Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim
Neovim plugin for interacting with LLM's and building editor integrated prompts.
https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim
ai chatgpt llm neovim neovim-plugin nvim nvim-plugin openai palm prompt-engineering prompts
Last synced: 7 days ago
JSON representation
Neovim plugin for interacting with LLM's and building editor integrated prompts.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim
- Owner: gsuuon
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-04-16T04:18:10.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-25T20:41:18.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-07T16:03:25.653Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: ai, chatgpt, llm, neovim, neovim-plugin, nvim, nvim-plugin, openai, palm, prompt-engineering, prompts
- Language: Lua
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.83 MB
- Stars: 311
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 21
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-neovim - gsuuon/model.nvim - Integrate LLMs via a prompt builder interface. Multi-providers including OpenAI (+ compatibles), PaLM, HuggingFace and local engines like llamacpp. (AI / (requires Neovim 0.5))
- awesome-ChatGPT-repositories - model.nvim - Neovim plugin for interacting with LLM's and building editor integrated prompts. (Browser-extensions)
README
# 🗿 model.nvim
Use AI models in Neovim for completions or chat. Build prompts programatically with lua. Designed for those who want to customize their prompts, experiment with multiple providers or use local models.
https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim/assets/6422188/3af3e65d-d13c-4196-abe1-07d605225c10
### Features
- 🎪 Provider agnostic. Comes with:
- hosted
- OpenAI ChatGPT (and compatible API's)
- Google PaLM, together, huggingface
- local
- llama.cpp
- ollama
- easy to add your own
- 🎨 Programmatic prompts in lua
- customize everything
- async and multistep prompts
- starter examples
- 🌠 Streaming completions
- directly in buffer
- transform/extract text
- append/replace/insert modes
- 🦜 Chat in `mchat` filetype buffer
- edit settings or messages at any point
- take conversations to different models
- treesitter highlights and folds
### Contents
- [Setup](#setup)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Config](#configuration)
- [Providers](#providers)
- [Reference](#reference)
- [Examples](#examples)
- [Contributing](#contributing)
If you have any questions feel free to ask in [discussions](https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim/discussions)
---
## Setup
### Requirements
- Nvim 0.9.0 or higher
- curl
### With [lazy.nvim](https://github.com/folke/lazy.nvim)
```lua
require('lazy').setup({
{
'gsuuon/model.nvim',
-- Don't need these if lazy = false
cmd = { 'M', 'Model', 'Mchat' },
init = function()
vim.filetype.add({
extension = {
mchat = 'mchat',
}
})
end,
ft = 'mchat',
keys = {
{'d', ':Mdelete', mode = 'n'},
{'s', ':Mselect', mode = 'n'},
{'', ':Mchat', mode = 'n' }
},
-- To override defaults add a config field and call setup()
-- config = function()
-- require('model').setup({
-- prompts = {..},
-- chats = {..},
-- ..
-- })
--
-- require('model.providers.llamacpp').setup({
-- binary = '~/path/to/server/binary',
-- models = '~/path/to/models/directory'
-- })
--end
}
})
```
### Treesitter
To get treesitter highlighting of [chat buffers](#chat-prompts) with markdown injections, use `:TSInstall mchat` after model.nvim has been loaded (if you're using Lazy run `:Lazy load model.nvim` first). The grammar repo is at [gsuuon/tree-sitter-mchat](https://github.com/gsuuon/tree-sitter-mchat/).
### Secrets
If you prefer to keep keys out of your environment, they can also be set programmatically using `:help vim.env` or using the `secrets` field of the model.nvim setup table. `config.secrets` takes a table of functions which return a string - the function is called when the key is used and the result is cached for subsequent calls:
```lua
require('model').setup({
secrets = {
PROVIDER_API_KEY = function()
return 'some key'
end
}
})
```
## Usage
https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim/assets/6422188/ae00076d-3327-4d97-9cc1-41acffead327
**model.nvim** comes with some [starter prompts](./lua/model/prompts/starters.lua) and makes it easy to build your own prompt library. For an example of a more complex agent-like multi-step prompt where we curl for openapi schema, ask gpt for relevant endpoint, then include that in a final prompt look at the `openapi` starter prompt.
