https://github.com/identiops/terraform-hcloud-k3s
Private k3s Kubernetes Terraform installer for Hetzner Cloud
https://github.com/identiops/terraform-hcloud-k3s
cloud hetzner k3s k8s kubernetes kubernetes-cluster terraform terraform-module
Last synced: 2 days ago
JSON representation
Private k3s Kubernetes Terraform installer for Hetzner Cloud
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/identiops/terraform-hcloud-k3s
- Owner: identiops
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-07-19T15:32:27.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-08-13T07:24:35.000Z (about 2 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-13T09:21:41.482Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: cloud, hetzner, k3s, k8s, kubernetes, kubernetes-cluster, terraform, terraform-module
- Language: HCL
- Homepage: https://identiops.com/projects/k3s
- Size: 3.7 MB
- Stars: 111
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 11
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-hcloud - terraform-hcloud-k3s
README
- 
- [](https://github.com/identiops/terraform-hcloud-k3s)
- terraform-hcloud-k3s is an [identiops.com project](https://identiops.com)
# Private k3s Kubernetes Terraform installer for Hetzner Cloud
This Terraform module creates a Kubernetes Cluster on
[Hetzner Cloud](https://console.hetzner.cloud/) infrastructure running Ubuntu
24.04. The module aims to be simple to use while providing an out-of-the-box
secure and maintainable setup. Thanks to Ubuntu's LTS version we get up to 5
years of peace and quiet before having to upgrade the cluster's operating
system!
Module published at:
- Terraform registry:
- OpenTofu registry:
What changed in the latest version? See
[CHANGELOG.md](https://github.com/identiops/terraform-hcloud-k3s/tree/main/CHANGELOG.md).
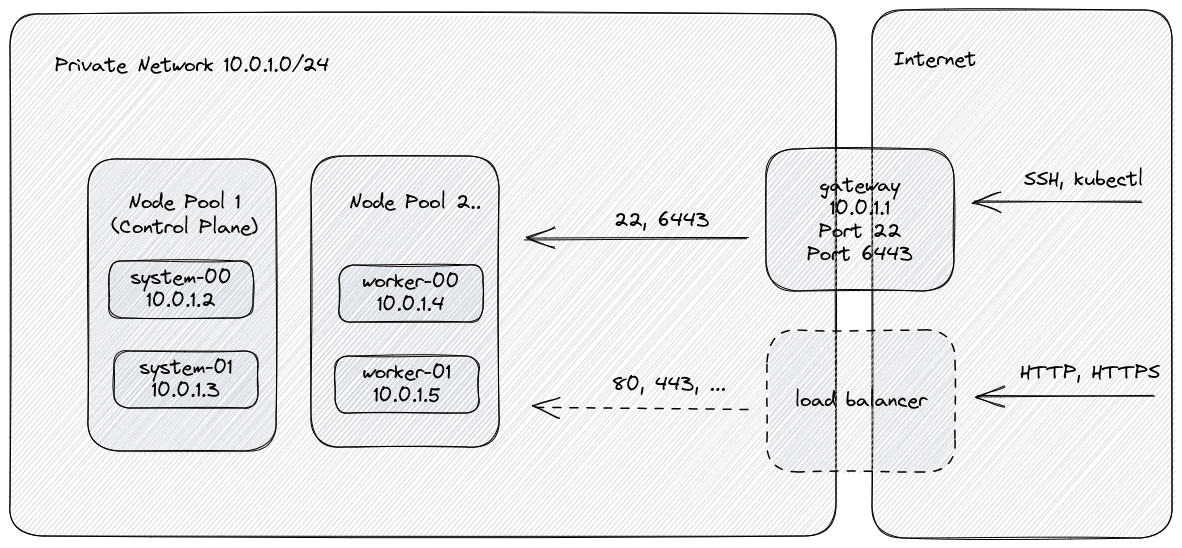
## Features
- [k3s](https://k3s.io/) based Kubernetes cluster.
- Node pools for managing cluster resources efficiently. Pools can be added,
resized, and removed at any time.
- Automated Kubernetes update management via
[System Upgrade Controller](https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller).
