https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt
Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm,Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm, Differential Evolution and TSP(Traveling salesman)
https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt
ant-colony-algorithm artificial-intelligence fish-swarms genetic-algorithm heuristic-algorithms immune immune-algorithm optimization particle-swarm-optimization pso simulated-annealing travelling-salesman-problem tsp
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm,Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm, Differential Evolution and TSP(Traveling salesman)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt
- Owner: guofei9987
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-12-05T10:20:41.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-06-23T12:28:48.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-26T11:17:13.571Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: ant-colony-algorithm, artificial-intelligence, fish-swarms, genetic-algorithm, heuristic-algorithms, immune, immune-algorithm, optimization, particle-swarm-optimization, pso, simulated-annealing, travelling-salesman-problem, tsp
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/en/
- Size: 382 KB
- Stars: 5,497
- Watchers: 49
- Forks: 1,002
- Open Issues: 68
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-sciml - guofei9987/scikit-opt: Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm,Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm, Differential Evolution and TSP(Traveling salesman)
- awesome-list - scikit-opt - Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm,Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm, Differential Evolution and TSP(Traveling salesman) (Machine Learning Framework / General Purpose Framework)
- awesome-datascience - scikit-opt
- awesome-python-machine-learning-resources - GitHub - 30% open · ⏱️ 15.07.2022): (Sklearn实用程序)
- StarryDivineSky - guofei9987/scikit-opt
- awesome-machine-learning - Scikit-Opt - Swarm Intelligence in Python (Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python) (Python / General-Purpose Machine Learning)
- fucking-awesome-datascience - scikit-opt
- awesome-machine-learning - Scikit-Opt - Swarm Intelligence in Python (Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python) (Python / General-Purpose Machine Learning)
- awesome-python-data-science - scikit-opt - Heuristic Algorithms for optimization. (Optimization / NLP)
- AiTreasureBox - guofei9987/scikit-opt - 11-03_6188_0](https://img.shields.io/github/stars/guofei9987/scikit-opt.svg)|Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Optimization Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm, Differential Evolution and TSP (Traveling Salesman Problem)| (Repos)
- fucking-awesome-machine-learning - Scikit-Opt - Swarm Intelligence in Python (Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python) (Python / General-Purpose Machine Learning)
- awesome-machine-learning - Scikit-Opt - Swarm Intelligence in Python (Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python) (Python / General-Purpose Machine Learning)
- awesome-meteo - scikit-opt
- awesome-python-data-science - scikit-opt - Heuristic Algorithms for optimization. (Optimization / Others)
- awesome-machine-learning - Scikit-Opt - Swarm Intelligence in Python (Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python) (Python / General-Purpose Machine Learning)
README
# [scikit-opt](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt)
[](https://pypi.org/project/scikit-opt/)
[](https://travis-ci.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/guofei9987/scikit-opt)
[](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/LICENSE)


[](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/fork)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/scikit-opt)
[](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/discussions)
Swarm Intelligence in Python
(Genetic Algorithm, Particle Swarm Optimization, Simulated Annealing, Ant Colony Algorithm, Immune Algorithm, Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm in Python)
- **Documentation:** [https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/en/](https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/en/)
- **文档:** [https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/zh/](https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/zh/)
- **Source code:** [https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt)
- **Help us improve scikit-opt** [https://www.wjx.cn/jq/50964691.aspx](https://www.wjx.cn/jq/50964691.aspx)
# install
```bash
pip install scikit-opt
```
For the current developer version:
```bach
git clone git@github.com:guofei9987/scikit-opt.git
cd scikit-opt
pip install .
```
# Features
## Feature1: UDF
**UDF** (user defined function) is available now!
For example, you just worked out a new type of `selection` function.