Prompts can have 5 different [modes](#segmentmode) which determine what happens to the response: append, insert, replace, buffer, insert_or_replace. The default is to append, and with no visual selection the default input is the entire buffer, so your response will be at the end of the file. Modes are configured on a per-prompt basis.
### Commands
#### Run prompts
Run a completion [prompt](#prompts)
- `:Model [name]` or `:M [name]` — Start a completion request of either the visual selection or the current buffer. Uses the default prompt if no prompt name is provided. Completions typically edit the current buffer.
Start a new [chat](#chat-prompts)
- `:Mchat [name] [instruction]` — Start a new chat buffer with the `name` [ChatPrompt](#chatprompt) for multi-turn conversation. Provide an optional instruction override. If you're currently in an `mchat` buffer you can use `-` to import the buffer's instruction to the new chat, e.g. `:Mchat openai -`, otherwise it will be the system instruction of the new chat prompt.
Run a chat buffer
- `:Mchat` — Request the assistant response in a chat buffer. You can save an `mchat` buffer as `my_conversation.mchat`, reload it later and run `:Mchat` with your next message to continue where you left off. You'll need to have the same ChatPrompt configured in setup.
##### Telescope extension
If you use [telescope](https://github.com/nvim-telescope/telescope.nvim), mchat buffers can be browsed with `:Telescope model mchat`.
#### Manage responses
Responses are inserted with extmarks, so once the buffer is closed the responses become normal text and won't work with the following commands.
Select response
https://github.com/gsuuon/llm.nvim/assets/6422188/fd5aca13-979f-4bcf-8570-f935fdebbf03
- `:Mselect` — Select the response under the cursor.
Delete response
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6422188/233774216-4e100122-3a93-4dfb-a7c7-df50f1221bdd.mp4
- `:Mdelete` — Delete the response under the cursor. If `prompt.mode == 'replace'` then replace with the original text.
Cancel response
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6422188/233773436-3e9d2a15-bc87-47c2-bc5b-d62d62480297.mp4
- `:Mcancel` — Cancel the active response under the cursor.
Show response
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6422188/233773449-3b85355b-bad1-4e40-a699-6a8f5cf4bcd5.mp4
- `:Mshow` — Flash the response under the cursor if there is one.
#### Manage context
There are some basic context management helpers which use the quickfix list:
- `:MCadd` — Add the current file
- `:MCremove` — Remove the current file
- `:MCclear` — Remove all entries
- `:MCpaste` — Paste the contents of the quickfix list files with filepaths and code fences
- an example:
````md
File: `src/index.tsx`
```typescriptreact
import App from "./App";
render( () => ), document.getElementById("root")!);
```
````
File content of the quickfix list (what `:MCpaste` inserts) can be accessed programmatically via `require('model.util.qflist').get_text()`, for example:
```lua
local qflist = require('model.util.qflist')
local starters = require('model.prompts.chats')
config.chats = {
['codellama:qfix'] = vim.tbl_deep_extend('force', starters['together:codellama'], {
system = 'You are an intelligent programming assistant',
create = function()
return qflist.get_text()
end
}),
}
```
### 🚧 WIP - Local vector store
Setup and usage
### Requirements
- Python 3.10+
- `pip install numpy openai tiktoken`
### Usage
Check the module functions exposed in [store](./lua/model/store/init.lua). This uses the OpenAI embeddings api to generate vectors and queries them by cosine similarity.
To add items call into the `model.store` lua module functions, e.g.
- `:lua require('model.store').add_lua_functions()`
- `:lua require('model.store').add_files('.')`
Look at `store.add_lua_functions` for an example of how to use treesitter to parse files to nodes and add them to the local store.
To get query results call `store.prompt.query_store` with your input text, desired count and similarity cutoff threshold (0.75 seems to be decent). It returns a list of {id: string, content: string}:
```lua
builder = function(input, context)
---@type {id: string, content: string}[]
local store_results = require('model.store').prompt.query_store(input, 2, 0.75)
-- add store_results to your messages
end
```
- `:Mstore [command]`
- `:Mstore init` — initialize a store.json file at the closest git root directory
- `:Mstore query ` — query a store.json
## Configuration
All [setup options](#setupoptions) are optional. Add new prompts to `options.prompts.[name]` and chat prompts to `options.chats.[name]`.
