https://github.com/google/langextract
A Python library for extracting structured information from unstructured text using LLMs with precise source grounding and interactive visualization.
https://github.com/google/langextract
gemini gemini-ai gemini-api gemini-flash gemini-pro information-extration large-language-models llm nlp python structured-data
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
A Python library for extracting structured information from unstructured text using LLMs with precise source grounding and interactive visualization.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/google/langextract
- Owner: google
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2025-07-08T20:46:06.000Z (7 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-08-09T05:47:47.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-09T07:07:42.151Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: gemini, gemini-ai, gemini-api, gemini-flash, gemini-pro, information-extration, large-language-models, llm, nlp, python, structured-data
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://pypi.org/project/langextract/
- Size: 9.9 MB
- Stars: 6,553
- Watchers: 37
- Forks: 370
- Open Issues: 40
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
- AiTreasureBox - google/langextract - 01-03_20049_36](https://img.shields.io/github/stars/google/langextract.svg)|A Python library for extracting structured information from unstructured text using LLMs with precise source grounding and interactive visualization.| (Repos)
- StarryDivineSky - google/langextract
- awesome-production-machine-learning - LangExtract - LangExtract is a Python library that uses LLMs to extract structured information from unstructured text documents based on user-defined instructions. It processes materials such as clinical notes or reports, identifying and organizing key details while ensuring the extracted data corresponds to the source text. (Industry Strength Information Retrieval)
- my-awesome - google/langextract - ai,gemini-api,gemini-flash,gemini-pro,information-extration,large-language-models,llm,nlp,python,structured-data pushed_at:2025-12 star:20.6k fork:1.4k A Python library for extracting structured information from unstructured text using LLMs with precise source grounding and interactive visualization. (Python)
- awesome-data-analysis - LangExtract - Google's library for structured information extraction from text using language models. (📖 Natural Language Processing (NLP) / Tools)
- awesome-repositories - google/langextract - A Python library for extracting structured information from unstructured text using LLMs with precise source grounding and interactive visualization. (Python)
README
# LangExtract
[](https://pypi.org/project/langextract/)
[](https://github.com/google/langextract)

## Table of Contents
- [Introduction](#introduction)
- [Why LangExtract?](#why-langextract)
- [Quick Start](#quick-start)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [API Key Setup for Cloud Models](#api-key-setup-for-cloud-models)
- [Using OpenAI Models](#using-openai-models)
- [Using Local LLMs with Ollama](#using-local-llms-with-ollama)
- [More Examples](#more-examples)
- [*Romeo and Juliet* Full Text Extraction](#romeo-and-juliet-full-text-extraction)
- [Medication Extraction](#medication-extraction)
- [Radiology Report Structuring: RadExtract](#radiology-report-structuring-radextract)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
- [Testing](#testing)
- [Disclaimer](#disclaimer)
## Introduction
LangExtract is a Python library that uses LLMs to extract structured information from unstructured text documents based on user-defined instructions. It processes materials such as clinical notes or reports, identifying and organizing key details while ensuring the extracted data corresponds to the source text.
## Why LangExtract?
1. **Precise Source Grounding:** Maps every extraction to its exact location in the source text, enabling visual highlighting for easy traceability and verification.
2. **Reliable Structured Outputs:** Enforces a consistent output schema based on your few-shot examples, leveraging controlled generation in supported models like Gemini to guarantee robust, structured results.
3. **Optimized for Long Documents:** Overcomes the "needle-in-a-haystack" challenge of large document extraction by using an optimized strategy of text chunking, parallel processing, and multiple passes for higher recall.
4. **Interactive Visualization:** Instantly generates a self-contained, interactive HTML file to visualize and review thousands of extracted entities in their original context.
5. **Flexible LLM Support:** Supports your preferred models, from cloud-based LLMs like the Google Gemini family to local open-source models via the built-in Ollama interface.
6. **Adaptable to Any Domain:** Define extraction tasks for any domain using just a few examples. LangExtract adapts to your needs without requiring any model fine-tuning.
7. **Leverages LLM World Knowledge:** Utilize precise prompt wording and few-shot examples to influence how the extraction task may utilize LLM knowledge. The accuracy of any inferred information and its adherence to the task specification are contingent upon the selected LLM, the complexity of the task, the clarity of the prompt instructions, and the nature of the prompt examples.
## Quick Start
> **Note:** Using cloud-hosted models like Gemini requires an API key. See the [API Key Setup](#api-key-setup-for-cloud-models) section for instructions on how to get and configure your key.
