https://github.com/guilhermestracini/poc-dotnet-dijkstra
🔬 Proof of Concept of Dijkstra's algorithm in .NET
https://github.com/guilhermestracini/poc-dotnet-dijkstra
concept dijkstra-algorithm edges poc poc-dijkstra proof simplenode
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
🔬 Proof of Concept of Dijkstra's algorithm in .NET
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/guilhermestracini/poc-dotnet-dijkstra
- Owner: GuilhermeStracini
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-04-20T23:52:25.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-06-09T16:20:25.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-09T17:27:36.413Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: concept, dijkstra-algorithm, edges, poc, poc-dijkstra, proof, simplenode
- Language: C#
- Homepage: https://guilhermestracini.github.io/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra/
- Size: 501 KB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# PoC .NET - Dijkstra
🔬 Proof of Concept of [Dijkstra's algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm) in .NET
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/guibranco/poc-dijkstra)
[](https://wakatime.com/badge/github/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra)
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra/maintainability)
[](https://codeclimate.com/github/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra/test_coverage)
[](https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra)
[](https://github.com/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra)
[](https://github.com/GuilhermeStracini/POC-dotnet-Dijkstra)
Based on Elemar Jr's post [Finding the best path between two points using Dijkstra (in portuguese)](https://www.elemarjr.com/pt/archive/encontrando-o-melhor-caminho-entre-dois-pontos-usando-dijkstra/)
---
## About
This PoC validates the usage of [Dijkstra's algorithm](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dijkstra%27s_algorithm) to find the fastest way between two points.
---
## Proofs
### Sample 1 - SimpleNode - Edges are bi-directional
In this sample, the direction of the edge is bi-directional. It means that connecting A to B node is the same as B to A.
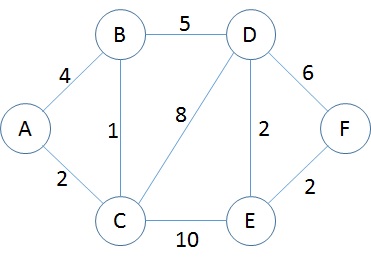
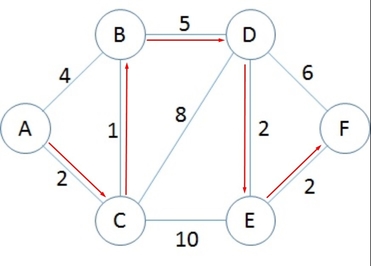
```cs
var a = new SimpleNode("A");
var b = new SimpleNode("B");
var c = new SimpleNode("C");
var d = new SimpleNode("D");
var e = new SimpleNode("E");
var f = new SimpleNode("F");
a.ConnectTo(b, 4);
a.ConnectTo(c, 2);
b.ConnectTo(c, 1);
b.ConnectTo(d, 5);
c.ConnectTo(d, 8);
c.ConnectTo(e, 10);
d.ConnectTo(f, 6);
d.ConnectTo(e, 2);
e.ConnectTo(f, 2);
var dijkstra = new Dijkstra.Dijkstra();
var result = dijkstra.FindShortestPath(a, f);
```
### Sample 2 - DirectionalNode - Edges are directional
In this sample, the connection works only in one way. If connected A to B, only A to B flow is allowed, B from A not.
We can use different values for the connection for each direction. A to B 5 then B to A 10
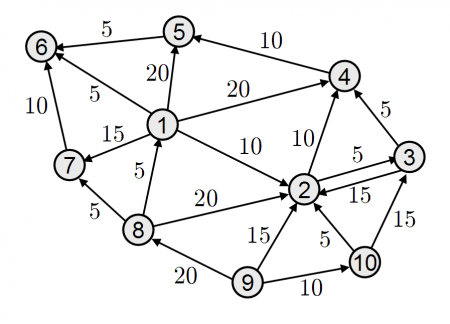
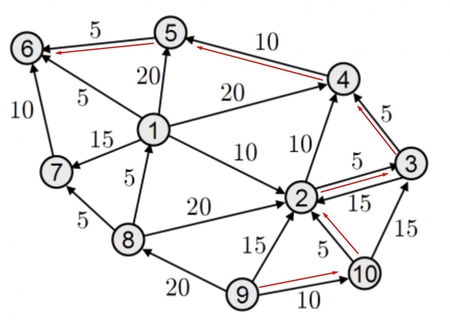
* Both directions made in 2<->3 nodes
```cs
var one = new DirectionalNode("1");
var two = new DirectionalNode("2");
var three = new DirectionalNode("3");
var four = new DirectionalNode("4");
var five = new DirectionalNode("5");
var six = new DirectionalNode("6");
var seven = new DirectionalNode("7");
var height = new DirectionalNode("8");
var nine = new DirectionalNode("9");
var ten = new DirectionalNode("10");
one.ConnectTo(two, 10);
one.ConnectTo(four, 20);
one.ConnectTo(five, 20);
one.ConnectTo(six, 5);
one.ConnectTo(seven, 15);
two.ConnectTo(four, 10);
two.ConnectTo(three, 5); //connects two and three with a value of 5
three.ConnectTo(four, 5);
three.ConnectTo(two, 15); //connects three and two with a value of 15
four.ConnectTo(five, 10);
five.ConnectTo(six, 5);
//six doesn't have outbound connections, only inbound
seven.ConnectTo(six, 10);
height.ConnectTo(one, 5);
height.ConnectTo(two, 20);
height.ConnectTo(seven, 5);
nine.ConnectTo(two, 15);
nine.ConnectTo(height, 20);
nine.ConnectTo(ten, 10);
ten.ConnectTo(two, 5);
ten.ConnectTo(three, 15);
var dijkstra = new Dijkstra.Dijkstra();
var result = dijkstra.FindShortestPath(nine, six);
```
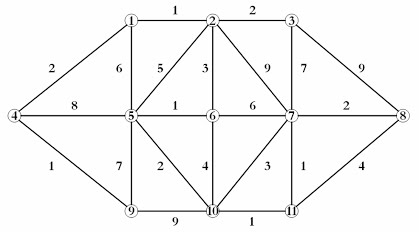
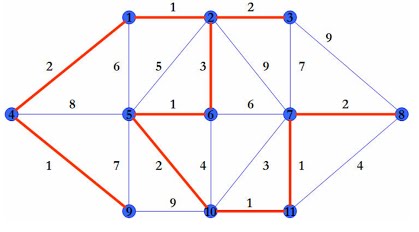
### Sample 3 - SimpleNode - More complex example
//TODO