```lua
require('model').setup({
default_prompt = {},
prompts = {...},
chats = {...},
hl_group = 'Comment',
join_undo = true,
})
```
### Prompts
[Prompts](#prompt) go in the `prompts` field of the setup table and are ran by the command `:Model [prompt name]` or `:M [prompt name]`. The commands tab-complete with the available prompts.
With lazy.nvim:
```lua
{
'gsuuon/model.nvim',
config = function()
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
instruct = { ... },
code = { ... },
ask = { ... }
}
})
end
}
```
A prompt entry defines how to handle a completion request - it takes in the editor input (either an entire file or a visual selection) and some context, and produces the api request data merging with any defaults. It also defines how to handle the API response - for example it can replace the selection (or file) with the response or insert it at the cursor positon.
Check out the [starter prompts](./lua/model/prompts/starters.lua) to see how to create prompts. Check out [the reference](#prompt) for the type definitions.
### Chat prompts
https://github.com/gsuuon/llm.nvim/assets/6422188/b5082daa-173a-4739-9690-a40ce2c39d15
[Chat prompts](#chatprompt) go in the `chats` field of the setup table.
```lua
{
'gsuuon/model.nvim',
config = function()
require('model').setup({
prompts = { ... },
chats = {
gpt4 = { ... },
mixtral = { ... }
starling = { ... }
}
})
end
}
```
Use `:Mchat [name]` to create a new mchat buffer with that chat prompt. The command will tab complete with available chat prompts. You can prefix the command with `:horizontal Mchat [name]` or `:tab Mchat [name]` to create the buffer in a horizontal split or new tab.
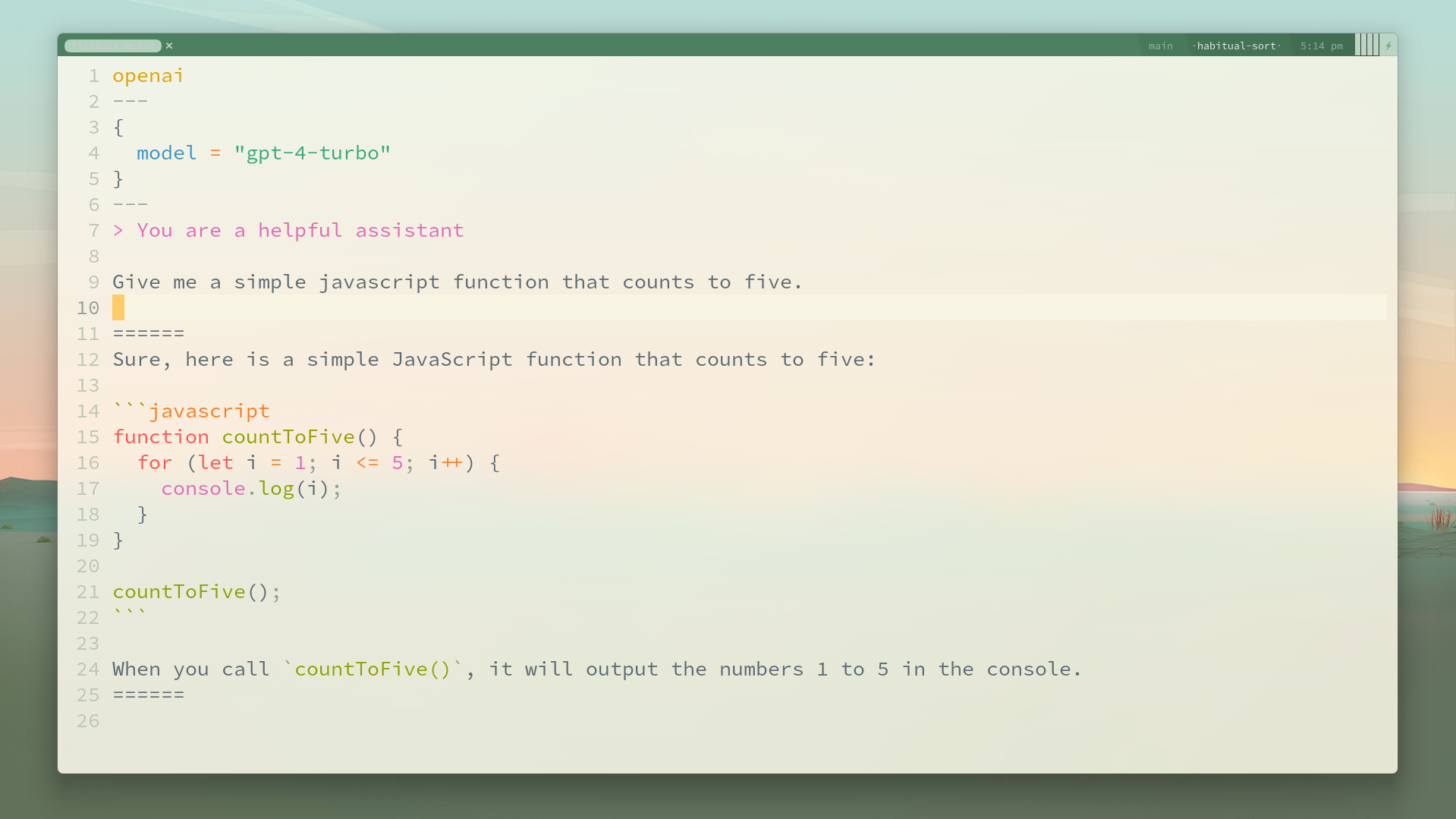
A brand new `mchat` buffer might look like this:
```
openai
---
{
params = {
model = "gpt-4-1106-preview"
}
}
---
> You are a helpful assistant
Count to three
```
Run `:Mchat` in the new buffer (with no name argument) to get the assistant response. You can edit any of the messages, params, options or system instruction (the first line, if it starts with `> `) as necessary throughout the conversation. You can also copy/paste to a new buffer, `:set ft=mchat` and run `:Mchat`.