- Automated operating system updates with automatic system reboots via
[kured](https://kured.dev).
- [Embedded container registry mirror](https://docs.k3s.io/installation/registry-mirror)
for fast pod startup times across nodes.
- [Private registry configuration](https://docs.k3s.io/installation/private-registry?_highlight=registries#configs)
to avoid manual configuration of
[pull secrets](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/).
- Creation of placement groups for to improve availability.
- Multi-region deployments.
- Secured default configuration:
- Deletion protection for all cloud resources.
- SSH key required for remote access.
- fail2ban limits SSH brute force attacks.
- Cluster nodes have no public network interface.
- Internal firewall active on all nodes for minimal exposure.
- Support for network policies via [Cilium](https://www.cilium.io/).
- [CSI hardening guide](https://docs.k3s.io/security/hardening-guide) applied:
- Kernel parameters defined.
- Audit log directory created.
- Network policies, pod security policies, admission policies and the
enabling of audit logs are up to the administrator of the cluster to
configure.
- Integration of Hetzner Cloud Controller Manager for managing cloud resources
from the within the cluster.
- Integration of Hetzner Cloud Storage Interface for managing volumes from the
within the cluster.
- Ansible integration with automatically generated inventory.
- Convenience scripts for retrieving the Kubernetes configuration and accessing
nodes via SSH and SCP.
- Calculation of monthly costs for every part of the deployment (see
`terraform output`).
- Documentation of common administrative tasks and troubleshooting approaches.
### To be added
- OIDC support for user authentication. Some configuration is in place, but it
hasn't been tested, yet.
- Support for [cluster auto scaler](https://github.com/kubernetes/autoscaler).
## Contents
1. [Getting Started](#getting-started)
1. [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
2. [Recommended Tools](#recommended-tools)
3. [Installation](#installation)
4. [Usage](#usage)
2. [Configuration](#configuration)
1. [Store terraform state in S3 bucket](#store-terraform-state-in-s3-bucket)
2. [Enable etcd backup to S3](#enable-etcd-backup-to-s3)
3. [OpenID Connect (OIDC) Authentication](#openid-connect-oidc-authentication)
4. [Persistent Volume Encryption](#persistent-volume-encryption)
5. [Adjust Sysctl Parameters](#adjust-sysctl-parameters)
6. [Private Registry Access](#private-registry-access)
3. [Maintenance](#maintenance)
1. [Access Kubernetes API via Port-Forwarding from Gateway](#access-kubernetes-api-via-port-forwarding-from-gateway)
2. [Ansible: Execute Commands on Nodes](#ansible-execute-commands-on-nodes)
3. [Add Ingress Controller and Load Balancer](#add-ingress-controller-and-load-balancer)
4. [Add Nodes or Node Pools](#add-nodes-or-node-pools)
5. [Remove Nodes or Node Pools](#remove-nodes-or-node-pools)
6. [Stop Automated Node Reboots](#stop-automated-node-reboots)
7. [Upgrade Operating System](#upgrade-operating-system)
1. [Gateway Node](#gateway-node)
2. [Node Pools](#node-pools)
8. [Update Kubernetes](#update-kubernetes)
9. [Update Cilium](#update-cilium)
10. [Update Hetzner Cloud Controller Manager (CCM)](#update-hetzner-cloud-controller-manager-ccm)
11. [Update Hetzner Cloud Storage Interface (CSI)](#update-hetzner-cloud-storage-interface-csi)
12. [Update Kured](#update-kured)
13. [Update Metrics Server](#update-metrics-server)
14. [Update System Upgrade Controller](#update-system-upgrade-controller)
4. [Deletion](#deletion)
5. [Troubleshooting](#troubleshooting)
1. [Gateway](#gateway)
1. [Verify packet masquerading is set up properly](#verify-packet-masquerading-is-set-up-properly)
2. [Verify firewall is set up properly](#verify-firewall-is-set-up-properly)
2. [Nodes](#nodes)
1. [Inspect local firewall settings](#inspect-local-firewall-settings)
2. [Verify correctness of date/timezone and locale](#verify-correctness-of-datetimezone-and-locale)
3. [Inspect cloud-init logs](#inspect-cloud-init-logs)
3. [Cluster](#cluster)
1. [Verify default route](#verify-default-route)
2. [Verify connectivity to the Internet](#verify-connectivity-to-the-internet)
3. [Verify name resolution](#verify-name-resolution)
4. [Verify cluster status](#verify-cluster-status)
5. [Verify Cilium Networking Status](#verify-cilium-networking-status)
6. [Verify k3s Cluster Configuration](#verify-k3s-cluster-configuration)
7. [Inspect cluster status and logs](#inspect-cluster-status-and-logs)
6. [Related Documentation](#related-documentation)
7. [Similar Projects](#similar-projects)
8. [Special Thanks](#special-thanks)
## Getting Started
### Prerequisites
WARNING: Apple Silicon is apparently not supported by important terraform
modules, see .
