https://github.com/germanaizek/docker-sandbox-windows
Sandbox zum testen verdächtiger software auf schädliche aktivitäten
https://github.com/germanaizek/docker-sandbox-windows
docker malware-analysis malware-analyzer malware-detection malware-dev malware-developing malware-research windows wine
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Sandbox zum testen verdächtiger software auf schädliche aktivitäten
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/germanaizek/docker-sandbox-windows
- Owner: GermanAizek
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-04-10T12:20:31.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-03T15:44:26.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-30T01:29:41.186Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: docker, malware-analysis, malware-analyzer, malware-detection, malware-dev, malware-developing, malware-research, windows, wine
- Language: Shell
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.08 MB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Docker Wine Sandbox for Windows
## Architecture (future plan)

## More information
[](https://github.com/scottyhardy/docker-wine/actions/workflows/build.yml)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/scottyhardy/docker-wine)
[](https://hub.docker.com/r/scottyhardy/docker-wine)
[](https://github.com/scottyhardy/docker-wine/network)
[](https://github.com/scottyhardy/docker-wine/stargazers)

>Docker image that includes Wine and Winetricks for running Windows applications on Linux and macOS
The docker-wine container can either be run with X11 forwarding or as an RDP server to suit your use case. The default is to use X11 forwarding which utilizes your machine's X server to render graphics directly into your current session and play sounds through pulseaudio (audio redirection on Linux only).
Using docker-wine with an RDP server allows the container to be run on a headless machine or a machine that may not be running an X server. You can then use a Remote Desktop client to connect to the container which may be located either on your local or a remote machine. This is currently the only solution if you require sound on macOS.
---
