https://github.com/gospacedev/exoseeker
AI-Powered Exoplanet Transit Data Analysis Web Interface
https://github.com/gospacedev/exoseeker
artificial-intelligence exoplanet-transits exoplanets gradient-boosting machine-learning matplotlib nasa nasa-data nasa-spaceapps-challenge numpy pandas perceptron-neural-networks random-forest sklearn streamlit
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
AI-Powered Exoplanet Transit Data Analysis Web Interface
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/gospacedev/exoseeker
- Owner: gospacedev
- Created: 2025-10-05T08:33:36.000Z (4 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-10-05T10:19:34.000Z (4 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-10-05T11:27:03.869Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: artificial-intelligence, exoplanet-transits, exoplanets, gradient-boosting, machine-learning, matplotlib, nasa, nasa-data, nasa-spaceapps-challenge, numpy, pandas, perceptron-neural-networks, random-forest, sklearn, streamlit
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://www.spaceappschallenge.org/2025/find-a-team/exoseeker/?tab=project
- Size: 2.06 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
ExoSeeker
Finding new worlds
ExoSeeker is an interactive web user interface for creating custom machine learning models to analyze Kepler objects of interest. It empowers anyone to easily discover potential exoplanets by having a streamlined process of taking in new data, building a unique machine learning model, and generating predicted objects of interest classifications.
## Features
- It has a user-friendly web interface that allows anyone to create their own AI models for identifying new exoplanets.
- Each component has a tooltip that provides useful information, such as instructions for uploading new data, properties of each estimator's main hyperparameters, and the description of each metric in the model evaluation.