- [Terraform](https://terraform.io) or [OpenTofu](https://opentofu.org/). Note
that you'll need Terraform v1.0 or newer to run this project.
- `bash` for executing the generated scripts.
- `jq` for executing the generated scripts.
- `kubectl` for interacting with the Kubernetes cluster.
- `ssh` for connecting to cluster nodes.
### Recommended Tools
- [Ansible cli](https://www.ansible.com/) for executing commands simultaneously
on multiple cluster nodes.
- [Cilium cli](https://github.com/cilium/cilium-cli) for verifying and
interacting with the Kubernetes networking layer.
- [Helm cli](https://helm.sh/) for installing and updating components inside the
cluster.
### Installation
1. Create a Hetzner Cloud API token.
- Register with [Hetzner Cloud](https://console.hetzner.cloud).
- Create a new project.
- Navigate to the security settings.
- Select the "API tokens" tab and add a new token with **read & write**
access and a second token with just **read** access.
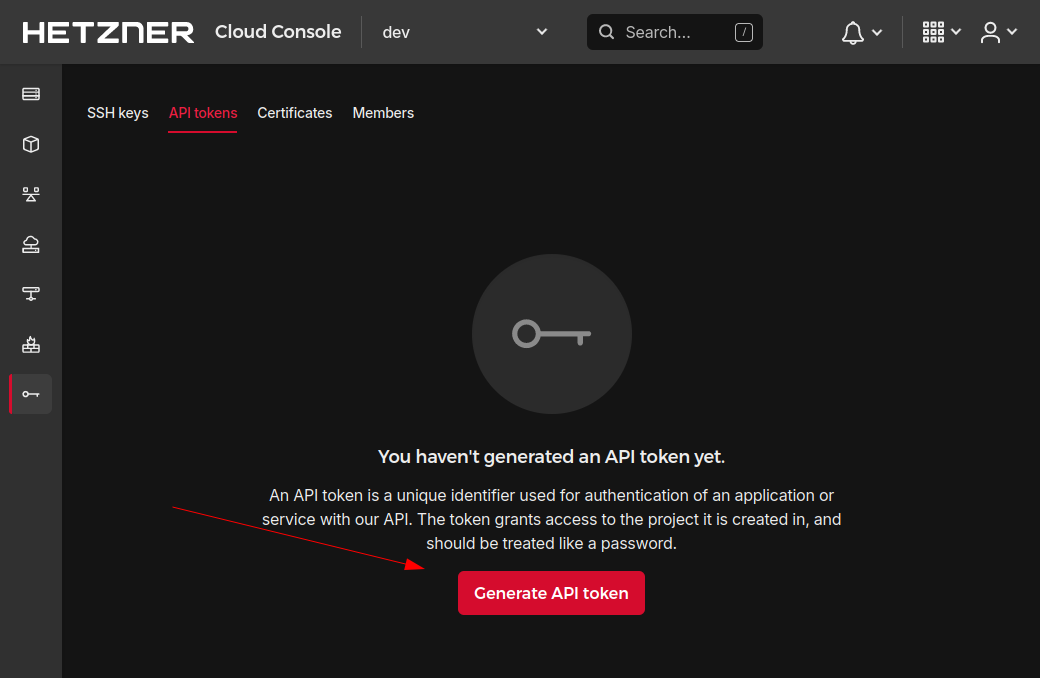
2. Store Hetzner Cloud API token locally. Either, pass the tokens to terraform
via an environment variable or create a file called `terraform.tfvars`:
```bash
# Either, enter your Hetzner Cloud API Token (it will be hidden)
read -sp "Hetzner Cloud API Token: " TF_VAR_hcloud_token
export TF_VAR_hcloud_token
read -sp "Hetzner Cloud API read only Token: " TF_VAR_hcloud_token_read_only
export TF_VAR_hcloud_token_read_only
# Or store the token in terraform.tfvars
touch terraform.tfvars
chmod 600 terraform.tfvars
cat >terraform.tfvars < Falkenstein),
and 24ms (Nuremberg -> Helsinki).
