Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/hash3liZer/Subrake
🚀 A DNS automated scanner and tool 🖱️ (Zone Transfer, DNS Zone Takeover, Subdomain Takeover).
https://github.com/hash3liZer/Subrake
bugbountytips dns-takeover reconnaissance subdomain-bruteforcing subdomain-enumeration subdomain-scanner subdomain-takeover zone-takeover zone-transfers
Last synced: about 5 hours ago
JSON representation
🚀 A DNS automated scanner and tool 🖱️ (Zone Transfer, DNS Zone Takeover, Subdomain Takeover).
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/hash3liZer/Subrake
- Owner: hash3liZer
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2018-10-21T07:31:12.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-21T21:49:24.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-22T02:19:49.811Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: bugbountytips, dns-takeover, reconnaissance, subdomain-bruteforcing, subdomain-enumeration, subdomain-scanner, subdomain-takeover, zone-takeover, zone-transfers
- Language: CSS
- Homepage: https://bit.ly/44onNOL
- Size: 1020 KB
- Stars: 275
- Watchers: 14
- Forks: 63
- Open Issues: 9
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

Subrake 🦅
A DNS automated scanner and tool (Zone Transfer, DNS Zone Takeover, Subdomain Takeover).
# Background 📈
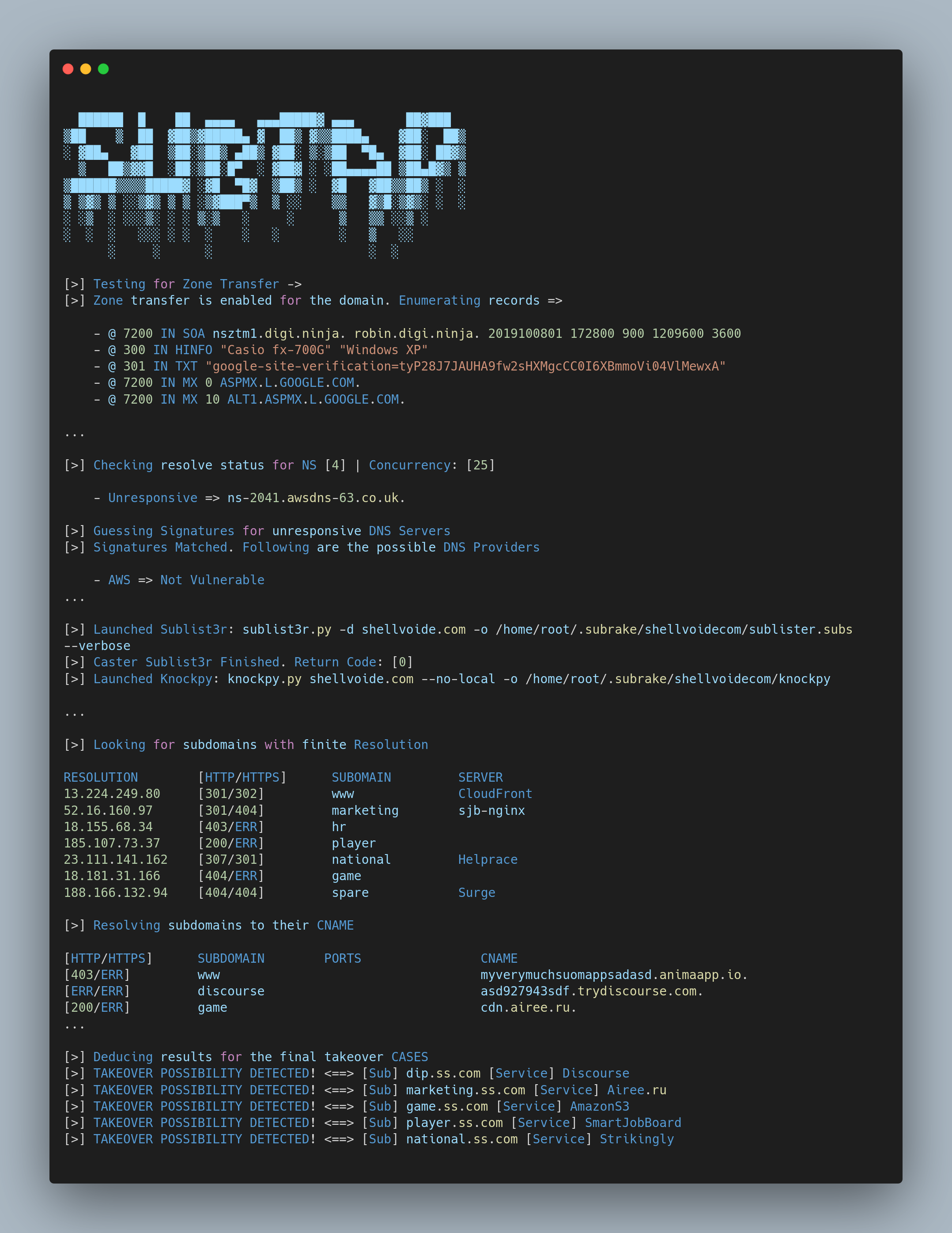
Subrake, initially started as a personal project of mine for subdomain enumeration is a now a detailed DNS scanning tool that can help you identify **Zone Transfers**, **DNS Zone Takeover** and **Subdomain Takeovers** all in a single go.
Zone Transfers have been there for years now and if enabled for some reason on a domain can allow another party to `enumerate` all the records from the Zone. They are actually used when the owner is to tranfer domain from one provider to another.
Subdomain Takeover unlike it sounds is the **takeover of the service** that the subdomain is pointing to. The service needs to be stale or not in use.
