https://github.com/giswqs/whitebox-frontends
WhiteboxTools Frontends
https://github.com/giswqs/whitebox-frontends
arcgis geomorphometry geoprocessing geospatial gis hydrology lidar python r remote-sensing rstats rstudio
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
WhiteboxTools Frontends
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/giswqs/whitebox-frontends
- Owner: giswqs
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-10-21T13:52:49.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: gh-pages
- Last Pushed: 2020-06-09T01:30:15.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-20T13:36:53.675Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: arcgis, geomorphometry, geoprocessing, geospatial, gis, hydrology, lidar, python, r, remote-sensing, rstats, rstudio
- Homepage: https://gishub.org/whitebox
- Size: 8.79 KB
- Stars: 20
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# WhiteboxTools Frontends
[](https://jblindsay.github.io/wbt_book)
[](https://github.com/giswqs/whitebox-frontends)
[](https://github.com/jblindsay/whitebox-tools)
[](https://github.com/giswqs/whitebox-python)
[](https://github.com/giswqs/whiteboxR)
[](https://github.com/giswqs/WhiteboxTools-ArcGIS)
[](https://jblindsay.github.io/wbt_book/qgis_plugin.html)
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
[](https://twitter.com/giswqs)
**WhiteboxTools** is an advanced geospatial data analysis platform developed by Prof. [John Lindsay](https://github.com/jblindsay) at the University of Guelph's [Geomorphometry and Hydrogeomatics Research Group](https://jblindsay.github.io/ghrg/index.html). The **[WhiteboxTools](https://github.com/jblindsay/whitebox-tools)** library currently contains **440** tools, which are each grouped based on their main function into one of the following categories: Data Tools, GIS Analysis, Hydrological Analysis, Image Analysis, LiDAR Analysis, Mathematical and Statistical Analysis, Stream Network Analysis, and Terrain Analysis. For a listing of available tools, complete with documentation and usage details, please see the [WhiteboxTools User Manual](https://jblindsay.github.io/wbt_book/available_tools/index.html).
**WhiteboxTools** can be accessed either from a [command prompt](#cmd) (i.e. terminal) or through one of the following front-ends:
- [Python Package](#python)
- [R Package](#r)
- [ArcGIS Python Toolbox](#arcgis)
- [QGIS Plugin](#qgis)
- [Command-line Interface](#cmd)
### Links
- GitHub repo:
- PyPI:
- conda-forge:
- Documentation:
- Maintainer: [Qiusheng Wu](https://wetlands.io)
### Installation
The **whitebox** Python package can be installed using the following command:
```python
pip install whitebox
```
The **whitebox** Python package is also available on [conda-forge](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/whitebox), which can be installed using the following command:
```python
conda install -c conda-forge whitebox
```
### Usage
Tool names in the whitebox Python package can be called using the snake_case convention (e.g. lidar_info). See below for an example Python script.