You can save the buffer with an `.mchat` extension to continue the chat later using the same settings shown in the header. `mchat` comes with some syntax highlighting and folds to show the various chat parts - name of the chatprompt runner, options and params in the header, and a system message.
Check out [the starter chat prompts](./lua/model/prompts/chats.lua) to see how to add your own. Check out [the reference](#chatprompt) for the type definitions.
### Library autoload
You can use `require('util').module.autoload` instead of a naked `require` to always re-require a module on use. This makes the feedback loop for developing prompts faster:
```diff
require('model').setup({
- prompts = require('prompt_library')
+ prompts = require('model.util').module.autoload('prompt_library')
})
```
I recommend setting this only during active prompt development, and switching to a normal `require` otherwise.
## Providers
The available providers are in [./lua/model/providers](./lua/model/providers).
- [openai](#openai-chatgpt)
- [llama.cpp](#llamacpp)
- [ollama](#ollama)
- [google palm](#google-palm)
- [together](#together)
- [huggingface](#huggingface-api)
- [kobold](#kobold)
- [langserve](#langserve)
- [your own](#adding-your-own)
### OpenAI ChatGPT
(default)
Set the `OPENAI_API_KEY` environment variable to your [api key](https://platform.openai.com/account/api-keys).
#### openai parameters
Parameters are documented [here](https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference/chat/create). You can override the [default parameters](lua/model/providers/openai.lua) for this provider by calling initialize:
```lua
config = function()
require('model.providers.openai').initialize({
model = 'gpt-4-1106-preview'
})
end
```
#### openai prompt options
OpenAI prompts can take an additional option field to talk to compatible API's.
```lua
compat = vim.tbl_extend('force', openai.default_prompt, {
options = {
url = 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/'
}
})
```
- `url?: string` - (Optional) Custom URL to use for API requests. Defaults to 'https://api.openai.com/v1/'. If `url` is provided then the environment key will not be sent, you'll need to include `authorization`.
- `endpoint?: string` - (Optional) Endpoint to use in the request URL. Defaults to 'chat/completions'.
- `authorization?: string` - (Optional) Authorization header to include in the request. Overrides any authorization given through the environment key.
