https://github.com/hughobrien/wlan-stats
Tool chain using tshark to pull data from pcaps, further process them in python, and graph the output in R.
https://github.com/hughobrien/wlan-stats
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Tool chain using tshark to pull data from pcaps, further process them in python, and graph the output in R.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/hughobrien/wlan-stats
- Owner: hughobrien
- License: mit
- Created: 2014-05-26T04:54:53.000Z (about 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2014-05-26T05:01:08.000Z (about 11 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-17T10:39:52.292Z (7 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 156 KB
- Stars: 2
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-network-stuff - **0**星
README
wlan-stats
==========
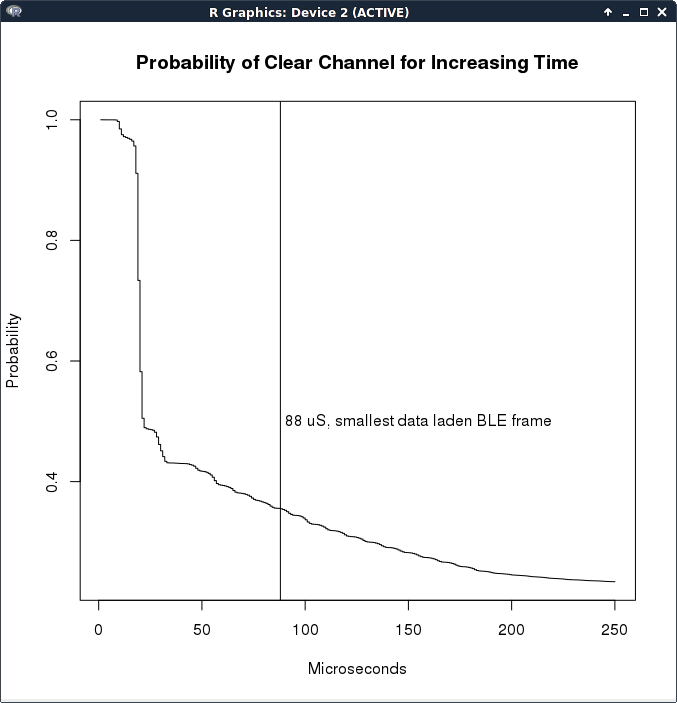
Research tool to tie together [Wireshark](https://www.wireshark.org/) and [R](http://www.r-project.org/) to do some complex inter-frame analysis. Specifically the channel idle time between successively received WLAN frames via [radiotap](http://www.radiotap.org/) extensions.
Operation
--------
[tshark](https://www.wireshark.org/docs/man-pages/tshark.html) is used to process a given pcap file and output selected fields into [CSV](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comma-separated_values) format (compressed).
These fields are defined in 'do-proc.sh'.
The python script 'proc.py' then reads the CSV and determines additional information only available by comparing two successive frames. e.g. given that radiotap supplies the start time (as claimed by the device) of the MAC section of each received WLAN frame, the channel idle time between two successive frames can be calculated:
To find time between the packets, given start time of MAC1 and MAC2
...[PHY1|MAC1]...[PHY2|MAC2]...
idle_time = start of MAC2 - start of MAC1 - length of MAC1 - length of PHY2
For this, the encoding of the frame preamble and MAC sections (which differ) for all combinatorially possible IEEE 802.11g variants must be calculated, stored, and then compared to the calculated value of the next successive frame to determine the idle time.
These idle times, along with other aggregate data such as modulation distribution, are emitted as CSV.
Finally 'gen-diags.py' uses basic looping to drive the generation of a variety of R scripts, which render graphs of the processed data.
Usage
-----
Once the fields extracted by tshark in 'do-proc.sh' match those expected by 'proc.py' usage is simply:
./do-proc.sh pcapfile
as 'do-proc.sh' handlese piping the data from tsark to python to the final csv.
To generate the graphs:
python gen_diags.py | R -q --vanilla
Demo
----