DNS Zone Takeover as compared to Subdomain Takeover can be more severe if exploited. It is the takeover of one of the zones of the domain. This allows much more than just creating the service on the backend. You can actually setup your own DNS records and play with them as you line
For more in-depth detail, you can read my blog here: [A Guide to Zone Transfer, DNS Zone Takeover and Subdomain Takeover](https://blog.shameerkashif.me/blog/2023/subrake-a-dns-automated-scanner/)
# About Subrake 💰
Subrake is DNS Assessment tool (mostly automated) with both a UI and CLI goes trough various phases in order to cover DNS issues. The tool is continuously undergoing changes and development and everybody is welcome to contribute to the project.
It was designed primarily for bug bounty and infosec industry but can be leveraged for blue teaming and internal pentests as well. It supports both a CLI and Web Based GUI Interface and supports multiple installation modes. The key features are:
### Features ⚖️
* ⚙️ All in one automated solution. Its working cycle is:
* 🪙 DNS Enumeration (DNS Records)
* 🪜 **Zone Transfer Detection** and enumerate records if enabled
* 💲 **DNS Zone Takeover Detection**
* 💴 False Positive Detection (Wildcard subdomains)
* 💶 Getting results from other tools (Sublist3r, Knock.py)
* 💷 Bruteforce using wordlists (Can work with multiple wordlists)
* 💵 Get 5 parameters for each subdomain (HTTP Codes, Resolution, Headers, CNAME, Ports)
* 💰 **Detect Subdomain Takeover**
* 🛒 Support for external tools. You can add your own functions.
* 🛍️ Automated and Manual Mode.
* 🗄️ Can run concurrent sessions.
* 🖼️ UI for Reports and results available in `csv` format.
* 🛎️ Flexible and Fast.
## Execution
[Subrake Execution](https://github.com/hash3liZer/Subrake/assets/29171692/994d8f80-efad-49ab-bcc4-69a9ac04c05a)
# Installation 💾
You can setup subrake by an automated mode or by manually cloning the repo and install through `setuptools`. The first provides more control and is flexible with a UI. But if you prefer a simple CLI mode or on `windows`, go through the `manual` section.