Extract structured information with just a few lines of code.
### 1. Define Your Extraction Task
First, create a prompt that clearly describes what you want to extract. Then, provide a high-quality example to guide the model.
```python
import langextract as lx
import textwrap
# 1. Define the prompt and extraction rules
prompt = textwrap.dedent("""\
Extract characters, emotions, and relationships in order of appearance.
Use exact text for extractions. Do not paraphrase or overlap entities.
Provide meaningful attributes for each entity to add context.""")
# 2. Provide a high-quality example to guide the model
examples = [
lx.data.ExampleData(
text="ROMEO. But soft! What light through yonder window breaks? It is the east, and Juliet is the sun.",
extractions=[
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="character",
extraction_text="ROMEO",
attributes={"emotional_state": "wonder"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="emotion",
extraction_text="But soft!",
attributes={"feeling": "gentle awe"}
),
lx.data.Extraction(
extraction_class="relationship",
extraction_text="Juliet is the sun",
attributes={"type": "metaphor"}
),
]
)
]
```
### 2. Run the Extraction
Provide your input text and the prompt materials to the `lx.extract` function.
```python
# The input text to be processed
input_text = "Lady Juliet gazed longingly at the stars, her heart aching for Romeo"
# Run the extraction
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash",
)
```
> **Model Selection**: `gemini-2.5-flash` is the recommended default, offering an excellent balance of speed, cost, and quality. For highly complex tasks requiring deeper reasoning, `gemini-2.5-pro` may provide superior results. For large-scale or production use, a Tier 2 Gemini quota is suggested to increase throughput and avoid rate limits. See the [rate-limit documentation](https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/rate-limits#tier-2) for details.
>
> **Model Lifecycle**: Note that Gemini models have a lifecycle with defined retirement dates. Users should consult the [official model version documentation](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/learn/model-versions) to stay informed about the latest stable and legacy versions.
### 3. Visualize the Results
The extractions can be saved to a `.jsonl` file, a popular format for working with language model data. LangExtract can then generate an interactive HTML visualization from this file to review the entities in context.
