https://github.com/gibsramen/evident_
Effect size calculations for microbiome data
https://github.com/gibsramen/evident_
data-visualization microbiome python qiime2 statistics visualization
Last synced: 8 days ago
JSON representation
Effect size calculations for microbiome data
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/gibsramen/evident_
- Owner: gibsramen
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2022-02-01T17:23:51.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-04-26T17:19:06.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-02T09:01:35.520Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: data-visualization, microbiome, python, qiime2, statistics, visualization
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.38 MB
- Stars: 5
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://github.com/gibsramen/evident/actions/workflows/main.yml)
[](https://github.com/gibsramen/evident/actions/workflows/q2.yml)
[](https://pypi.org/project/evident)
# evident
Evident is a tool for performing effect size and power calculations on microbiome diversity data.
## Installation
You can install the most up-to-date version of evident from PyPi using the following command:
```bash
pip install evident
```
## QIIME 2
evident is also available as a [QIIME 2](https://qiime2.org/) plugin.
Make sure you have activated a QIIME 2 environment and run the same installation command as above.
To check that evident installed correctly, run the following from the command line:
```bash
qiime evident --help
```
You should see something like this if evident installed correctly:
```bash
Usage: qiime evident [OPTIONS] COMMAND [ARGS]...
Description: Perform power analysis on microbiome diversity data. Supports
calculation of effect size given metadata covariates and supporting
visualizations.
Plugin website: https://github.com/gibsramen/evident
Getting user support: Please post to the QIIME 2 forum for help with this
plugin: https://forum.qiime2.org
Options:
--version Show the version and exit.
--example-data PATH Write example data and exit.
--citations Show citations and exit.
--help Show this message and exit.
Commands:
alpha-effect-size-by-category Alpha diversity effect size by category.
alpha-power-analysis Alpha diversity power analysis.
beta-effect-size-by-category Beta diversity effect size by category.
beta-power-analysis Beta diversity power analysis.
plot-power-curve Plot power curve.
visualize-results Tabulate evident results.
```
## Standalone Usage
evident requires two input files:
1. Either an alpha or beta diversity file
2. Sample metadata
First, open Python and import evident
```python
import evident
```
Next, load your diversity file and sample metadata.
For alpha diversity, this should be a pandas Series.
For beta diversity, this should be an scikit-bio DistanceMatrix.
Sample metadata should be a pandas DataFrame.
We'll be using an alpha diversity vector for this tutorial but the commands are nearly the same for beta diversity distance matrices.
```python
import pandas as pd
metadata = pd.read_table("data/metadata.tsv", sep="\t", index_col=0)
faith_pd = metadata["faith_pd"]
```
The main data structure in evident is the 'DiversityHandler'.
This is the way that evident stores the diversity data and metadata for power calculations.
For our alpha diversity example, we'll load the `AlphaDiversityHandler` class from evident.
`AlphaDiversityHandler` takes as input the pandas Series with the diversity values and the pandas DataFrame containing the sample metadata.
By default, evident will only consider metadata columns with, at max, 5 levels.
To modify this behavior, provide a value for the `max_levels_per_category` argument.
Additionally, evident will not consider any category levels represented by fewer than 3 samples.
To modify this behavior, use the `min_count_per_level` argument.
```python
adh = evident.AlphaDiversityHandler(faith_pd, metadata)
```
Next, let's say we want to get the effect size of the diversity differences between two groups of samples.
We have in our example a column in the metadata "classification" comparing two groups of patients with Crohn's disease.
First, we'll look at the mean of Faith's PD between these two groups.
```python
metadata.groupby("classification").agg(["count", "mean", "std"])["faith_pd"]
```
which results in
```
count mean std
classification
B1 99 13.566110 3.455625
Non-B1 121 9.758946 3.874911
```
Looks like there's a pretty large difference between these two groups.
What we would like to do now is calculate the effect size of this difference.
Because we are comparing only two groups, we can use Cohen's d.
evident automatically chooses the correct effect size to calculate - either Cohen's d if there are only two categories or Cohen's f if there are more than 2.
```python
adh.calculate_effect_size(column="classification")
```
This tells us that our effect size is 1.03.