## Getting Started
Using the `docker-wine` script is the easiest way to get started and should be all you need for Linux, macOS and Windows (WSL2 - sounds is broken).
### Download the `docker-wine` script
On WSL2:
```bash
apt update && apt install docker xauth pulseaudio
```
When Docker Desktop starts, go to `Settings > Resources > WSL Integration`.
The Docker-WSL integration is enabled on the default WSL distribution, which is Ubuntu
To change your default WSL distro, run:
```bash
wsl --set-default
```
Installing `docker-wine` and run rdp access
```bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cihuuy/docker-wine/master/docker-wine && chmod +x docker-wine && ./docker-wine --rdp
```
On Linux:
```bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/cihuuy/docker-wine/master/docker-wine && chmod +x docker-wine && ./docker-wine --rdp
```
## Run `docker-wine` with X11 forwarding
Running the script with no other arguments will start an interactive bash session:
```bash
./docker-wine
```
You can override the default interactive bash session by adding `wine`, `winetricks`, `winecfg` or any other valid commands with their associated arguments:
```bash
./docker-wine wine notepad
```
## Run `docker-wine` with Xvfb
Starts up a frame buffer display defaulting to: Xvfb :95 -screen 0 320x200x8
Exports DISPLAY to the server number :95
```bash
./docker-wine --xvfb
```
### Customizable options
```bash
./docker-wine --xvfb=:95,0,320x200x8
```
## Run `docker-wine` attached with notty
```bash
./docker-wine --notty
```
## Run `docker-wine` with RDP server
Run with the `--rdp` option to start the RDP server with an interactive bash session:
```bash
./docker-wine --rdp
```
Or, you can run the container as a detached daemon that runs in the background. To start the daemon:
```bash
./docker-wine --rdp=start
```
Then to stop the daemon:
```bash
./docker-wine --rdp=stop
```
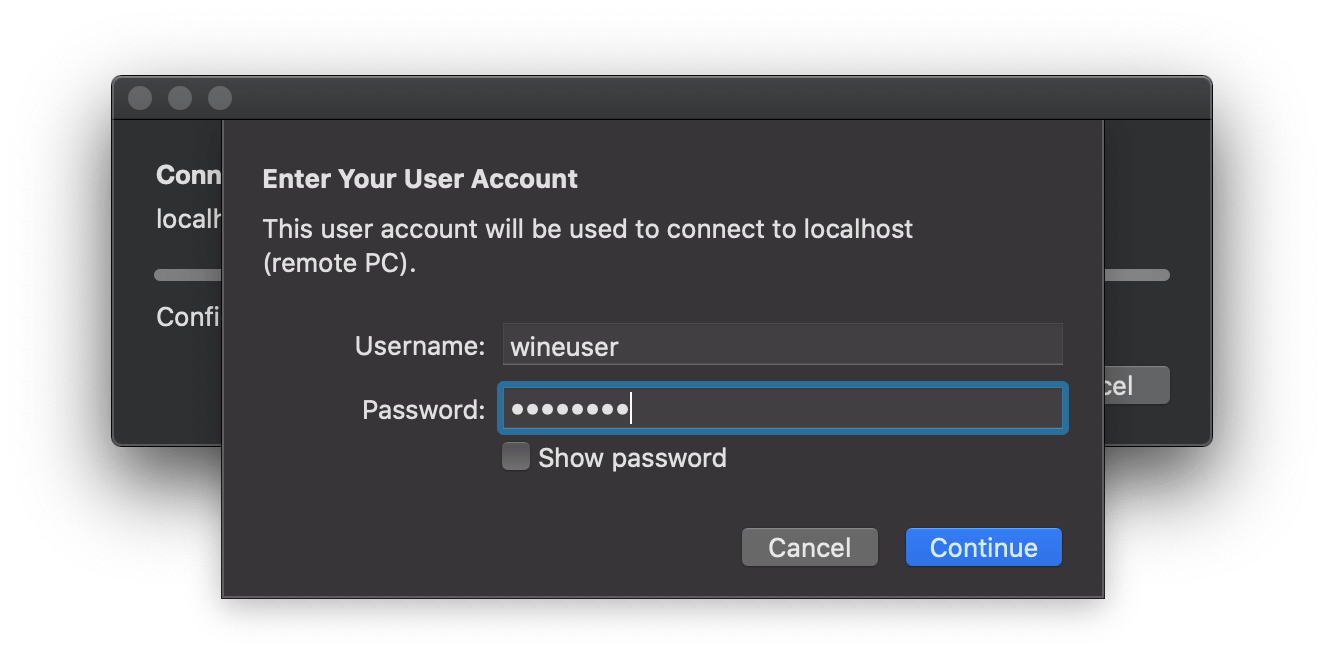
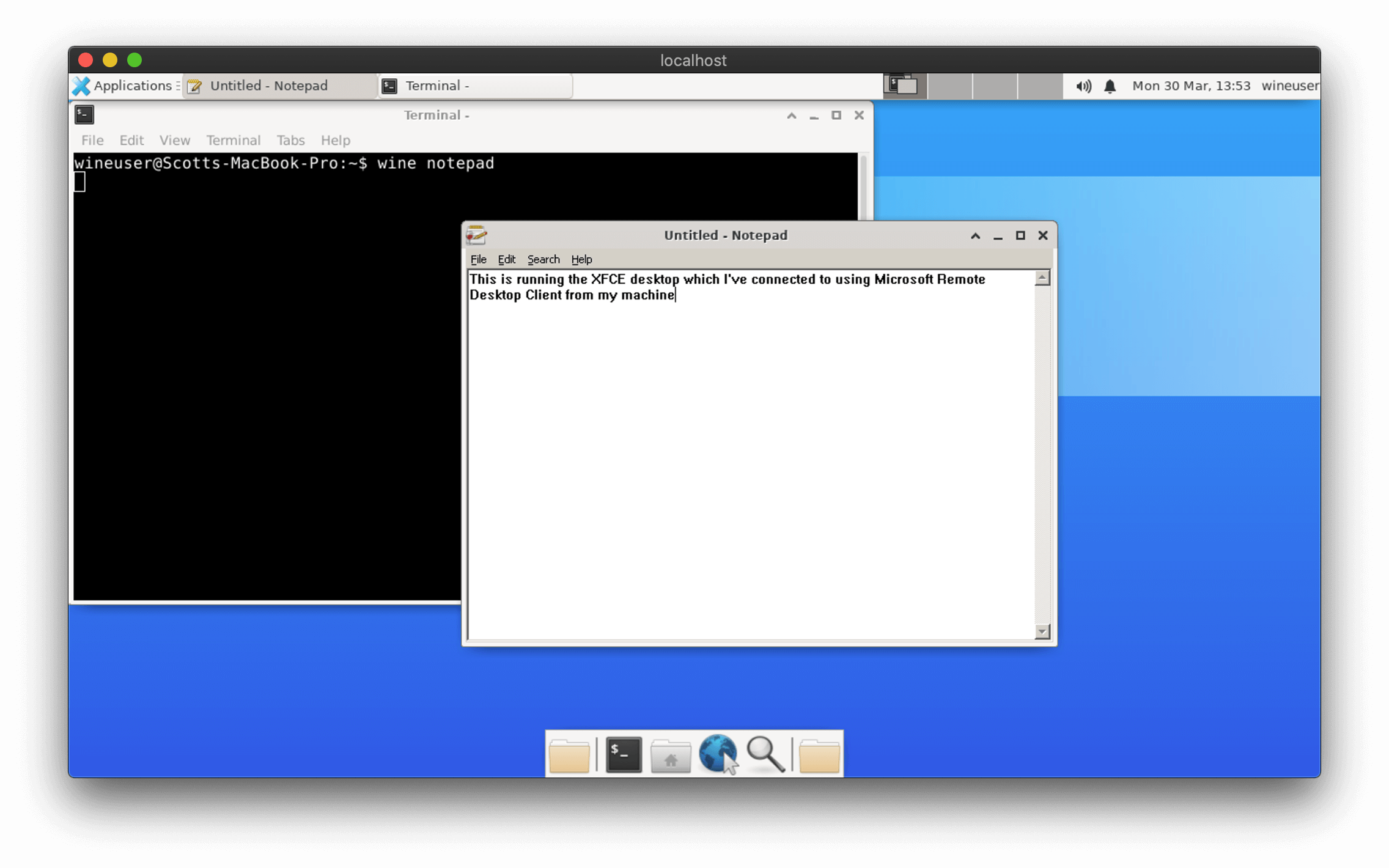
## Connecting with an RDP client
All Windows desktops and servers come with the Remote Desktop Connection client pre-installed and macOS users can download the Microsoft Remote Desktop application for free from the App Store. For Linux users, I'd suggest using the Remmina Remote Desktop client.