For example, to configure it for Mistral AI "La plateforme":
```lua
{
"gsuuon/model.nvim",
cmd = { "Model", "Mchat" },
init = function()
vim.filetype.add({ extension = { mchat = "mchat" } })
end,
ft = "mchat",
keys = { { "h", ":Model", mode = "v" } },
config = function()
local mistral = require("model.providers.openai")
local util = require("model.util")
require("model").setup({
hl_group = "Substitute",
prompts = util.module.autoload("prompt_library"),
default_prompt = {
provider = mistral,
options = {
url = "https://api.mistral.ai/v1/",
authorization = "Bearer YOUR_MISTRAL_API_KEY",
},
builder = function(input)
return {
model = "mistral-medium",
temperature = 0.3,
max_tokens = 400,
messages = {
{
role = "system",
content = "You are helpful assistant.",
},
{ role = "user", content = input },
},
}
end,
},
})
end,
},
```
### LlamaCpp
This provider uses the [llama.cpp server](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/examples/server/README.md).
You can start the server manually or have it autostart when you run a llamacpp prompt. To autostart the server call `require('model.providers.llamacpp').setup({})` in your config function and set a `model` in the prompt options (see below). Leave `model` empty to not autostart. The server restarts if the prompt model or args change.
#### Setup
1. Build [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp)
1. Download the model you want to use, e.g. [Zephyr 7b beta](https://huggingface.co/TheBloke/zephyr-7B-beta-GGUF/tree/main)
1. Setup the llamacpp provider if you plan to use autostart:
```lua
config = function()
require('model').setup({ .. })
require('model.providers.llamacpp').setup({
binary = '~/path/to/server/binary',
models = '~/path/to/models/directory'
})
end
```
1. Use the llamacpp provider in a prompt:
```lua
local llamacpp = require('model.providers.llamacpp')
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
zephyr = {
provider = llamacpp,
options = {
model = 'zephyr-7b-beta.Q5_K_M.gguf',
args = {
'-c', 8192,
'-ngl', 35
}
},
builder = function(input, context)
return {
prompt =
'<|system|>'
.. (context.args or 'You are a helpful assistant')
.. '\n\n<|user|>\n'
.. input
.. '\n<|assistant|>',
stops = { '' }
}
end
}
}
})
```
#### LlamaCpp setup options
Setup `require('model.providers.llamacpp').setup({})`
- `binary: string` - path to the llamacpp server binary executable
- `models: string` - path to the parent directory of the models (joined with `prompt.model`)
#### LlamaCpp prompt options
- `model?: string` - (optional) The path to the model file to use with server autostart. If not specified, the server will not be started.
- `args?: string[]` - (optional) An array of additional arguments to pass to the server at startup. Use this to specify things like context size `-c` or gpu layers `-ngl` that are specific to the model.
- `url?: string` - (optional) Override the default server url. This can be useful for connecting to a remote server or a customized local one.
### Ollama
This uses the [ollama](https://github.com/jmorganca/ollama/tree/main) REST server's [`/api/generate` endpoint](https://github.com/jmorganca/ollama/blob/main/docs/api.md#generate-a-completion). `raw` defaults to true, and `stream` is always true.
Example prompt with starling:
```lua
['ollama:starling'] = {
provider = ollama,
params = {
model = 'starling-lm'
},
builder = function(input)
return {
prompt = 'GPT4 Correct User: ' .. input .. '<|end_of_turn|>GPT4 Correct Assistant: '
}
end
},
```
### Google PaLM
Set the `PALM_API_KEY` environment variable to your [api key](https://makersuite.google.com/app/apikey).
The PaLM provider defaults to the text model (`text-bison-001`). The builder's return params can include `model = 'chat-bison-001'` to use the chat model instead.
Params should be either a [generateText](https://developers.generativeai.google/api/rest/generativelanguage/models/generateText#request-body) body by default, or a [generateMessage](https://developers.generativeai.google/api/rest/generativelanguage/models/generateMessage#request-body) body if using `model = 'chat-bison-001'`.
```lua
palm = {
provider = palm,
builder = function(input, context)
return {
model = 'text-bison-001',
prompt = {
text = input
},
temperature = 0.2
}
end
}
```
### Together
Set the `TOGETHER_API_KEY` environment variable to your [api key](https://api.together.xyz/settings/api-keys). Talks to the [together inference endpoint](https://docs.together.ai/reference/inference).