- Hetzner doesn't support mounting volumes on servers in another region! The
most simple setup is to just distribute the control plane nodes across
multiple regions, disable the scheduling of workloads on control plane
nodes and keep all worker nodes pools within one region. For better
availability of workloads, worker node pools should be distributed across
regions. This requires a configuration of
[taints and tolerations](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/taint-and-toleration/)
and
[node affinity](https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/scheduling-eviction/assign-pod-node/)
to ensure that pods with volumes are schedules in the correct region.
- Depending on the selected server regions the `network_zone` setting should
be adjusted.
- Hetzner's load balancers are bound to one region. Therefore, a
multi-regional cluster with one load balancer is not sufficent for dealing
with zone outages. The load balancer would go down with the region it's
hosted in. If a protection against zone outages is required, a global load
balancer should be deployed elsewhere, as
[described by Google](https://cloud.google.com/load-balancing/docs/load-balancing-overview).
6. Initialize the configuration: `terraform init`
7. Apply the configuration: `terraform apply`
8. Grab a coffee and enjoy the servers popping up in Hetzner's cloud console.
Wait for about 5 minutes.
9. Test SSH access to the cluster: `./ssh-node cluster`
- ATTENTION: don't hammer the cluster with failing SSH requests, or you'll be
banned by your cluster automatically! If the request fails, because the
cluster node isn't ready yet, wait another minute.
10. Once SSH connection is established, double check that everything is working
as expected:
- Did the node initialization finish successfully? `cloud-init status`
- Is the cluster up and running? `kubectl cluster-info`
11. If the tests were successful, retrieve the Kubernetes configuration and
store it locally: `./setkubeconfig`
12. Forward the cluster port locally since it's not exposed to the Internet by
default. Do this every time you want to interact with the cluster:
`./ssh-node gateway`
13. **On your local machine** test cluster access: `kubectl get nodes`
Enjoy your new cluster! 🚀
### Usage
Start using your favorite Kubernetes tools to interact with the cluster. One of
the first steps usually involves
[deploying an ingress controller](#add-ingress-controller-and-load-balancer)
since this configuration doesn't ship one.
In addition, a few convenience scripts were created to help with maintenance:
- `setkubeconfig`: retrieves and stores the Kubernetes configuration locally.
- `unsetkubeconfig`: removes the cluster from the local Kubernetes
configuration.
- `ls-nodes`: lists the nodes that are part of the cluster for access via
`ssh-node` and `scp-node`.
- `ssh-node`: SSH wrapper for connecting to cluster nodes.
- `scp-node`: SCP wrapper for connecting to cluster nodes.
- `.ssh/config`: SSH configuration for connecting to cluster nodes.
- `.ansible/hosts`: Ansible hosts configuration for executing commands on
multiple nodes in parallel.
## Configuration
### Store terraform state in S3 bucket
- Add an "s3" backend section to `main.tf`, with the appropriate parameters. See
example below for Wasabi.
- Set access key id and access key in environment variables `AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID`
and `AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY`.