For the hostname, use `localhost` if the container is hosted on the same machine you're running your Remote Desktop client on and for remote connections just use the name or IP address of the machine you are connecting to.
NOTE: To connect to a remote machine, it will require TCP port 3389 to be exposed through the firewall.
To log in, use the following default user account details:
```bash
Username: wineuser
Password: wineuser
```
## Additional options when running `docker-wine`
Start the container as root:
```bash
./docker-wine --as-root
```
Or start the container as yourself with the same username, UID, GID and home path (especially useful when binding to local file system):
```bash
./docker-wine --as-me
```
You can combine options:
```bash
./docker-wine --as-root --rdp
```
You can also use standard docker syntax to add as many additional environment variables, devices and volumes as you need:
```bash
./docker-wine --env="MY_ENV_VAR=some_value" --device=/dev/snd --volume="myvol:/some/path:ro" --volume="/usr/data:data"
```
See the `docker-wine` help for a full list of options:
```bash
./docker-wine --help
```
## Securing your password
The default password is `wineuser` and it will change to your own username by default if you use the `--as-me` argument. You can override the default password by using `--password="your_password"` but even though this password is encrypted before passing it to the container, your password still appears in plain text in the process list for any other user connected to the same host machine. Depending on your use case, this could be a problem.
One solution is to use `--password-prompt` and be prompted to enter the user password when you instantiate the docker-wine container. This will prevent your password from appearing in your machine's process list, but does require manually entering the password each time.
If prompting is undesirable, the solution is to encrypt your password _before_ passing it to the `docker-wine` script, using `openssl`. This command will produce an MD5 encrypted hash of your password with a random salt which means each run will produce a different hash:
```bash
openssl passwd -1 -salt $(openssl rand -base64 6) "your_password"
```
One method of using this secure string would be to store it to disk:
```bash
echo $(openssl passwd -1 -salt $(openssl rand -base64 6) "your_password") > ~/.docker-wine
```
Then simply `cat` the file when using the `docker-wine` script:
```bash
./docker-wine --rdp --as-me --secure-password="$(cat ~/.docker-wine)"
```
## Build and run locally on your own computer
First, clone the repository from GitHub:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/scottyhardy/docker-wine.git
cd docker-wine
```
To build the container, simply run:
```bash
./build
```
To run the your locally built container, use `docker-wine` with the `--local` switch:
```bash
./docker-wine --local wine notepad
```
## Volume container winehome
When the docker-wine container is instantiated with the `docker-wine` script, a volume container named `winehome` is created and is mapped to the user's home within the container. Using a volume container allows the docker-wine container to be safely removed after every execution as user data will persist as long as the `winehome` volume is not removed. This effectively allows the `docker-wine` image to be swapped out for a newer version at anytime.
You can manually create the `winehome` volume container by running:
```bash
docker volume create winehome
```
If you don't want the volume container, you can delete it by using:
```bash
docker volume rm winehome
```
## Troubleshooting
To test video, try opening Notepad:
```bash
./docker-wine wine notepad
```
To test sound, try using `pacat`:
```bash
./docker-wine pacat -vv /dev/urandom
```
## Uninstalling
It simple, just execute for removing container:
```
sudo docker rmi -f docker-wine
```