https://github.com/hantmac/tmax
`tmax` is a powerful tool to help you get terminal cmd directly.
https://github.com/hantmac/tmax
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
`tmax` is a powerful tool to help you get terminal cmd directly.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/hantmac/tmax
- Owner: hantmac
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-12-30T04:18:49.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-04-16T04:20:57.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-26T20:54:53.288Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Go
- Size: 103 KB
- Stars: 40
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
_
| |_ _ __ ___ __ ___ __
| __| '_ ` _ \ / _` \ \/ /
| |_| | | | | | (_| |> <
\__|_| |_| |_|\__,_/_/\_\
### What is `tmax`?
The positioning of `tmax` is a command line tool with a little artificial intelligence.
If you frequently deal with the terminal daily, tmax will greatly improve your work efficiency.
### The design idea of tmax
- Have a local storage as a knowledge base
- Efficient search algorithm and accurate feedback
- Full command line interaction
- Make your very long cmd short
### How tmax works?
#### build tmax
For linux and macos you can install tmax as follows.
Use `make build` and you will get `tmax` in the directory.
``
chmod +x tmax && cp tmax /usr/local/bin
``
### Install tmax
- go get
If you have golang environment, use `go get` to install tmax
```shell script
go get -u github.com/hantmac/tmax
```
- brew install
For mac os, you can use `brew`:
```shell script
brew tap hantmac/tap && brew install --build-from-source tmax
```
- binary file
If you use unix, you can download binary file to use tmax:
```shell script
wget https://github.com/hantmac/tmax/releases/download/v0.1.0/tmax_v0.1.0_linux_x86_64.tar.gz && \
tar -zxvf tmax_v0.1.0_linux_x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/bin && chmod +x /usr/local/bin/tmax
```
#### Before using tmax
Then, you need to `tmax generate` to generate a config file in `$HOME/.tmax.yaml` and the file look like as follows:
```yaml
custom:
check: curl 127.0.0.1:8080/health
k8s:
filternodecpu: kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.status.capacity.cpu}{'\t'}{.status.capacity.memory}{'\n'}{end}"
filternodetaint: kubectl get nodes -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.spec.taints[*].key}{'\n'}{end}"
corednsedit: kubectl edit cm coredns -nkube-system
allnode: kubectl get no
alldeploy: kubectl get deploy
allpod: kubectl get pod -A
busyboxrun: kubectl run busybox --rm -ti --image=busybox /bin/sh
allnodeip: kubectl get node -o=jsonpath="{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{'\t'}{.status.addresses[0].address}{'\n'}{end}"
podResource: kubectl get pod -o custom-columns=NAME:metadata.name,podIP:status.podIP,hostIp:spec.containers[0].resources
getns: kubectl get ns
createdemo: kubectl create deployment nginx --image=nginx
exposedemo: kubectl expose deployment nginx --port=80
getnetwork: kubectl get networkpolicy
runbox: kubectl run busybox --rm -ti --image=busybox /bin/sh
unix:
"tar": "tar -xjvf test.tar.bz2"
```
As you can see, there are many long commands those hard to keep in your mind.
If you want to quickly get a long command, even if you have memorized it, it takes a long time to type it into the console,
not to mention that sometimes you can't remember such a long command.
At this moment, `tmax` appeared, it will solve the problem just mentioned.
### What will tmax bring me?
`tmax` has 3 modes: directly mode, search mode and interactive mode. And `tmax` will make your very long terminal cmd short, improve your operation efficiency.
#### directly mode
If you clearly know the key you want to execute the command, you can use directly mode.
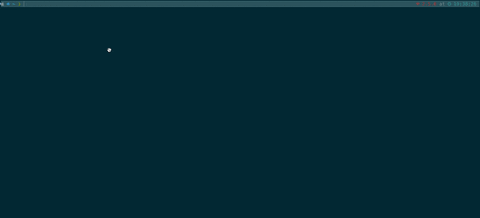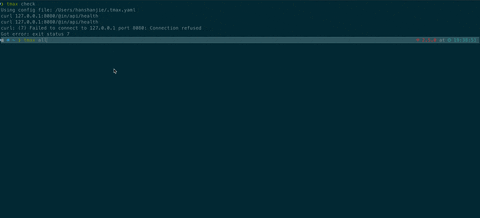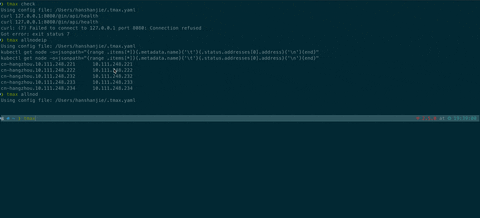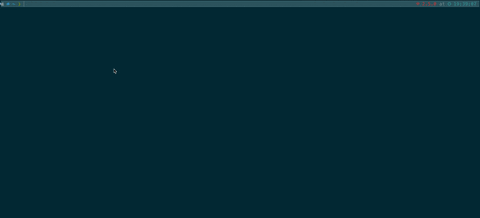
Use 'tmax somekey' , example: `tmax check` will execute `curl 127.0.0.1:8080/health`
##### additional param
First, suppose we define the following short command in the configuration file `~/.tmax.yaml`:

Now I want to see the simple information of a certain pod, just execute:
```shell script
tmax getpod myapp-deploy
```
`myapp-deploy` is a custom parameter, you can even add parameters later:
```shell script
tmax getpod myapp-deploy -n YOUR_NAMESPACE
```

You can freely customize your own tmax configuration file according to the required custom parameters.
##### template parameter
You should notice that custom parameters can only be appended after the `tmax` command.
If you want to add a variable parameter in the middle, you can't use it.
For example, if you want to make a taint for a k8s node, and this taint is commonly used by your company,
you must execute `kubectl taint node node-1.1.1.1 reserved=mynode:NoSchedule`,
and the name of the node will become a variable The parameters and the taint name are fixed, so the good way is to enter the node name to complete the command.
Don't panic, `tmax` supports template parameters. For the above command we can add in `~/.tmax.yaml`:
```shell script
taintnode: kubectl taint node {{.n}} reserved=cd-staging:NoSchedule
```
Just execute the following content to complete the `taint` command:
```shell script
tmax taintnode -n YOUR_NODE_NAME
```
or you have an `exec` cmd like:
```shell script
exec: kubectl exec -it {{.p}} -- sh
```
Just execute the following cmd to exec into a pod:
```shell script
tmax exec -p YOUR_POD_NAME
```
#### search mode
If you know the general content of the command you want to execute,
you can use the search mode to find and execute it.
Use `tmax s CONTENTOFCMD`, example: `tmax s pod` or `tmax search pod`.

#### interactive search mode
If you don't want to search, tmax has interactive mode.
Just type `tmax` and `enter` to interactive mode.

### Support
[]( https://www.jetbrains.com/?from=tmax)