https://github.com/gkonovalov/android-vad
Android Voice Activity Detection (VAD) library. Supports WebRTC VAD GMM, Silero VAD DNN, Yamnet VAD DNN models.
https://github.com/gkonovalov/android-vad
android audio-processing deep-neural-networks dnn gmm neural-networks offline on-device-ai onnx-models real-time silero silero-vad speech-detection speech-recoginition vad voice-activity-detection voice-activity-detector voice-detection webrtc yamnet
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
Android Voice Activity Detection (VAD) library. Supports WebRTC VAD GMM, Silero VAD DNN, Yamnet VAD DNN models.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/gkonovalov/android-vad
- Owner: gkonovalov
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-11-28T02:00:23.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-31T10:52:36.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-09T06:04:50.261Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: android, audio-processing, deep-neural-networks, dnn, gmm, neural-networks, offline, on-device-ai, onnx-models, real-time, silero, silero-vad, speech-detection, speech-recoginition, vad, voice-activity-detection, voice-activity-detector, voice-detection, webrtc, yamnet
- Language: C
- Homepage:
- Size: 5.18 MB
- Stars: 323
- Watchers: 9
- Forks: 69
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
## Android Voice Activity Detection (VAD)
Android [VAD](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voice_activity_detection) library is designed to process audio in
real-time and identify presence of human speech in audio samples that contain a mixture of speech
and noise. The VAD functionality operates offline, performing all processing tasks directly on the mobile device.
The repository offers three distinct models for voice activity detection:
[WebRTC VAD](https://chromium.googlesource.com/external/webrtc/+/branch-heads/43/webrtc/common_audio/vad/) [[1]](#1)
is based on a Gaussian Mixture Model [(GMM)](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mixture_model#Gaussian_mixture_model)
which is known for its exceptional speed and effectiveness in distinguishing between noise and silence.
However, it may demonstrate relatively lower accuracy when it comes to differentiating speech from background noise.
[Silero VAD](https://github.com/snakers4/silero-vad) [[2]](#2) is based on a Deep Neural Networks
[(DNN)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deep_learning) and utilizes the
[ONNX Runtime Mobile](https://onnxruntime.ai/docs/install/#install-on-web-and-mobile) for execution.
It provides exceptional accuracy and achieves processing time that is very close to WebRTC VAD.
[Yamnet VAD](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/research/audioset/yamnet) [[3]](#3) is based on a Deep Neural Networks
[(DNN)](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Deep_learning) and employs the Mobilenet_v1 depthwise-separable
convolution architecture. For execution utilizes the [Tensorflow Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/android) runtime.
Yamnet VAD can predict [521](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/audioset/yamnet/yamnet_class_map.csv)
audio event classes (such as speech, music, animal sounds and etc).
It was trained on [AudioSet-YouTube](https://research.google.com/audioset/) corpus.
WebRTC VAD is lightweight (only 158 KB) and provides exceptional speed in audio processing, but it may exhibit lower accuracy
compared to DNN models. WebRTC VAD can be invaluable in scenarios where a small and fast library is necessary and where sacrificing accuracy is acceptable.
In situations where high accuracy is critical, models like Silero VAD and Yamnet VAD are more preferable.