- ExoSeeker allows for stacking multiple estimators, enabling the harnessing of the strength of one to increase the model's performance.
- The user can mix and match multiple models, tweak each one's main hyperparameters, empowering the user to create fully customized machine learning models.
## Prerequisites
Please use Python version >= 3.13.7
## Installation
Clone the repository:
```powershell
git clone https://github.com/gospacedev/exoplanet.git
```
Create a virtual environment:
```powershell
python -m venv exoseeker-venv
```
Activate the virtual environment:
```powershell
exoseeker-venv/Scripts/Activate.ps1
```
Install the requirements:
```powershell
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
Run the web interface:
```powershell
streamlit run app.py
```
## Getting Started
1. Go to the exoplanet archive dataset from [Kepler Objects of Interest](https://exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/TblView/nph-tblView?app=ExoTbls&config=cumulative)
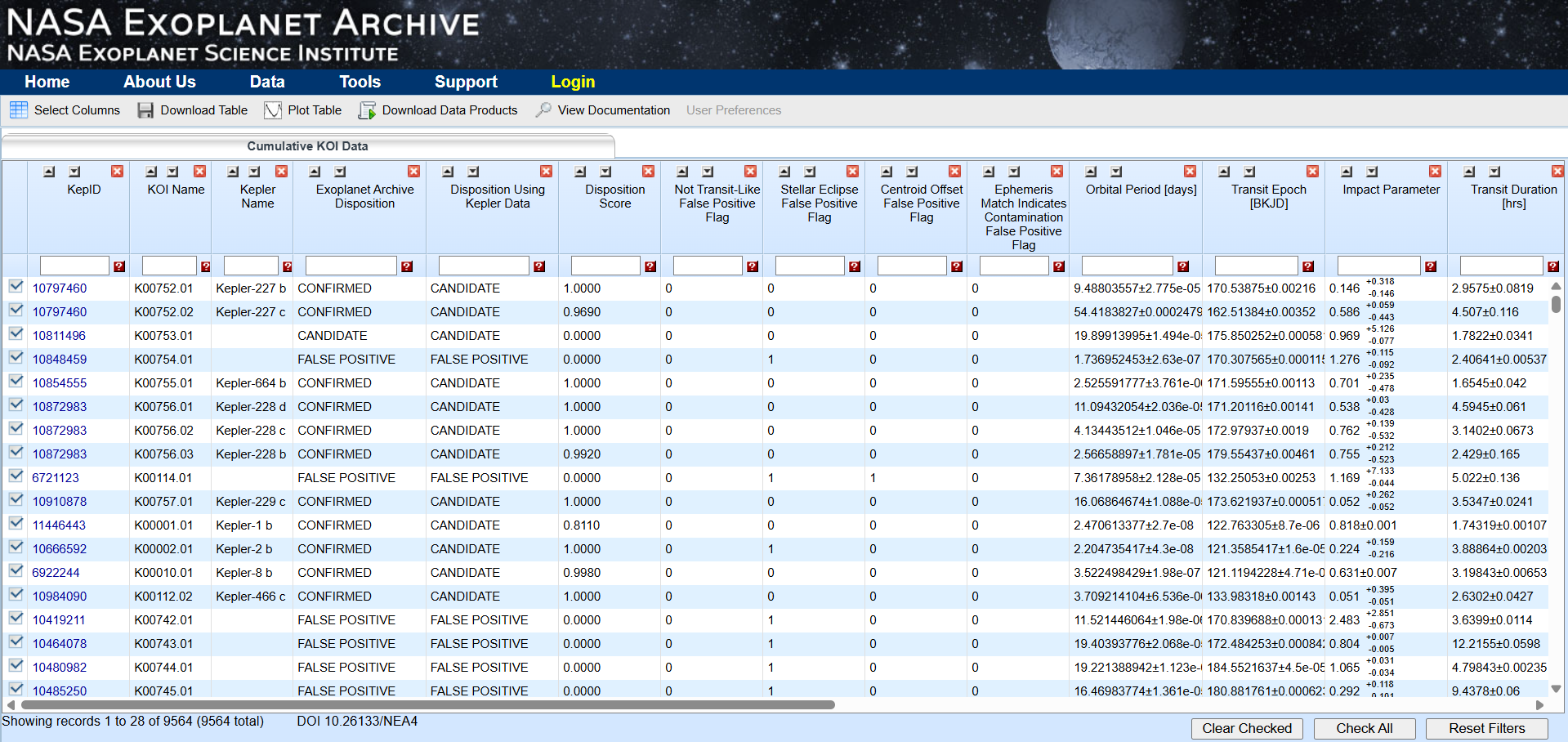