```python
# Save the results to a JSONL file
lx.io.save_annotated_documents([result], output_name="extraction_results.jsonl", output_dir=".")
# Generate the visualization from the file
html_content = lx.visualize("extraction_results.jsonl")
with open("visualization.html", "w") as f:
f.write(html_content)
```
This creates an animated and interactive HTML file:
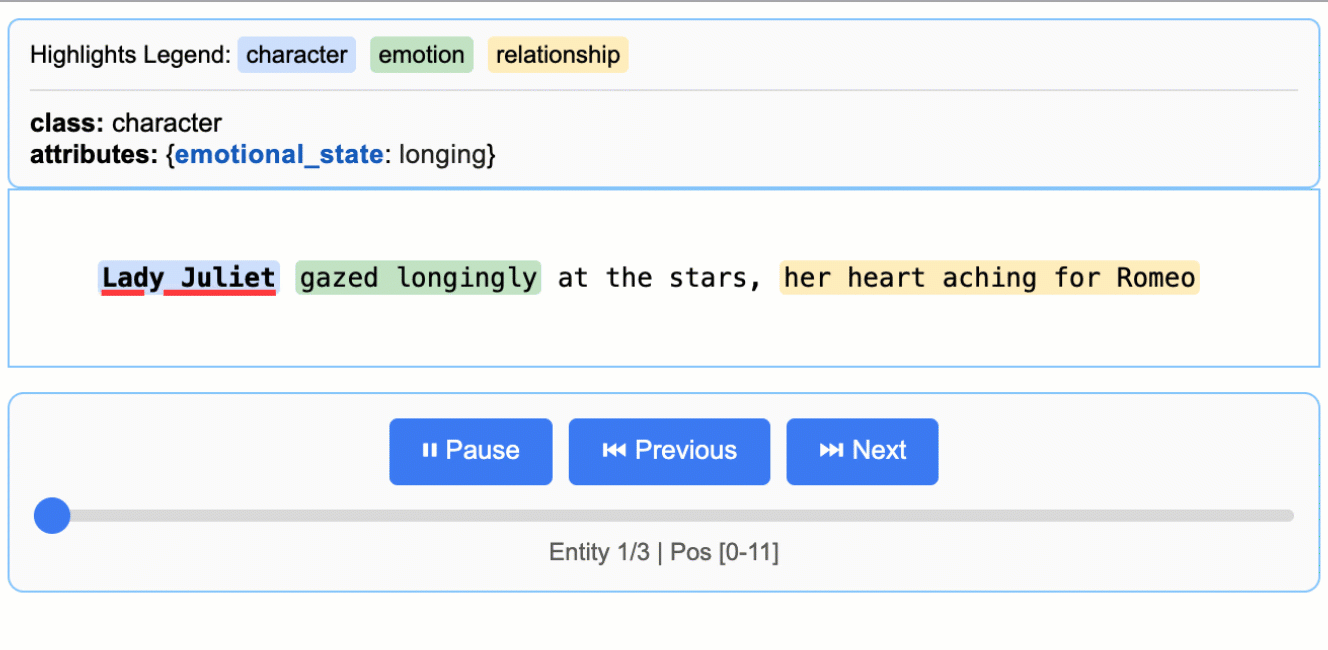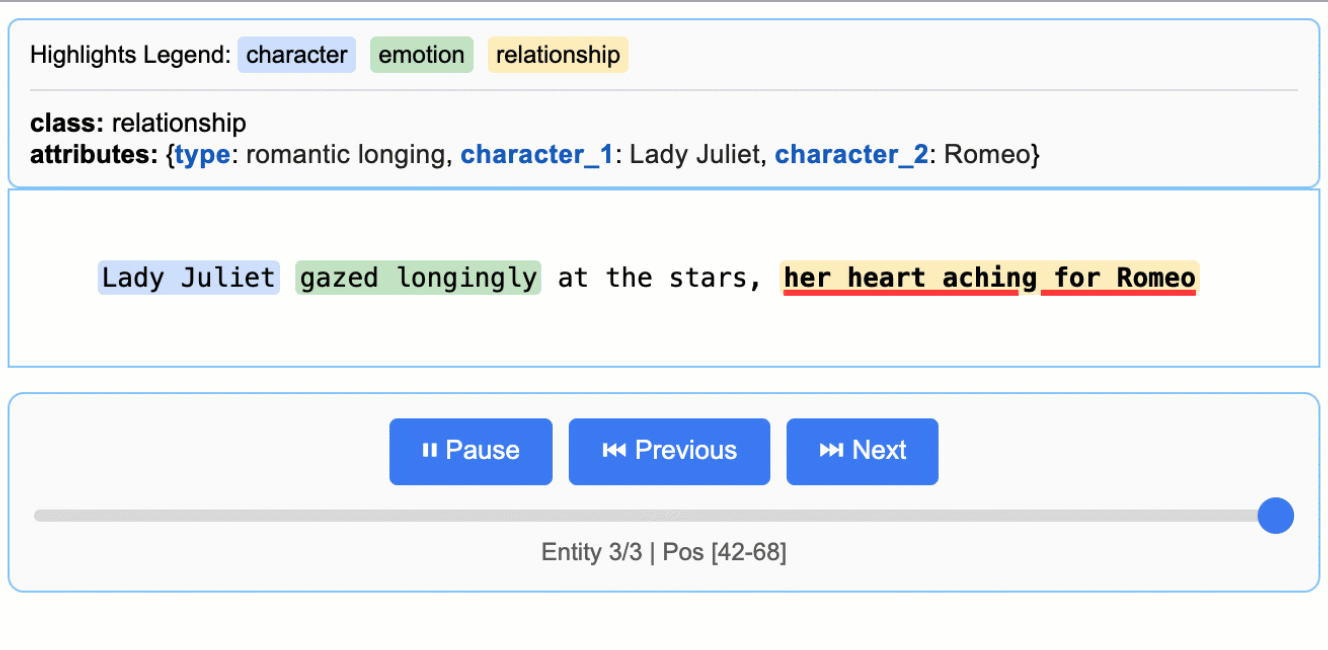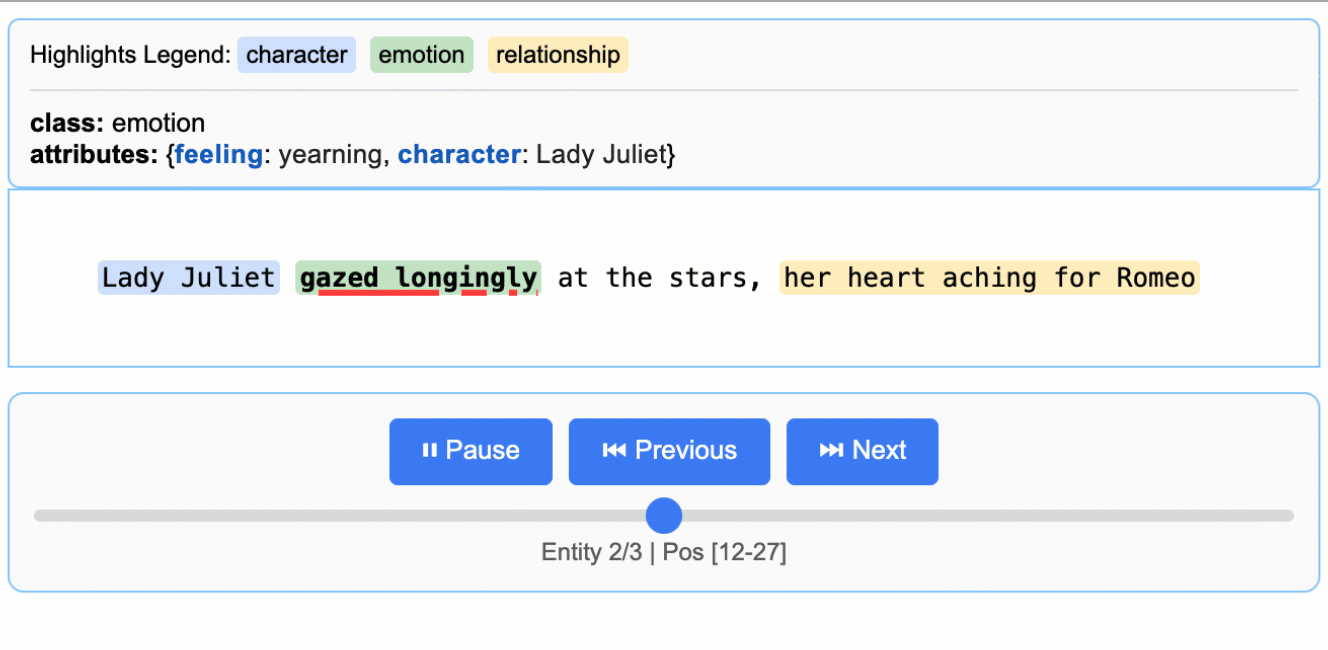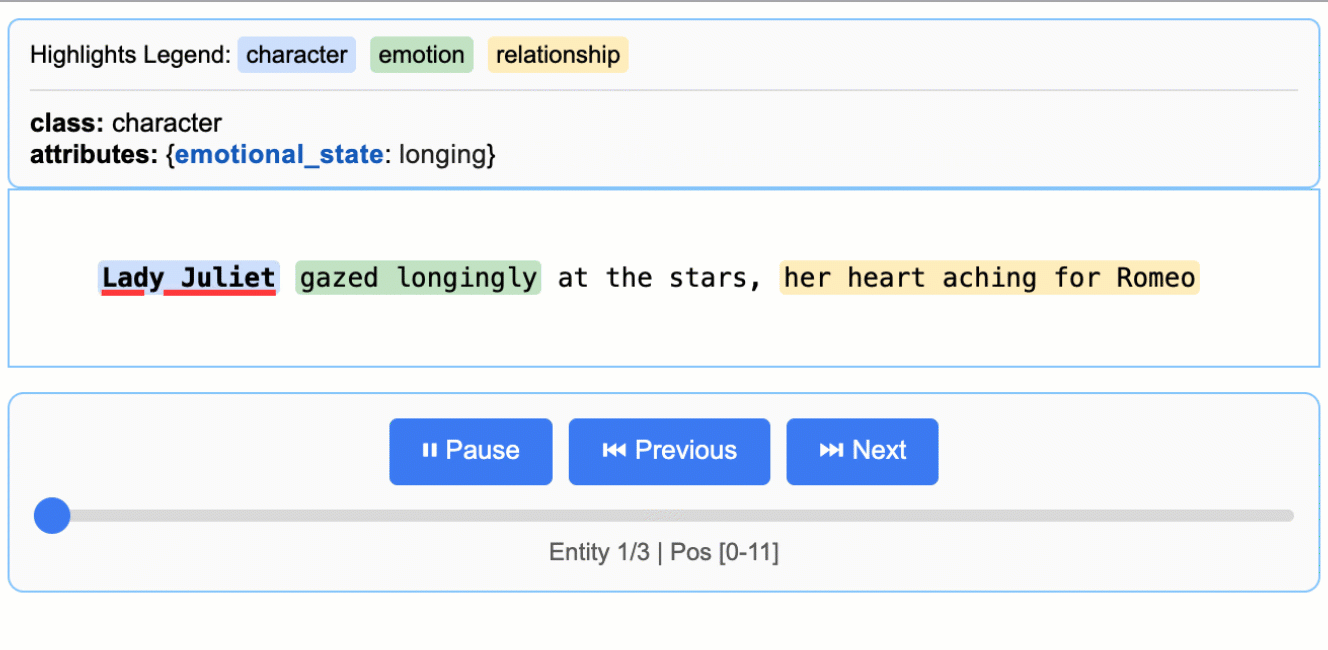
> **Note on LLM Knowledge Utilization:** This example demonstrates extractions that stay close to the text evidence - extracting "longing" for Lady Juliet's emotional state and identifying "yearning" from "gazed longingly at the stars." The task could be modified to generate attributes that draw more heavily from the LLM's world knowledge (e.g., adding `"identity": "Capulet family daughter"` or `"literary_context": "tragic heroine"`). The balance between text-evidence and knowledge-inference is controlled by your prompt instructions and example attributes.
