2020 4th International Conference on Intelligent Systems, Metaheuristics & Swarm Intelligence,
New York, NY, USA, mar. 2020, pp. 19–23. doi: [10.1145/3396474.3396493](https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.1145/3396474.3396493).
[6] I. Fister, I. Fister Jr., D. Novak and D. Verber, [Data squashing as preprocessing in association rule mining](https://iztok-jr-fister.eu/static/publications/300.pdf), 2022 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Singapore, Singapore, 2022, pp. 1720-1725, doi: [10.1109/SSCI51031.2022.10022240](https://doi.org/10.1109/SSCI51031.2022.10022240).
## 📖 See also
[1] [NiaARM.jl: Numerical Association Rule Mining in Julia](https://github.com/firefly-cpp/NiaARM.jl)
[2] [arm-preprocessing: Implementation of several preprocessing techniques for Association Rule Mining (ARM)](https://github.com/firefly-cpp/arm-preprocessing)
## 🔑 License
This package is distributed under the MIT License. This license can be found online at .
## Disclaimer
This framework is provided as-is, and there are no guarantees that it fits your purposes or that it is bug-free. Use it at your own risk!
## 🫂 Contributors
Thanks goes to these wonderful people ([emoji key](https://allcontributors.org/docs/en/emoji-key)):

zStupan
💻 🐛 📖 🖋 🤔 💡

Iztok Fister Jr.
💻 🐛 🧑🏫 🚧 🤔

Erkan Karabulut
💻 🐛

Tadej Lahovnik
📖

Ben Beasley
📖

Dusan Fister
🎨
This project follows the [all-contributors](https://github.com/all-contributors/all-contributors) specification. Contributions of any kind welcome!