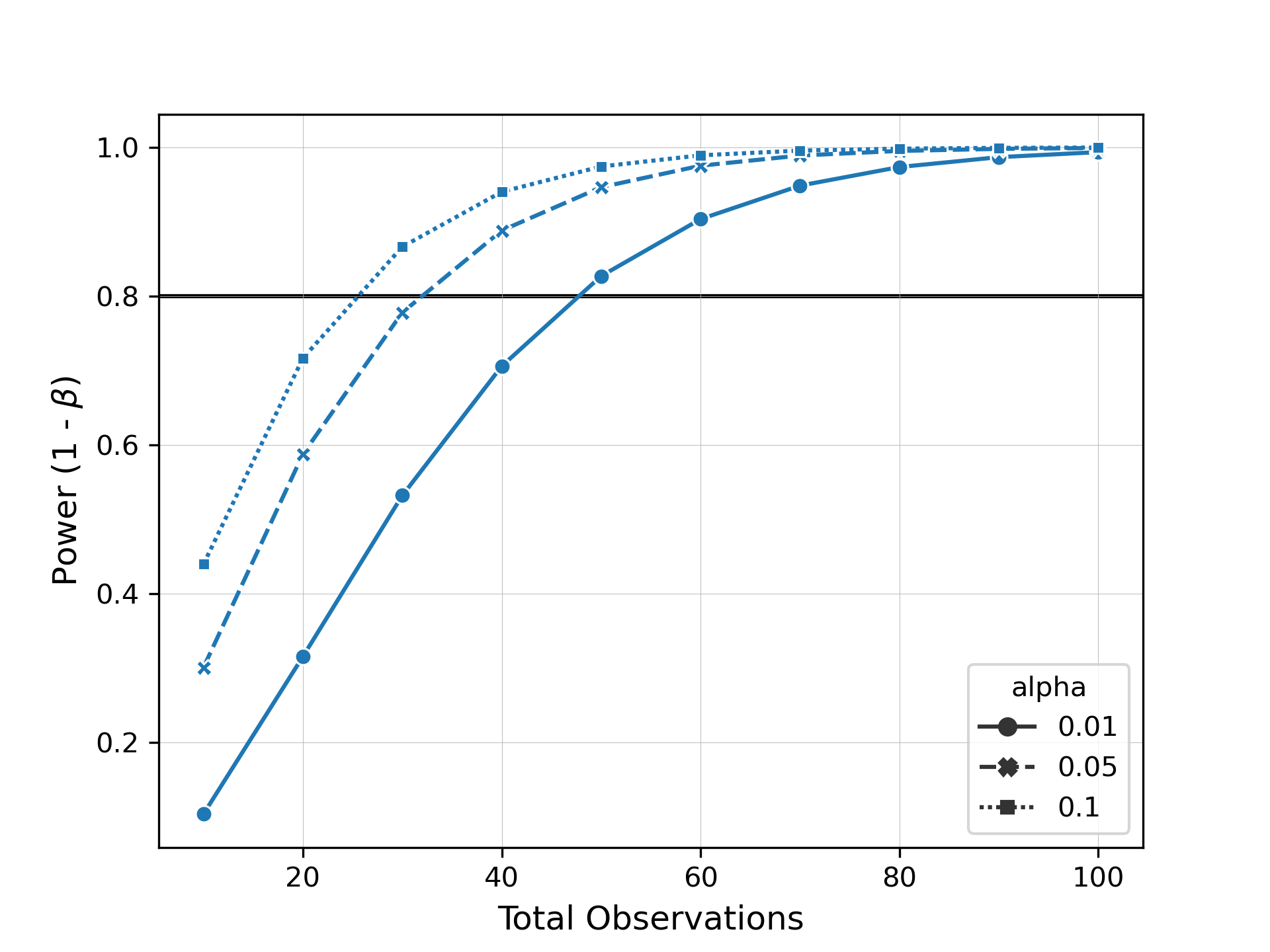
Now let's say we want to see how many samples we need to be able to detect this difference with a power of 0.8.
evident allows you to easily specify arguments for alpha, power, or total observations for power analysis.
We can then plot these results as a power curve to summarize the data.