```lua
['together:phind/codellama34b_v2'] = {
provider = together,
params = {
model = 'Phind/Phind-CodeLlama-34B-v2',
max_tokens = 1024
},
builder = function(input)
return {
prompt = '### System Prompt\nYou are an intelligent programming assistant\n\n### User Message\n' .. input ..'\n\n### Assistant\n'
}
end
},
```
### Huggingface API
Set the `HUGGINGFACE_API_KEY` environment variable to your [api key](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens).
Set the model field on the params returned by the builder (or the static params in `prompt.params`). Set `params.stream = false` for models which don't support it (e.g. `gpt2`). Check [huggingface api docs](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/detailed_parameters) for per-task request body types.
```lua
['hf:starcoder'] = {
provider = huggingface,
options = {
model = 'bigcode/starcoder'
},
builder = function(input)
return { inputs = input }
end
},
```
### Kobold
For older models that don't work with llama.cpp, koboldcpp might still support them. Check their [repo](https://github.com/LostRuins/koboldcpp/) for setup info.
### Langserve
Set the `output_parser` to correctly parse the contents returned from the `/stream` endpoint and use the `builder` to construct the input query. The below uses the [example langserve application](https://github.com/langchain-ai/langserve-launch-example) to make a joke about the input text.
```lua
['langserve:make-a-joke'] = {
provider = langserve,
options = {
base_url = 'https://langserve-launch-example-vz4y4ooboq-uc.a.run.app/',
output_parser = langserve.generation_chunk_parser,
},
builder = function(input, context)
return {
topic = input,
}
end
},
```
### Adding your own
[Providers](#provider) implement a simple interface so it's easy to add your own. Just set your provider as the `provider` field in a prompt. Your provider needs to kick off the request and call the handlers as data streams in, finishes, or errors. Check [the hf provider](./lua/model/providers/huggingface.lua) for a simpler example supporting server-sent events streaming. If you don't need streaming, just make a request and call `handler.on_finish` with the result.
Basic provider example:
```lua
local test_provider = {
request_completion = function(handlers, params, options)
vim.notify(vim.inspect({params=params, options=options}))
handlers.on_partial('a response')
handlers.on_finish()
end
}
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
test_prompt = {
provider = test_provider,
builder = function(input, context)
return {
input = input,
context = context
}
end
}
}
})
```
---
## Reference
The following are types and the fields they contain:
#### SetupOptions
Setup `require('model').setup(SetupOptions)`
- `default_prompt?: string` - The default prompt to use with `:Model` or `:M`. Default is the openai starter.
- `prompts?: {string: Prompt}` - A table of custom prompts to use with `:M [name]`. Keys are the names of the prompts. Default are the starters.
- `chats?: {string: ChatPrompt}` - A table of chat prompts to use with `:Mchat [name]`. Keys are the names of the chats.
- `hl_group?: string` - The default highlight group for in-progress responses. Default is `'Comment'`.
- `join_undo?: boolean` - Whether to join streaming response text as a single undo command. When true, unrelated edits during streaming will also be undone. Default is `true`.
#### Prompt
`params` are generally data that go directly into the request sent by the provider (e.g. content, temperature). `options` are used by the provider to know how to handle the request (e.g. server url or model name if a local LLM).
Setup `require('model').setup({prompts = { [prompt name] = Prompt, .. }})`
Run `:Model [prompt name]` or `:M [prompt name]`
- `provider: Provider` - The provider for this prompt, responsible for requesting and returning completion suggestions.
- [`builder: ParamsBuilder`](#paramsbuilder) - Converts input (either the visual selection or entire buffer text) and [context](#context) to request parameters. Returns either a table of params or a function that takes a callback with the params.
- `transform?: fun(string): string` - Optional function that transforms completed response text after on_finish, e.g. to extract code.
- `mode?: SegmentMode | StreamHandlers` - Response handling mode. Defaults to 'append'. Can be one of 'append', 'replace', 'buffer', 'insert', or 'insert_or_replace'. Can be a table of [StreamHandlers](#streamhandlers) to manually handle the provider response.