Clone the repo and jump into it:
```bash
$ git clone https://github.com/hash3liZer/Subrake.git
$ cd ./Subrake
```
## Automated Setup 🛠️
You can setup `subrake` through vagrant (with KVM) where a machine will be spawned and everything will be automatically setup. Install the requirements first:
```python
$ apt update
$ apt install -y qemu qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon libvirt-clients bridge-utils virt-manager vagrant vagrant-libvirt
```
Then inside the repo, run `vagrant` up:
```python
$ vagrant up
```
This will take a while to provision the server. After done, you will receive the URL: `http://127.0.0.1:9090`
The default credentials are: `subrake/password`. You can change them during provisioning as well:
```python
$ SUBRAKE_USERNAME="username" SUBRAKE_PASSWORD="password" vagrant up
```
After done, you can manage the state of your newly created machine through these commands:
```python
# See the machine status
$ vagrant status
# Suspend the machine
$ vagrant suspend
# Resume machine
$ vagrant resume
# Shutdown machine
$ vagrant halt
# Start back
$ vagrant up
# Delete the machine
$ vagrant destroy
```
## Manual Setup 🪛
With the manual setup, you can directly jump into directory and the `setuptools` for installation
Install the requirements and run `setup.py`:
```bash
$ pip3 install -r requirements.txt
$ python3 setup.py install
```
Verify if subrake is installed or not:
```bash
subrake --help
```
## Docker 🐳
You can also build the docker image from `Dockerfile`:
```bash
$ docker build -t subrake:latest .
```
Verify the docker container:
```bash
$ docker run --rm subrake --help
```
# Deployment 🚩
You can deploy the script on a baremetal server as well. To do so, get a fresh `ubuntu 20.04` server up and running and run the following command:
```python
$ chmod +x ./installer.sh
$ ./installer.sh --deploy
```
The server is then accessible at: `0.0.0.0:9090`. You can setup an `nginx` service and use it s a reverse proxy.
# Usage 💬
## User Interface 🔳
With the UI, you can directly jump to the `Subtap a Domain` page and run a scan. Expect a couple questions for the scan:
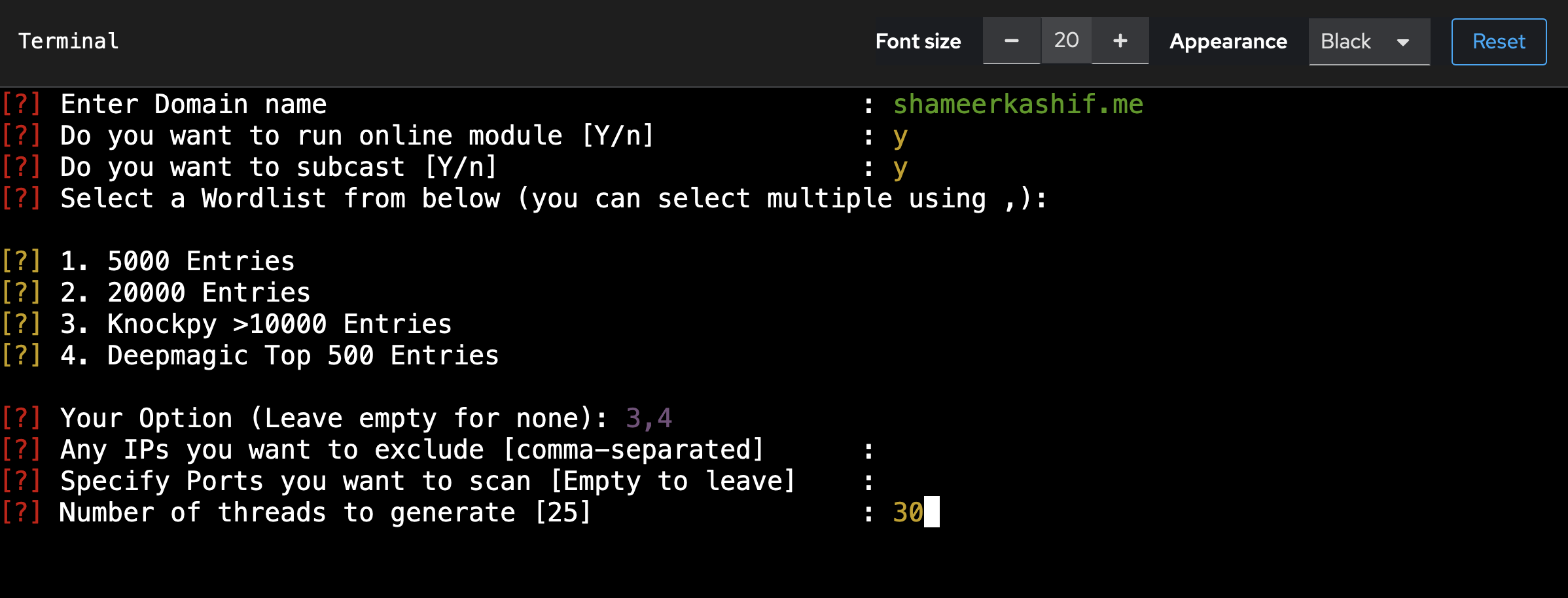
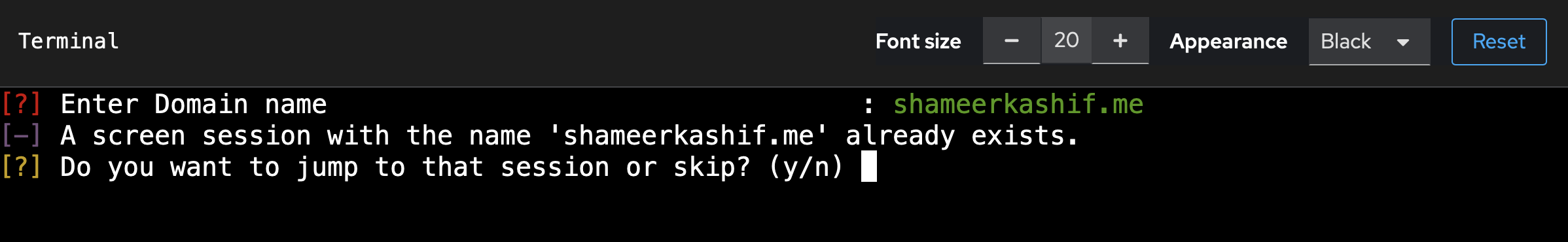
The scan is launched inside a `tmux` session. You can press `CTRL+E => d` to exit the running screen and launch a new scan. Also, to pause the screen and move up and down, you can press `CTRL+E => [`. Its just TMUX shortcuts with the global bind key changed to `CTRL+E`.
You can also jump back to a running screen by entering its name again:
### Reports
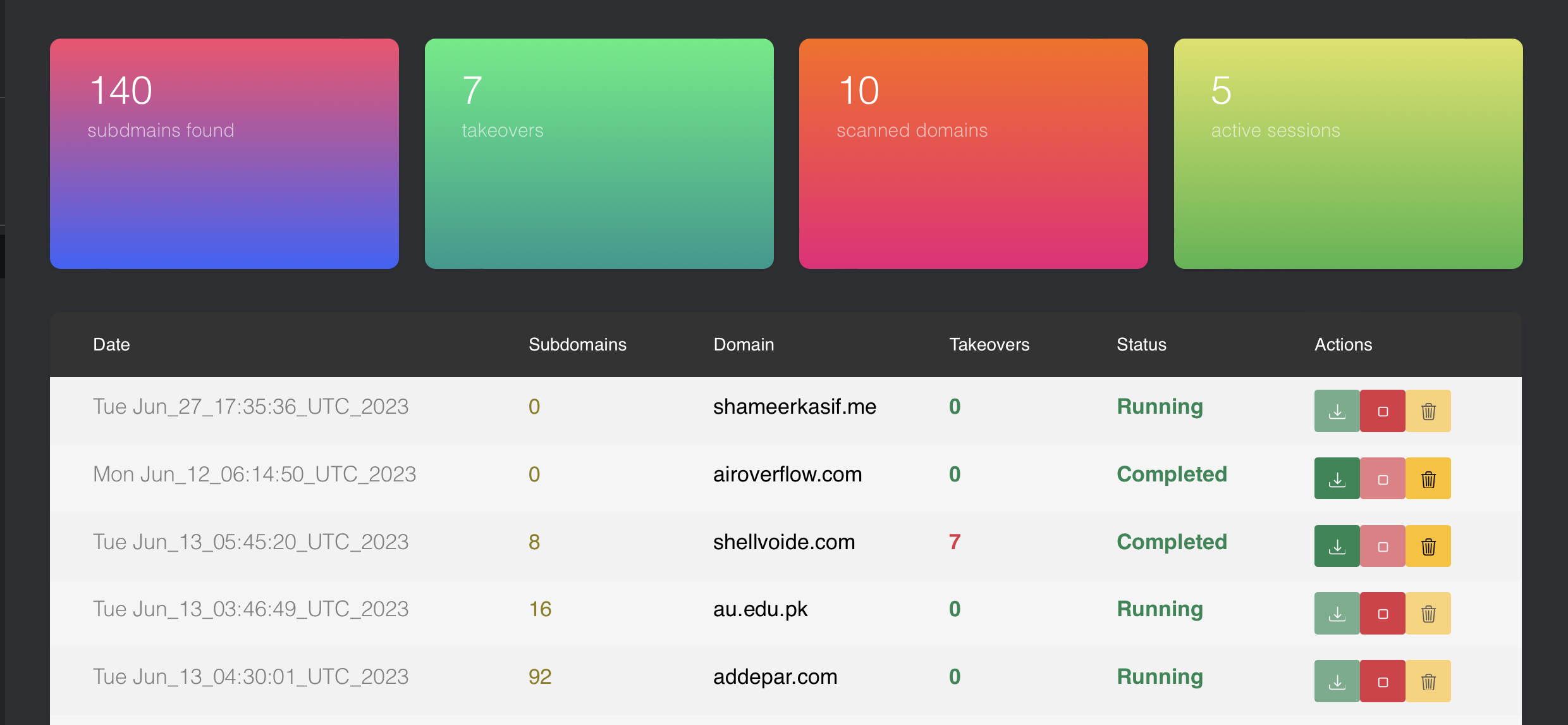
