https://github.com/goessl/rdx
Radix conversion module.
https://github.com/goessl/rdx
binary hexadecimal infinite lightweight number number-system-conversion number-system-converter number-systems number-theory numbers octal pip pip3 python python3 radix unlimited
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
Radix conversion module.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/goessl/rdx
- Owner: goessl
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-08-22T00:10:35.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-09-06T18:16:54.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-28T10:56:53.397Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: binary, hexadecimal, infinite, lightweight, number, number-system-conversion, number-system-converter, number-systems, number-theory, numbers, octal, pip, pip3, python, python3, radix, unlimited
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 206 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# rdx
A radix conversion module.
Implementation of
- [How to convert an integer to a string in any base?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2267362/how-to-convert-an-integer-to-a-string-in-any-base)
- [How to find length of digits in an integer?](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/2189800/how-to-find-length-of-digits-in-an-integer)
## Installation
```
pip install rdx
```
## Usage
This module provides the following functions:
- `int_to_digits(n, b=10)`:
Returns the digits of number `n` in base `b`.
- `digits_to_int(d, b=10)`:
Returns the number represented by the digits `d`
in base `b`.
```python
>>> from rdx import *
>>> int_to_digits(42, 2)
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1]
>>> int_to_digits(42, 16)
[10, 2]
>>> digits_to_int([27, 1], 42)
69
```
- `int_to_len_digits(n, b=10)`:
Returns the amount of digits the number `n` represented in base `b` needs.
```python
>>> int_to_len_digits(1024, 2)
11
```
- `digits_to_characters(d, alphabet=digits+ascii_letters)`:
Converts integer digits `d` to characters of the given alphabet.
- `characters_to_digits(s, alphabet=digits+ascii_letters)`:
Converts characters `s` of the given alphabet to integer digits.
```python
>>> digits_to_characters([0, 1, 9, 10, 15, 16])
['0', '1', '9', 'a', 'f', 'g']
>>> characters_to_digits(['0', '1', '9', 'a', 'f', 'g'])
[0, 1, 9, 10, 15, 16]
```
- `digits_to_string(d, alphabet=string.digits+string.ascii_letters)`:
Converts integer digits `d` to a right-to-left string in the given alphabet.
- `string_to_digits(s, alphabet=string.digits+string.ascii_letters)`:
Converts a right-to-left string `s` in the given alphabet to integer digits.
```python
>>> digits_to_string([0, 0, 15])
'f00'
>>> string_to_digits('f12')
[2, 1, 15]
```
## Conventions
### Data type
Currently digits or characters are returned as lists.
In the future this will be switched to tuples
as they are more similar to strings,
and a digit representation is similar to a string.
Digit or character arguments should be provided in form of an iterable,
not an iterator, as in most functions the will be iterated twice
and an iterator will be exhausted after the first run.
### Ordering
As a digit representation a list of integers is used,
where every element represents a digit, all ordered in ascending positions.
So the lowest digit at position with index 0, will be at position 0.
But this also means, that when a list of digits is printed,
it will be ordered left-to-right,
opposed to the usual human-readable right-to-left.
E.g. `12` (twelve) corresponds to `[2, 1]`.
### `int_to_len_digits(n)` vs `len(int_to_digits(n))`
`len(int_to_digits(n))` is the naive and non-optimal approach.
`int_to_len_digits(n)` calculates the number of digits intelligently as
`int(log(n, b))+1` as mentioned
in the [discussion](https://stackoverflow.com/a/2189827/7367030).