```python
from evident.plotting import plot_power_curve
import numpy as np
alpha_vals = [0.01, 0.05, 0.1]
obs_vals = np.arange(10, 101, step=10)
results = adh.power_analysis(
"classification",
alpha=alpha_vals,
total_observations=obs_vals
)
plot_power_curve(results, target_power=0.8, style="alpha", markers=True)
```
When we inspect this plot, we can see how many samples we would need to collect to observe the same effect size at different levels of significance and power.
## Interactive power curve with Bokeh
evident allows users to *interactively* perform effect size and power calculations using [Bokeh](https://docs.bokeh.org/en/latest/).
To create a Bokeh app, use the following command:
```python
from evident.interactive import create_bokeh_app
create_bokeh_app(adh, "app")
```
This will save the necessary files into a new directory `app/`.
Navigate to the directory containing `app/` (**not** `app/` itself) and execute this command from your terminal:
```bash
bokeh serve --show app
```
This should open up a browser window where you can modify the chosen column, significance, level, and observations.
We also provide a command line script to generate an interactive app using some test data.
You can access this script at `evident/tests/make_interactive.py`.

Note that because evident uses Python to perform the power calculations, it is at the moment not possible to embded this interactive app into a standalone webpage.
## QIIME 2 Usage
evident provides support for the popular QIIME 2 framework of microbiome data analysis.
We assume in this tutorial that you are familiar with using QIIME 2 on the command line.
If not, we recommend you read the excellent [documentation](https://docs.qiime2.org/) before you get started with evident.
Note that we have only tested evident on QIIME 2 version 2021.11.
If you are using a different version and encounter an error please let us know via an issue.
As with the standalone version, evident requires a diversity file and a sample metadata file.
These inputs are expected to conform to QIIME 2 standards.
To calculate power, we can run the following command:
```bash
qiime evident alpha-power-analysis \
--i-alpha-diversity faith_pd.qza \
--m-sample-metadata-file metadata.qza \
--m-sample-metadata-column classification \
--p-alpha 0.01 0.05 0.1 \
--p-total-observations $(seq 10 10 100) \
--o-power-analysis-results results.qza
```
Notice how we used `$(seq 10 10 100)` to provide input into the `--p-total-observations` argument.
`seq` is a command on UNIX-like systems that generates a sequence of numbers.
In our example, we used `seq` to generate the values from 10 to 100 in intervals of 10 (10, 20, ..., 100).
With this results artifact, we can visualize the power curve to get a sense of how power varies with number of observations and significance level.
Run the following command:
```bash
qiime evident plot-power-curve \
--i-power-analysis-results results.qza \
--p-target-power 0.8 \
--p-style alpha \
--o-visualization power_curve.qzv
```
You can view this visualization at [view.qiime2.org](https://view.qiime2.org/) directly in your browser.
## Parallelization
evident provides support for parallelizing effect size calculations through [joblib](https://joblib.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parallel.html).
Parallelization is performed across different columns when using `effect_size_by_category` and `pairwise_effect_size_by_category`.
Consider parallelization if you have a lot of samples and/or a lot of different metadata categories of interest.
By default, no parallelization is performed.
With Python:
```python
from evident.effect_size import effect_size_by_category
effect_size_by_category(
adh,
["classification", "cd_resection", "cd_behavior"],
n_jobs=2
)
```
With QIIME 2:
```bash
qiime evident alpha-effect-size-by-category \
--i-alpha-diversity faith_pd.qza \
--m-sample-metadata-file metadata.qza \
--p-columns classification sex cd_behavior \
--p-n-jobs 2 \
--o-effect-size-results alpha_effect_sizes.qza
```
## Help with evident
If you encounter a bug in evident, please post a GitHub issue and we will get to it as soon as we can.
We welcome any ideas or documentation updates/fixes so please submit an issue and/or a pull request if you have thoughts on making evident better.
If your question is regarding the QIIME 2 version of evident, consider posting to the [QIIME 2 forum](https://forum.qiime2.org/).
You can open an issue on the [Community Plugin Support](https://forum.qiime2.org/c/community-plugin-support/24) board and tag [@gibsramen](https://forum.qiime2.org/u/gibsramen) if required.