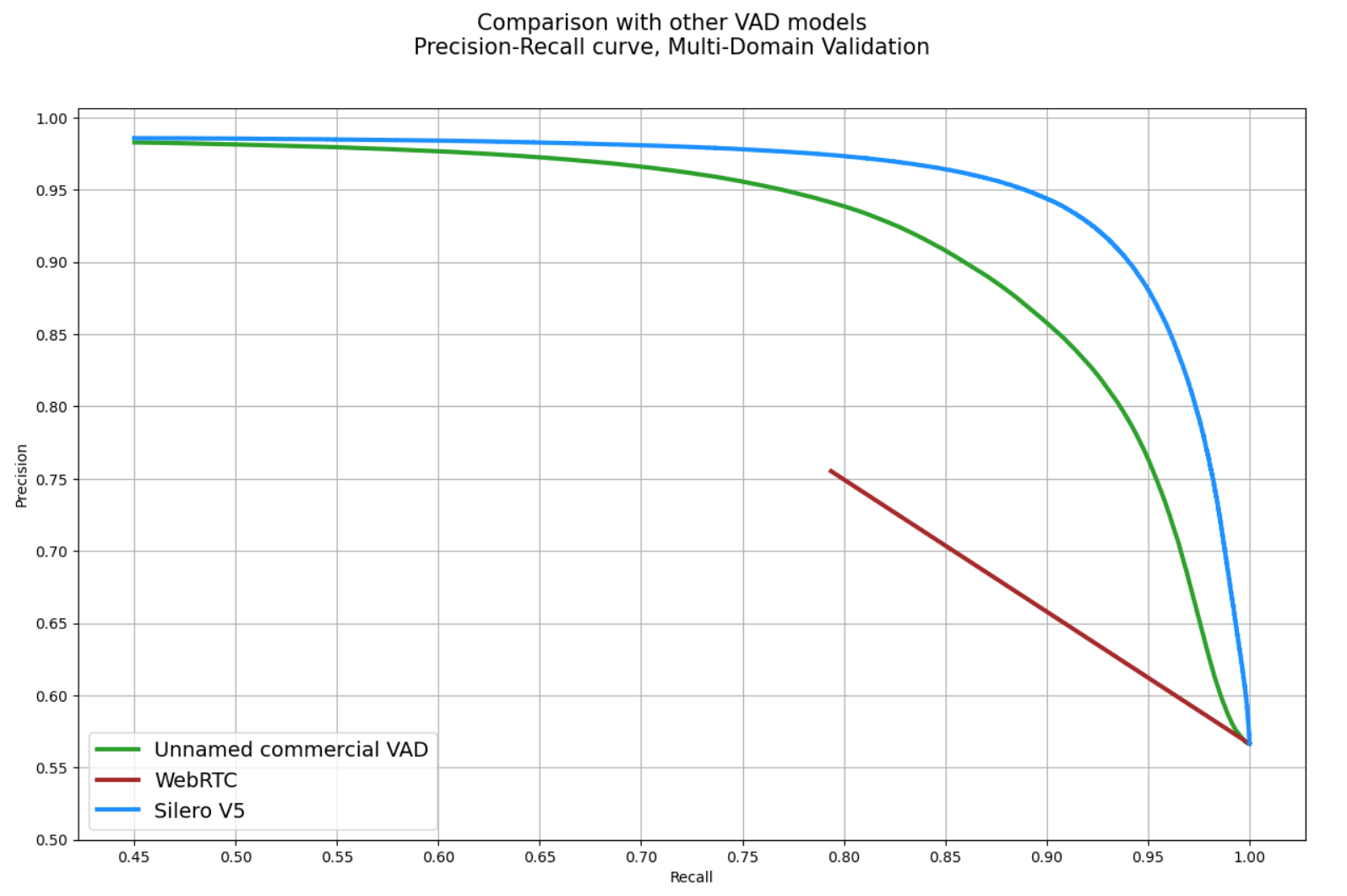
For more detailed insights and a comprehensive comparison between DNN and GMM, refer to the following comparison
[Silero VAD vs WebRTC VAD](https://github.com/snakers4/silero-vad/wiki/Quality-Metrics#vs-other-available-solutions).
## WebRTC VAD
#### Parameters
WebRTC VAD library only accepts **16-bit Mono PCM audio stream** and can work with next Sample Rates,
Frame Sizes and Modes.
| Valid Sample Rate | Valid Frame Size |
|:-----------------:|:----------------:|
| 8000Hz | 80, 160, 240 |
| 16000Hz | 160, 320, 480 |
| 32000Hz | 320, 640, 960 |
| 48000Hz | 480, 960, 1440 |
| Valid Mode |
|:----------------|
| NORMAL |
| LOW_BITRATE |
| AGGRESSIVE |
| VERY_AGGRESSIVE |
Recommended parameters for WebRTC VAD:
* Sample Rate (required) - **16KHz** - The sample rate of the audio input.
* Frame Size (required) - **320** - The frame size of the audio input.
* Mode (required) - **VERY_AGGRESSIVE** - The confidence mode of the VAD model.
* Silence Duration (optional) - **300ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for silence segments.