Now, your `selection` function is like this:
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L1)
```python
# step1: define your own operator:
def selection_tournament(algorithm, tourn_size):
FitV = algorithm.FitV
sel_index = []
for i in range(algorithm.size_pop):
aspirants_index = np.random.choice(range(algorithm.size_pop), size=tourn_size)
sel_index.append(max(aspirants_index, key=lambda i: FitV[i]))
algorithm.Chrom = algorithm.Chrom[sel_index, :] # next generation
return algorithm.Chrom
```
Import and build ga
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L12)
```python
import numpy as np
from sko.GA import GA, GA_TSP
demo_func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + (x[1] - 0.05) ** 2 + (x[2] - 0.5) ** 2
ga = GA(func=demo_func, n_dim=3, size_pop=100, max_iter=500, prob_mut=0.001,
lb=[-1, -10, -5], ub=[2, 10, 2], precision=[1e-7, 1e-7, 1])
```
Regist your udf to GA
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L20)
```python
ga.register(operator_name='selection', operator=selection_tournament, tourn_size=3)
```
scikit-opt also provide some operators
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s4](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L22)
```python
from sko.operators import ranking, selection, crossover, mutation
ga.register(operator_name='ranking', operator=ranking.ranking). \
register(operator_name='crossover', operator=crossover.crossover_2point). \
register(operator_name='mutation', operator=mutation.mutation)
```
Now do GA as usual
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s5](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L28)
```python
best_x, best_y = ga.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
```
> Until Now, the **udf** surport `crossover`, `mutation`, `selection`, `ranking` of GA
> scikit-opt provide a dozen of operators, see [here](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/tree/master/sko/operators)
For advanced users:
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_udf.py#s6](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_udf.py#L31)
```python
class MyGA(GA):
def selection(self, tourn_size=3):
FitV = self.FitV
sel_index = []
for i in range(self.size_pop):
aspirants_index = np.random.choice(range(self.size_pop), size=tourn_size)
sel_index.append(max(aspirants_index, key=lambda i: FitV[i]))
self.Chrom = self.Chrom[sel_index, :] # next generation
return self.Chrom
ranking = ranking.ranking
demo_func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + (x[1] - 0.05) ** 2 + (x[2] - 0.5) ** 2
my_ga = MyGA(func=demo_func, n_dim=3, size_pop=100, max_iter=500, lb=[-1, -10, -5], ub=[2, 10, 2],
precision=[1e-7, 1e-7, 1])
best_x, best_y = my_ga.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
```
## feature2: continue to run
(New in version 0.3.6)
Run an algorithm for 10 iterations, and then run another 20 iterations base on the 10 iterations before:
```python
from sko.GA import GA
func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2
ga = GA(func=func, n_dim=1)
ga.run(10)
ga.run(20)
```
## feature3: 4-ways to accelerate
- vectorization
- multithreading
- multiprocessing
- cached
see [https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/example_function_modes.py](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/example_function_modes.py)
## feature4: GPU computation
We are developing GPU computation, which will be stable on version 1.0.0
An example is already available: [https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_gpu.py](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_gpu.py)
# Quick start
## 1. Differential Evolution
**Step1**:define your problem
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_de.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_de.py#L1)
```python
'''
min f(x1, x2, x3) = x1^2 + x2^2 + x3^2
s.t.
x1*x2 >= 1
x1*x2 <= 5
x2 + x3 = 1
0 <= x1, x2, x3 <= 5
'''
def obj_func(p):
x1, x2, x3 = p
return x1 ** 2 + x2 ** 2 + x3 ** 2
constraint_eq = [
lambda x: 1 - x[1] - x[2]
]
constraint_ueq = [
lambda x: 1 - x[0] * x[1],
lambda x: x[0] * x[1] - 5
]
```
**Step2**: do Differential Evolution
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_de.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_de.py#L25)
```python
from sko.DE import DE
de = DE(func=obj_func, n_dim=3, size_pop=50, max_iter=800, lb=[0, 0, 0], ub=[5, 5, 5],
constraint_eq=constraint_eq, constraint_ueq=constraint_ueq)
best_x, best_y = de.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
```
## 2. Genetic Algorithm
**Step1**:define your problem
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga.py#L1)
```python
import numpy as np
def schaffer(p):
'''
This function has plenty of local minimum, with strong shocks
global minimum at (0,0) with value 0
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Test_functions_for_optimization
'''
x1, x2 = p
part1 = np.square(x1) - np.square(x2)
part2 = np.square(x1) + np.square(x2)
return 0.5 + (np.square(np.sin(part1)) - 0.5) / np.square(1 + 0.001 * part2)
```
**Step2**: do Genetic Algorithm
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga.py#L16)
```python
from sko.GA import GA
ga = GA(func=schaffer, n_dim=2, size_pop=50, max_iter=800, prob_mut=0.001, lb=[-1, -1], ub=[1, 1], precision=1e-7)
best_x, best_y = ga.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, '\n', 'best_y:', best_y)
```
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga.py#L22)
```python
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Y_history = pd.DataFrame(ga.all_history_Y)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 1)
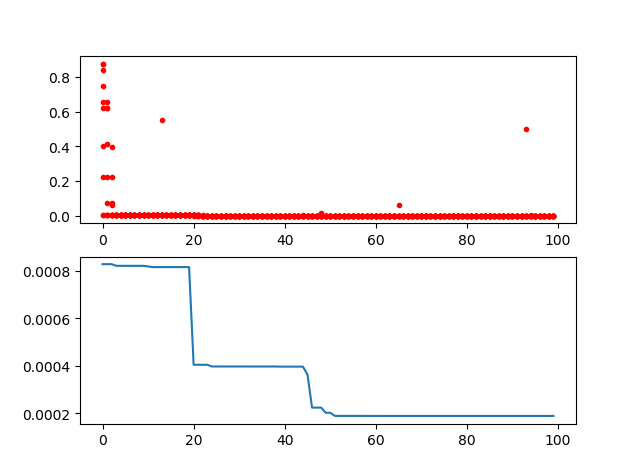
ax[0].plot(Y_history.index, Y_history.values, '.', color='red')
Y_history.min(axis=1).cummin().plot(kind='line')
plt.show()
```
### 2.2 Genetic Algorithm for TSP(Travelling Salesman Problem)
Just import the `GA_TSP`, it overloads the `crossover`, `mutation` to solve the TSP
