https://github.com/fluent-cms/fluent-cms
Open-source headless CMS built with ASP.NET Core (C#) and React, featuring REST APIs, GraphQL, and a GrapesJS page designer.
https://github.com/fluent-cms/fluent-cms
asp-net-core asp-net-core-mvc asp-net-core-web-api cms csharp drag-and-drop entity-framework-core grapesjs graphql graphql-server handlebars headless headless-cms hooks open-source react restfull-api wysiwyg-html-editor
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Open-source headless CMS built with ASP.NET Core (C#) and React, featuring REST APIs, GraphQL, and a GrapesJS page designer.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/fluent-cms/fluent-cms
- Owner: FormCms
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-06-17T13:30:37.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-16T20:46:05.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-19T10:15:52.932Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: asp-net-core, asp-net-core-mvc, asp-net-core-web-api, cms, csharp, drag-and-drop, entity-framework-core, grapesjs, graphql, graphql-server, handlebars, headless, headless-cms, hooks, open-source, react, restfull-api, wysiwyg-html-editor
- Language: C#
- Homepage: https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/
- Size: 137 MB
- Stars: 185
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 15
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-dotnet - fluent-cms - RESTful CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) APIs, Admin Panel web pages,a GraphQL-style query designer and a WYSIWYG web page designer, all fully configurable without writing code. (CMS)
- fucking-awesome-dotnet - fluent-cms - RESTful CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) APIs, Admin Panel web pages,a GraphQL-style query designer and a WYSIWYG web page designer, all fully configurable without writing code. (CMS)
- awesome-csharp - fluent-cms - RESTful CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) APIs, Admin Panel web pages, a GraphQL-style query designer and a WYSIWYG web page designer, all fully configurable without writing code. (🗒️ Cheatsheets / 📦 Libraries)
README
# FormCMS, powered by Asp.net Core(c#) and React, featuring Rest APIs, GraphQL and Grapes.js Page designer.
Welcome to [FormCMS](https://github.com/FormCMS/FormCMS)! 🚀
[](https://github.com/FormCMS/FormCMS/stargazers)
Our mission is to make **data modeling**, **backend development**, and **frontend development** as simple and intuitive as filling out a **form** 📋
We’d love for you to contribute to FormCMS! Check out our [CONTRIBUTING guide](https://github.com/formcms/formcms/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) to get started.
Love FormCMS? Show your support by giving us a ⭐ on GitHub and help us grow! 🌟
Have suggestions? Connect with us on Reddit! https://www.reddit.com/r/FormCMS/
---
## What is FormCMS?
**FormCMS** is an open-source Content Management System designed to streamline and accelerate web development workflows. Ideal for CMS projects and general web applications, it minimizes repetitive REST/GraphQL API development while offering powerful tools for data management, page design, and user interaction.
### Key Features
1. **Data Modeling and CRUD with RESTful APIs**
FormCMS provides robust data modeling capabilities and built-in RESTful APIs for Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations. These are complemented by a React-based admin panel, enabling efficient and intuitive data management for developers and content creators.
2. **GraphQL Queries and Grapes.js Page Designer**
Leverage GraphQL to fetch multiple related entities in a single query, boosting client-side performance, security, and flexibility. Additionally, the integrated [Grapes.js](https://grapesjs.com/) page designer, powered by [Handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/), allows for effortless creation of dynamic, data-bound pages, streamlining the design process.
3. **User Social Activity**
FormCMS now includes user engagement features, allowing users to like, share, and save content, with the system tracking view counts. Users can access their interaction history, liked posts, and saved posts through a dedicated user portal, enhancing interactivity and personalization.
---
## New CMS? — Data Modeling
### Data Modeling in Current CMS Solutions
Most CMS solutions support entity customization and adding custom properties, but they implement these changes in three distinct ways:
1. **Denormalized Key-Value Storage**: Custom properties are stored in a table with columns like ContentItemId, Key, and Value.
2. **JSON Data Storage**: Some CMS platforms store custom properties as JSON data in a document database, while others use relational databases.
3. **Manually Created C# Classes**: Writing code adds custom properties to create classes that the system uses with Entity Framework.
#### The Pros and Cons:
- **Key-Value Storage**: This approach offers flexibility but suffers from performance inefficiencies and lacks relational integrity.
- **Document Database**: Storing data as documents lacks a structured format and makes data integrity harder to enforce.
- **C# Classes**: While my preferred method, it lacks flexibility. Any minor changes require rebuilding and redeploying the system.
### Data Modeling with FormCMS
In contrast, FormCMS adopts a normalized, structured data approach, where each property is mapped to a corresponding table field:
1. **Maximized Relational Database Functionality**: By leveraging indexing and constraints, FormCMS enhances performance and ensures data integrity.
2. **Data Accessibility**: This model allows for easy data integration with other applications, Entity Framework, or even non-C# languages.
3. **Support for Relationships**: FormCMS enables complex relationships (many-to-one, one-to-many, many-to-many), making it easy to provide GraphQL Query out of the box and provide more advanced querying capabilities.
---
## New CMS? — GraphQL Issues
### Key Challenges
1. **Security & Over-Fetching** – Complex or poorly optimized queries can overload the backend, exposing vulnerabilities and impacting performance.
2. **Caching Limitations** – GraphQL lacks built-in CDN caching, making performance optimization harder.
3. **N+1 Query Problem** – Individual resolver calls can lead to inefficient database queries.
---
### Solution: Persisted Queries with GET Requests
Many GraphQL frameworks support persisted queries with GET requests, enabling caching and improved performance.
---
### How FormCMS Solves These Issues
FormCMS automatically saves GraphQL queries and converts them into RESTful GET requests. For example:
```graphql
query TeacherQuery($id: Int) {
teacherList(idSet: [$id]) {
id firstname lastname
skills { id name }
}
}
```
becomes `GET /api/queries/TeacherQuery`.
- **Security & Efficiency** – Only Admins can define GraphQL queries, preventing abuse. Backend and frontend teams optimize queries to avoid excessive data requests.
- **Caching** – GET requests enable efficient CDN caching, while ASP.NET Core’s hybrid cache further boosts performance.
- **Performance** – Related entities are retrieved in a single optimized query, avoiding the N+1 problem.
By transforming GraphQL into optimized REST-like queries, FormCMS ensures a secure, efficient, and scalable API experience.
---
## Online Course System Demo
### Live Demo
- **Public Site:** [fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/)
- **Admin Panel:** [fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/admin](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/admin)
- **Email:** `admin@cms.com`
- **Password:** `Admin1!`
### Additional Resources
- **GraphQL Playground:** [fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph)
- **Documentation:** [fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/doc/index.html](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/doc/index.html)
### Examples Source Code
example code can be found at /formCMS/examples
- for Sqlite: run the SqliteDemo project
- for SqlServer: run the SqlServerDemo/SqlServerAppHost project
- for PostgreSQL : run the PostgresDemo/PostgresAppHost project
Defult login:
- Eamil : `samdmin@cms.com`
- Password: `Admin1!`
After login to `Admin Panel`, you can go to `Tasks`, click `Import Demo Data`, to import demo data.
---
## Online Course System Backend
This section provides detailed guidance on developing a foundational online course system, encompassing key entities: `teacher`, `course`, `lesson`,`skill`, and `material`.
### Database Schema
#### 1. **Teachers Table**
The `Teachers` table maintains information about instructors, including their personal and professional details.
| **Field** | **Header** | **Data Type** |
|-------------------|------------------|---------------|
| `id` | ID | Int |
| `firstname` | First Name | String |
| `lastname` | Last Name | String |
| `email` | Email | String |
| `phone_number` | Phone Number | String |
| `image` | Image | String |
| `bio` | Bio | Text |
#### 2. **Courses Table**
The `Courses` table captures the details of educational offerings, including their scope, duration, and prerequisites.
| **Field** | **Header** | **Data Type** |
|-------------------|------------------|---------------|
| `id` | ID | Int |
| `name` | Course Name | String |
| `status` | Status | String |
| `level` | Level | String |
| `summary` | Summary | String |
| `image` | Image | String |
| `desc` | Description | Text |
| `duration` | Duration | String |
| `start_date` | Start Date | Datetime |
#### 3. **Lessons Table**
The `Lessons` table contains detailed information about the lessons within a course, including their title, content, and associated teacher.
| **Field** | **Header** | **Data Type** |
|-------------------|-------------------|---------------|
| `id` | ID | Int |
| `name` | Lesson Name | String |
| `description` | Description | Text |
| `teacher` | Teacher | Int (Foreign Key) |
| `course` | Course | Int (Foreign Key) |
| `created_at` | Created At | Datetime |
| `updated_at` | Updated At | Datetime |
#### 4. **Skills Table**
The `Skills` table records competencies attributed to teachers.
| **Field** | **Header** | **Data Type** |
|-------------------|------------------|---------------|
| `id` | ID | Int |
| `name` | Skill Name | String |
| `years` | Years of Experience | Int |
| `created_by` | Created By | String |
| `created_at` | Created At | Datetime |
| `updated_at` | Updated At | Datetime |
#### 5. **Materials Table**
The `Materials` table inventories resources linked to courses.
| **Field** | **Header** | **Data Type** |
|-------------------|-------------|---------------|
| `id` | ID | Int |
| `name` | Name | String |
| `type` | Type | String |
| `image` | Image | String |
| `link` | Link | String |
| `file` | File | String |
---
### Relationships
- **Courses to Teachers**: Man-to-One(Each teacher can teach multiple courses; each course is assigned to one teacher. A teacher can exist independently of a course).
- **Teachers to Skills**: Many-to-Many (Multiple teachers can share skills, and one teacher may have multiple skills).
- **Courses to Materials**: Many-to-Many (A course may include multiple materials, and the same material can be used in different courses).
