https://github.com/garrettj403/czt
Chirp Z-Transform
https://github.com/garrettj403/czt
czt dft dsp fourier-transform frequency-domain signal-processing z-transform
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Chirp Z-Transform
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/garrettj403/czt
- Owner: garrettj403
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-11-25T15:22:31.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-20T07:34:08.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-30T11:06:37.980Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: czt, dft, dsp, fourier-transform, frequency-domain, signal-processing, z-transform
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 12.2 MB
- Stars: 44
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 16
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGES.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Chirp Z-Transform (CZT)
=======================
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/czt)
[](https://github.com/garrettj403/CZT/actions/workflows/ci.yml)
[](https://github.com/garrettj403/CZT/actions/workflows/linter.yml)
From [Wikipedia](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chirp_Z-transform):
> The chirp Z-transform (CZT) is a generalization of the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). While the DFT samples the Z plane at uniformly-spaced points along the unit circle, the chirp Z-transform samples along spiral arcs in the Z-plane, corresponding to straight lines in the S plane. The DFT, real DFT, and zoom DFT can be calculated as special cases of the CZT.
Getting Started
---------------
You can install the CZT package using ``pip``:
```bash
# to install the latest release (from PyPI)
pip install czt
# to install the latest commit (from GitHub)
git clone https://github.com/garrettj403/CZT.git
cd CZT
pip install -e .
# to install dependencies for examples
pip install -e .[examples]
# to install dependencies for testing
pip install -e .[testing]
```
Example
-------
Consider the following time-domain signal:
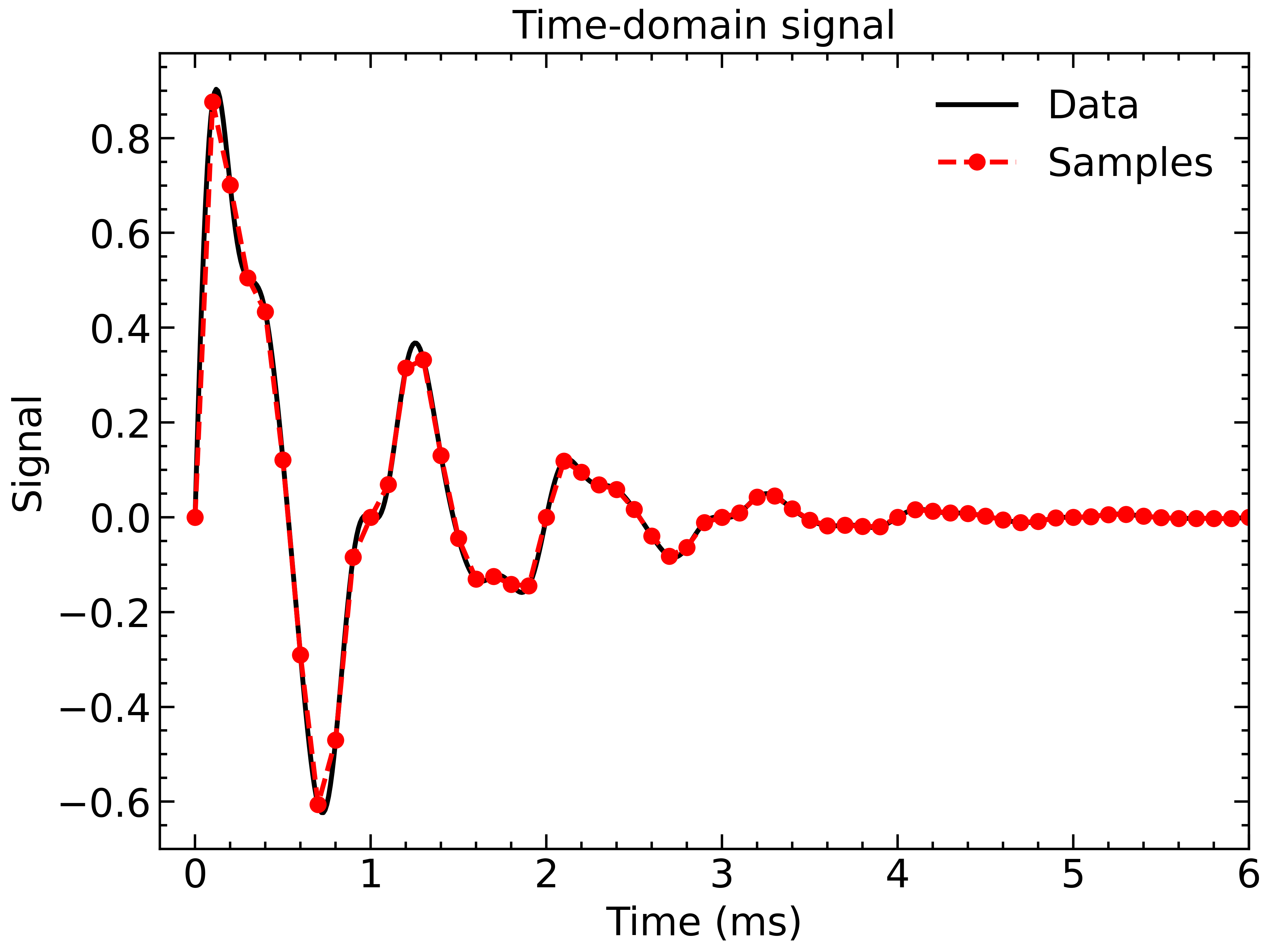
This is an exponentially decaying sine wave with some distortion from higher-order frequencies. We can convert this signal to the frequency-domain to investigate the frequency content using the Chirp Z-Transform (CZT):