**Step1**: define your problem. Prepare your points coordinate and the distance matrix.
Here I generate the data randomly as a demo:
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#L1)
```python
import numpy as np
from scipy import spatial
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
num_points = 50
points_coordinate = np.random.rand(num_points, 2) # generate coordinate of points
distance_matrix = spatial.distance.cdist(points_coordinate, points_coordinate, metric='euclidean')
def cal_total_distance(routine):
'''The objective function. input routine, return total distance.
cal_total_distance(np.arange(num_points))
'''
num_points, = routine.shape
return sum([distance_matrix[routine[i % num_points], routine[(i + 1) % num_points]] for i in range(num_points)])
```
**Step2**: do GA
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#L19)
```python
from sko.GA import GA_TSP
ga_tsp = GA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points, size_pop=50, max_iter=500, prob_mut=1)
best_points, best_distance = ga_tsp.run()
```
**Step3**: Plot the result:
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ga_tsp.py#L26)
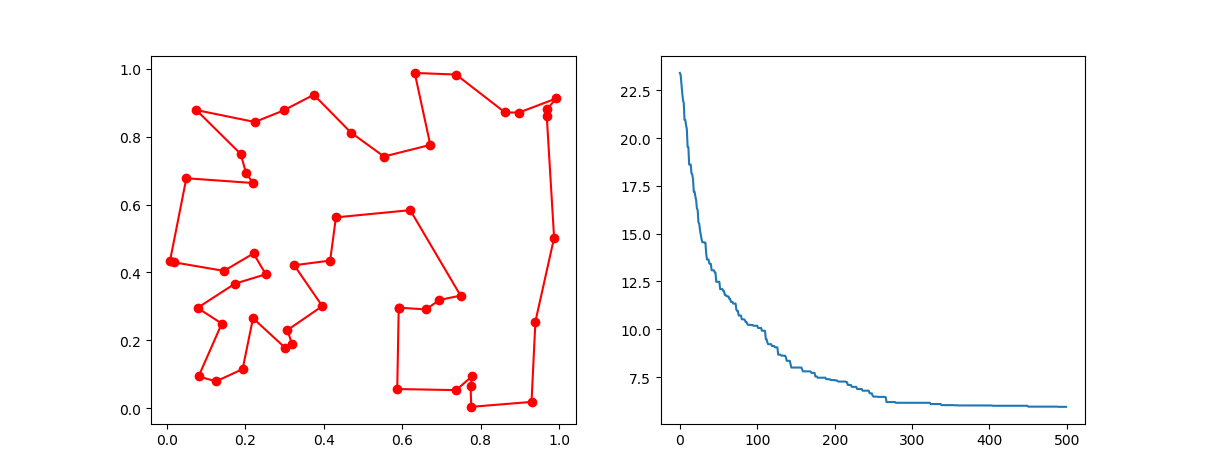
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_points, [best_points[0]]])
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]
ax[0].plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1], 'o-r')
ax[1].plot(ga_tsp.generation_best_Y)
plt.show()
```
## 3. PSO(Particle swarm optimization)
### 3.1 PSO
**Step1**: define your problem:
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_pso.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_pso.py#L1)
```python
def demo_func(x):
x1, x2, x3 = x
return x1 ** 2 + (x2 - 0.05) ** 2 + x3 ** 2
```
**Step2**: do PSO
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_pso.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_pso.py#L6)
```python
from sko.PSO import PSO