2. Download the cumulative dataset from "Download Table"
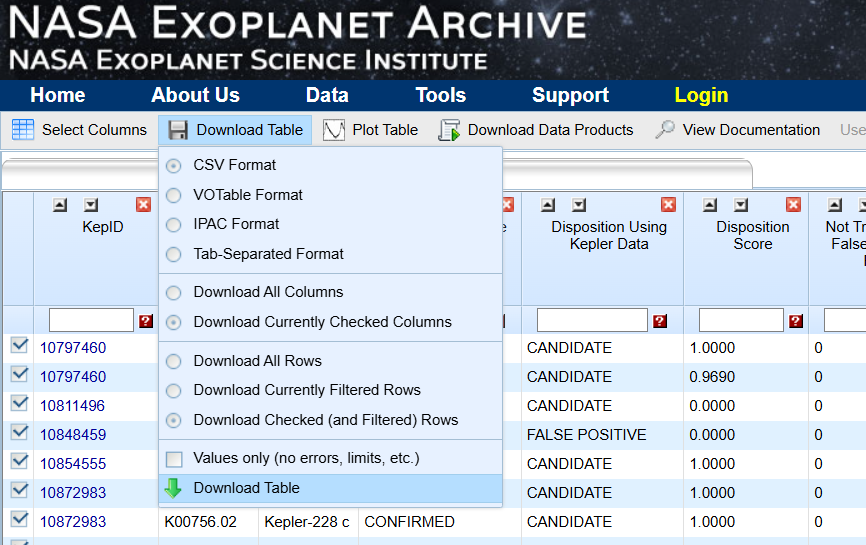
3. You can use the Jupyter notebook named "create_traning_and_target_data.ipynb" to split the downloaded dataset into two files:
- training_dataset.csv: a copy of the cumulative dataset with the last one thousand rows dropped
- target_data.csv: the last one thousand rows of the downloaded data with the exoplanet disposition removed to be used for predictions
4. The training dataset can then be uploaded as training data to Exoseeker
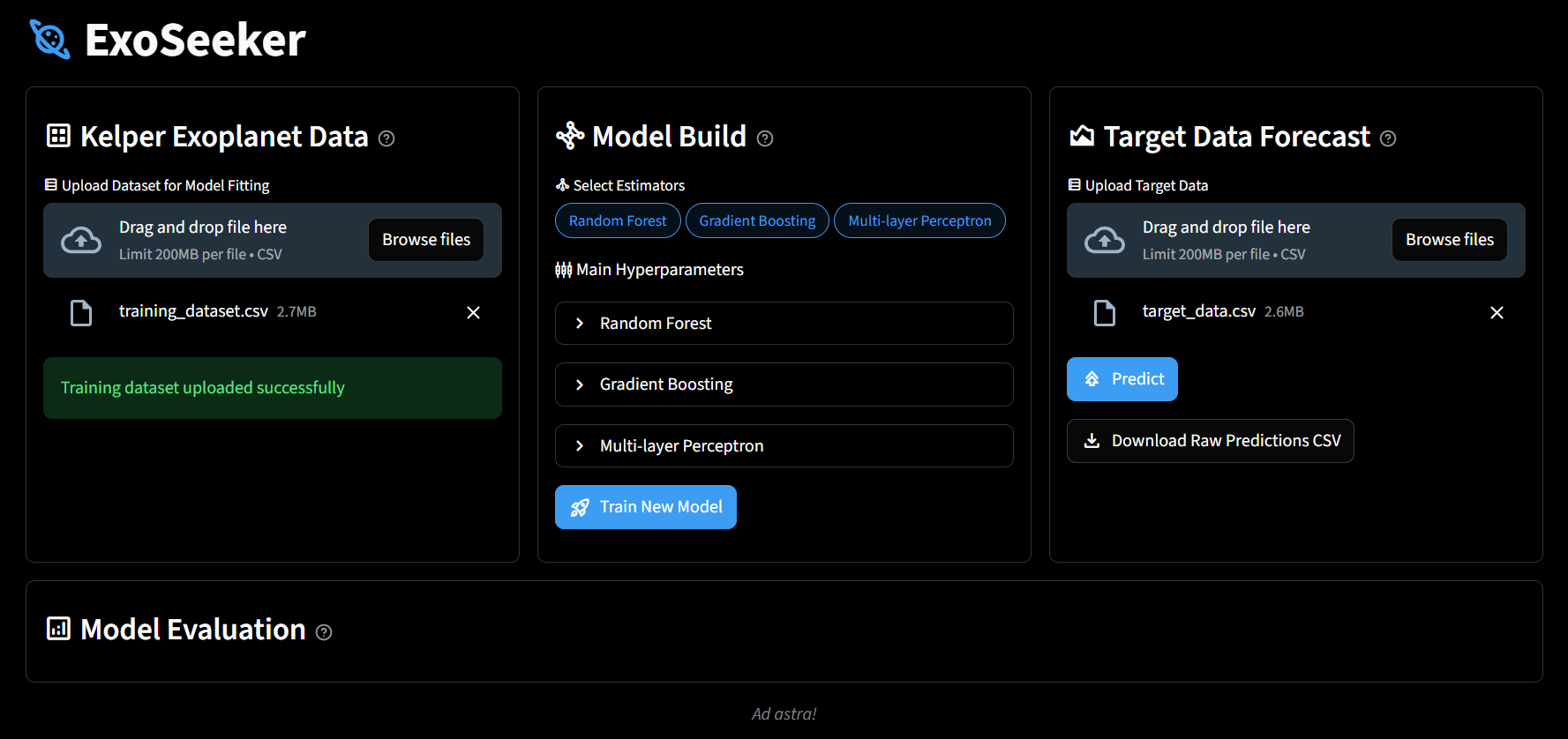
5. You can create your own custom machine learning model in the model build section, select estimators, and adjust their main hyperparameters
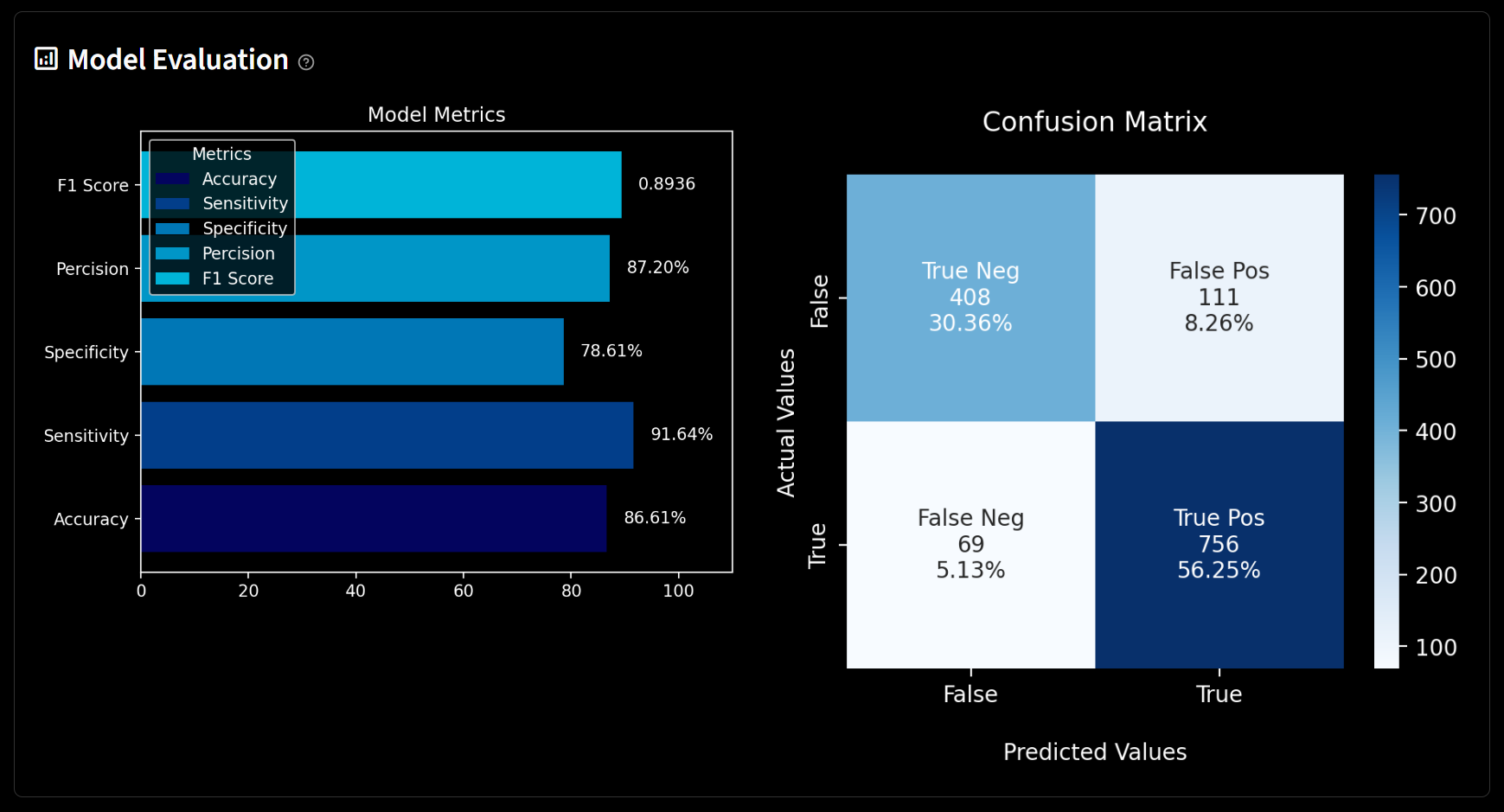
6. Once the model has been trained, it would be saved locally as a pickle file, and its performance would be visualized in the model evaluation
7. You can then go to the target data forecast to run predictions on target_data.csv