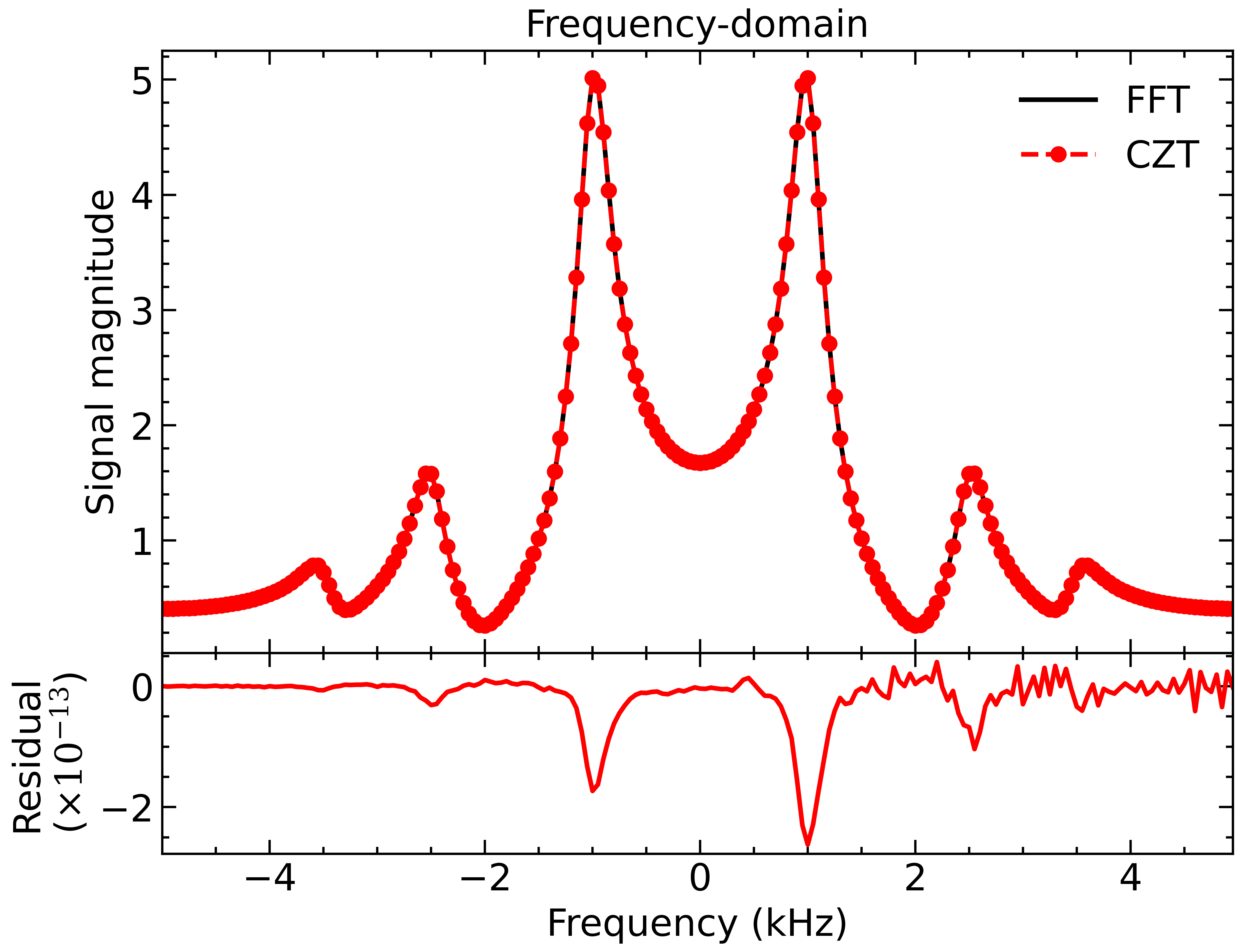
Note that the CZT also allows us to calculate the frequency response over an arbitrary frequency range:
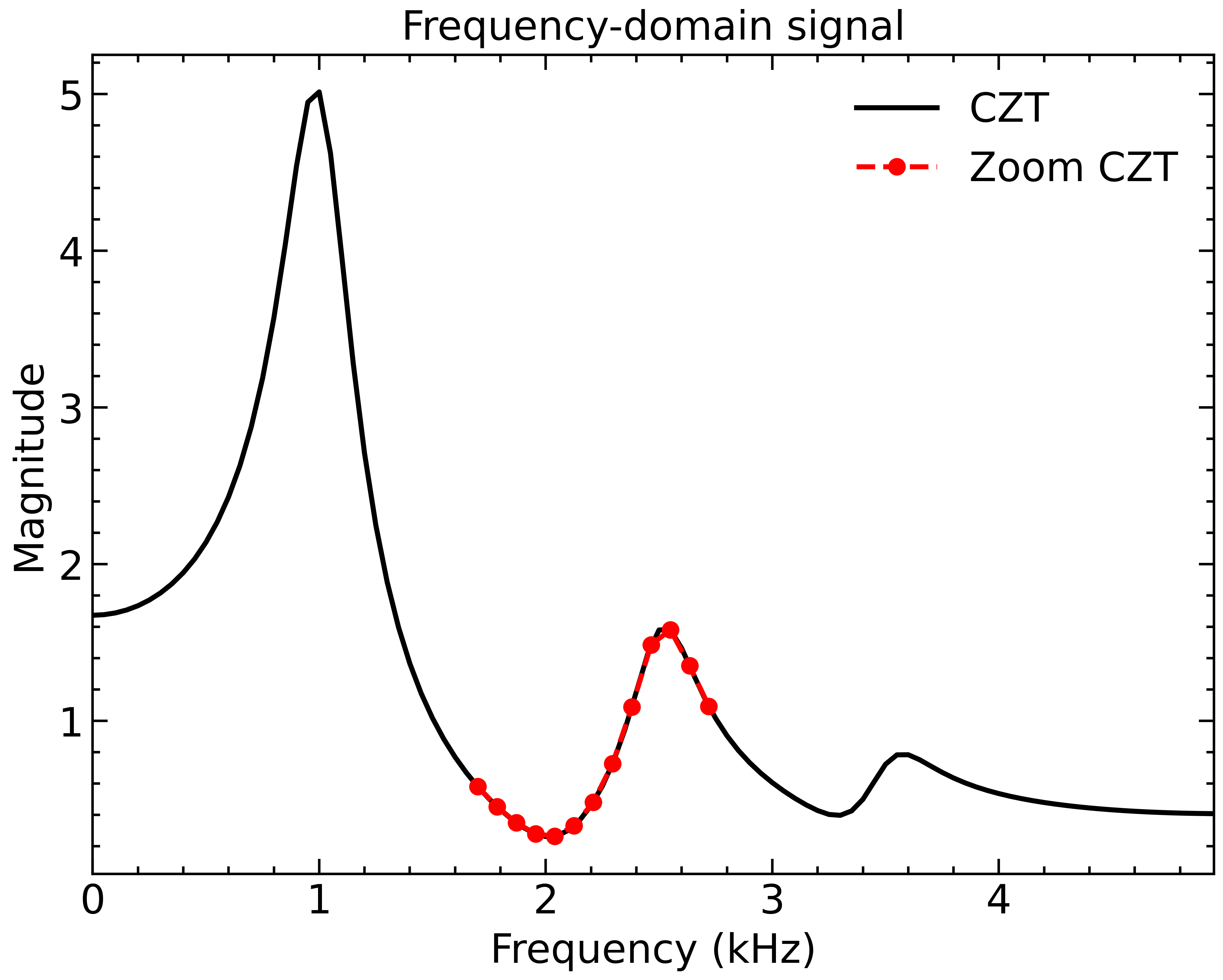
We can see that the signal has frequency components at 1 kHz, 2.5 kHz and 3.5 kHz. To remove the distortion and isolate the 1 kHz signal, we can apply a simple window in the frequency-domain:
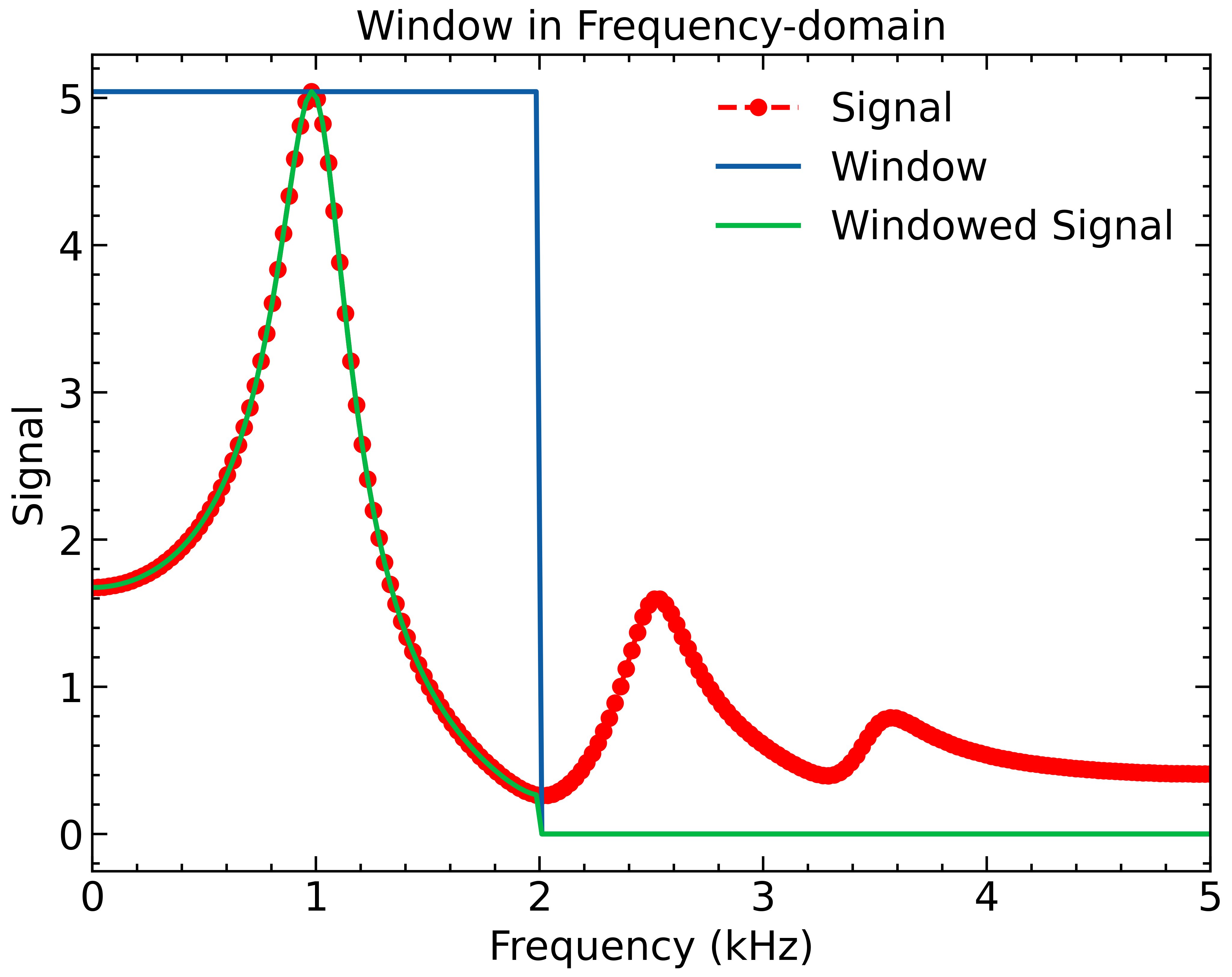
Finally, we can use the Inverse Chirp Z-Transform (ICZT) to transform back to the time domain:
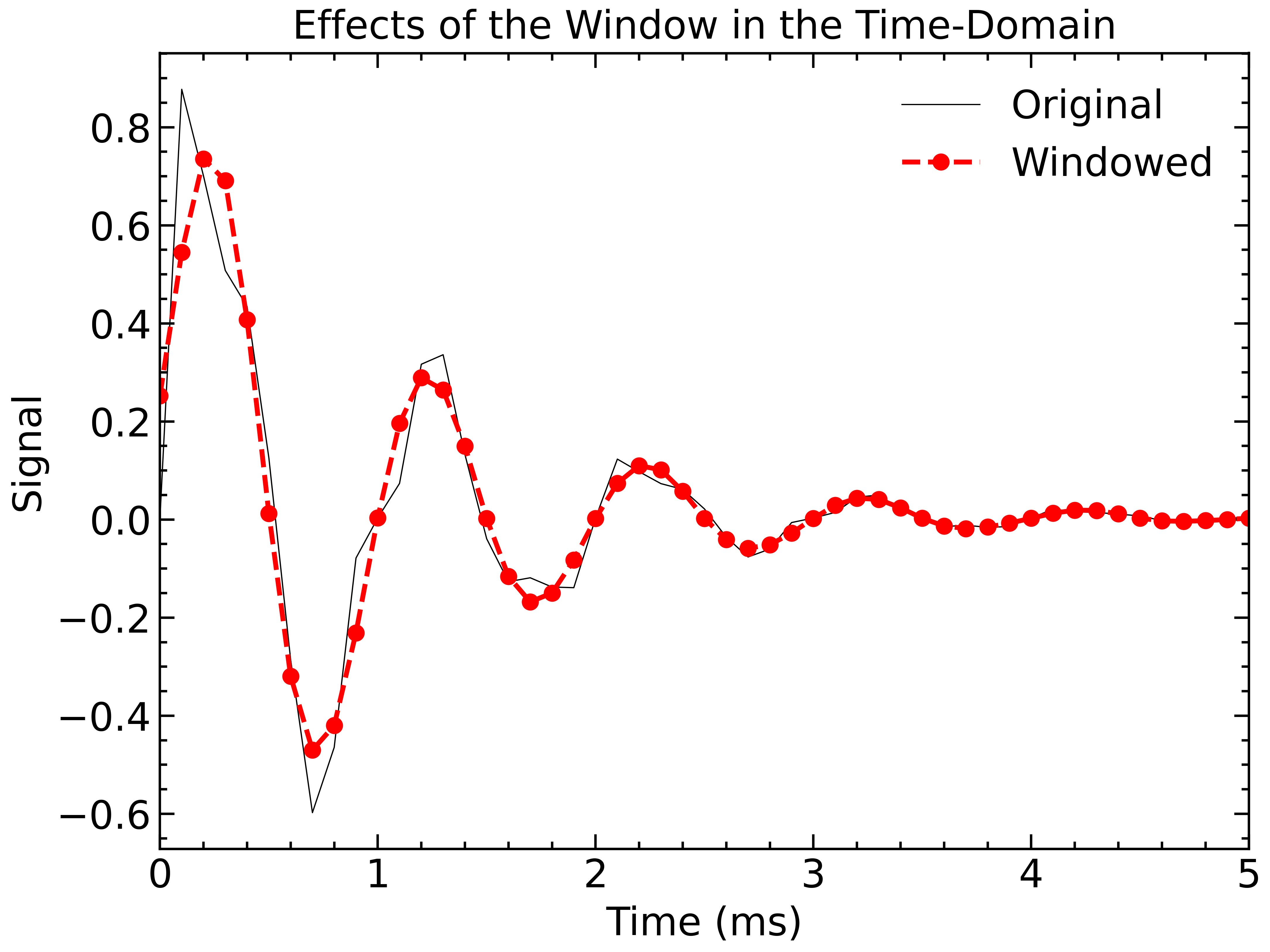
As we can see, we were able to remove the higher-order frequencies that were distorting our 1 kHz signal.
You can find this example and others in the [``examples/``](https://github.com/garrettj403/CZT/blob/main/examples/) directory.
References
----------
- [L. Rabiner, R. Schafer and C. Rader, "The chirp z-transform algorithm," *IEEE Transactions on Audio and Electroacoustics*, vol. 17, no. 2, pp. 86-92, Jun. 1969, doi: 10.1109/TAU.1969.1162034.](https://web.ece.ucsb.edu/Faculty/Rabiner/ece259/Reprints/015_czt.pdf)
- [V. Sukhoy and A. Stoytchev, "Generalizing the inverse FFT off the unit circle," *Scientific Reports*, vol. 9, no. 14443, Oct. 2019, doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50234-9.](https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-50234-9)
- [Chirp Z-Transform (Wikipedia)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chirp_Z-transform)
- [Discrete Fourier Transform (Wikipedia)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Discrete_Fourier_transform)