https://github.com/gmostofabd/8051-dc-motor
👨💻 This repository demonstrates how to interface a DC motor with the 8051 microcontroller using the L298 driver to handle the extra current required to run the motor. The project includes complete assembly code, Proteus simulation files, and documentation, along with screenshots and photos from testing.
https://github.com/gmostofabd/8051-dc-motor
8051 assembly circuit code dc description design download file hex microcontroller motor programming proteus schematics simulation
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
👨💻 This repository demonstrates how to interface a DC motor with the 8051 microcontroller using the L298 driver to handle the extra current required to run the motor. The project includes complete assembly code, Proteus simulation files, and documentation, along with screenshots and photos from testing.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/gmostofabd/8051-dc-motor
- Owner: gmostofabd
- Created: 2021-06-01T16:03:30.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-10-04T17:16:58.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-19T23:44:13.424Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: 8051, assembly, circuit, code, dc, description, design, download, file, hex, microcontroller, motor, programming, proteus, schematics, simulation
- Language: HTML
- Homepage: https://gmostofabd.github.io/8051-DC-Motor/
- Size: 3.69 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# ⚙️ **8051 DC Motor Interfacing**

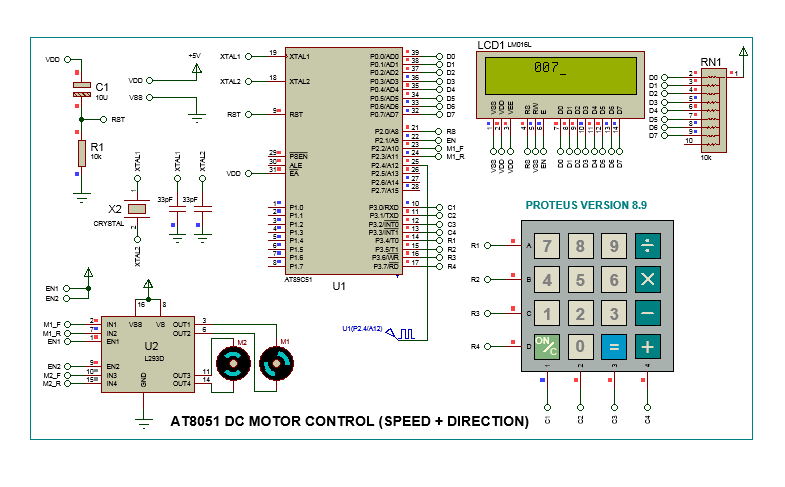
This repository demonstrates how to interface a DC motor with the 8051 microcontroller using the **L298** driver to handle the extra current required to run the motor. The project includes complete assembly code, Proteus simulation files, and documentation, along with screenshots and photos from testing.
## 📦 **Project Overview**
The project showcases the integration of a **DC motor** with the **AT89C51** microcontroller, part of the 8051 family. The DC motor is driven via the **L298** H-Bridge motor driver, which provides the necessary current amplification to control the motor's direction and speed efficiently. The Proteus simulation files allow you to visualize and test the functionality before implementing it on hardware.
### **Key Features:**
- **DC Motor Control**: Forward and reverse motor control using the 8051 microcontroller.
- **L298 Driver**: Used to supply the necessary current for the DC motor operation.
- **Proteus Simulation**: Includes simulation files for DC motor interfacing with the 8051 MCU.
- **Test Results**: Screenshots and photos from actual tests provide insights into the project's performance.
## 🔧 **Hardware Components**
- **AT89C51 Microcontroller**: Manages control signals for the DC motor.
- **L298**: H-Bridge motor driver, used to control the direction and speed of the DC motor.
- **DC Motor**: The motor being controlled by the microcontroller and driver circuit.
- **Power Supply**: Provides the necessary voltage and current for the system.
## 🖥️ **Simulation & Testing**
This project was simulated using **Proteus Design Suite** to verify the DC motor's behavior and control before real-world implementation. The repository includes:
- Assembly code for controlling the DC motor.