```python
import os
import pkg_resources
import whitebox
wbt = whitebox.WhiteboxTools()
print(wbt.version())
print(wbt.help())
# identify the sample data directory of the package
data_dir = os.path.dirname(pkg_resources.resource_filename("whitebox", 'testdata/'))
wbt.set_working_dir(data_dir)
wbt.verbose = False
wbt.feature_preserving_smoothing("DEM.tif", "smoothed.tif", filter=9)
wbt.breach_depressions("smoothed.tif", "breached.tif")
wbt.d_inf_flow_accumulation("breached.tif", "flow_accum.tif")
```
**WhiteboxTools** also provides a Graphical User Interface (GUI) - **WhiteboxTools Runner**, which can be invoked using the following Python script:
```python
import whitebox
whitebox.Runner()
```
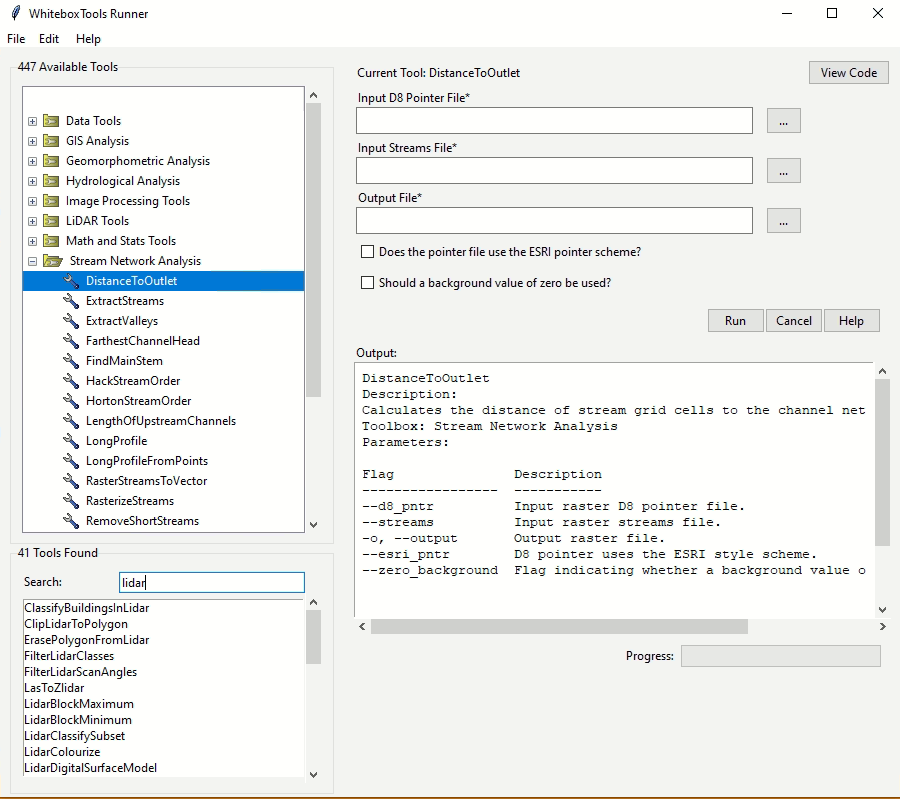
### Links
- GitHub repo:
- R-Forge:
- Documentation:
- Maintainer: [Qiusheng Wu](https://wetlands.io)
### Installation
The **whitebox** R package is available on [R-Forge](https://r-forge.r-project.org/R/?group_id=2337), which can be installed using the following command:
```R
install.packages("whitebox", repos="http://R-Forge.R-project.org")
```
You can alternatively install the development version of whitebox from [GitHub](https://github.com/giswqs/whiteboxR) as follows:
```R
if (!require(devtools)) install.packages('devtools')
devtools::install_github("giswqs/whiteboxR")
```
### RStudio Screenshot
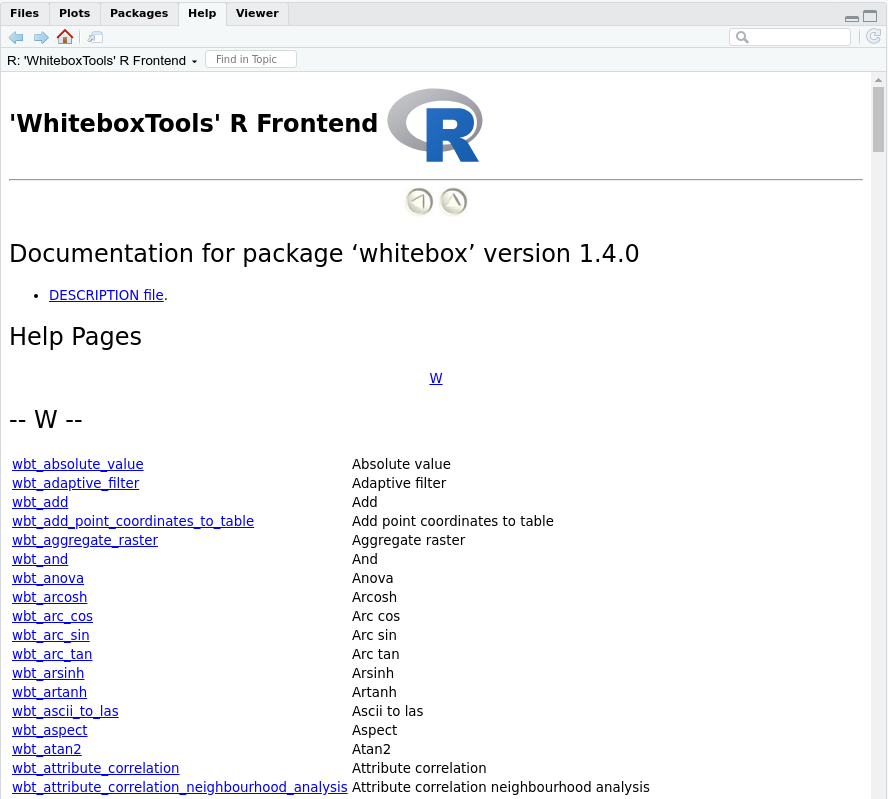
### Usage
Tool names in the **whitebox** R package can be called using the snake_case (e.g. wbt_lidar_info). See below for an example.