### Scan Results
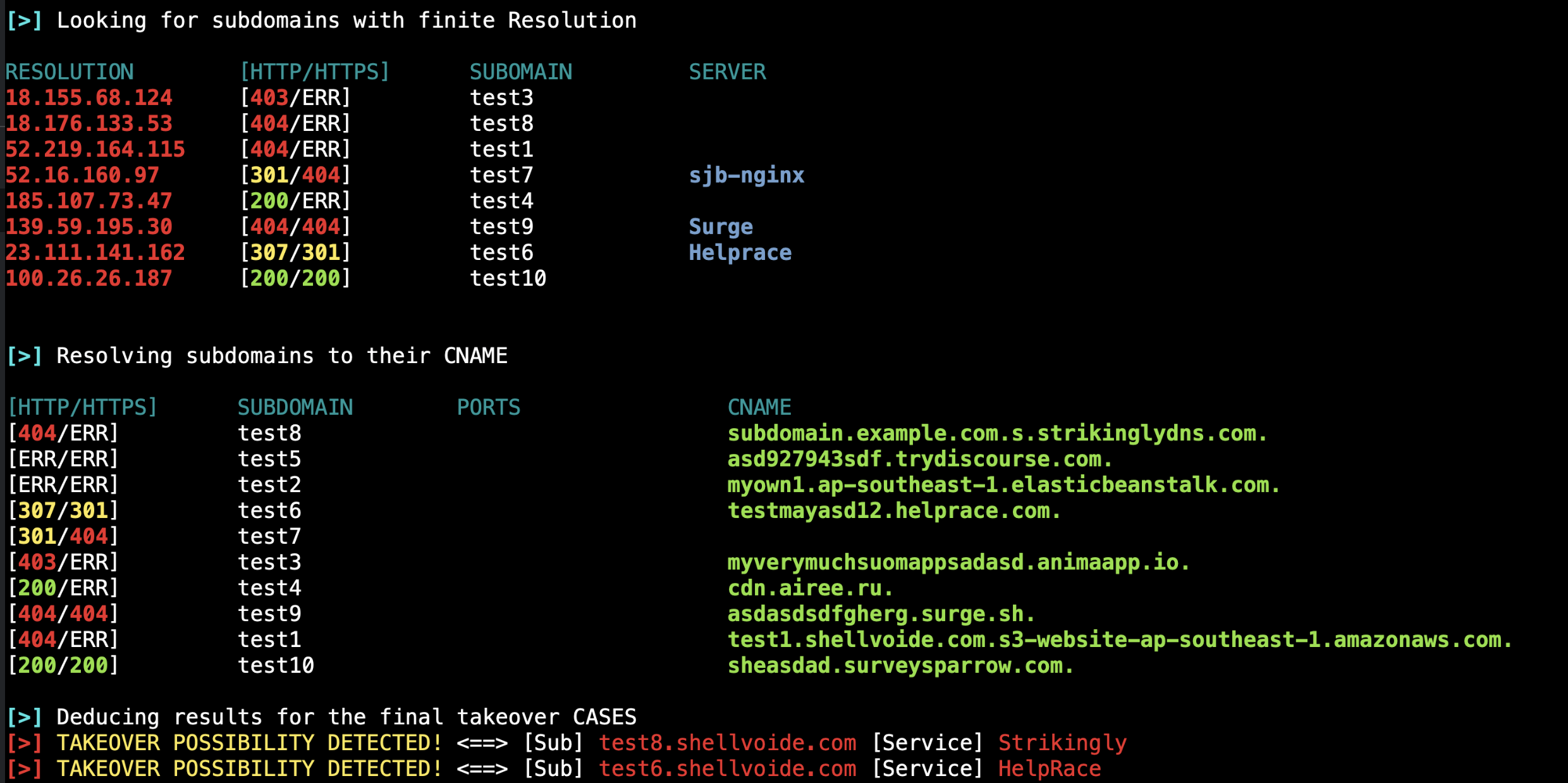
## Command line 🟰
On command line, you an directly access the tool by typing `subrake`. Here are a couple example of using subrake:
A simple run with default options:
```python
$ subrake -d google.com
```
Subrake with Multiple Threads:
```python
$ subtake -d google.com -t 50
```
Subrake with modules and a wordlist:
```python
$ subrake -d google.com --wordlists SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt
```
Subrake with OSINT results + Multiple SecLists subdomains list:
**Note: Subdomains with similar names will automatically be filtered and counted as 1**
```python
$ subrake -d google.com --wordlists SecLists/Discovery/DNS/namelist.txt,SecLists/Discovery/DNS/dns-Jhaddix.txt
```
Subrake without search engine + Output from multiple tools combined + IP Filtering (Note that you can integrate your tools into subrake):