- Proteus simulation file showing motor operation.
- Screenshots and photos taken during the testing phase.
---
### 🚀 **Steps to Run the Project:**
1. **Clone this repository**:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/yourusername/8051_DC_Motor_Interfacing.git
```
2. **Open the Proteus Simulation**:
Load the provided simulation file in **Proteus Design Suite** and run it to observe the motor's behavior.
3. **Compile and Upload the Code**:
Use **MIDE-51** or any other 8051-compatible IDE to compile the assembly code and generate the HEX file.
4. **Test on Hardware**:
After programming the microcontroller, assemble the circuit with the DC motor and L298, and power it on to observe real-time results.
---
## 📄 **Included Files:**
- **Assembly Code**: The code to drive the DC motor using the 8051 microcontroller.
- **Proteus Simulation Files**: Pre-built simulation to test and visualize the circuit.
- **HEX File**: Ready-to-upload HEX code for the microcontroller.
- **Screenshots & Photos**: Visual proof of successful testing on both Proteus and hardware.
---
## 👨💻 **Code View**
```assembly
; 8051 Assembly Code for DC Motor Control using L298 Driver
ORG 0000H ; Start Program at address 0
MOV P1, #00H ; Initialize Port 1 (connected to L298)
MOV DPTR, #MYCODE ; Load the address of the code block
LCALL MOTOR_CTRL ; Call the motor control routine
; DC Motor Control Subroutine
MOTOR_CTRL:
MOV A, P1 ; Load the current value of Port 1 into Accumulator
CPL A ; Complement the Accumulator (toggle motor direction)
MOV P1, A ; Send the toggled value to Port 1
ACALL DELAY ; Call delay for motor timing
RET ; Return from subroutine
DELAY:
MOV R0, #255 ; Load the maximum count for delay loop
DELAY_LOOP:
DJNZ R0, DELAY_LOOP ; Decrement R0 until it reaches zero
RET ; Return from delay subroutine
END
```
---
## ⚙️ **Understanding DC Motor Operation and Speed Control** ⚙️
**DC Motors** convert electrical power into mechanical motion and are used in numerous applications, from **remote-controlled cars** to **industrial machines**. They operate using **direct current (DC)**, unlike **AC motors**, and are ideal for **variable speed** applications.

DC motors are integral in modern **electronics** and **robotics** due to their simplicity, **efficiency**, and precise **control**. This guide explores the core operation principles of DC motors and the most common speed control techniques.
---
### 🚀 **Basic Construction**
| **DC Motor Components** | **Components Description** |
| -----------------------| ---------------------------|
|

| - **Rotor (Armature)**: The rotating part of the motor.
- **Stator**: The stationary part, producing the magnetic field.
- **Commutator**: Can be **brushed** or **brushless**, depending on the motor type.
- **Field Magnets**: Create the magnetic field that interacts with the rotor.
DC motors operate based on the **interaction** between the magnetic fields of the **rotor** and the **stator**. |
### 🚀 **Operating Principle**
DC motors operate on **Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetism**, where a **current-carrying conductor** in a **magnetic field** experiences a force. This is governed by **Fleming’s Left-Hand Rule** for electric motors, stating that the direction of motion is perpendicular to both the current and magnetic field.
**Mathematically**:
\[ F = BIL \]
- **F**: Force
- **B**: Magnetic field strength
- **I**: Current
- **L**: Length of the conductor
---
### 🚀 **Why Speed Control of a DC Motor is Important?**

Controlling the speed of a DC motor is essential in numerous applications. For instance, in **conveyor systems**, the motor may need slow speeds for loading and faster speeds for transferring materials. **Precise speed regulation** enhances the performance and longevity of the motor, while reducing mechanical stress and ensuring **energy efficiency**.
### 🚀 **Benefits of Speed Control:**
- **Precision**: Ensures efficient operation in critical applications.