But to avoid errors due to [`math.log`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/math.html#math.log)
using floating point arithmetic
[`sympy.log`](https://docs.sympy.org/latest/modules/functions/elementary.html#sympy.functions.elementary.exponential.log)
is used, adding a hefty overhead. A comparison for time critical applications:
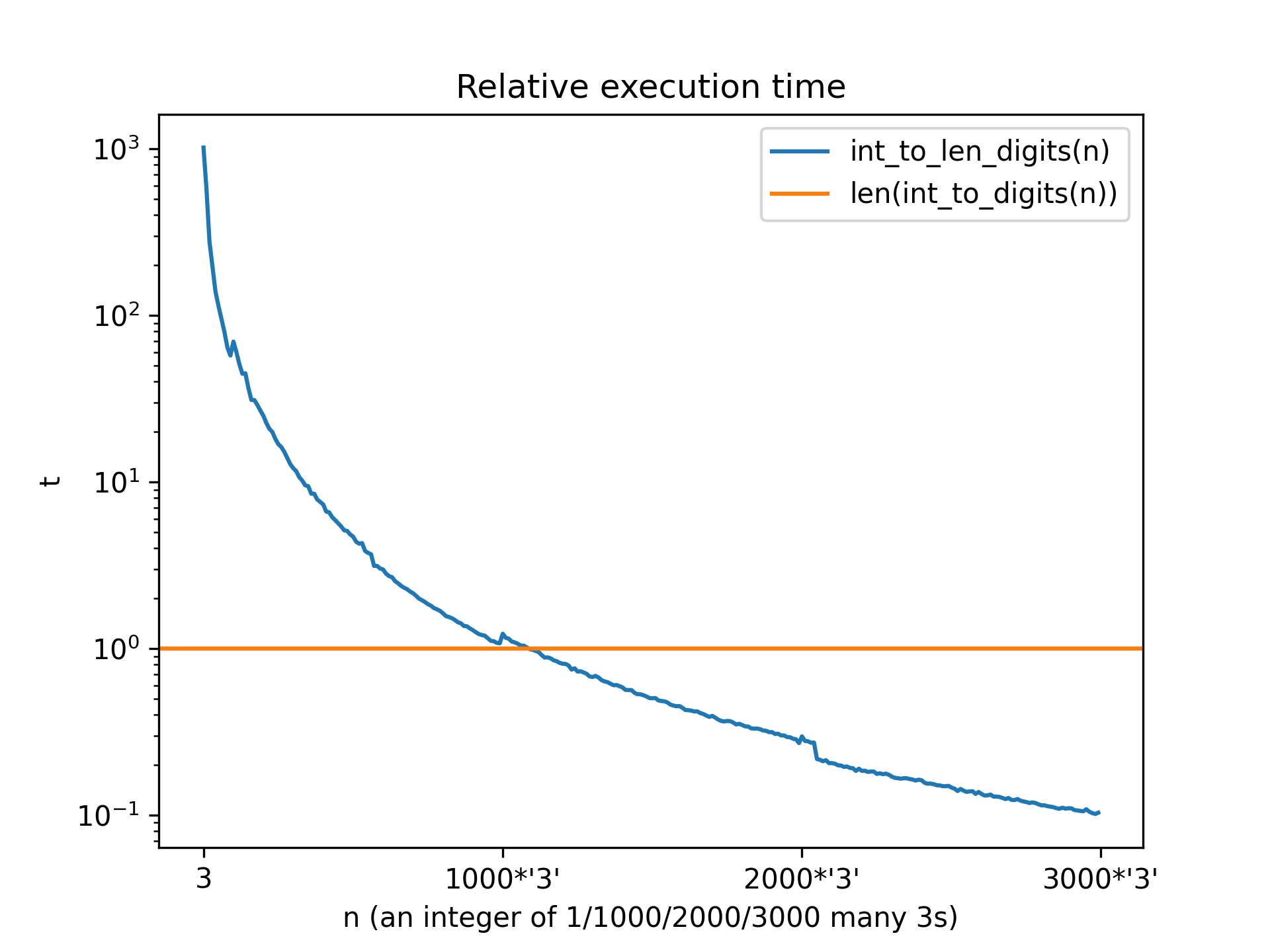
(integers with just 3s were choosen because random values introduce to much
noise and because 100... seemed to risky for a systematic error and 33... lies
exactly between those 100...s on a logarithmic scale)
## TODO
- [ ] put digits in tuples instead of lists
- [ ] non-standard positional numeral systems
- [ ] [mixed radix](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mixed_radix)
- [ ] [factorial](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Factorial_number_system)
- [ ] primorial
- [ ] ...
- [ ] [negative base](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Negative_base)
- [ ] [complex base](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quater-imaginary_base)
## License (MIT)
Copyright (c) 2023 Sebastian Gössl
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
SOFTWARE.