* Speech Duration (optional) - **50ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for speech segments.
#### Usage
WebRTC VAD can identify speech in short audio frames, returning results for each frame.
By utilizing parameters such as **silenceDurationMs** and **speechDurationMs**, you can enhance the
capability of VAD, enabling the detection of prolonged utterances while minimizing false positive
results during pauses between sentences.
Java example:
```java
VadWebRTC vad = Vad.builder()
.setSampleRate(SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K)
.setFrameSize(FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_320)
.setMode(Mode.VERY_AGGRESSIVE)
.setSilenceDurationMs(300)
.setSpeechDurationMs(50)
.build();
boolean isSpeech = vad.isSpeech(audioData);
vad.close();
```
Kotlin example:
```kotlin
VadWebRTC(
sampleRate = SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K,
frameSize = FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_320,
mode = Mode.VERY_AGGRESSIVE,
silenceDurationMs = 300,
speechDurationMs = 50
).use { vad ->
val isSpeech = vad.isSpeech(audioData)
}
```
An example of how to detect speech in an audio file:
```kotlin
VadWebRTC(
sampleRate = SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K,
frameSize = FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_320,
mode = Mode.VERY_AGGRESSIVE,
silenceDurationMs = 600,
speechDurationMs = 50
).use { vad ->
val chunkSize = vad.frameSize.value * 2
requireContext().assets.open("hello.wav").buffered().use { input ->
val audioHeader = ByteArray(44).apply { input.read(this) }
var speechData = byteArrayOf()
while (input.available() > 0) {
val frameChunk = ByteArray(chunkSize).apply { input.read(this) }
if (vad.isSpeech(frameChunk)) {
speechData += frameChunk
} else {
if (speechData.isNotEmpty()) {
val speechFile = File("/folder/", "${nanoTime()}.wav")
FileOutputStream(speechFile).use { output ->
output.write(audioHeader)
output.write(speechData)
}
speechData = byteArrayOf()
}
}
}
}
}
```
## Silero VAD
#### Parameters
Silero VAD library only accepts **16-bit Mono PCM audio stream** and can work with next Sample Rates,
Frame Sizes and Modes.
| Valid Sample Rate | Valid Frame Size |
|:-----------------:|:----------------:|
| 8000Hz | 256, 512, 768 |
| 16000Hz | 512, 1024, 1536 |
| Valid Mode |
|:----------------|
| OFF |
| NORMAL |
| AGGRESSIVE |
| VERY_AGGRESSIVE |
Recommended parameters for Silero VAD:
* Context (required) - The Context is required to facilitate reading the model file from the Android file system.
* Sample Rate (required) - **16KHz** - The sample rate of the audio input.
* Frame Size (required) - **512** - The frame size of the audio input.
* Mode (required) - **NORMAL** - The confidence mode of the VAD model.
* Silence Duration (optional) - **300ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for silence segments.
* Speech Duration (optional) - **50ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for speech segments.
#### Usage
Silero VAD can identify speech in short audio frames, returning results for each frame.
By utilizing parameters such as **silenceDurationMs** and **speechDurationMs**, you can enhance the
capability of VAD, enabling the detection of prolonged utterances while minimizing false positive
results during pauses between sentences.
Java example:
```java
VadSilero vad = Vad.builder()
.setContext(requireContext())
.setSampleRate(SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K)
.setFrameSize(FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_512)
.setMode(Mode.NORMAL)
.setSilenceDurationMs(300)
.setSpeechDurationMs(50)
.build();
boolean isSpeech = vad.isSpeech(audioData);
vad.close();
```
Kotlin example:
```kotlin
VadSilero(
requireContext(),
sampleRate = SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K,
frameSize = FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_512,
mode = Mode.NORMAL,
silenceDurationMs = 300,
speechDurationMs = 50
).use { vad ->
val isSpeech = vad.isSpeech(audioData)
}
```
## Yamnet VAD
#### Parameters
Yamnet VAD library only accepts **16-bit Mono PCM audio stream** and can work with next Sample Rates,
Frame Sizes and Modes.
| Valid Sample Rate | Valid Frame Size |
|:-----------------:|:------------------:|
| 16000Hz | 243, 487, 731, 975 |
| | 243, 487, 731, 975 |
| Valid Mode |
|:----------------|
| OFF |
| NORMAL |
| AGGRESSIVE |
| VERY_AGGRESSIVE |
Recommended parameters for Yamnet VAD:
* Context (required) - The Context is required to facilitate reading the model file from the Android file system.