- `hl_group?: string` - Highlight group of active response.
- `params?: table` - Static request parameters for this prompt.
- `options?: table` - Optional options for the provider.
#### Provider
- `request_completion: fun(handler: StreamHandlers, params?: table, options?: table): function` - Requests a completion stream from the provider and returns a cancel callback. Feeds completion parts back to the prompt runner using handler methods and calls on_finish after completion is done.
- `default_prompt? : Prompt` - Default prompt for this provider (optional).
- `adapt?: fun(prompt: StandardPrompt): table` - Adapts a standard prompt to params for this provider (optional).
#### ParamsBuilder
(function)
- `fun(input: string, context: Context): table | fun(resolve: fun(params: table))` - Converts input (either the visual selection or entire buffer text) and [context](#context) to request parameters. Returns either a table of params or a function that takes a callback with the params.
#### SegmentMode
(enum)
Exported as `local mode = require('model').mode`
- `APPEND = 'append'` - Append to the end of input.
- `REPLACE = 'replace'` - Replace input.
- `BUFFER = 'buffer'` - Create a new buffer and insert.
- `INSERT = 'insert'` - Insert at the cursor position.
- `INSERT_OR_REPLACE = 'insert_or_replace'` - Insert at the cursor position if no selection, or replace the selection.
#### StreamHandlers
- `on_partial: fun(partial_text: string): nil` - Called by the provider to pass partial incremental text completions during a completion request.
- `on_finish: fun(complete_text?: string, finish_reason?: string): nil` - Called by the provider when the completion is done. Takes an optional argument for the completed text (`complete_text`) and an optional argument for the finish reason (`finish_reason`).
- `on_error: fun(data: any, label?: string): nil` - Called by the provider to pass error data and an optional label during a completion request.
#### ChatPrompt
`params` are generally data that go directly into the request sent by the provider (e.g. content, temperature). `options` are used by the provider to know how to handle the request (e.g. server url or model name if a local LLM).
Setup `require('model').setup({chats = { [chat name] = ChatPrompt, .. }})`
Run `:Mchat [chat name]`
- `provider: Provider` - The provider for this chat prompt.
- `create: fun(input: string, context: Context): string | ChatContents` - Converts input and context into the first message text or ChatContents, which are written into the new chat buffer.
- `run: fun(messages: ChatMessage[], config: ChatConfig): table | fun(resolve: fun(params: table): nil )` - Converts chat messages and configuration into completion request params. This function returns a table containing the required params for generating completions, or it can return a function that takes a callback to resolve the params.
- `system?: string` - Optional system instruction used to provide specific instructions for the provider.
- `params?: table` - Static request parameters that are provided to the provider during completion generation.
- `options?: table` - Provider options, which can be customized by the user to modify the chat prompt behavior.
#### ChatMessage
- `role: 'user' | 'assistant'` - Indicates whether this message was generated by the user or the assistant.
- `content: string` - The actual content of the message.
#### ChatConfig
- `system?: string` - Optional system instruction used to provide context or specific instructions for the provider.
- `params?: table` - Static request parameters that are provided to the provider during completion generation.
- `options?: table` - Provider options, which can be customized by the user to modify the chat prompt behavior.
#### ChatContents
- `config: ChatConfig` - Configuration for this chat buffer, used by `chatprompt.run`. This includes information such as the system instruction, static request parameters, and provider options.
- `messages: ChatMessage[]` - Messages in the chat buffer.
#### Context
- `before: string` - The text present before the selection or cursor.
- `after: string` - The text present after the selection or cursor.
- `filename: string` - The filename of the buffer containing the selected text.
- `args: string` - Any additional command arguments provided to the plugin.
- `selection?: Selection` - An optional `Selection` object representing the selected text, if available.
#### Selection
- `start: Position` - The starting position of the selection within the buffer.
- `stop: Position` - The ending position of the selection within the buffer.
#### Position
- `row: number` - The 0-indexed row of the position within the buffer.
- `col: number or vim.v.maxcol` - The 0-indexed column of the position within the line. If `vim.v.maxcol` is provided, it indicates the end of the line.
## Examples
### Prompts
```lua
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
['prompt name'] = ...
