Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/flavio-fernandes/rdo-nodes
Vagrant provisioning to setup centos 7 box as RDO nodes
https://github.com/flavio-fernandes/rdo-nodes
Last synced: 4 days ago
JSON representation
Vagrant provisioning to setup centos 7 box as RDO nodes
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/flavio-fernandes/rdo-nodes
- Owner: flavio-fernandes
- License: epl-1.0
- Created: 2015-01-05T22:24:27.000Z (almost 10 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-05-10T12:02:15.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-26T19:13:54.852Z (8 days ago)
- Language: HTML
- Size: 48.8 KB
- Stars: 5
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# RDO-NODES
This repo provides a Vagrantfile with provisioning that one can use to easily
get a cluster of nodes configured with RDO Packstack.
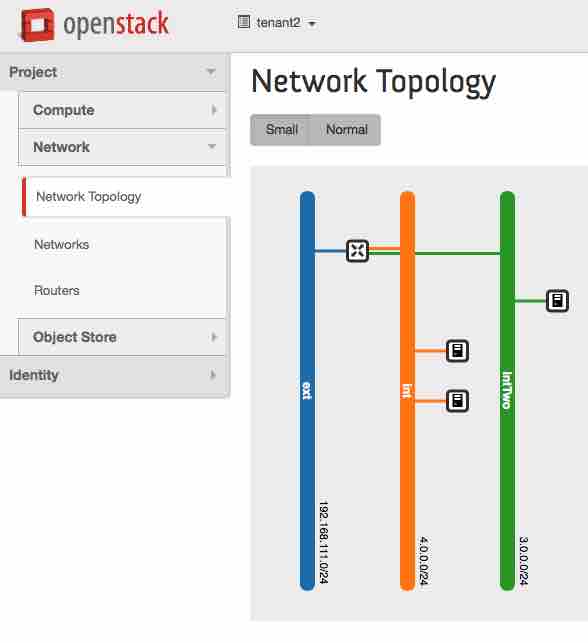
**More info on using repository is available [here][4].**
##Pre-requisites:
**Generate ssh keys! See: dotSshDir/id_rsa.erb.README**
### [Vagrant][0] (and a hypervisor, like Virtual Box)
### [Vagrant Reload Provisioner][1]
As part of the provisioning, the vms are expected to be rebooted. In order to accomplish that,
we require the vagrant's reload plugin. Install this by issuing the following command:
$ vagrant plugin install vagrant-reload
### Number of compute nodes
If you would like more than two compute nodes, you can set the following environment variable:
$ export RDO_NUM_COMPUTE_NODES=3
$ vagrant up
Once you finish vagrant up, consider using [Vagrant Sahara][2] so you do not have to wait long
in order to get a clean set of openstack nodes.
The checked in configuration uses an internal network as the 'shared subnet' by which the provider
of the openstack would give access to the *outside* world. If you would like to connect that
internal network to your real outside network, consider using [Router Node][3], which
would give you a NAT router to play with. That is what I use and tested to ensure a clean
integration.
After 'vagrant up' is done, you will have at least 3 nodes: control, neutron and compute-1. They
will be running Centos 7 and be up to date. In my setup, it took about 20 minutes to have that
provisioned.
In order to easily start openstack and get the example tenant vms running, do this [from the control node]:
$ vagrant ssh
$ sudo su -
# cd /root/ && ./openstack_part0.sh
# cd /root/ && ./openstack_part1.sh
# su - vagrant
$ cd /home/vagrant && openstack_part2.sh
$ cd /home/vagrant && openstack_part3.sh
A brief description of what each bash script does:
- **openstack_part0.sh**: install openstack-packstack package and run packstack, using the file in /root/answers.txt. This step may take ~20 minutes.
- **openstack_part1.sh**: create tenants and deploy admin network
- **openstack_part2.sh**: deploy tenant vms for tenant1
- **openstack_part3.sh**: deploy tenant vms for tenant2
Like mentioned before, more info on using repository is available [here][4].
[0]: https://www.vagrantup.com/ "Vagrant"
[1]: https://github.com/aidanns/vagrant-reload "Vagrant Reload"
[2]: https://github.com/jedi4ever/sahara "Vagrant Sahara"
[3]: https://github.com/flavio-fernandes/router-node "Router Node"
[4]: http://flaviof.com/blog/work/how-to-openstack-from-vagrant.html "OpenStack using Vagrant"