- **Courses to Lessons**: One-to-Many (Each course can have multiple lessons, but each lesson belongs to one course. A lesson cannot exist without a course, as it has no meaning on its own).
---
### Schema Creation via FormCMS Schema Builder
#### Accessing Schema Builder
After launching the web application, locate the **Schema Builder** menu on the homepage to start defining your schema.
#### Adding Entities
[Example Configuration](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/list.html?schema=entity)
1. Navigate to the **Entities** section of the Schema Builder.
2. Create entities such as "Teacher" and "Course."
3. For the `Course` entity, add attributes such as `name`, `status`, `level`, and `description`.
---
### Defining Relationships
[Example Configuration](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=27)
#### 1. **Course and Teacher (Many-to-One Relationship)**
To establish a many-to-one relationship between the `Course` and `Teacher` entities, you can include a `Lookup` attribute in the `Course` entity. This allows selecting a single `Teacher` record when adding or updating a `Course`.
| **Attribute** | **Value** |
|-----------------|--------------|
| **Field** | `teacher` |
| **DataType** | Lookup |
| **DisplayType** | Lookup |
| **Options** | Teacher |
**Description:** When a course is created or modified, a teacher record can be looked up and linked to the course.
#### 2 **Course and Lesson(One-to-Many Relationship)**
To establish a one-to-many relationship between the `Course` and `Lesson` entities, use a `Collection` attribute in the `Course` entity. This enables associating multiple lessons with a single course.
| **Attribute** | **Value** |
|-----------------|------------|
| **Field** | `lessons` |
| **DataType** | Collection |
| **DisplayType** | EditTable |
| **Options** | Lesson |
**Description:** When managing a course , you can manage lessons of this course.
#### 3. **Course and Materials (Many-to-Many Relationship)**
To establish a many-to-many relationship between the `Course` and `Material` entities, use a `Junction` attribute in the `Course` entity. This enables associating multiple materials with a single course.
| **Attribute** | **Value** |
|---------------|-------------|
| **Field** | `materials` |
| **DataType** | Junction |
| **DisplayType** | Picklist |
| **Options** | Material |
**Description:** When managing a course, you can select multiple material records from the `Material` table to associate with the course.
---
## **Admin Panel**
The last chapter introduced how to model entities, this chapter introduction how to use Admin-Panel to manage data of those entities.
### **Display Types**
The Admin Panel supports various UI controls to display attributes:
- `"text"`: Single-line text input.
- `"textarea"`: Multi-line text input.
- `"editor"`: Rich text input.
- `"dictionary"`: Key-Value pairs
- `"number"`: Single-line text input for numeric values only.
- `"localDatetime"`: Datetime picker for date and time inputs, displayed as the browser's timezone.
- `"datetime"`: Datetime picker for date and time inputs.
- `"date"`: Date picker for date-only inputs.
- `"image"`: Upload a single image, storing the image URL.
- `"gallery"`: Upload multiple images, storing their URLs.
- `"file"`: Upload a file, storing the file URL.
- `"dropdown"`: Select an item from a predefined list.
- `"multiselect"`: Select multiple items from a predefined list.
- `"lookup"`: Select an item from another entity with a many-to-one relationship (requires `Lookup` data type).
- `"treeSelect"`: Select an item from another entity with a many-to-one relationship (requires `Lookup` data type), items are organized as tree.
- `"picklist"`: Select multiple items from another entity with a many-to-many relationship (requires `Junction` data type).
- `"tree"`: Select multiple items from another entity with a many-to-many relationship (requires `Junction` data type), items are organized as a tree.
- `"edittable"`: Manage items of a one-to-many sub-entity (requires `Collection` data type).
---
[See this example how to configure entity `category`, so it's item can be organized as tree.](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=103)
### **DataType to DisplayType Mapping Table**
Below is a mapping of valid `DataType` and `DisplayType` combinations:
| **DataType** | **DisplayType** | **Description** |
|---------------|-----------------|-----------------------------------------------|
| Int | Number | Input for integers. |
| Datetime | LocalDatetime | Datetime picker for local datetime. |
| Datetime | Datetime | Datetime picker for date and time inputs. |
| Datetime | Date | Date picker for date-only inputs. |
| String | Number | Input for numeric values. |
| String | Datetime | Datetime picker for date and time inputs. |
| String | Date | Date picker for date-only inputs. |
| String | Text | Single-line text input. |
| String | Textarea | Multi-line text input. |
| String | Image | Single image upload. |
| String | Gallery | Multiple image uploads. |
| String | File | File upload. |
| String | Dropdown | Select an item from a predefined list. |
| String | Multiselect | Select multiple items from a predefined list. |
| Text | Multiselect | Select multiple items from a predefined list. |
| Text | Gallery | Multiple image uploads. |
| Text | Textarea | Multi-line text input. |
| Text | Editor | Rich text editor. |
| Text | Dictionary | Key-Value Pair |
| Lookup | Lookup | Select an item from another entity. |
| Lookup | TreeSelect | Select an item from another entity. |
| Junction | Picklist | Select multiple items from another entity. |
| Lookup | Tree | Select multiple items from another entity. |
| Collection | EditTable | Manage items of a sub-entity. |
---
### **List Page**
[Example Course List Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course?offset=0&limit=20)
The **List Page** displays entities in a tabular format, supporting sorting, searching, and pagination for efficient browsing or locating of specific records.
#### **Sorting**
Sort records by clicking the `↑` or `↓` icon in the table header.
- [Order by Created At Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course?offset=0&limit=20&sort[created_at]=-1)
- [Order by Name Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course?offset=0&limit=20&sort[name]=1)
#### **Filtering**
Apply filters by clicking the Funnel icon in the table header.
- [Filter by Created At (2024-09-07)](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course?offset=0&limit=20&created_at[dateIs]=2024-09-07&sort[created_at]=1)
- [Filter by Course Name (Starts with A or C)](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course?offset=0&limit=20&name[operator]=or&name[startsWith]=A&name[startsWith]=C&sort[created_at]=1)
#### **Duplicate**
Clicking the duplicate button opens the "Add New Data" page with prefilled values from the selected record for quick entry.
---
### **Detail Page**
Detail page provides an interface to manage single record.
#### Example of display types `date`,`image`, `gallery`, `muliselect`, `dropdown`,
[Lesson Detail Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/lesson/6?ref=https%3A%2F%2Ffluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net%2F_content%FormCMS%2Fadmin%2Fentities%2Fcourse%2F27%3Fref%3Dhttps%253A%252F%252Ffluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net%252F_content%FormCMS%252Fadmin%252Fentities%252Fcourse%253Foffset%253D0%2526limit%253D20).
#### Example of `lookup`,`picklist`,`edittable`
[Course Detail Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course/22)
---
## Publish / Preview Content
This feature allows content creators to plan and organize their work, saving drafts for later completion.
### Content Publication Status
Content can have one of the following publication statuses:
- **`draft`**
- **`scheduled`**
- **`published`**
- **`unpublished`**
Only content with the status **`published`** can be retrieved through GraphQL queries.
---
### Setting Default Publication Status in the Schema Builder
When defining an entity in the Schema Builder, you can configure its default publication status as either **`draft`** or **`published`**.
---
### Managing Publication Status in the Admin Panel
On the content edit page, you can:
- **Publish**: Make content immediately available.
- **Unpublish**: Remove content from public view.
- **Schedule**: Set a specific date and time for the content to be published.
---
### Preview Draft/Scheduled/Unpublished Content
By default, only published content appears in query results.
If you want to preview how the content looks on a page before publishing, you can add the query parameter `preview=1` to the page URL.
For a more convenient approach, you can set the **Preview URL** in the **Entity Settings** page.
[Example Entity Settings Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=27)
Once set, you can navigate to the **Entity Management** page and simply click the **Preview** button to view the content in preview mode.
[Example Content Manage Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/admin/entities/course/3?ref=https%3A%2F%2Ffluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net%2F_content%2FFormCMS%2Fadmin%2Fentities%2Fcourse%3Foffset%3D0%26limit%3D20#)
---
### Publication Worker
The **Publication Worker** automates the process of updating scheduled items in batches, transitioning them to the **`published`** status at the appropriate time.
---
## Concurrent Update Protection
Protect user from dirty write(concurrent update)
### How does it work?
Return the updated_at timestamp when fetching the item. When updating, compare the stored updated_at with the one in the request. If they differ, reject the update
### When Is updatedAt Checked
- During updates
- During Deletions
If a concurrent modification is detected, the system will throw the following exception:
"Error: Concurrent Write Detected. Someone else has modified this item since you last accessed it. Please refresh the data and try again."
---
## Audit Logging
Audit logging in FormCMS helps maintain accountability and provides a historical record of modifications made to entities within the system.
### Audit Log Entity
An audit log entry captures essential information about each modification. The entity structure includes the following fields:
- **UserId** (*string*): The unique identifier of the user performing the action.
- **UserName** (*string*): The name of the user.
- **Action** (*ActionType*): The type of action (Create, update, Delete) performed.
- **EntityName** (*string*): The name of the entity affected.
- **RecordId** (*string*): The unique identifier of the record modified.
- **RecordLabel** (*string*): A human-readable label for the record.
- **Payload** (*Record*): The data associated with the action.
- **CreatedAt** (*DateTime*): The timestamp when the action occurred.
### When Is Audit Log Added
An audit log entry is created when a user performs any of the following actions:
- **Creating** a new record.
- **Updating** an existing record.
- **Deleting** a record.
### How to view Audit Log
Audit logs can be accessed and searched by users with appropriate permissions. The following roles have access:
- **Admin**
- **Super Admin**
These users can:
- View a list of audit logs.
- Search logs by user, entity, or action type.
- Filter logs by date range.
### Benefits of Audit Logging
- Ensures transparency and accountability.
- Helps with troubleshooting and debugging.
- Provides insights into system usage and modifications.
- Supports compliance with regulatory requirements.