- Reconfigure terraform: `terraform init -reconfigure`
```terraform
terraform {
# ...
backend "s3" {
# INFO: Set via `terraform init -reconfigure`
bucket = "terraform"
key = "prod/terraform.tfstate"
# access_key = {}
# secret_key = {}
# skip_get_ec2_platforms = true
region = "eu-central-2"
skip_credentials_validation = true
skip_metadata_api_check = true
skip_region_validation = true
skip_requesting_account_id = true
skip_s3_checksum = true
use_path_style = true
endpoints = {
iam = "https://iam.eu-central-2.wasabisys.com" # special endpoint URL required, see https://wasabi-support.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360003362071-How-do-I-use-Terraform-with-Wasabi-
sts = "https://sts.eu-central-2.wasabisys.com" # special endpoint URL required, see https://wasabi-support.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360003362071-How-do-I-use-Terraform-with-Wasabi-
s3 = "https://s3.eu-central-2.wasabisys.com" # special endpoint URL required, see https://wasabi-support.zendesk.com/hc/en-us/articles/360003362071-How-do-I-use-Terraform-with-Wasabi-
}
}
# ...
}
```
### Enable etcd backup to S3
- Extend `main.tf` with the following variables:
```terraform
variable "etcd_s3_region" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "etcd_s3_endpoint" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "etcd_s3_access_key" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "etcd_s3_secret_key" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
variable "etcd_s3_bucket" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
```
- Set the following module parameters before initializing the cluster's control
plane nodes:
```terraform
control_plane_k3s_init_additional_options = "--etcd-s3 --etcd-s3-region=${var.etcd_s3_region} --etcd-s3-endpoint=s3.${var.etcd_s3_endpoint} --etcd-s3-access-key=${var.etcd_s3_access_key} --etcd-s3-secret-key=${var.etcd_s3_secret_key} --etcd-s3-bucket=${var.etcd_s3_bucket} --etcd-s3-folder=$(hostname)"
```
- Etcd will automatically create a snapshot every day and keep it for three
days.
### OpenID Connect (OIDC) Authentication
TODO: add example
### Persistent Volume Encryption
- Ensure `cryptsetup` is installed on all nodes. By default it is installed.
- Encryption is configured per `StorageClass`.
- Follow the instructions at
[hcloud-csi Volumes Encrypted with LUKS](https://github.com/hetznercloud/csi-driver/blob/main/docs/kubernetes/README.md#volumes-encrypted-with-luks)
to create a secret and link it to a storage class.
- All future volumes created with this `StorageClass` will be encrypted.
### Adjust Sysctl Parameters
- Sysctl paramerts can be adjusted if needed via the `sysctl_settings` variable.
- Caution is advised!
- A common issue are truncated `kubectl log` outputs when the variables
`fs.inotify.max_user_instances` and `fs.inotify.max_user_watches` are set too
low. The values are increased by the default configuration. Furthere
adjustments might be needed.
### Private Registry Access
Usually,
[pull secrets](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/pull-image-private-registry/)
need to be configured to access container images stored in private registries.
This terraform module provides access to k3s'
[Private Registry Configuration](https://docs.k3s.io/installation/private-registry).
Add a private registry configuration with the following setting:
```terraform
module "cluster" {
# ...
registries = {
mirrors = {
"*" = null
}
configs = {
"registry-1.docker.io" = {
auth = {
token = var.dockerio_access_token
}
}
}
}
# ...
}
variable "dockerio_access_token" {
type = string
sensitive = true
}
```
## Maintenance
### Access Kubernetes API via Port-Forwarding from Gateway
By default, the Kubernetes API port is not exposed on the internet, see option
`gateway_firewall_k8s_open`. Therefore, it is required to forward the Kubernetes
API port `6443` from the gateway.
A limited account `kubeapi` was created on the gateway that restricts SSH keys
configured via option `ssh_keys_kubeapi` to forward the single port. A
corresponding SSH config entry is created. The following command connects to the
gateway with the restricted user account:
```bash
./ssh-node kubeapi
```
With the established connection and a proper `KUBECONFIG`, the cluster can be
accessed:
```bash
kubectl get nodes
```
### Ansible: Execute Commands on Nodes
This module automatically generates an
[Ansible inventory](https://docs.ansible.com/ansible/latest/inventory_guide/intro_inventory.html#connecting-to-hosts-behavioral-inventory-parameters)
in file `.ansible/hosts`. It can be leveraged to interact with the nodes and
node pools of the cluster.