* Sample Rate (required) - **16KHz** - The sample rate of the audio input.
* Frame Size (required) - **243** - The frame size of the audio input.
* Mode (required) - **NORMAL** - The confidence mode of the VAD model.
* Silence Duration (optional) - **30ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for silence segments.
* Speech Duration (optional) - **30ms** - The minimum duration in milliseconds for speech segments.
#### Usage
Yamnet VAD can identify [521](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/research/audioset/yamnet/yamnet_class_map.csv)
audio event classes (such as speech, music, animal sounds and etc) in small audio frames.
By utilizing parameters such as **silenceDurationMs** and **speechDurationMs** and specifying
sound category (ex. classifyAudio(**"Speech"**, audioData)), you can enhance the capability of VAD,
enabling the detection of prolonged utterances while minimizing false positive results during
pauses between sentences.
Java example:
```java
VadYamnet vad = Vad.builder()
.setContext(requireContext())
.setSampleRate(SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K)
.setFrameSize(FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_243)
.setMode(Mode.NORMAL)
.setSilenceDurationMs(30)
.setSpeechDurationMs(30)
.build();
SoundCategory sc = vad.classifyAudio("Speech", audioData);
if ("Speech".equals(sc.getLabel())) {
System.out.println("Speech Detected: " + sc.getScore());
} else {
System.out.println("Noise Detected: " + sc.getScore());
}
vad.close();
```
Kotlin example:
```kotlin
VadYamnet(
requireContext(),
sampleRate = SampleRate.SAMPLE_RATE_16K,
frameSize = FrameSize.FRAME_SIZE_243,
mode = Mode.NORMAL,
silenceDurationMs = 30,
speechDurationMs = 30
).use { vad ->
val sc = vad.classifyAudio("Cat", audioData)
when (sc.label) {
"Cat" -> println("Cat Detected: " + sc.score)
else -> println("Noise Detected: " + sc.score)
}
}
```
## Requirements
#### Android API
WebRTC VAD - Android **API 16** and later.
Silero VAD - Android **API 21** and later.
Yamnet VAD - Android **API 23** and later.
#### JDK
JDK **8** or later.
## Download
[](https://jitpack.io/#gkonovalov/android-vad)
Gradle is the only supported build configuration, so just add the dependency to your project `build.gradle` file:
1. Add it in your root build.gradle at the end of repositories:
```groovy
allprojects {
repositories {
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
}
```
2. Add one dependency from list below:
#### WebRTC VAD
```groovy
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.gkonovalov.android-vad:webrtc:2.0.9'
}
```
#### Silero VAD
```groovy
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.gkonovalov.android-vad:silero:2.0.9'
}
```
#### Yamnet VAD
```groovy
dependencies {
implementation 'com.github.gkonovalov.android-vad:yamnet:2.0.9'
}
```
You also can download precompiled AAR library and APK files from GitHub's [releases page](https://github.com/gkonovalov/android-vad/releases).
## References
[1]
[WebRTC VAD](https://chromium.googlesource.com/external/webrtc/+/branch-heads/43/webrtc/common_audio/vad/) -
Voice Activity Detector from Google which is reportedly one of the best available: it's fast,
modern and free. This algorithm has found wide adoption and has recently become one of the
gold-standards for delay-sensitive scenarios like web-based interaction.
[2]
[Silero VAD](https://github.com/snakers4/silero-vad) - pre-trained enterprise-grade Voice Activity Detector,
Number Detector and Language Classifier hello@silero.ai.
[3]
[Yamnet VAD](https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/research/audioset/yamnet) -
YAMNet is a pretrained deep neural network that can predicts 521 audio event classes based on the AudioSet-YouTube
corpus, employing the Mobilenet_v1 depthwise-separable convolution architecture.
------------
Georgiy Konovalov 2025 (c) [MIT License](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)