By maintaining a detailed audit trail, the System enhances security and operational efficiency, ensuring that all modifications are tracked and can be reviewed when necessary.
---
## Asset Library
The Asset Library centralizes the management of uploaded assets (e.g., images, files), supporting both local and cloud storage. It enables reuse, optimizes storage, and provides robust permissions and extensibility for various cloud providers.
### Overview
Assets are stored in a repository, each identified by a unique `Path` (e.g., `2025-03/abc123`, where `2025-03` is a folder based on `yyyy-MM` and `abc123` is a ULID) and a fixed `Url` (e.g., `/files/2025-03/abc123` or a cloud-specific URL). Relationships to data entities are tracked via `AssetLink` records. The system supports local storage by default and integrates with cloud storage providers (e.g., Azure Cloud Storage) via the `IFileStore` interface. For images, uploads are resized to a default maximum width of 1200 pixels and a compression quality of 75, configurable in `SystemSettings`.
---
### Core Features
#### Adding Assets to Data
In forms with `image`, `file`, or `gallery` fields, users can:
- **Upload**: Upload a new file via `IFileStore.Upload`. The system generates a unique `Path` (e.g., `2025-03/abc123`), sets a `Url` (local or cloud-based), and records metadata (`Name`, `Size`, `Type`, `CreatedBy`, `CreatedAt`). Images are resized (max width: 1200px, quality: 75) before saving to the chosen storage provider in the `2025-03` folder. A default `Title` is derived from `Name`.
- **Choose**: Select an existing asset from a dialog with:
- `Gallery View`: Thumbnails for images.
- `List View`: Table with `Name`, `Title`, `Size`, `CreatedAt`, and `Type`. Filterable by keyword, size range, or date range; sortable in ascending/descending order.
- Selection links the asset, incrementing `LinkCount` and adding an `AssetLink`.
- **Delete**: Remove the asset reference from the entity, reducing `LinkCount`.
- **Edit**: Update `Title` or metadata.
#### Managing Orphan Assets
The **Asset List Page** lists assets with `Name`, `Title`, `Size`, `Type`, `CreatedAt`, and `LinkCount`. Assets with `LinkCount` of 0 (orphans) can be deleted via `IFileStore.Del`, removing them from storage (e.g., the `2025-03` folder) and the system.
#### Replacing Files
On the **Asset Detail Page**, users can replace content:
- Upload a new file via `IFileStore.Upload` to the same `Path` (e.g., `2025-03/abc123`), updating `Size`, `Type`, and `UpdatedAt`.
- Images are resized per settings (max width: 1200px, quality: 75).
- `Path` and `Url` remain unchanged, ensuring continuity for linked entities.
#### Updating Metadata
On the **Asset Detail Page**, users can modify:
- **Title**: Change the display name (defaults to `Name`).
- **Metadata**: Update key-value pairs (e.g., `{"AltText": "Description"}`), updating `UpdatedAt`.
---
### Cloud Storage Integration
The Asset Library supports cloud storage through the `IFileStore` interface, with Azure Cloud Storage as an example. Other providers (e.g., Google Cloud Storage, AWS S3) can be integrated by implementing this interface and registering it in the dependency injection container.
#### `IFileStore` Interface
```csharp
namespace FormCMS.Infrastructure.FileStore;
public record FileMetadata(long Size, string ContentType);
public interface IFileStore
{
Task Upload(IEnumerable<(string, IFormFile)> files, CancellationToken ct);
Task Upload(string localPath, string path, CancellationToken ct);
Task GetMetadata(string filePath, CancellationToken ct);
string GetUrl(string file);
Task Download(string path, string localPath, CancellationToken ct);
Task Del(string file, CancellationToken ct);
}
```
#### Functionality
- **Upload**: Stores files in the provider, using the folder structure (e.g., `2025-03/abc123`).
- **GetMetadata**: Retrieves `Size` and `ContentType`.
- **GetUrl**: Returns the asset’s URL (e.g., `https://.blob.core.windows.net//2025-03/abc123` for Azure).
- **Download**: Retrieves the file to a local path.
- **Del**: Deletes the file from its folder.
#### Extending to Other Providers
To use Google Cloud Storage, AWS S3, or others:
1. Implement `IFileStore` with provider-specific logic (e.g., S3’s `PutObject` for uploads to `2025-03/abc123`).
2. Register it in dependency injection (e.g., `services.AddScoped()`).
#### Example: Azure Cloud Storage
- Uploads files to Azure Blob Storage under the `2025-03` folder (e.g., `2025-03/abc123`).
- Generates URLs like `https://.blob.core.windows.net//2025-03/abc123`.
- Supports metadata retrieval and deletion via Azure APIs.
---
### Permissions
A role-based system controls asset access:
- **Super Admin**: Full control over all assets, including those in cloud folders (e.g., `2025-03`).
- **No Permissions**: No asset interaction.
- **Restricted Read**: Choose only self-uploaded assets.
- **Full Read**: Choose any asset.
- **Restricted Write**: Manage only self-uploaded assets.
- **Full Write**: Manage all assets (except assigning).
Permissions filter the library dialog and validate actions against ownership and storage location.
---
### Configuration
- **Image Compression** (`ImageCompressionOptions`):
- `MaxWidth`: Default 1200px.
- `Quality`: Default 75 (0-100).
- **Asset URL**: Local prefix defaults to `/files` (e.g., `/files/2025-03/abc123`); cloud URLs depend on the provider (via `IFileStore.GetUrl`).
- **Storage Provider**: Set via dependency injection (e.g., Azure, local).
---
### Benefits
- **Reuse**: Assets are shared across entities, reducing redundancy.
- **Storage**: Orphan deletion, image resizing, and folder-based organization (e.g., `2025-03`) optimize usage; cloud storage scales capacity.
- **Consistency**: Fixed `Url` ensures seamless updates.
- **Flexibility**: Metadata, replacements, and cloud extensibility adapt to needs.
- **Tracking**: `LinkCount` and `AssetLink` monitor usage.
- **SEO**: `Title` as alt text enhances image discoverability.
- **Scalability**: Cloud integration (e.g., Azure) and `IFileStore` support growing storage demands.
---
## Date and Time
The Date and Time system in FormCMS manages how dates and times are displayed and stored, supporting three distinct formats: `localDatetime`, `datetime`, and `date`. It ensures accurate representation across time zones and consistent storage in the database.
### Overview
FormCMS provides three display formats for handling date and time data, each serving a specific purpose:
`localDatetime`: Displays dates and times adjusted to the user's browser time zone (e.g., a start time that varies by location).
`datetime`: Zone-agnostic, showing the same date and time universally (e.g., a fixed event time).
`date`: Zone-agnostic, displaying only the date without time (e.g., a birthday).
---
### Display Formats
#### `localDatetime`
- **Purpose**: Represents a date and time that adjusts to the user's local time zone, ideal for events like start times where the local context matters.
- **Behavior**: The system converts the stored UTC `datetime` to the browser's time zone for display. For example, an event starting at `2025-03-19 14:00 UTC` would appear as `2025-03-19 09:00 EST` for a user in New York (UTC-5) or `2025-03-19 23:00 JST` for a user in Tokyo (UTC+9).
- **Storage**: When entered, the system converts the user’s local input to UTC before saving. For instance, `2025-03-19 09:00 EST` is stored as `2025-03-19 14:00 UTC`.
- **Use Case**: Event schedules, deadlines, or anything requiring local time awareness.
#### `datetime`
- **Purpose**: Displays a fixed date and time that remains consistent regardless of the user’s time zone, suitable for universal reference points.
- **Behavior**: No conversion occurs; the stored value is shown as-is. For example, `2025-03-19 14:00` is displayed as `2025-03-19 14:00` everywhere.
- **Storage**: Saved exactly as input, without time zone adjustments, assuming it’s a universal time.
- **Use Case**: Logs, publication timestamps, or system events where a single point in time applies globally.
#### `date`
- **Purpose**: Represents only a date without time, zone-agnostic, and consistent across all users.
- **Behavior**: Displayed as a date only (e.g., `2025-03-19`), with no time component or zone consideration.
- **Storage**: Stored as a `datetime` with the time set to `00:00:00` (midnight), typically in UTC for consistency, but the time portion is ignored in display.
- **Use Case**: Birthdays, anniversaries, or any date-specific data where time is irrelevant.
---
### Storage in Database
- **System-Generated Timestamps**: All automatically generated times (e.g., `CreatedAt`, `UpdatedAt`) are stored as UTC `datetime` values (e.g., `2025-03-19 14:00:00Z`). This ensures a universal reference point for auditing and synchronization.
- **`localDatetime` Handling**:
Input: Converted from the user’s local time (based on browser settings) to UTC before storage.
Output: Converted from UTC back to the user’s local time zone for display.
- **`datetime` Handling**: Stored and retrieved as entered, with no conversion, assuming it’s a fixed point in time.
- **`date` Handling**: Stored as a `datetime` with the time component set to `00:00:00` (e.g., `2025-03-19 00:00:00Z`), though only the date part is used in display.
---
### Examples
1. **Event Start (`localDatetime`)**:
- User in New York enters: `2025-03-19 09:00 EST`.
- Stored as: `2025-03-19 14:00:00Z` (UTC).
- Displayed in Tokyo: `2025-03-19 23:00 JST`.
2. **Log Entry (`datetime`)**:
- Entered and stored as: `2025-03-19 14:00`.
- Displayed everywhere as: `2025-03-19 14:00`.
3. **Birthday (`date`)**:
- Entered as: `2025-03-19`.
- Stored as: `2025-03-19 00:00:00Z`.
- Displayed as: `2025-03-19`.
---
### Benefits
- **Consistency**: UTC storage for system times ensures reliable auditing and cross-time-zone integrity.
- **Flexibility**: `localDatetime` adapts to user locations, while `datetime` and `date` provide universal clarity.