pso = PSO(func=demo_func, n_dim=3, pop=40, max_iter=150, lb=[0, -1, 0.5], ub=[1, 1, 1], w=0.8, c1=0.5, c2=0.5)
pso.run()
print('best_x is ', pso.gbest_x, 'best_y is', pso.gbest_y)
```
**Step3**: Plot the result
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_pso.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_pso.py#L13)
```python
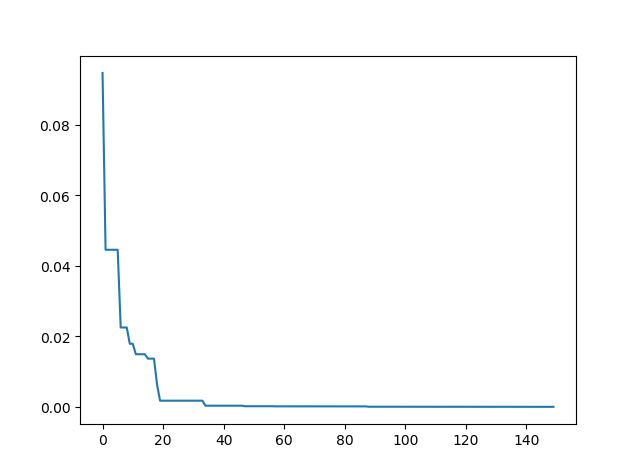
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(pso.gbest_y_hist)
plt.show()
```
### 3.2 PSO with nonlinear constraint
If you need nolinear constraint like `(x[0] - 1) ** 2 + (x[1] - 0) ** 2 - 0.5 ** 2<=0`
Codes are like this:
```python
constraint_ueq = (
lambda x: (x[0] - 1) ** 2 + (x[1] - 0) ** 2 - 0.5 ** 2
,
)
pso = PSO(func=demo_func, n_dim=2, pop=40, max_iter=max_iter, lb=[-2, -2], ub=[2, 2]
, constraint_ueq=constraint_ueq)
```
Note that, you can add more then one nonlinear constraint. Just add it to `constraint_ueq`
More over, we have an animation:
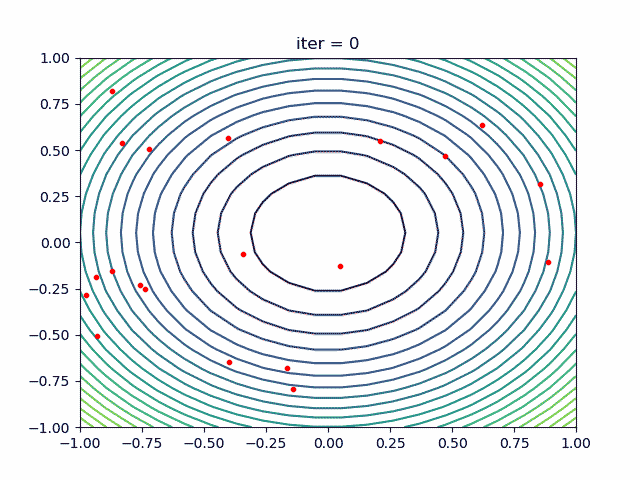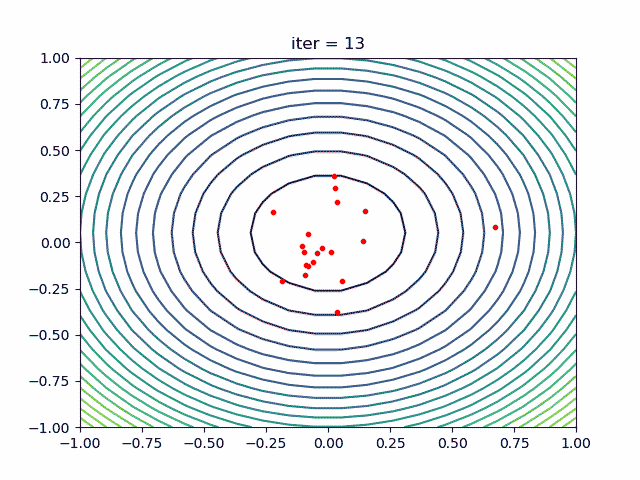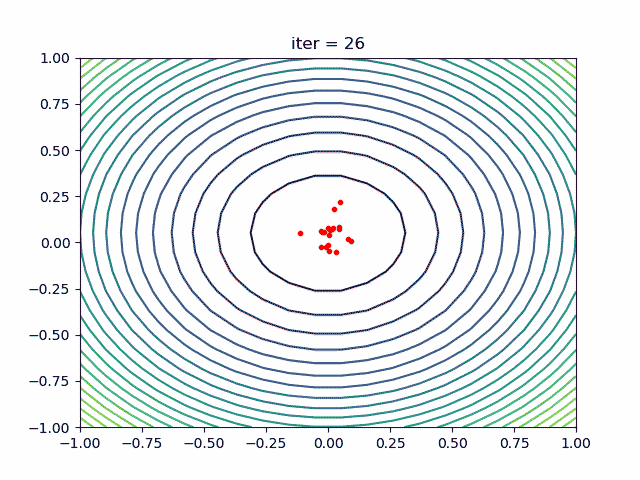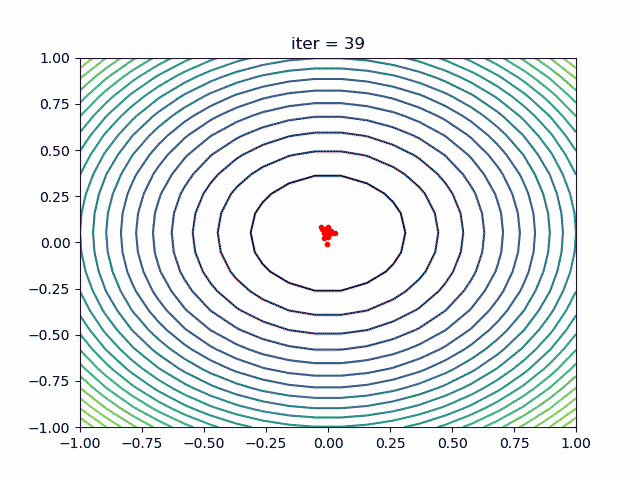
↑**see [examples/demo_pso_ani.py](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_pso_ani.py)**
## 4. SA(Simulated Annealing)
### 4.1 SA for multiple function
**Step1**: define your problem
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_sa.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa.py#L1)
```python
demo_func = lambda x: x[0] ** 2 + (x[1] - 0.05) ** 2 + x[2] ** 2
```
**Step2**: do SA
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_sa.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa.py#L3)
```python
from sko.SA import SA
sa = SA(func=demo_func, x0=[1, 1, 1], T_max=1, T_min=1e-9, L=300, max_stay_counter=150)
best_x, best_y = sa.run()
print('best_x:', best_x, 'best_y', best_y)
```
**Step3**: Plot the result
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_sa.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa.py#L10)