Example: Execute a command on all control plane nodes
```bash
ANSIBLE_INVENTORY="$PWD/.ansible/hosts" ansible all_control_plane_nodes -a "kubectl cluster-info"
```
### Add Ingress Controller and Load Balancer
Since this module doesn't ship an ingress controller, one of the first
configurations applied to the cluster is usually an ingress controller. Good
starting points for an ingress controller are:
- [traefik](https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/traefik/traefik)
- [ingress-nginx](https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx)
The ingress controller, like the rest of the cluster, is not directly exposed to
the Internet. Therefore, it is necessary to add a load balancer that is directly
exposed to the Internet and has access to the local network of the cluster. The
load balancer is added to the cluster simply by adding annotations to the
ingress controller's service. Hetzner's Cloud Controller Manager will use the
annotations to deploy and configure the load balancer.
The following annotations should be used:
- Resource name: `load-balancer.hetzner.cloud/name: "ingress-lb"`
- Protocol, just `tcp` - the ingress controller will take care of the HTTP
connection: `load-balancer.hetzner.cloud/protocol: "tcp"`
- Location, same as the one used for the cluster:
`load-balancer.hetzner.cloud/location: "nbg1"`
- Connection to the servers, must be set to `true`:
`load-balancer.hetzner.cloud/use-private-ip: "true"`
- Size, see [options](https://docs.hetzner.com/cloud/load-balancers/overview):
`load-balancer.hetzner.cloud/type: "lb11"`
- See
[list of all supported Load Balancer Annotations](https://github.com/hetznercloud/hcloud-cloud-controller-manager/blob/main/internal/annotation/load_balancer.go).
Furthermore, for domain names to work, it is required to point DNS records to
the IP address of load balancer.
[external-dns](https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/external-dns/external-dns)
is a helpful tool that can automate this task from within the cluster. For this
to work well with Ingress resources, the ingress controller needs to
[expose the published service information](https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/v0.14.0/faq/#which-service-and-ingress-controllers-are-supported)
on the Ingress resources.
### Add Nodes or Node Pools
The number of nodes in a node pool can be increased at any point. Just increase
the count and apply the new configuration via `terraform apply`. After a few
minutes the additional nodes will appear in the cluster.
In the same way, node pools can be added to the configuration without any
precaution.
### Remove Nodes or Node Pools
Removing nodes requires the following steps:
1. Identify the nodes and node pools that shall be removed. If the number of
nodes in a node pool needs to be decreased, the nodes will be removed from
the highest to the lowest number. Example: when the number of nodes in pool
`system` is decreased from `3` to `2`, node `cluster-system-02` will be
removed and nodes `cluster-system-01` and `cluster-system-00` will remain.
2. Drain all nodes that will be removed of pods:
`kubectl drain cluster-system-02`
3. Wait until all pods have been migrated to other nodes before continuing.
- If you drained the wrong node, you can reactivate the node with:
`kubectl uncordon cluster-system-02`
4. Update the terrafrom configuration and apply it: `terraform apply`
- Review the plan to verify that the drained nodes will be deleted.
5. Delete nodes from cluster: `kubectl delete node cluster-system-02`
### Stop Automated Node Reboots
Nodes are rebooting automatically when they receive updates that require a
reboot. The kured service triggers reboots of nodes one by one. Reboots can be
disabled system-wide by annotating the Daemonset, see
.
### Upgrade Operating System
An operating system update is not recommended, e.g. from Ubuntu 22.04 to 24.04.
Instead, the corresponding nodes should be replaced!
#### Gateway Node
1. Set new image as `default_image`. Attention: before changing the default
image, make sure that each node pool has its own appropriate `image` setting.
2. Delete the node in the [Hetzner Console](https://console.hetzner.cloud/)
3. Reapply the configuration: `terraform apply`
The gateway will reappear again within a few minutes. This will disrupt the
Internet access of the cluster's nodes for tasks like fetching package updates.