### Scaling to Longer Documents
For larger texts, you can process entire documents directly from URLs with parallel processing and enhanced sensitivity:
```python
# Process Romeo & Juliet directly from Project Gutenberg
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents="https://www.gutenberg.org/files/1513/1513-0.txt",
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash",
extraction_passes=3, # Improves recall through multiple passes
max_workers=20, # Parallel processing for speed
max_char_buffer=1000 # Smaller contexts for better accuracy
)
```
This approach can extract hundreds of entities from full novels while maintaining high accuracy. The interactive visualization seamlessly handles large result sets, making it easy to explore hundreds of entities from the output JSONL file. **[See the full *Romeo and Juliet* extraction example →](https://github.com/google/langextract/blob/main/docs/examples/longer_text_example.md)** for detailed results and performance insights.
## Installation
### From PyPI
```bash
pip install langextract
```
*Recommended for most users. For isolated environments, consider using a virtual environment:*
```bash
python -m venv langextract_env
source langextract_env/bin/activate # On Windows: langextract_env\Scripts\activate
pip install langextract
```
### From Source
LangExtract uses modern Python packaging with `pyproject.toml` for dependency management:
*Installing with `-e` puts the package in development mode, allowing you to modify the code without reinstalling.*
```bash
git clone https://github.com/google/langextract.git
cd langextract
# For basic installation:
pip install -e .
# For development (includes linting tools):
pip install -e ".[dev]"
# For testing (includes pytest):
pip install -e ".[test]"
```
### Docker
```bash
docker build -t langextract .
docker run --rm -e LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY="your-api-key" langextract python your_script.py
```
## API Key Setup for Cloud Models
When using LangExtract with cloud-hosted models (like Gemini or OpenAI), you'll need to
set up an API key. On-device models don't require an API key. For developers
using local LLMs, LangExtract offers built-in support for Ollama and can be
extended to other third-party APIs by updating the inference endpoints.
### API Key Sources
Get API keys from:
* [AI Studio](https://aistudio.google.com/app/apikey) for Gemini models
* [Vertex AI](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/sdks/overview) for enterprise use
* [OpenAI Platform](https://platform.openai.com/api-keys) for OpenAI models
### Setting up API key in your environment
**Option 1: Environment Variable**
```bash
export LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY="your-api-key-here"
```
**Option 2: .env File (Recommended)**
Add your API key to a `.env` file:
```bash
# Add API key to .env file
cat >> .env << 'EOF'
LANGEXTRACT_API_KEY=your-api-key-here
EOF
# Keep your API key secure
echo '.env' >> .gitignore
```
In your Python code:
```python
import langextract as lx
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description="Extract information...",
examples=[...],
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash"
)
```
**Option 3: Direct API Key (Not Recommended for Production)**
You can also provide the API key directly in your code, though this is not recommended for production use:
```python
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description="Extract information...",
examples=[...],
model_id="gemini-2.5-flash",
api_key="your-api-key-here" # Only use this for testing/development
)
```
## Using OpenAI Models
LangExtract supports OpenAI models (requires optional dependency: `pip install langextract[openai]`):
```python
import langextract as lx
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gpt-4o", # Automatically selects OpenAI provider
api_key=os.environ.get('OPENAI_API_KEY'),
fence_output=True,
use_schema_constraints=False
)
```
Note: OpenAI models require `fence_output=True` and `use_schema_constraints=False` because LangExtract doesn't implement schema constraints for OpenAI yet.