- **Energy Savings**: Reduces power consumption when appropriate.
- **Optimized Performance**: Allows for adjustments in response to varying loads.
- **Extended Lifespan**: Reduces wear and tear on the motor, prolonging its life.
---
## 🎯 **Key Speed Control Concepts**
### 1. 🔋 **Voltage Control**
By adjusting the **applied voltage**, you can directly control the motor speed. A higher voltage results in increased speed, while a lower voltage reduces it.
### 2. ⚡ **Pulse Width Modulation (PWM)**
**PWM** is an efficient way to control DC motor speed by quickly switching the power on and off. Adjusting the **duty cycle** alters the motor's speed without wasting energy:
- **Higher Duty Cycle**: More power, higher speed.
- **Lower Duty Cycle**: Less power, lower speed.
### 3. 🔄 **Current Control**
Controlling the **current** allows for precise **torque regulation**, which is especially useful in applications requiring high levels of accuracy, such as **robotics**.
---
## 📉 **Speed Regulation Techniques**
1. **Variable Voltage Supply**: Adjusting input voltage using **resistors** or **power electronics**.
2. **PWM Control**: Efficiently managing speed without overheating.
3. **Feedback Systems**: Using **sensors** like **encoders** or **tachometers** for dynamic speed adjustment.
---
## 🛠️ **Applications of DC Motors**
- 🏎️ **Robotics**: Smooth control of motor speeds for wheels and joints.
- 🚁 **Drones**: Precise speed regulation for stability.
- 🚗 **Electric Vehicles**: Energy-efficient speed control for motors.
---
## ⚗️ **Experiments Gallery**
Exp. 1: 8051 LED
This experiment demonstrates how to blink an LED using the 8051 microcontroller.

Exp. 2: Push Button Interfacing
Learn how to interface a push button with the 8051 to control outputs.

Exp. 3: Seven Segment Display
Discover how to interface and display numbers on a seven-segment display.
| | | |
|:-------------------------:|:-------------------------:|:-------------------------:|
| 8051 LED |
8051 LED |  8051 Push Button |
8051 Push Button |  8051 Stepper Motor|
8051 Stepper Motor|
| |
|  |
| |
|
| |
| .png?raw=true) |
| |
|
---
## 📘 **Further Reading**
- [DC Motor Basics](https://example-link.com/dcmotor)
- [Pulse Width Modulation Techniques](https://example-link.com/pwm)
---
🌟 **Explore the fascinating world of DC motors** and unlock endless possibilities in electronics and robotics!
🔗 **Follow Us for More Tutorials:**
- [Website](https://melabBD.com)
- [YouTube](https://youtube.com/melabBD)
- [GitHub](https://github.com/melabBD)
---
### 🚀 **Torque, Current, and Power**
DC motors draw more **current** under load, and their **torque** is directly proportional to the electrical current flowing through them. It's essential to account for these parameters to ensure optimal motor performance and avoid overheating.
**Thermal Management** is crucial, as overloaded motors can **stall** and overheat. Devices like **Phidgets DC Motor Controllers** offer **current-limiting features** to prevent motor damage and ensure safe operation.
### 🚀 **Braking**
DC motors can also resist movement through **electromotive force (EMF)**, a phenomenon used for braking. By connecting the motor terminals together, the motor resists fast rotation, providing a braking effect.
---
### 🚀 **Conclusion**
By utilizing appropriate **speed control techniques**, DC motors can provide **precise motion control** across various applications. Understanding the underlying principles and methods allows for **optimized performance**, **energy savings**, and **longer motor lifespan**.
Whether you're working on **robotics**, **drones**, or **electric vehicles**, mastering DC motor speed control is key to unlocking their full potential.
For detailed information on DC motor types, such as **Brushed** vs **Brushless Motors**, or motors like **Permanent Magnet** or **Shunt DC Motors**, check out the links provided above!
---