- **Simplicity**: Clear separation of use cases reduces confusion in data entry and display.
- **Scalability**: Standardized UTC storage supports global applications without time zone conflicts.
---
## Export and Import Data
This feature allows you to export or import data
This feature is helpful for the following scenarios:
1. Migrating data from one server to another, or even between different types of databases.
2. Backing up your data.
3. Cleaning data by exporting only the latest schema, excluding audit log data.
### Exporting Data
1. Log in to the 'Admin Panel' and navigate to `Tasks`.
2. Click `Add Export Task`.
3. Wait a few minutes, then refresh the page. Once the task is complete, you can download the exported zip file.
### Importing Data
1. Log in to the 'Admin Panel' and go to `Tasks`.
2. Click `Add Import Task`, then select the zip file you wish to import.
3. Wait a few minutes, then refresh the page to check if the task was successful.
---
## Customizing the Admin Panel
FormCms' modular component structure makes it easy to modify UI text, replace components, or swap entire pages.
### FormCmsAdminSdk and FormCmsAdminApp
The FormCms Admin Panel is built with React and split into two projects:
- **[FormCmsAdminSdk](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminSdk)**
This SDK handles backend interactions and complex state management. It is intended to be a submodule of your own React App. It follows a minimalist approach, relying only on:
- `"react"`, `"react-dom"`, `"react-router-dom"`: Essential React and routing dependencies.
- `"axios"` and `"swr"`: For API access and state management.
- `"qs"`: Converts query objects to strings.
- `"react-hook-form"`: Manages form inputs.
- **[FormCmsAdminApp](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminApp)**
A demo implementation showing how to build a React app with the FormCmsAdminSdk. Fork this project to customize the layout, UI text, or add features.
### Why is FormCmsAdminSdk a Submodule Instead of an NPM package?
A **Git submodule** embeds an external repository (e.g., [FormCmsAdminSdk](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminSdk)) as a subdirectory in your project. Unlike NPM packages, which deliver bundled code, submodules provide the full, readable source, pinned to a specific commit. This offers flexibility for customization, debugging, or upgrading the SDK directly in your repository.
To update a submodule:
```
git submodule update --remote
```
Then commit the updated reference in your parent repository.
### Setting Up Your Custom AdminPanelApp
To create a custom AdminPanelApp with submodules, start with the example repo [FormCmsAdminApp](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminApp):
```
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminApp.git
```
The `--recurse-submodules` flag ensures the SDK submodule is cloned alongside the main repo.
```
cd FormCmsAdminApp
pnpm install
```
Start the formCms backend, you might need to modify .env.development, change the Api url to your backend.
```
VITE_REACT_APP_API_URL='http://127.0.0.1:5000/api'
```
Start the React App
```
pnpm dev
```
### Deploying Your Customized Admin Panel
After customizing, build your app:
```
pnpm build
```
Copy the contents of the `dist` folder to `\wwwroot\admin` to replace the default Admin Panel.
### Customizing Layout and Logo
The SDK ([FormCmsAdminSdk](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminSdk)) includes an integrated router and provides three hooks for menu items:
- `useEntityMenuItems`
- `useAssetMenuItems`
- `useSystemMenuItems`
Use these to design your app’s layout and update the logo within this structure.
### Modifying Page Text
Each page (a root-level component tied to the router) can use a corresponding `use***Page` hook from the SDK. These hooks handle state and API calls, returning components for your UI.
To customize text:
- Pass specific prompts and labels via the `pageConfig` argument in the hook.
- For text shared across pages, use the `componentConfig` argument.
### Swapping UI Components
Replace table columns, input fields, or other UI components with your custom versions as needed.
---
## **GraphQL Query**
FormCMS simplifies frontend development by offering robust GraphQL support.
### Getting Started
#### Accessing the GraphQL IDE
To get started, launch the web application and navigate to `/graph`. You can also try our [online demo](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph).
---
#### Singular vs. List Response
For each entity in FormCMS, two GraphQL fields are automatically generated:
- ``: Returns a record.
- ``: Returns a list of records.
**Single Course **
```graphql
{
course {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20course%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
**List of Courses **
```graphql
{
courseList {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
---
#### Field Selection
You can query specific fields for both the current entity and its related entities.
**Example Query:**
```graphql
{
courseList{
id
name
teacher{
id
firstname
lastname
skills{
id
name
}
}
materials{
id,
name
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20teacher%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20skills%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%20%20materials%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
---
#### Filtering with `Value Match` in FormCMS
FormCMS provides flexible filtering capabilities using the `idSet` field (or any other field), enabling precise data queries by matching either a single value or a list of values.
**Filter by a Single Value Example:**
```graphql
{
courseList(idSet: 5) {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(idSet%3A5)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
**Filter by Multiple Values Example:**
```graphql
{
courseList(idSet: [5, 7]) {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(idSet%3A%5B5%2C7%5D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
---
#### Advanced Filtering with `Operator Match` in FormCMS
FormCMS supports advanced filtering options with `Operator Match`, allowing users to combine various conditions for precise queries.
##### `matchAll` Example:
Filters where all specified conditions must be true.
In this example: `id > 5 and id < 15`.
```graphql
{
courseList(id: {matchType: matchAll, gt: 5, lt: 15}) {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(id%3A%7BmatchType%3AmatchAll%2Cgt%3A5%2Clt%3A15%7D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
##### `matchAny` Example:
Filters where at least one of the conditions must be true.
In this example: `name starts with "A"` or `name starts with "I"`.
```graphql
{
courseList(name: [{matchType: matchAny}, {startsWith: "A"}, {startsWith: "I"}]) {
id
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(name%3A%5B%7BmatchType%3AmatchAny%7D%2C%20%7BstartsWith%3A%22A%22%7D%2C%7BstartsWith%3A%22I%22%7D%5D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
---
#### `Filter Expressions` in FormCMS
Filter Expressions allow precise filtering by specifying a field, including nested fields using JSON path syntax. This enables filtering on subfields for complex data structures.
***Example: Filter by Teacher's Last Name***
This query returns courses taught by a teacher whose last name is "Circuit."
```graphql
{
courseList(filterExpr: {field: "teacher.lastname", clause: {equals: "Circuit"}}) {
id
name
teacher {
id
lastname
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(filterExpr%3A%20%7Bfield%3A%20%22teacher.lastname%22%2C%20clause%3A%20%7Bequals%3A%20%22Circuit%22%7D%7D)%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20teacher%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D)
---
#### Sorting
Sorting by a single field
```graphql
{
courseList(sort:nameDesc){
id,
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(sort%3AnameDesc)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
Sorting by multiple fields
```graphql
{
courseList(sort:[level,id]){
id,
level
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(sort%3A%5Blevel%2Cid%5D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20level%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D%0A)
---
#### Sort Expressions in FormCMS
Sort Expressions allow sorting by nested fields using JSON path syntax.
***Example: Sort by Teacher's Last Name***
```graphql
{
courseList(sortExpr:{field:"teacher.lastname", order:Desc}) {
id
name
teacher {
id
lastname
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList(sortExpr%3A%7Bfield%3A%22teacher.lastname%22%2C%20order%3ADesc%7D)%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20teacher%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D)
---
#### Pagination
Pagination on root field
```graphql
{
courseList(offset:2, limit:3){
id,
name
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%20%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20courseList(offset%3A2%2C%20limit%3A3)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A)
Pagination on sub field
```graphql
{
courseList{
id,
name
materials(limit:2){
id,
name
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%20%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20courseList%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20materials(limit%3A2)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A)
---
#### Variable
Variables are used to make queries more dynamic, reusable, and secure.
##### Variable in `Value filter`
```
query ($id: Int!) {
teacher(idSet: [$id]) {
id
firstname
lastname
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24id%3A%20Int!)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacher(idSet%3A%20%5B%24id%5D)%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%0A%20%20%22id%22%3A3%0A%7D)
##### Variable in `Operator Match` filter
```
query ($id: Int!) {
teacherList(id:{equals:$id}){
id
firstname
lastname
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24id%3A%20Int!)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(id%3A%7Bequals%3A%24id%7D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%0A%20%20%22id%22%3A%203%0A%7D)
##### Variable in `Filter Expression`
```
query ($years: String) {
teacherList(filterExpr:{field:"skills.years",clause:{gt:$years}}){
id
firstname
lastname
skills{
id
name
years
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24years%3A%20String)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(filterExpr%3A%7Bfield%3A%22skills.years%22%2Cclause%3A%7Bgt%3A%24years%7D%7D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%20%20skills%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20years%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%0A%20%20%22years%22%3A%20%229%22%0A%7D)
##### Variable in Sort
```
query ($sort_field:TeacherSortEnum) {
teacherList(sort:[$sort_field]) {
id
firstname
lastname
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24sort_field%3ATeacherSortEnum)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(sort%3A%5B%24sort_field%5D)%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%22sort_field%22%3A%20%22idDesc%22%7D)
##### Variable in Sort Expression
```
query ($sort_order: SortOrderEnum) {
courseList(sortExpr:{field:"teacher.id", order:$sort_order}){
id,
name,
teacher{
id,
firstname
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24sort_order%3A%20%20SortOrderEnum)%20%7B%0A%20%20courseList(sortExpr%3A%7Bfield%3A%22teacher.id%22%2C%20order%3A%24sort_order%7D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20name%2C%0A%20%20%20%20teacher%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%0A%20%20%22sort_order%22%3A%20%22Asc%22%0A%7D)
##### Variable in Pagination
```
query ($offset:Int) {
teacherList(limit:2, offset:$offset) {
id
firstname
lastname
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24offset%3AInt)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(limit%3A2%2C%20offset%3A%24offset)%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&variables=%7B%0A%09%22offset%22%3A%202%0A%7D)
---
#### Required vs Optional
If you want a variable to be mandatory, you can add a `!` to the end of the type
```
query ($id: Int!) {
teacherList(id:{equals:$id}){
id
firstname
lastname
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20(%24id%3A%20Int!)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(id%3A%7Bequals%3A%24id%7D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D)
Explore the power of FormCMS GraphQL and streamline your development workflow!