## Using Local LLMs with Ollama
LangExtract supports local inference using Ollama, allowing you to run models without API keys:
```python
import langextract as lx
result = lx.extract(
text_or_documents=input_text,
prompt_description=prompt,
examples=examples,
model_id="gemma2:2b", # Automatically selects Ollama provider
model_url="http://localhost:11434",
fence_output=False,
use_schema_constraints=False
)
```
**Quick setup:** Install Ollama from [ollama.com](https://ollama.com/), run `ollama pull gemma2:2b`, then `ollama serve`.
For detailed installation, Docker setup, and examples, see [`examples/ollama/`](examples/ollama/).
## More Examples
Additional examples of LangExtract in action:
### *Romeo and Juliet* Full Text Extraction
LangExtract can process complete documents directly from URLs. This example demonstrates extraction from the full text of *Romeo and Juliet* from Project Gutenberg (147,843 characters), showing parallel processing, sequential extraction passes, and performance optimization for long document processing.
**[View *Romeo and Juliet* Full Text Example →](https://github.com/google/langextract/blob/main/docs/examples/longer_text_example.md)**
### Medication Extraction
> **Disclaimer:** This demonstration is for illustrative purposes of LangExtract's baseline capability only. It does not represent a finished or approved product, is not intended to diagnose or suggest treatment of any disease or condition, and should not be used for medical advice.
LangExtract excels at extracting structured medical information from clinical text. These examples demonstrate both basic entity recognition (medication names, dosages, routes) and relationship extraction (connecting medications to their attributes), showing LangExtract's effectiveness for healthcare applications.
**[View Medication Examples →](https://github.com/google/langextract/blob/main/docs/examples/medication_examples.md)**
### Radiology Report Structuring: RadExtract
Explore RadExtract, a live interactive demo on HuggingFace Spaces that shows how LangExtract can automatically structure radiology reports. Try it directly in your browser with no setup required.
**[View RadExtract Demo →](https://huggingface.co/spaces/google/radextract)**
## Contributing
Contributions are welcome! See [CONTRIBUTING.md](https://github.com/google/langextract/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) to get started
with development, testing, and pull requests. You must sign a
[Contributor License Agreement](https://cla.developers.google.com/about)
before submitting patches.
### Adding Custom Model Providers
LangExtract supports custom LLM providers through a plugin system. You can add support for new models by creating an external Python package that registers with LangExtract's provider registry. This allows you to:
- Add new model support without modifying the core library
- Distribute your provider independently
- Maintain custom dependencies
For detailed instructions, see the [Provider System Documentation](langextract/providers/README.md).
## Testing
To run tests locally from the source:
```bash
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/google/langextract.git
cd langextract
# Install with test dependencies
pip install -e ".[test]"
# Run all tests
pytest tests
```
Or reproduce the full CI matrix locally with tox:
```bash
tox # runs pylint + pytest on Python 3.10 and 3.11
```
### Ollama Integration Testing
If you have Ollama installed locally, you can run integration tests:
```bash
# Test Ollama integration (requires Ollama running with gemma2:2b model)
tox -e ollama-integration
```
This test will automatically detect if Ollama is available and run real inference tests.
## Development
### Code Formatting
This project uses automated formatting tools to maintain consistent code style:
```bash
# Auto-format all code
./autoformat.sh
# Or run formatters separately
isort langextract tests --profile google --line-length 80
pyink langextract tests --config pyproject.toml
```
### Pre-commit Hooks
For automatic formatting checks:
```bash
pre-commit install # One-time setup
pre-commit run --all-files # Manual run
```
### Linting
Run linting before submitting PRs:
```bash
pylint --rcfile=.pylintrc langextract tests
```
See [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) for full development guidelines.
## Disclaimer
This is not an officially supported Google product. If you use
LangExtract in production or publications, please cite accordingly and
acknowledge usage. Use is subject to the [Apache 2.0 License](https://github.com/google/langextract/blob/main/LICENSE).
For health-related applications, use of LangExtract is also subject to the
[Health AI Developer Foundations Terms of Use](https://developers.google.com/health-ai-developer-foundations/terms).
---
**Happy Extracting!**