Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/hashlag/neighbours
Weighted kNN classifier and Nadaraya-Watson kernel regressor implementation based on random projection forest
https://github.com/hashlag/neighbours
knn machine-learning
Last synced: 3 days ago
JSON representation
Weighted kNN classifier and Nadaraya-Watson kernel regressor implementation based on random projection forest
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/hashlag/neighbours
- Owner: hashlag
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-01-28T11:23:55.000Z (10 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-02-06T18:19:25.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-02-07T18:56:15.324Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: knn, machine-learning
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 77.1 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Neighbours
Weighted kNN classifier and Nadaraya-Watson kernel regressor implementation based on random projection forest.
### Classifier description
This project implements weighted kNN classifier with kernel smoothing.
Built-in smoothing kernels:
* rectangular
* gaussian
* epanechnikov
Built-in distance metrics:
* euclidean
* manhattan
Custom distance metrics and smoothing kernels are supported.
Demo: `demo/classifier_demo.py`
### Regressor description
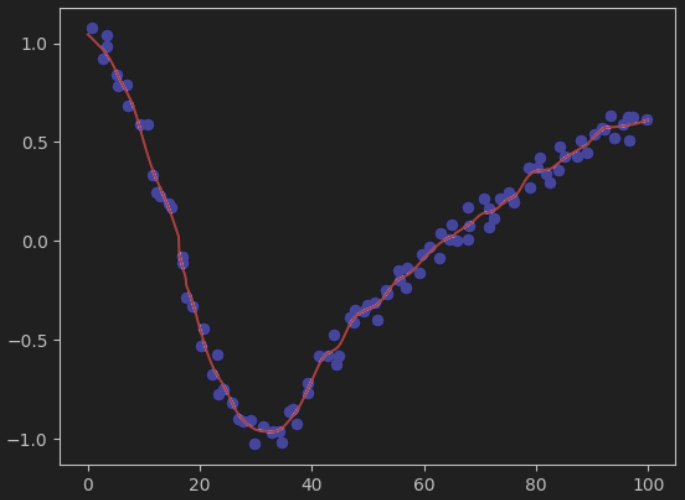
Nadaraya-Watson kernel regressor is implemented.
Demo: `demo/regressor_demo.py`
### Neighbors search algorithm
Random projection forest is used to search for neighbours.
RP trees are built by recursive binary splits of space by selected hyperplanes.
On each step algorithm chooses two random objects from the train set
and calculates a hyperplane symmetrically separating these two objects in feature space.
Such hyperplanes become splitting nodes of an RP tree.
Each resulting subset is split again if it contains more than `m` (hyperparameter) objects.
Hyperplane in each splitting node is represented with an equation of the form
w · x + b = 0, where w is a vector normal to the hyperplane and b is an offset.
For simplicity, we assume what points may be located either "to the right"
or "to the left" of the hyperplane.
We also define points belonging to a hyperplane as located "to the left."
So for any point x we can clearly determine its location:
```
w · x + b > 0 point x is located "to the right"
w · x + b ≤ 0 point x is located "to the left"
```
Since nodes are organized into a tree, we can perform search by evaluating the expression and proceeding to the corresponding child node.
### Installation
```shell
pip install git+https://github.com/hashlag/neighbours.git
```
### Usage
Import the package, for example, as
```python
import neighbours as ns
```
Now you can use the classifier
```python
import numpy as np
# KNNClassifier(features, classes_count, trees_count, maximum number of samples in one leaf of an RP tree)
classifier = ns.KNNClassifier(2, 3, 10, 7)
train = np.array([[2, 1], [10, 15], [1, 3] ...])
class_labels = np.array([0, 1, 0 ...])
# load samples into classifier and build an RP forest
classifier.load(train, class_labels)
# target object representation
sample = np.array([1, 1])
# specify distance metric, smoothing kernel, window width and obtain a prediction
prediction = classifier.predict(sample, ns.distance.euclidean, ns.kernel.gaussian, 1)
print(prediction)
```
### Dependencies
The only third-party dependency is `numpy`.
### License
This project is licensed under [the MIT License](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/hashlag/neighbours/main/LICENSE).