***
***
### Saved Query
**Realtime queries** may expose excessive technical details, potentially leading to security vulnerabilities.
**Saved Queries** address this issue by abstracting the GraphQL query details. They allow clients to provide only variables, enhancing security while retaining full functionality.
---
#### Transitioning from **Real-Time Queries** to **Saved Queries**
##### Using `OperationName` as the Saved Query Identifier
In FormCMS, the **Operation Name** in a GraphQL query serves as a unique identifier for saved queries. For instance, executing the following query automatically saves it as `TeacherQuery`:
```graphql
query TeacherQuery($id: Int) {
teacherList(idSet: [$id]) {
id
firstname
lastname
skills {
id
name
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=query%20TeacherQuery(%24id%3A%20Int)%20%7B%0A%20%20teacherList(idSet%3A%5B%24id%5D)%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20firstname%0A%20%20%20%20lastname%0A%20%20%20%20skills%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%2C%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D&operationName=TeacherQuery)
---
##### Saved Query Endpoints
FormCMS generates two API endpoints for each saved query:
1. **List Records:**
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery)
2. **Single Record:**
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/single/](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/single)
---
##### Using REST API Query Strings as Variables
The Saved Query API allows passing variables via query strings:
- **Single Value:**
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/?id=3](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/?id=3)
- **Array of Values:**
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?id=3&id=4](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?id=3&id=4)
This passes `[3, 4]` to the `idSet` argument.
---
#### Additional Features of `Saved Query`
Beyond performance and security improvements, `Saved Query` introduces enhanced functionalities to simplify development workflows.
---
##### Pagination by `offset`
Built-in variables `offset` and `limit` enable efficient pagination. For example:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=2&offset=2](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=2&offset=2)
---
##### `offset` Pagination for Subfields
To display a limited number of subfield items (e.g., the first two skills of a teacher), use the JSON path variable, such as `skills.limit`:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?skills.limit=2](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?skills.limit=2)
---
##### Pagination by `cursor`
For large datasets, `offset` pagination can strain the database. For example, querying with `offset=1000&limit=10` forces the database to retrieve 1010 records and discard the first 1000.
To address this, `Saved Query` supports **cursor-based pagination**, which reduces database overhead.
Example response for [https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3):
```json
[
{
"hasPreviousPage": false,
"cursor": "eyJpZCI6M30"
},
{
},
{
"hasNextPage": true,
"cursor": "eyJpZCI6NX0"
}
]
```
- If `hasNextPage` of the last record is `true`, use the cursor to retrieve the next page:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3&last=eyJpZCI6NX0](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3&last=eyJpZCI6NX0)
- Similarly, if `hasPreviousPage` of the first record is `true`, use the cursor to retrieve the previous page:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3&first=eyJpZCI6Nn0](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?limit=3&first=eyJpZCI6Nn0)
---
##### Cursor-Based Pagination for Subfields
Subfields also support cursor-based pagination. For instance, querying [https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?skills.limit=2](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery?skills.limit=2) returns a response like this:
```json
[
{
"id": 3,
"firstname": "Jane",
"lastname": "Debuggins",
"hasPreviousPage": false,
"skills": [
{
"hasPreviousPage": false,
"cursor": "eyJpZCI6MSwic291cmNlSWQiOjN9"
},
{
"hasNextPage": true,
"cursor": "eyJpZCI6Miwic291cmNlSWQiOjN9"
}
],
"cursor": "eyJpZCI6M30"
}
]
```
To fetch the next two skills, use the cursor:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/part/skills?limit=2&last=eyJpZCI6Miwic291cmNlSWQiOjN9](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/TeacherQuery/part/skills?limit=2&last=eyJpZCI6Miwic291cmNlSWQiOjN9)
Below is a rewritten version of the **Asset Type** and **Distinct** chapters from your GraphQL Query documentation. The rewrite aims to improve clarity, structure, and readability while preserving the technical details.
---
### Asset Type
In FormCMS, attributes with display types such as `image`, `file`, or `gallery` are represented as **Asset Objects** in GraphQL query results. These objects correspond to assets stored in the system's centralized Asset Library (see the **Asset Library** section for details). When querying entities with these attributes, the response includes structured asset data, such as the asset’s `Path`, `Url`, `Name`, `Title`, and other metadata.
#### Example Query
Consider a `course` entity with an `image` field:
```graphql
{
courseList {
id
name
image {
id
path
url
name
title
size
type
}
}
}
```
[Try it here](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/graph?query=%7B%0A%20%20courseList%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20image%20%7B%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20id%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20path%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20url%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20name%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20title%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20size%0A%20%20%20%20%20%20type%0A%20%20%20%20%7D%0A%20%20%7D%0A%7D)
#### Response Example
```json
{
"data": {
"courseList": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Introduction to GraphQL",
"image": {
"id": "abc123",
"path": "2025-03-abc123",
"url": "/files/2025-03-abc123",
"name": "graphql_intro.jpg",
"title": "GraphQL Course Banner",
"size": 102400,
"type": "image/jpeg"
}
}
]
}
}
```
#### Benefits
- **Consistency**: The `url` field provides a fixed access point to the asset, ensuring reliable retrieval across the application.
- **Metadata**: Fields like `title` can be used as captions or `alt` text for images, enhancing accessibility and SEO.
- **Flexibility**: The Asset Object structure supports various file types (`image`, `file`, `gallery`) with a uniform response format.
---
### Distinct
When querying related entities in FormCMS, joining tables can result in duplicate records due to one-to-many relationships. The `DISTINCT` keyword helps eliminate these duplicates, but it has limitations that require careful query design.
#### Why Use `DISTINCT`?
Consider the following data structure:
- **Posts**: `[{id: 1, title: "p1"}]`
- **Tags**: `[{id: 1, name: "t1"}, {id: 2, name: "t2"}]`
- **Post_Tag**: `[{post_id: 1, tag_id: 1}, {post_id: 1, tag_id: 2}]`
A query joining these tables might look like this in SQL:
```sql
SELECT posts.id, posts.title
FROM posts
LEFT JOIN post_tag ON posts.id = post_tag.post_id
LEFT JOIN tags ON post_tag.tag_id = tags.id
WHERE tags.id > 0;
```
Without `DISTINCT`, the result duplicates the post for each tag:
```json
[
{"id": 1, "title": "p1"}, // For tag_id: 1
{"id": 1, "title": "p1"} // For tag_id: 2
]
```
Using `DISTINCT` ensures each post appears only once:
```sql
SELECT DISTINCT posts.id, posts.title
FROM posts
LEFT JOIN post_tag ON posts.id = post_tag.post_id
LEFT JOIN tags ON post_tag.tag_id = tags.id
WHERE tags.id > 0;
```
Result:
```json
[
{"id": 1, "title": "p1"}
]
```
#### Limitation of `DISTINCT`
In some databases, such as SQL Server, `DISTINCT` cannot be applied to fields of type `TEXT` (or large data types like `NTEXT` or `VARCHAR(MAX)`). Including such fields in a query with `DISTINCT` causes errors.
#### Solution/Workaround
To address this limitation, split the entity’s queries into two parts:
1. **List Query**: Retrieves a lightweight list of records without `TEXT` fields, using `DISTINCT` to avoid duplicates.
```
{
postList {
id
title
}
}
```
2. **Detail Query**: Retrieves full details, including `TEXT` fields, by querying a single record using its ID.
```
{
post(idSet: 1) {
id
title
description # TEXT field
}
}
```
#### Example with GraphQL
List query to avoid duplicates:
```
{
postList {
id
title
tags {
id
name
}
}
}
```
Detail query for a specific post:
```graphql
{
post(idSet: 1) {
id
title
description # TEXT field, only queried here
tags {
id
name
}
}
}
```
#### Benefits
- **Efficiency**: The list query remains lightweight and deduplicated.
- **Compatibility**: Avoids database-specific limitations on `DISTINCT`.
- **Flexibility**: Developers can fetch detailed data only when needed.
---
---
## Drag and Drop Page Designer
The page designer utilizes the open-source GrapesJS and Handlebars, enabling seamless binding of `GrapesJS Components` with `FormCMS Queries` for dynamic content rendering.
---
### Page Types: Landing Page, Detail Page, and Home Page
#### **Landing Page**
A landing page is typically the first page a visitor sees.
- **URL format**: `/page/`
- **Structure**: Comprised of multiple sections, each section retrieves data via a `query`.
**Example**:
[Landing Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/)
This page fetches data from:
- [https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?status=featured](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?status=featured)
- [https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?level=Advanced](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?level=Advanced)
---
#### **Detail Page**
A detail page provides specific information about an item.
- **URL format**: `/page//`
- **Data Retrieval**: FormCMS fetches data by passing the router parameter to a `query`.
**Example**:
[Course Detail Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/pages/course/22)
This page fetches data from:
[https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/one?course_id=22](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/one?course_id=22)
---
#### **Home Page**
The homepage is a special type of landing page named `home`.
- **URL format**: `/pages/home`
- **Special Behavior**: If no other route matches the path `/`, FormCMS renders `/pages/home` by default.
**Example**:
The URL `/` will be resolved to `/pages/home` unless explicitly overridden.
---
### Introduction to GrapesJS Panels
Understanding the panels in GrapesJS is crucial for leveraging FormCMS's customization capabilities in the Page Designer UI. This section explains the purpose of each panel and highlights how FormCMS enhances specific areas to streamline content management and page design.

1. **Style Manager**:
- Used to customize CSS properties of elements selected on the canvas.
- *FormCMS Integration*: This panel is left unchanged by FormCMS, as it already provides powerful styling options.