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
plt.plot(pd.DataFrame(sa.best_y_history).cummin(axis=0))
plt.show()
```
Moreover, scikit-opt provide 3 types of Simulated Annealing: Fast, Boltzmann, Cauchy. See [more sa](https://scikit-opt.github.io/scikit-opt/#/en/more_sa)
### 4.2 SA for TSP
**Step1**: oh, yes, define your problems. To boring to copy this step.
**Step2**: DO SA for TSP
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_sa_tsp.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa_tsp.py#L21)
```python
from sko.SA import SA_TSP
sa_tsp = SA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, x0=range(num_points), T_max=100, T_min=1, L=10 * num_points)
best_points, best_distance = sa_tsp.run()
print(best_points, best_distance, cal_total_distance(best_points))
```
**Step3**: plot the result
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_sa_tsp.py#s3](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa_tsp.py#L28)
```python
from matplotlib.ticker import FormatStrFormatter
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 2)
best_points_ = np.concatenate([best_points, [best_points[0]]])
best_points_coordinate = points_coordinate[best_points_, :]
ax[0].plot(sa_tsp.best_y_history)
ax[0].set_xlabel("Iteration")
ax[0].set_ylabel("Distance")
ax[1].plot(best_points_coordinate[:, 0], best_points_coordinate[:, 1],
marker='o', markerfacecolor='b', color='c', linestyle='-')
ax[1].xaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.3f'))
ax[1].yaxis.set_major_formatter(FormatStrFormatter('%.3f'))
ax[1].set_xlabel("Longitude")
ax[1].set_ylabel("Latitude")
plt.show()
```
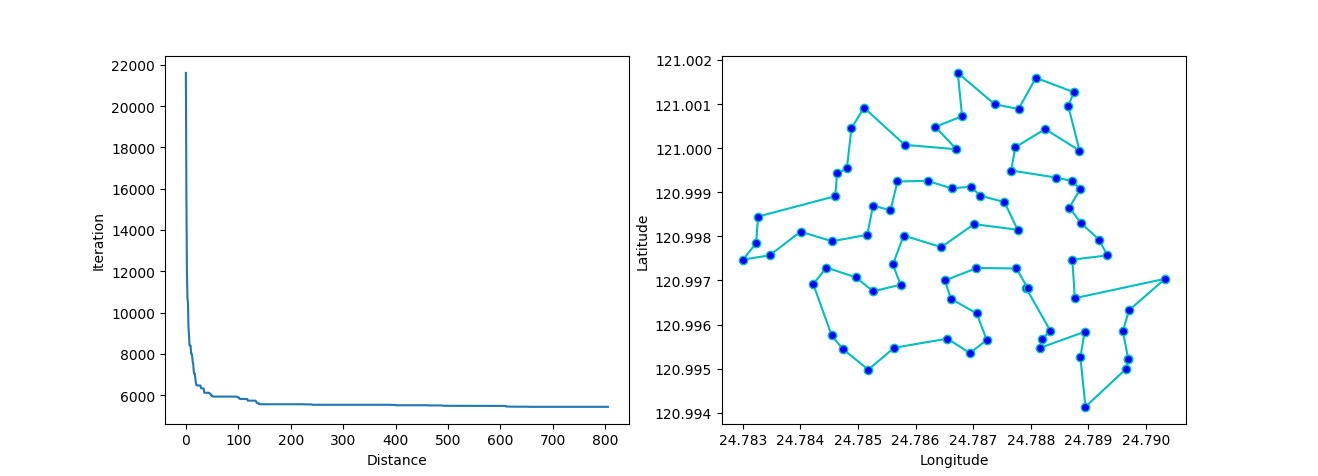
More: Plot the animation:
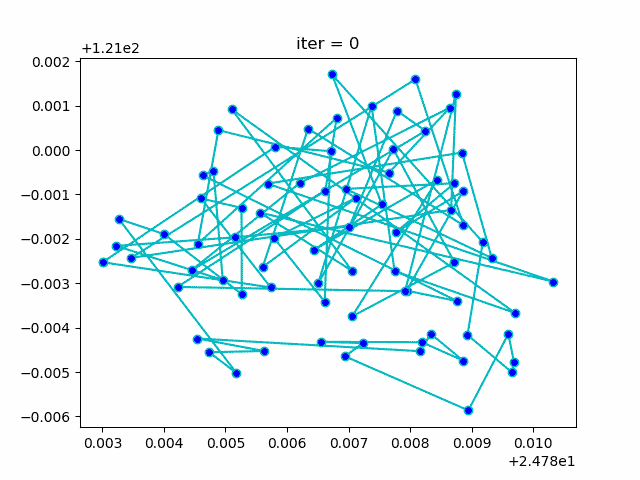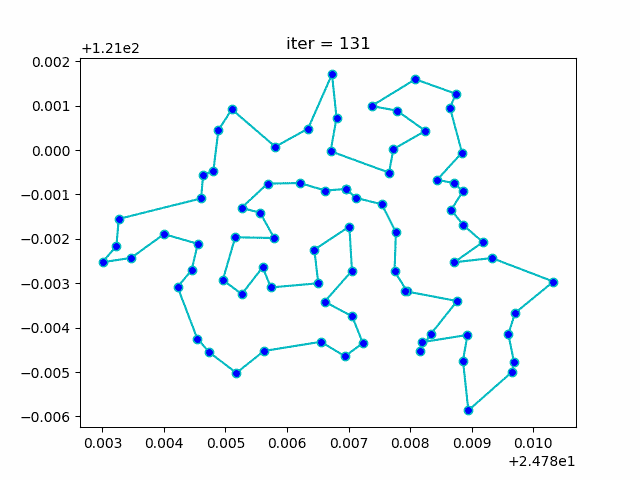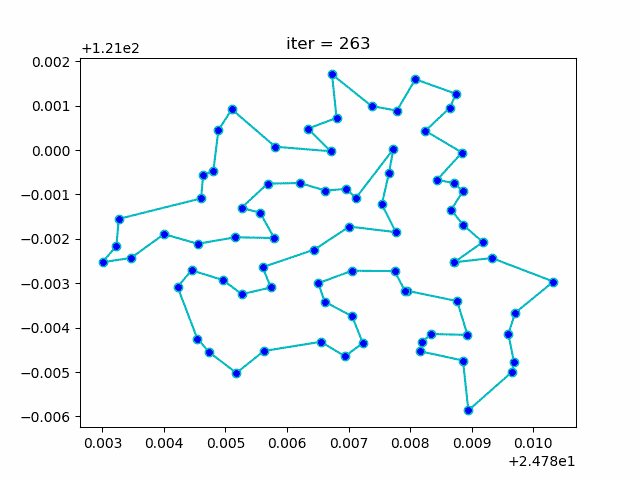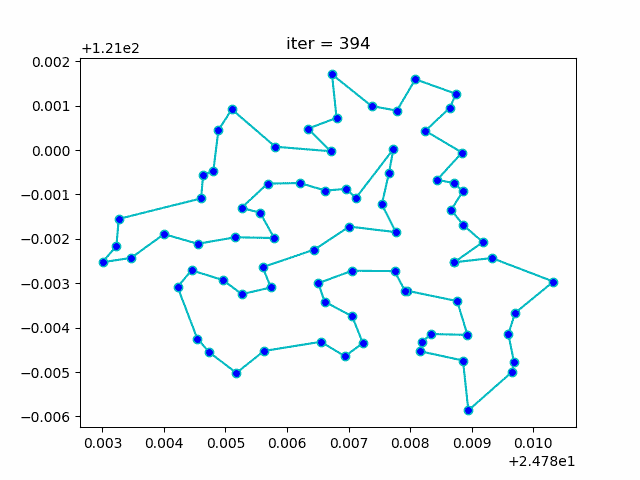
↑**see [examples/demo_sa_tsp.py](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_sa_tsp.py)**