```python
$ domain="google.com"
$ subfinder -d $domain -nW -o $domain/1.txt && sublist3r -d $domain -o $domain/2.txt && cat $domain/* >> /tmp/output.txt
$ subrake -d $domain -w tmp/output.txt --filter --skip-search
```
Subrake with Port Scanning:
**NOTE: The port 80,443 will be scanned by default for every host under HTTP/HTTPS banner. So, there's no need to specify them here**
```python
$ subrake -d google.com --ports 8080,8443,8000,23,445
```
## Manual 📑
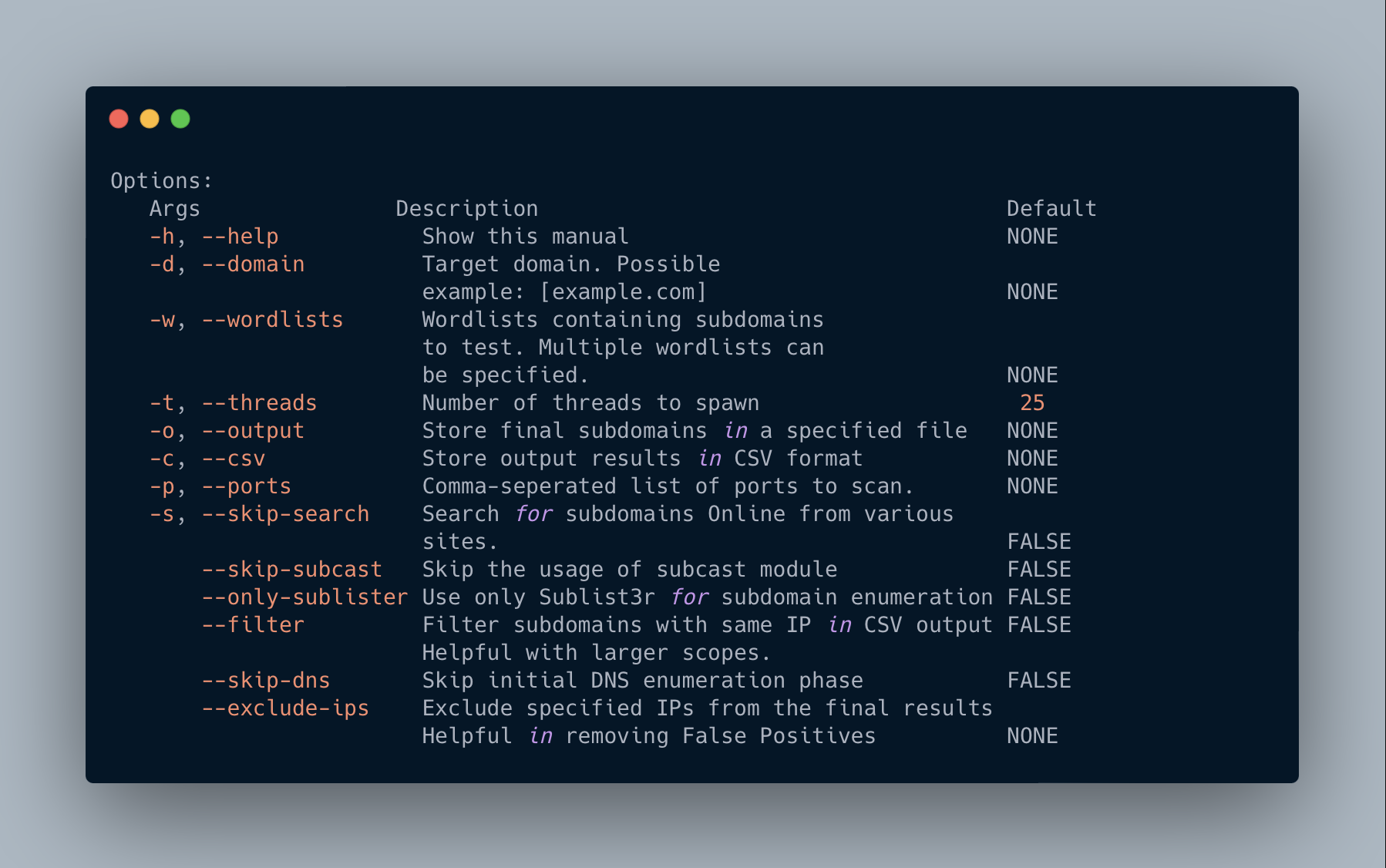
# ToDo LIST 📜
Feel free to open pull requests and a feature. You can contribute by:
- [ ] Add more vulnerable services. Currently 10
- [ ] Improve Insatllation script.
- [x] Add GUI Mode
- [x] Add Docker support.
## Get me at ☎️
* Email: [email protected]
* Discord: hash3liZer#5786
* Blog: https://blog.shameerkashif.me