2. **Traits Panel**:
- Allows modification of attributes for selected elements.
- *FormCMS Integration*: Custom traits are added to this panel, enabling users to bind data to components dynamically.
3. **Layers Panel**:
- Displays a hierarchical view of elements on the page, resembling a DOM tree.
- *FormCMS Integration*: While FormCMS does not alter this panel, it’s helpful for locating and managing FormCMS blocks within complex page designs.
4. **Blocks Panel**:
- Contains pre-made components that can be dragged and dropped onto the page.
- *FormCMS Integration*: FormCMS enhances this panel by adding custom-designed blocks tailored for its CMS functionality.
By familiarizing users with these panels and their integration points, this chapter ensures a smoother workflow and better utilization of FormCMS's advanced page-building tools.
---
### Data Binding: Singleton or List
FormCMS leverages [Handlebars expressions](https://github.com/Handlebars-Net/Handlebars.Net) for dynamic data binding in pages and components.
---
#### **Singleton**
Singleton fields are enclosed within `{{ }}` to dynamically bind individual values.
- **Example Page Settings:** [Page Schema Settings](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/page.html?schema=page&id=33)
- **Example Query:** [Retrieve Course Data](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?course_id=22)
- **Example Rendered Page:** [Rendered Course Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/pages/course/22)
---
#### **List**
`Handlebars` supports iterating over arrays using the `{{#each}}` block for repeating data structures.
```handlebars
{{#each course}}
{{/each}}
```
In FormCMS, you won’t explicitly see the `{{#each}}` statement in the Page Designer. If a block's data source is set to `data-list`, the system automatically generates the loop.
- **Example Page Settings:** [Page Schema Settings](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/page.html?schema=page&id=32)
- **Example Rendered Page:** [Rendered List Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/)
- **Example Queries:**
- [Featured Courses](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?status=featured)
- [Advanced Level Courses](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/api/queries/course/?level=Advanced)
---
#### **Steps to Bind a Data Source**
To bind a `Data List` to a component, follow these steps:
1. Drag a block from the **Data List** category in the Page Designer.
2. Open the **Layers Panel** and select the `Data List` component.
3. In the **Traits Panel**, configure the following fields:
| **Field** | **Description** |
|---------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Query** | The query to retrieve data. |
| **Qs** | Query string parameters to pass (e.g., `?status=featured`, `?level=Advanced`). |
| **Offset** | Number of records to skip. |
| **Limit** | Number of records to retrieve. |
| **Pagination**| Options for displaying content: |
| | - **Button**: Divides content into multiple pages with navigation buttons (e.g., "Next," "Previous," or numbered buttons). |
| | - **Infinite Scroll**: Automatically loads more content as users scroll. Ideal for a single component at the bottom of the page. |
| | - **None**: Displays all available content at once without requiring additional user actions. |
---
## Online Course System Frontend
Having established our understanding of FormCMS essentials like Entity, Query, and Page, we're ready to build a frontend for an online course website.
---
### Key Pages
- **Home Page (`home`)**: The main entry point, featuring sections like *Featured Courses* and *Advanced Courses*. Each course links to its respective **Course Details** page.
- **Course Details (`course/{course_id}`)**: Offers detailed information about a specific course and includes links to the **Teacher Details** page.
- **Teacher Details (`teacher/{teacher_id}`)**: Highlights the instructor’s profile and includes a section displaying their latest courses, which link back to the **Course Details** page.
```plaintext
Home Page
|
|
+-------------------+
| |
v v
Latest Courses Course Details
| |
| |
v v
Course Details <-------> Teacher Details
```
---
### Designing the Home Page
1. **Drag and Drop Components**: Use the FormCMS page designer to drag a `Content-B` component.
2. **Set Data Source**: Assign the component's data source to the `course` query.
3. **Link Course Items**: Configure the link for each course to `/pages/course/{{id}}`. The Handlebars expression `{{id}}` is dynamically replaced with the actual course ID during rendering.

---
### Creating the Course Details Page
1. **Page Setup**: Name the page `course/{course_id}` to capture the `course_id` parameter from the URL (e.g., `/pages/course/20`).
2. **Query Configuration**: The variable `{course_id:20}` is passed to the `course` query, generating a `WHERE id IN (20)` clause to fetch the relevant course data.
3. **Linking to Teacher Details**: Configure the link for each teacher item on this page to `/pages/teacher/{{teacher.id}}`. Handlebars dynamically replaces `{{teacher.id}}` with the teacher’s ID. For example, if a teacher object has an ID of 3, the link renders as `/pages/teacher/3`.
---
### Creating the Teacher Details Page
1. **Page Setup**: Define the page as `teacher/{teacher_id}` to capture the `teacher_id` parameter from the URL.
2. **Set Data Source**: Assign the `teacher` query as the page’s data source.
#### Adding a Teacher’s Courses Section
- Drag a `ECommerce A` component onto the page.
- Set its data source to the `course` query, filtered by the teacher’s ID (`WHERE teacher IN (3)`).

When rendering the page, the `PageService` automatically passes the `teacher_id` (e.g., `{teacher_id: 3}`) to the query.
---
## Navigation by Category
Category trees and breadcrumbs provide structure, context, and clarity, enabling users to find and navigate data more efficiently.
### **Demo of Category Tree and Breadcrumb Navigation**
- **Category Tree Navigation**:
[View Demo](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/course)
- **Breadcrumb Navigation**:
[View Demo](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/course/27)
---
### **Creating a Category Entity**
To create a category entity in the Schema Builder, include `parent` and `children` attributes.
- **Example Configuration**:
[Edit Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=103)
---
### **Configuration Options for Navigation**
- **DataType: `lookup`** & **DisplayType: `TreeSelect`**
Use this configuration to display a category as a property.
[Edit Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=96)
- **DataType: `junction`** & **DisplayType: `Tree`**
Use this configuration to enable category-based navigation.
[Edit Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/edit.html?schema=entity&id=27)
---
### **Using Navigation Components in Page Designer**
- **Tree Layer Menu**:
Use the `Tree Layer Menu` component for hierarchical navigation.
[Edit Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/page.html?schema=page&id=42)
- **Breadcrumbs**:
Use the `Breadcrumbs` component to display navigation paths.
[Edit Example](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/page.html?schema=page&id=33)
---
## Schema Version Control
FormCMS saves each version of schemas, allowing users to roll back to earlier versions. Admins can freely test draft versions, while only published versions take effect.
### Requirements
To illustrate this feature, let's take a `Page` as an example. Once a page is published, it becomes publicly accessible. You may need version control for two main reasons:
- You want to make changes but ensure they do not take effect until thoroughly tested.
- If issues arise in the latest version, you need the ability to roll back to a previous version.
### Choosing a Version
After making changes, the latest version's status changes to `draft` in the [Page List Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/list.html?type=page).
To manage versions, click the `View History` button to navigate to the [History Version List Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/history.html?schemaId=01JKKB85KWA651945N5W0T6PJR).
Here, you can select any version and set it to `published` status.
### Testing a `Draft` Version
To preview a draft version, append `sandbox=1` as a query parameter in the URL: [Preview Draft Version Page](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/story/?sandbox=1).
Alternatively, click the `View Page` button on the `Page Design` page.
### Compare schema Changes
You can compare the difference between different versions, use the [Schema Diff Tool](https://fluent-cms-admin.azurewebsites.net/_content/FormCMS/schema-ui/diff.html?schemaId=01JKKA93AJG2HNY648H9PC16PN&type=query&oldId=126&newId=138).
### Duplicate
You can duplicate any schema version and save it as a new schema.
---
## Social Activity
The Social Activity feature enhances user engagement by enabling views, likes, saves, and shares. It also provides detailed analytics to help understand content performance.
### Endpoints
- `GET /api/activities/{entityName}/{recordId:long}`
Increments the view count by 1. Returns the active status and count for: like, view, share, and save.
- `GET /api/activities/record/{entityName}/{recordId}?type={view|share}`
Retrieves activity info of type `view` or `share` for a given entity record.
- `POST /api/activities/toggle/{entityName}/{recordId}?type={like|save}&active={true|false}`
Toggles the activity (like or save) on or off based on the `active` flag.
### Challenges
The system cannot leverage traditional output caching due to dynamic nature of the content, which may lead to high database load under heavy traffic.
To address this, buffered writes are introduced. Activity events are first stored in a buffer (in-memory or Redis), and then periodically flushed to the database, balancing performance and accuracy.
---
### Load Testing
Below is a test script using [k6](https://k6.io/) to simulate traffic and measure performance:
```javascript
import http from 'k6/http';
import { check } from 'k6';
import { Trend } from 'k6/metrics';
const ResponseTime = new Trend('response_time', true);
export const options = {
stages: [
{ duration: '30s', target: 300 },
{ duration: '30s', target: 300 },
{ duration: '30s', target: 0 },
],
thresholds: {
'http_req_failed': ['rate<0.01'],
'http_req_duration': ['p(95)<500'],
'response_time': ['p(95)<500'],
},
};
export default function () {
const id = Math.floor(Math.random() * 100) + 1;
const res = http.get(`http://localhost:5000/api/activities/post/${id}`);
ResponseTime.add(res.timings.duration);
check(res, { 'status is 200': (r) => r.status === 200 });
}
```
---
### Performance Comparison
#### No Buffer
- ✅ Simple to deploy and debug
- ❌ High database load under heavy traffic
- ⏱ Avg. response time: **35.28ms**
- 🧪 Total requests: **509,762**
- 📉 Throughput: ~**5,664 req/s**
#### Redis Buffer
- ✅ High performance
- ✅ Scalable across instances
- ❌ More complex infrastructure (requires Redis setup)
- ⏱ Avg. response time: **11.78ms**
- 🧪 Total requests: **1,520,072**
- 📉 Throughput: ~**16,889 req/s**
#### Memory Buffer
- ✅ Highest performance
- ✅ Easy to deploy
- ❌ Not horizontally scalable (buffer is local to instance)
- ⏱ Avg. response time: **4ms**
- 🧪 Total requests: **4,132,111**
- 📉 Throughput: ~**45,912 req/s**
---
### Summary
Each buffering strategy has its tradeoffs:
| Strategy | Performance | Scalability | Complexity | Avg Response Time |
|----------------|-------------|-------------|------------|-------------------|
| No Buffer | Medium | High | Low | ~35ms |
| Memory Buffer | High | Low | Low | ~4ms |
| Redis Buffer | High | High | Medium | ~12ms |
Choose the approach based on your system’s scalability requirements and infrastructure constraints.