## 5. ACA (Ant Colony Algorithm) for tsp
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_aca_tsp.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_aca_tsp.py#L17)
```python
from sko.ACA import ACA_TSP
aca = ACA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points,
size_pop=50, max_iter=200,
distance_matrix=distance_matrix)
best_x, best_y = aca.run()
```
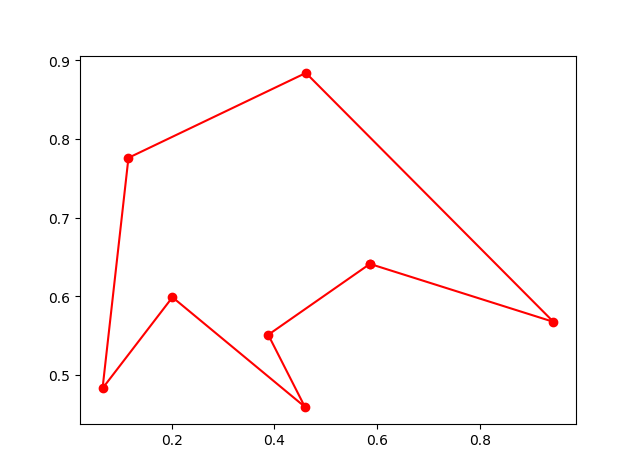
## 6. immune algorithm (IA)
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_ia.py#s2](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_ia.py#L6)
```python
from sko.IA import IA_TSP
ia_tsp = IA_TSP(func=cal_total_distance, n_dim=num_points, size_pop=500, max_iter=800, prob_mut=0.2,
T=0.7, alpha=0.95)
best_points, best_distance = ia_tsp.run()
print('best routine:', best_points, 'best_distance:', best_distance)
```
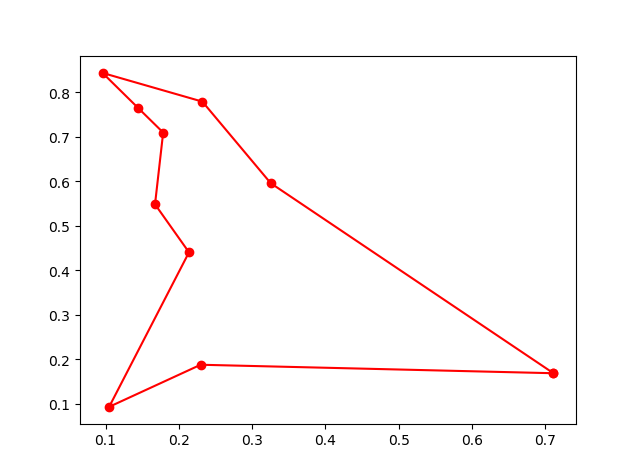
## 7. Artificial Fish Swarm Algorithm (AFSA)
-> Demo code: [examples/demo_afsa.py#s1](https://github.com/guofei9987/scikit-opt/blob/master/examples/demo_afsa.py#L1)
```python
def func(x):
x1, x2 = x
return 1 / x1 ** 2 + x1 ** 2 + 1 / x2 ** 2 + x2 ** 2
from sko.AFSA import AFSA
afsa = AFSA(func, n_dim=2, size_pop=50, max_iter=300,
max_try_num=100, step=0.5, visual=0.3,
q=0.98, delta=0.5)
best_x, best_y = afsa.run()
print(best_x, best_y)
```
# Projects using scikit-opt
- [Yu, J., He, Y., Yan, Q., & Kang, X. (2021). SpecView: Malware Spectrum Visualization Framework With Singular Spectrum Transformation. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 16, 5093-5107.](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9607026/)
- [Zhen, H., Zhai, H., Ma, W., Zhao, L., Weng, Y., Xu, Y., ... & He, X. (2021). Design and tests of reinforcement-learning-based optimal power flow solution generator. Energy Reports.](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352484721012737)