```R
library(whitebox)
# Set input raster DEM file
dem <- system.file("extdata", "DEM.tif", package="whitebox")
# Run tools
wbt_feature_preserving_smoothing(dem, "./smoothed.tif", filter=9, verbose_mode = TRUE)
wbt_breach_depressions("./smoothed.tif", "./breached.tif")
wbt_d_inf_flow_accumulation(dem, "./flow_accum.tif")
```
### Links
- GitHub repo:
- Maintainer: [Qiusheng Wu](https://wetlands.io)
### Installation
#### Step 1: Download the toolbox
1. Go to the [WhiteboxTools-ArcGIS GitHub repo](https://github.com/giswqs/WhiteboxTools-ArcGIS) and click the green button (**[Clone or download](https://gishub.org/whitebox-arcgis-download)**) on the upper-right corner of the page to download the toolbox as a zip file.

2. Depcompress the downloaded zip file.
#### Step 2: Connect to the toolbox
1. Navigate to the **Folder Connections** node in the catalog window tree.
2. Right-click the node and choose **Connect To Folder**.

3. Type the path or navigate to the **WhiteboxTools-ArcGIS** folder and click **OK**.
4. Browse into the toolbox and start using its tools.

### Usage
Open any tool within the toolbox and start using it. Check out the [WhiteboxTools User Mannual](https://jblindsay.github.io/wbt_book/) for more detailed help documentation of each tool.

### ArcGIS Pro Screenshot
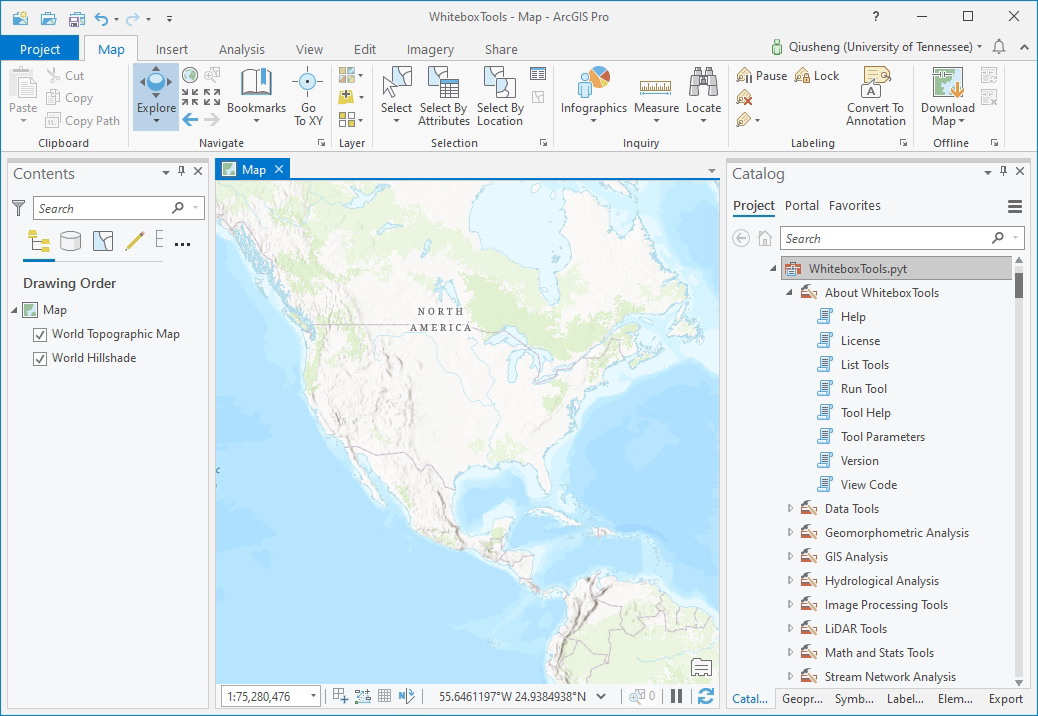
### ArcMap Screenshots
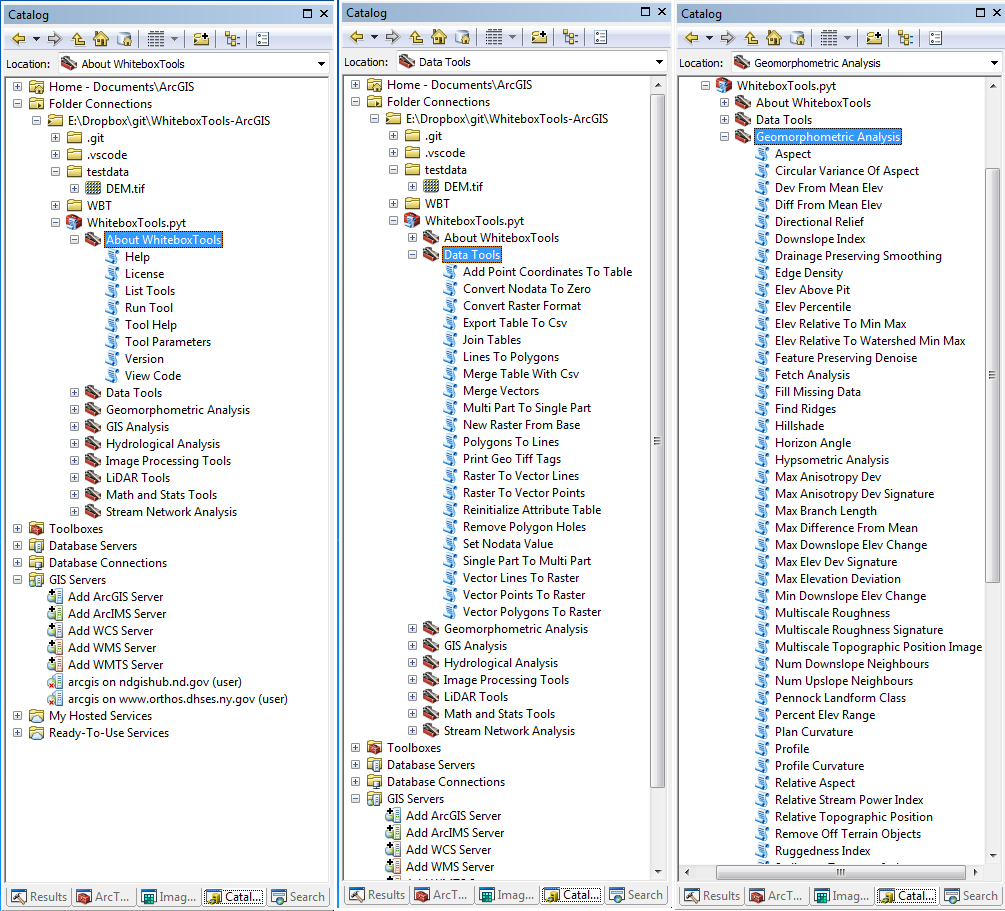
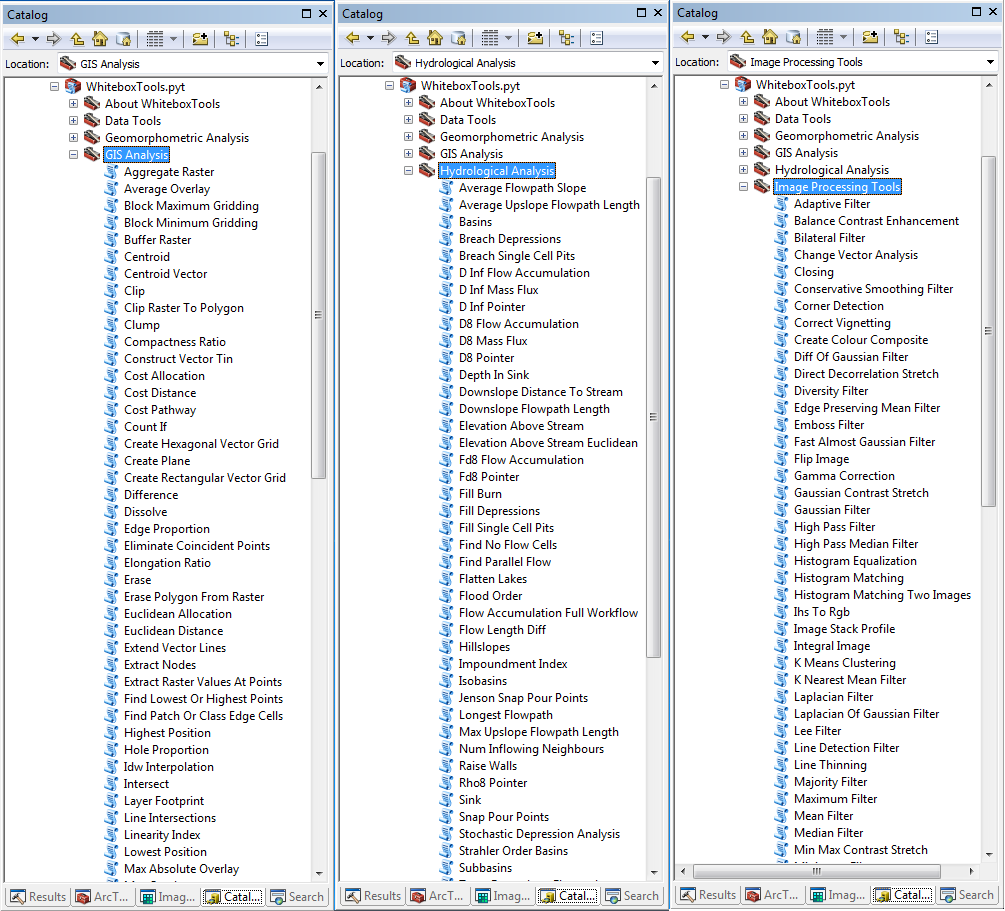
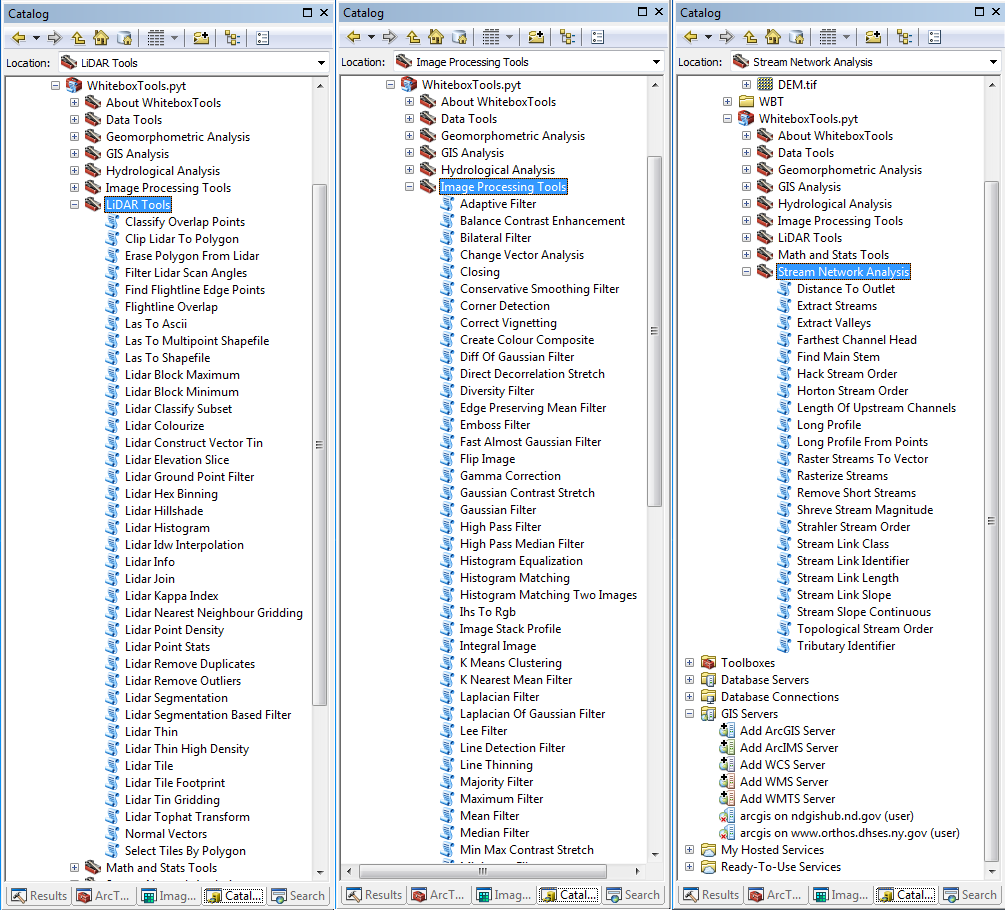
### Links
- Documentation:
- GitHub repo: https://github.com/alexbruy/processing-wbt
- Maintainer: [Alexander Bruy](https://wiki.osgeo.org/wiki/User:Alexbruy)
### Installation
Please follow the installation guide [here](https://jblindsay.github.io/wbt_book/qgis_plugin.html).
### Screenshot
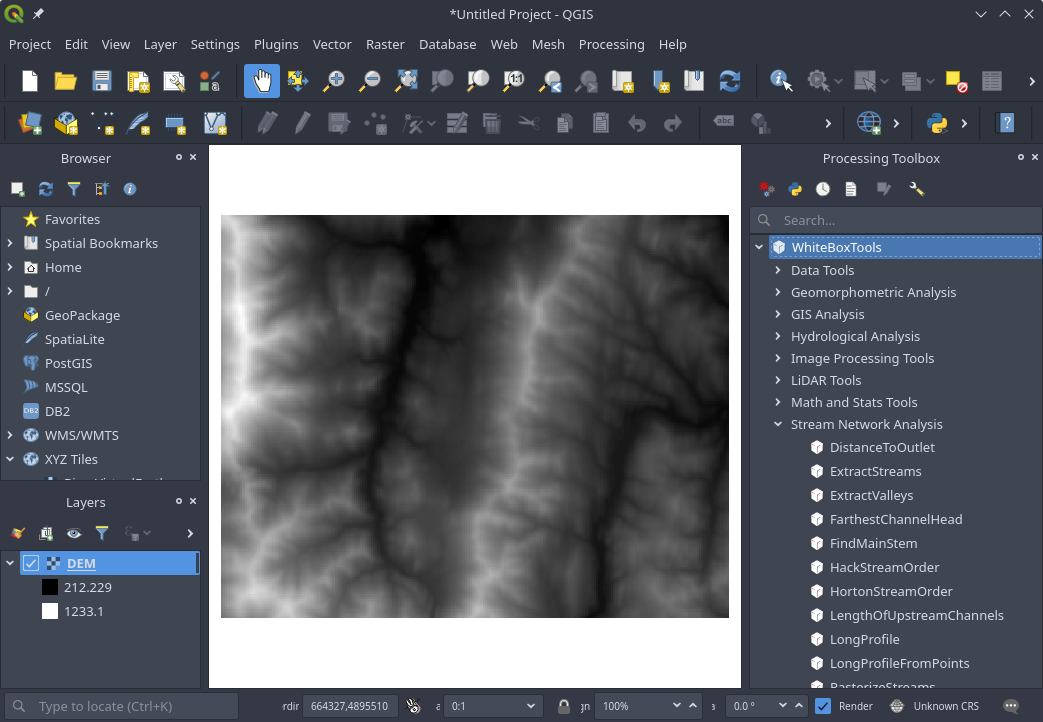
### Links
- GitHub repo:
- User Manual:
- Maintainer: [John Lindsay](https://jblindsay.github.io/ghrg/index.html)