---
## User Portal
Users can access their view history, liked posts, and bookmarked posts in a personalized portal.
The **User Portal** in FormCMS provides a centralized interface for users to manage their social activity, including viewing their interaction history, liked posts, and bookmarked content. This enhances user engagement by offering a tailored experience to revisit and organize content.
### History
Users can view a list of all items they have previously accessed, such as pages, posts, or other content. Each item in the history is displayed with a clickable link, allowing users to easily revisit the content.
### Liked Items
The Liked Items section displays all posts or content that the user has liked. Users can browse their liked items, with options to unlike content or click through to view the full item, fostering seamless interaction with preferred content.
### Bookmarked Items
Users can organize and view their saved content in the Bookmarked Items section. Bookmarks can be grouped into custom folders for easy categorization, enabling users to efficiently manage and access their saved items by folder or as a complete list.
### Configuration
The User Portal displays items with the following metadata:
- **Image**: A thumbnail or visual representation of the item.
- **Title**: The primary name or heading of the item.
- **Subtitle**: A brief description or secondary text for the item.
- **URL**: The link to access the full item.
- **PublishedAt**: The publication date and time of the item.
Metadata mappings are configured on the **Entity Settings** page, where administrators can define how data fields map to the portal's display. The following settings are available:
- **PageUrl**: Specifies the base URL for item links (e.g., "/content/").
- **BookmarkQuery**: Defines the query used to fetch bookmarked items.
- **BookmarkQueryParamName**: Sets the parameter name for the query (e.g., "id").
- **BookmarkTitleField**: Maps the field containing the item's title.
- **BookmarkSubtitleField**: Maps the field for the item's subtitle.
- **BookmarkImageField**: Maps the field for the item's image URL.
- **BookmarkPublishTimeField**: Maps the field for the item's publication timestamp.
These settings allow for flexible customization, ensuring the User Portal displays content accurately and consistently across history, liked items, and bookmarked items.
---
## Optimizing Caching
FormCMS employs advanced caching strategies to boost performance.
For detailed information on ASP.NET Core caching, visit the official documentation: [ASP.NET Core Caching Overview](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/performance/caching/overview?view=aspnetcore-9.0).
### Cache Schema
FormCMS automatically invalidates schema caches whenever schema changes are made. The schema cache consists of two types:
1. **Entity Schema Cache**
Caches all entity definitions required to dynamically generate GraphQL types.
2. **Query Schema Cache**
Caches query definitions, including dependencies on multiple related entities, to compose efficient SQL queries.
By default, schema caching is implemented using `IMemoryCache`. However, you can override this by providing a `HybridCache`. Below is a comparison of the two options:
#### **IMemoryCache**
- **Advantages**:
- Simple to debug and deploy.
- Ideal for single-node web applications.
- **Disadvantages**:
- Not suitable for distributed environments. Cache invalidation on one node (e.g., Node A) does not propagate to other nodes (e.g., Node B).
#### **HybridCache**
- **Key Features**:
- **Scalability**: Combines the speed of local memory caching with the consistency of distributed caching.
- **Stampede Resolution**: Effectively handles cache stampede scenarios, as verified by its developers.
- **Limitations**:
The current implementation lacks "Backend-Assisted Local Cache Invalidation," meaning invalidation on one node does not instantly propagate to others.
- ** FormCMS Strategy**:
FormCMS mitigates this limitation by setting the local cache expiration to 20 seconds (one-third of the distributed cache expiration, which is set to 60 seconds). This ensures cache consistency across nodes within 20 seconds, significantly improving upon the typical 60-second delay in memory caching.
To implement a `HybridCache`, use the following code:
```csharp
builder.AddRedisDistributedCache(connectionName: CmsConstants.Redis);
builder.Services.AddHybridCache();
```
### Cache Data
FormCMS does not automatically invalidate data caches. Instead, it leverages ASP.NET Core's output caching for a straightforward implementation. Data caching consists of two types:
1. **Query Data Cache**
Caches the results of queries for faster access.
2. **Page Cache**
Caches the output of rendered pages for quick delivery.
By default, output caching is disabled in FormCMS. To enable it, configure and inject the output cache as shown below:
```csharp
builder.Services.AddOutputCache(cacheOption =>
{
cacheOption.AddBasePolicy(policyBuilder => policyBuilder.Expire(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(1)));
cacheOption.AddPolicy(CmsOptions.DefaultPageCachePolicyName,
b => b.Expire(TimeSpan.FromMinutes(2)));
cacheOption.AddPolicy(CmsOptions.DefaultQueryCachePolicyName,
b => b.Expire(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)));
});
// After builder.Build();
app.UseOutputCache();
```
---
## Aspire Integration
FormCMS leverages Aspire to simplify deployment.
### Architecture Overview
A scalable deployment of FormCMS involves multiple web application nodes, a Redis server for distributed caching, and a database server, all behind a load balancer.
```
+------------------+
| Load Balancer |
+------------------+
|
+-----------------+-----------------+
| |
+------------------+ +------------------+
| Web App 1 | | Web App 2 |
| +-----------+ | | +-----------+ |
| | Local Cache| | | | Local Cache| |
+------------------+ +------------------+
| |
| |
+-----------------+-----------------+
| |
+------------------+ +------------------+
| Database Server | | Redis Server |
+------------------+ +------------------+
```
---
### Local Emulation with Aspire and Service Discovery
[Example Web project on GitHub](https://github.com/formcms/formcms/tree/main/server/FormCMS.Course)
[Example Aspire project on GitHub](https://github.com/formcms/formcms/tree/main/server/FormCMS.Course.AppHost)
To emulate the production environment locally, FormCMS leverages Aspire. Here's an example setup:
```csharp
var builder = DistributedApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Adding Redis and PostgreSQL services
var redis = builder.AddRedis(name: CmsConstants.Redis);
var db = builder.AddPostgres(CmsConstants.Postgres);
// Configuring the web project with replicas and references
builder.AddProject(name: "web")
.WithEnvironment(CmsConstants.DatabaseProvider, CmsConstants.Postgres)
.WithReference(redis)
.WithReference(db)
.WithReplicas(2);
builder.Build().Run();
```
### Benefits:
1. **Simplified Configuration**:
No need to manually specify endpoints for the database or Redis servers. Configuration values can be retrieved using:
```csharp
builder.Configuration.GetValue();
builder.Configuration.GetConnectionString();
```
2. **Realistic Testing**:
The local environment mirrors the production architecture, ensuring seamless transitions during deployment.
By adopting these caching and deployment strategies, FormCMS ensures improved performance, scalability, and ease of configuration.
---
## Query with Document DB
Optimizing query performance by syncing relational data to a document database, such as MongoDB, significantly improves speed and scalability for high-demand applications.
### Limitations of ASP.NET Core Output Caching
ASP.NET Core's output caching reduces database access when repeated queries are performed. However, its effectiveness is limited when dealing with numerous distinct queries:
1. The application server consumes excessive memory to cache data. The same list might be cached multiple times in different orders.
2. The database server experiences high load when processing numerous distinct queries simultaneously.
### Using Document Databases to Improve Query Performance
For the query below, FormCMS joins the `post`, `tag`, `category`, and `author` tables:
```graphql
query post_sync($id: Int) {
postList(idSet: [$id], sort: id) {
id, title, body, abstract
tag {
id, name
}
category {
id, name
}
author {
id, name
}
}
}
```
By saving each post along with its related data as a single document in a document database, such as MongoDB, several improvements are achieved:
- Reduced database server load since data retrieval from multiple tables is eliminated.
- Reduced application server processing, as merging data is no longer necessary.
### Performance Testing
Using K6 scripts with 1,000 virtual users concurrently accessing the query API, the performance difference between PostgreSQL and MongoDB was tested, showing MongoDB to be significantly faster:
```javascript
export default function () {
const id = Math.floor(Math.random() * 1000000) + 1; // Random id between 1 and 1,000,000
/* PostgreSQL */
// const url = `http://localhost:5091/api/queries/post_sync/?id=${id}`;
/* MongoDB */
const url = `http://localhost:5091/api/queries/post/?id=${id}`;
const res = http.get(url);
check(res, {
'is status 200': (r) => r.status === 200,
'response time is < 200ms': (r) => r.timings.duration < 200,
});
}
/*
MongoDB:
http_req_waiting...............: avg=50.8ms min=774µs med=24.01ms max=3.23s p(90)=125.65ms p(95)=211.32ms
PostgreSQL:
http_req_waiting...............: avg=5.54s min=11.61ms med=4.08s max=44.67s p(90)=13.45s p(95)=16.53s
*/
```
### Synchronizing Query Data to Document DB
#### Architecture Overview

#### Enabling Message Publishing in WebApp
To enable publishing messages to the Message Broker, use Aspire to add a NATS resource. Detailed documentation is available in [Microsoft Docs](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/aspire/messaging/nats-integration?tabs=dotnet-cli).