- [Heinrich, K., Zschech, P., Janiesch, C., & Bonin, M. (2021). Process data properties matter: Introducing gated convolutional neural networks (GCNN) and key-value-predict attention networks (KVP) for next event prediction with deep learning. Decision Support Systems, 143, 113494.](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S016792362100004X)
- [Tang, H. K., & Goh, S. K. (2021). A Novel Non-population-based Meta-heuristic Optimizer Inspired by the Philosophy of Yi Jing. arXiv preprint arXiv:2104.08564.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08564)
- [Wu, G., Li, L., Li, X., Chen, Y., Chen, Z., Qiao, B., ... & Xia, L. (2021). Graph embedding based real-time social event matching for EBSNs recommendation. World Wide Web, 1-22.](https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11280-021-00934-y)
- [Pan, X., Zhang, Z., Zhang, H., Wen, Z., Ye, W., Yang, Y., ... & Zhao, X. (2021). A fast and robust mixture gases identification and concentration detection algorithm based on attention mechanism equipped recurrent neural network with double loss function. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 342, 129982.](https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0925400521005517)
- [Castella Balcell, M. (2021). Optimization of the station keeping system for the WindCrete floating offshore wind turbine.](https://upcommons.upc.edu/handle/2117/350262)
- [Zhai, B., Wang, Y., Wang, W., & Wu, B. (2021). Optimal Variable Speed Limit Control Strategy on Freeway Segments under Fog Conditions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.14406.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.14406)
- [Yap, X. H. (2021). Multi-label classification on locally-linear data: Application to chemical toxicity prediction.](https://etd.ohiolink.edu/apexprod/rws_olink/r/1501/10?clear=10&p10_accession_num=wright162901936395651)