}
})
```
Ask for additional user instruction
https://github.com/gsuuon/llm.nvim/assets/6422188/0e4b2b68-5873-42af-905c-3bd5a0bdfe46
```lua
ask = {
provider = openai,
params = {
temperature = 0.3,
max_tokens = 1500
},
builder = function(input)
local messages = {
{
role = 'user',
content = input
}
}
return util.builder.user_prompt(function(user_input)
if #user_input > 0 then
table.insert(messages, {
role = 'user',
content = user_input
})
end
return {
messages = messages
}
end, input)
end,
}
```
Create a commit message based on `git diff --staged`
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6422188/233807212-d1830514-fe3b-4d38-877e-f3ecbdb222aa.mp4
```lua
['commit message'] = {
provider = openai,
mode = mode.INSERT,
builder = function()
local git_diff = vim.fn.system {'git', 'diff', '--staged'}
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'Write a short commit message according to the Conventional Commits specification for the following git diff: ```\n' .. git_diff .. '\n```'
}
}
}
end,
}
```
Modify input to append messages
https://user-images.githubusercontent.com/6422188/233748890-5dac719a-eb9a-4f76-ab9d-8eba3694a350.mp4
#### `lua/prompt_library.lua`
```lua
--- Looks for `
Replace text with Spanish
```lua
local openai = require('model.providers.openai')
local segment = require('model.util.segment')
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
['to spanish'] =
{
provider = openai,
hl_group = 'SpecialComment',
builder = function(input)
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'Translate to Spanish',
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input,
}
}
}
end,
mode = segment.mode.REPLACE
}
}
})
```
Notifies each stream part and the complete response
```lua
local openai = require('model.providers.openai')
require('model').setup({
prompts = {
['show parts'] = {
provider = openai,
builder = openai.default_builder,
mode = {
on_finish = function (final)
vim.notify('final: ' .. final)
end,
on_partial = function (partial)
vim.notify(partial)
end,
on_error = function (msg)
vim.notify('error: ' .. msg)
end
}
},
}
})
```
### Configuration
You can move prompts into their own file and use `util.module.autoload` to quickly iterate on prompt development.
Setup
#### `config = function()`
```lua
local openai = require('model.providers.openai')
-- configure default model params here for the provider
openai.initialize({
model = 'gpt-3.5-turbo-0301',
max_tokens = 400,
temperature = 0.2,
})
local util = require('model.util')
require('model').setup({
hl_group = 'Substitute',
prompts = util.module.autoload('prompt_library'),
default_prompt = {
provider = openai,
builder = function(input)
return {
temperature = 0.3,
max_tokens = 120,
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'You are helpful assistant.',
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input,
}
}
}
end
}
})
```
Prompt library
#### `lua/prompt_library.lua`
```lua
local openai = require('model.providers.openai')
local segment = require('model.util.segment')
return {
code = {
provider = openai,
builder = function(input)
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'You are a 10x super elite programmer. Continue only with code. Do not write tests, examples, or output of code unless explicitly asked for.',
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input,
}
}
}
end,
},
['to spanish'] = {
provider = openai,
hl_group = 'SpecialComment',
builder = function(input)
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'Translate to Spanish',
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input,
}
}
}
end,
mode = segment.mode.REPLACE
},
['to javascript'] = {
provider = openai,
builder = function(input, ctx)
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = 'Convert the code to javascript'
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input
}
}
}
end,
},
['to rap'] = {
provider = openai,
hl_group = 'Title',
builder = function(input)
return {
messages = {
{
role = 'system',
content = "Explain the code in 90's era rap lyrics"
},
{
role = 'user',
content = input
}
}
}
end,
}
}
```
## Contributing
New starter prompts, providers and bug fixes are welcome! If you've figured out some useful prompts and want to share, check out the [discussions](https://github.com/gsuuon/model.nvim/discussions/24).
### Roadmap
I'm hoping to eventually add the following features - I'd appreciate help with any of these.
#### Local retrieval augmented generation
The basics are here - a simple json vectorstore based on the git repo, querying, cosine similarity comparison. It just needs a couple more features to improve the DX of using from prompts.
#### Enhanced context
Make treesitter and LSP info available in prompt context.