Add the following line to the Aspire HostApp project:
```csharp
builder.AddNatsClient(AppConstants.Nats);
```
Add the following lines to the WebApp project:
```csharp
builder.AddNatsClient(AppConstants.Nats);
var entities = builder.Configuration.GetRequiredSection("TrackingEntities").Get()!;
builder.Services.AddNatsMessageProducer(entities);
```
FormCMS publishes events for changes made to entities listed in `appsettings.json`:
```json
{
"TrackingEntities": [
"post"
]
}
```
#### Enabling Message Consumption in Worker App
Add the following to the Worker App:
```csharp
var builder = Host.CreateApplicationBuilder(args);
builder.AddNatsClient(AppConstants.Nats);
builder.AddMongoDBClient(AppConstants.MongoCms);
var apiLinksArray = builder.Configuration.GetRequiredSection("ApiLinksArray").Get()!;
builder.Services.AddNatsMongoLink(apiLinksArray);
```
Define the `ApiLinksArray` in `appsettings.json` to specify entity changes and the corresponding query API:
```json
{
"ApiLinksArray": [
{
"Entity": "post",
"Api": "http://localhost:5001/api/queries/post_sync",
"Collection": "post",
"PrimaryKey": "id"
}
]
}
```
When changes occur to the `post` entity, the Worker Service calls the query API to retrieve aggregated data and saves it as a document.
#### Migrating Query Data to Document DB
After adding a new entry to `ApiLinksArray`, the Worker App will perform a migration from the start to populate the Document DB.
### Replacing Queries with Document DB
#### Architecture Overview

To enable MongoDB queries in your WebApp, use the Aspire MongoDB integration. Details are available in [Microsoft Docs](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/aspire/database/mongodb-integration?tabs=dotnet-cli).
Add the following code to your WebApp:
```csharp
builder.AddMongoDBClient(connectionName: AppConstants.MongoCms);
var queryLinksArray = builder.Configuration.GetRequiredSection("QueryLinksArray").Get()!;
builder.Services.AddMongoDbQuery(queryLinksArray);
```
Define `QueryLinksArray` in `appsettings.json` to specify MongoDB queries:
```json
{
"QueryLinksArray": [
{ "Query": "post", "Collection": "post" },
{ "Query": "post_test_mongo", "Collection": "post" }
]
}
```
The WebApp will now query MongoDB directly for the specified collections.
---
## Integrating it into Your Project
Follow these steps to integrate FormCMS into your project using a NuGet package.
You can reference the code from https://github.com/FormCMS/FormCMS/tree/main/examples
1. **Create a New ASP.NET Core Web Application**.
2. **Add the NuGet Package**:
To add FormCMS, run the following command:
```
dotnet add package FormCMS
```
3. **Modify `Program.cs`**:
Add the following line before `builder.Build()` to configure the database connection (use your actual connection string):
```
builder.AddSqliteCms("Data Source=cms.db");
var app = builder.Build();
```
Currently, FormCMS supports `AddSqliteCms`, `AddSqlServerCms`, and `AddPostgresCms`.
4. **Initialize FormCMS**:
Add this line after `builder.Build()` to initialize the CMS:
```
await app.UseCmsAsync();
```
This will bootstrap the router and initialize the FormCMS schema table.
---
## Adding Business Logic
Learn how to customize your application by adding validation logic, hook functions, and producing events to Kafka.
### Adding Validation Logic with Simple C# Expressions
#### Simple C# Validation
You can define simple C# expressions in the `Validation Rule` of attributes using [Dynamic Expresso](https://github.com/dynamicexpresso/DynamicExpresso). For example, a rule like `name != null` ensures the `name` attribute is not null.
Additionally, you can specify a `Validation Error Message` to provide users with feedback when validation fails.
#### Using Regular Expressions
`Dynamic Expresso` supports regular expressions, allowing you to write rules like `Regex.IsMatch(email, "^[a-zA-Z0-9_.+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9-]+\\.[a-zA-Z0-9-.]+$")`.
> Note: Since `Dynamic Expresso` doesn't support [verbatim strings](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/csharp/language-reference/tokens/verbatim), you must escape backslashes (`\`).
---
### Extending Functionality with Hook Functions
To implement custom business logic, such as verifying that a `teacher` entity has valid email and phone details, you can register hook functions to run before adding or updating records:
```csharp
var registry = app.GetHookRegistry();
// Hook function for pre-add validation
registry.EntityPreAdd.Register("teacher", args =>
{
VerifyTeacher(args.RefRecord);
return args;
});
// Hook function for pre-update validation
registry.EntityPreUpdate.Register("teacher", args =>
{
VerifyTeacher(args.RefRecord);
return args;
});
```
---
### Producing Events to an Event Broker (e.g., Kafka)
To enable asynchronous business logic through an event broker like Kafka, you can produce events using hook functions. This feature requires just a few additional setup steps:
1. Add the Kafka producer configuration:
```csharp
builder.AddKafkaMessageProducer("localhost:9092");
```
2. Register the message producer hook:
```csharp
app.RegisterMessageProducerHook();
```
Here’s a complete example:
```csharp
builder.AddSqliteCms("Data Source=cmsapp.db").PrintVersion();
builder.AddKafkaMessageProducer("localhost:9092");
var app = builder.Build();
await app.UseCmsAsync(false);
app.RegisterMessageProducerHook();
```
With this setup, events are produced to Kafka, allowing consumers to process business logic asynchronously.
---
## Development Guide
The backend is written in ASP.NET Core, the Admin Panel uses React, and the Schema Builder is developed with jQuery.
### Overview
The system comprises three main components:
1. **Backend** - Developed in ASP.NET Core.
2. **Admin Panel** - Built using React.
3. **Schema Builder** - Created with jQuery.
#### System Diagram
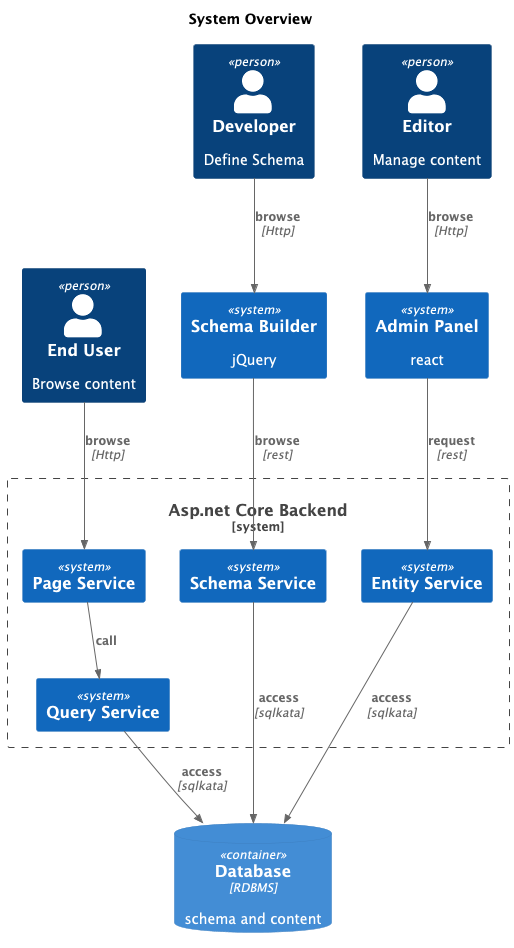
### Repository Links
- [**Backend Server**](https://github.com/formcms/formcms/tree/main/server/FormCMS)
- [**Admin Panel Sdk**](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminSdk)
- [**Admin Panel App**](https://github.com/FormCms/FormCmsAdminApp)
- [**Schema Builder**](https://github.com/formcms/formcms/tree/main/server/FormCMS/wwwroot/schema-ui)
---
### Backend Server
#### Tools
- **ASP.NET Core**
- **SqlKata** ([SqlKata Documentation](https://sqlkata.com/))
#### Architecture
The backend is influenced by Domain-Driven Design (DDD).

Code organization follows this diagram:

##### Core (Domain Layer)
The **Core layer** encapsulates:
- **Descriptors**: Includes `Entity`, `Filter`, `Sort`, and similar components for building queries.
- **HookFactory**: Maintains a global `Hook Registry`, enabling developers to integrate custom plugins.
> **Note**: The Core layer is independent of both the Application and Infrastructure layers.
##### Application Layer
The **Application layer** provides the following functionalities:
1. **CMS**: Entity CRUD, GraphQL Queries, and Page Designer.
2. **Auth**: Manages permissions and roles.
3. **DataLink**: Integrates DocumentDB and Event Streams for scalability.
> Includes `Builders` to configure Dependency Injection and manage Infrastructure components.
##### Infrastructure Layer
The **Infrastructure layer** defines reusable system infrastructural components.
- Application services depend on interfaces instead of implementations.
- Components are designed for portability and can be reused across other projects.
##### Util Layer
A separate **Util component** contains static classes with pure functions.
- Accessible across all layers.
---
### Admin Panel UI
#### Tools
- **React**
- **PrimeReact** ([PrimeReact UI Library](https://primereact.org/))
- **SWR** ([Data Fetching/State Management](https://swr.vercel.app/))
#### Admin Panel Sequence

---
### Schema Builder UI
#### Tools
- **jsoneditor** ([JSON Editor Documentation](https://github.com/json-editor/json-editor))
---
## Testing Strategy
This chapter describes the systems' automated testing strategy
Favors integration testing over unit testing because integration tests can catch more real-world issues.
For example, when inserting a record into the database, multiple modules are involved:
- `EntitiesHandler`
- `EntitiesService`
- `Entity` (in core)
- `Query executors` (e.g., `SqlLite`, `Postgres`, `SqlServer`)
Writing unit tests for each function and mocking its upstream and downstream services can be tedious.
Instead, FormCMS focuses on checking the input and output of RESTful API endpoints in its integration tests.
### Integration Testing for FormCMS.Course `/formcms/server/FormCMS.Course.Tests`
This project focuses on verifying the functionalities of the FormCMS.Course example project.
### New Feature Testing `/formcms/server/FormCMS.App.Tests`
This project is dedicated to testing experimental functionalities, like MongoDB and Kafka plugins.