- [Gebhard, L. (2021). Expansion Planning of Low-Voltage Grids Using Ant Colony Optimization Ausbauplanung von Niederspannungsnetzen mithilfe eines Ameisenalgorithmus.](https://ad-publications.cs.uni-freiburg.de/theses/Master_Lukas_Gebhard_2021.pdf)
- [Ma, X., Zhou, H., & Li, Z. (2021). Optimal Design for Interdependencies between Hydrogen and Power Systems. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications.](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9585654)
- [de Curso, T. D. C. (2021). Estudo do modelo Johansen-Ledoit-Sornette de bolhas financeiras.](https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/67649721/TCC_Thibor_Final-with-cover-page-v2.pdf?Expires=1639140872&Signature=LDZoVsAGO0mLMlVsQjnzpLlRhLyt5wdIDmBjm1yWog5bsx6apyRE9aHuwfnFnc96uvam573wiHMeV08QlK2vhRcQS1d0buenBT5fwoRuq6PTDoMsXmpBb-lGtu9ETiMb4sBYvcQb-X3C7Hh0Ec1FoJZ040gXJPWdAli3e1TdOcGrnOaBZMgNiYX6aKFIZaaXmiQeV3418~870bH4IOQXOapIE6-23lcOL-32T~FSjsOrENoLUkcosv6UHPourKgsRufAY-C2HBUWP36iJ7CoH0jSTo1e45dVgvqNDvsHz7tmeI~0UPGH-A8MWzQ9h2ElCbCN~UNQ8ycxOa4TUKfpCw__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAJLOHF5GGSLRBV4ZA)
- [Wu, T., Liu, J., Liu, J., Huang, Z., Wu, H., Zhang, C., ... & Zhang, G. (2021). A Novel AI-based Framework for AoI-optimal Trajectory Planning in UAV-assisted Wireless Sensor Networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications.](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9543607)
- [Liu, H., Wen, Z., & Cai, W. (2021, August). FastPSO: Towards Efficient Swarm Intelligence Algorithm on GPUs. In 50th International Conference on Parallel Processing (pp. 1-10).](https://dl.acm.org/doi/abs/10.1145/3472456.3472474)
- [Mahbub, R. (2020). Algorithms and Optimization Techniques for Solving TSP.](https://raiyanmahbub.com/images/Research_Paper.pdf)
- [Li, J., Chen, T., Lim, K., Chen, L., Khan, S. A., Xie, J., & Wang, X. (2019). Deep learning accelerated gold nanocluster synthesis. Advanced Intelligent Systems, 1(3), 1900029.](https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/aisy.201900029)