### Installation
You can download a copy of the **WhiteboxTools** executable for your operating system from the [Geomorphometry and Hydrogeomatics Research Group website](https://jblindsay.github.io/ghrg/WhiteboxTools/download.html). Once you've downloaded WhiteboxTools and decompressed (unzipped) the folder, you can open a command prompt and start using it.
### Usage
**WhiteboxTools** is a command-line program and can be run by calling it with appropriate commands and arguments, from a terminal application. The following commands are recognized by the **WhiteboxTools** library:
| Command | Description |
| ---------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ |
| --cd, --wd | Changes the working directory; used in conjunction with --run flag. |
| -h, --help | Prints help information. |
| -l, --license | Prints the whitebox-tools license. |
| --listtools | Lists all available tools, with tool descriptions. Keywords may also be used, --listtools slope. |
| -r, --run | Runs a tool; used in conjunction with --cd flag; -r="LidarInfo". |
| --toolbox | Prints the toolbox associated with a tool; --toolbox=Slope. |
| --toolhelp | Prints the help associated with a tool; --toolhelp="LidarInfo". |
| --toolparameters | Prints the parameters (in json form) for a specific tool; --toolparameters=\"LidarInfo\". |
| -v | Verbose mode. Without this flag, tool outputs will not be printed. |
| --viewcode | Opens the source code of a tool in a web browser; --viewcode=\"LidarInfo\". |
| --version | Prints the version information. |
Generally, the Unix convention is that single-letter arguments (options) use a single hyphen (e.g. -h) while word-arguments (longer, more descriptive argument names) use double hyphen (e.g. --help). The same rule is used for passing arguments to tools as well. Use the _--toolhelp_ argument to print information about a specific tool (e.g. --toolhelp=Clump). Tool names can be specified either using the snake_case or CamelCase convention (e.g. _lidar_info_ or _LidarInfo_).
For examples of how to call functions and run tools from _WhiteboxTools_, see the _whitebox_example.py_ Python script, which itself uses the _whitebox_tools.py_ script as an interface for interacting with the executable file.
In addition to direct command-line and script-based interaction, a very basic user-interface called _WB Runner_ can be used to call the tools within the _WhiteboxTools_ executable file, providing the required tool arguments.
**Example command prompt:**
```
>>./whitebox_tools --wd='/Users/johnlindsay/Documents/data/' --run=DevFromMeanElev
--input='DEM clipped.dep' --output='DEV raster.dep' -v
```
Notice the quotation marks (single or double) used around directories and filenames, and string tool arguments in general. Use the '-v' flag (run in verbose mode) to force the tool print output to the command prompt. Please note that the whitebox_tools executable file must have permission to be executed; on some systems, this may require setting special permissions. The '>>' is shorthand for the command prompt and is not intended to be typed. Also, the above example uses the forward slash character (/), the directory path separator used on unix based systems. On Windows, users should use the back slash character (\\) instead.