However, it will not affect the services that are provided via load balancers!
After redeploying the gateway, ssh connections will fail because a new
cryptographic has been generated for the node. Delete the deprecated key from
the `.ssh/known_hosts` file, open a new ssh connection and accept the new public
key.
#### Node Pools
Nodes should not be updated manually via `agt-get`, but be replaced. For control
plane nodes, it is recommended to create a back-up of the etcd data store on an
external s3 storage, see [k3s Cluster Datastore](https://docs.k3s.io/datastore).
1. For control plane pools only: Create a new etcd snapshot, see
[k3s etcd-snapshot](https://docs.k3s.io/cli/etcd-snapshot).
2. Then, perform the following steps on consecutively on all existing node pools
until they have all been replaced.
Start the replacement with the node pool with the `cluster_can_init` setting:
3. Ensure that there's another control plane node pool. If there's no other
control plane node pool, create a temporary one that is deleted after the
successful replacement of the node pool with the `cluster_can_init` setting.
4. When the second control plane node pool is up and running, the node pool with
the `cluster_can_init` setting must be deleted and replaced in one
application of the configuration.
- Ensure that the `cluster_init_action.init` and `cluster_init_action.reset`
settings are disabled.
- Drain the old nodes: `kubectl drain node-xyz`
- Once all pods have been migrated, delete the old nodes:
`kubectl delete node node-xyz`
- Then rename the node pool to achieve deletion and replacement in one
configuration change.
- Apply the configuration: `terraform apply`
- Once the new control plane node pool with the `cluster_can_init` setting is
again up and running, the temporary control plane node pool can be deleted.
Perform these steps for all remaining node pools:
5. Add a new node pool and set the `image` setting to the new version.
6. Once the new node pool is up and running, drain the old nodes:
`kubectl drain node-xyz`
7. Once all pods have been migrated, delete the old nodes:
`kubectl delete node node-xyz`
8. Remove the node pool from the terraform configuration.
9. Reapply the configuration: `terraform apply`
### Update Kubernetes
1. Determine the next Kubernetes version, see
[k3s channels](https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels),
[k3s images tags](https://hub.docker.com/r/rancher/k3s/tags), and
[k3s upgrade image tags](https://hub.docker.com/r/rancher/k3s-upgrade/tags).
2. Write the upgrade plan, see
[instructions](https://docs.k3s.io/upgrades/automated) and
[examples](https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller#example-plans).
3. Apply an upgrade plan.
4. Update the `image` variable in the configuration for future nodes to be
deployed with the correct image.
Example upgrade plan:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller
# Upgrade plan for control plane nodes
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
metadata:
name: k3s-server
namespace: cattle-system
spec:
# When a channel is used, rather than a specific version,
# the plan keeps updating the cluster continuously
channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/v1.32
# version v1.30.0+k3s1
concurrency: 1
drain:
# disableEviction: true
force: true
skipWaitForDeleteTimeout: 60
nodeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- { key: k3s-upgrade, operator: Exists }
# Updates can be disabled by setting this label on nodes
- { key: k3s-upgrade, operator: NotIn, values: ["disabled", "false"] }
- { key: k3os.io/mode, operator: DoesNotExist }
- { key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane, operator: Exists }
serviceAccountName: system-upgrade-controller
upgrade:
image: rancher/k3s-upgrade
---
# Upgrade plan for worker nodes
apiVersion: upgrade.cattle.io/v1
kind: Plan
metadata:
name: k3s-agent
namespace: cattle-system
spec:
# When a channel is used, rather than a specific version,
# the plan keeps updating the cluster continuously
channel: https://update.k3s.io/v1-release/channels/v1.32
# version v1.30.0+k3s1
concurrency: 1
drain:
# disableEviction: true
force: true
skipWaitForDeleteTimeout: 60
nodeSelector:
matchExpressions:
- { key: k3s-upgrade, operator: Exists }
# Updates can be disabled by setting this label on nodes
- { key: k3s-upgrade, operator: NotIn, values: ["disabled", "false"] }
- { key: k3os.io/mode, operator: DoesNotExist }
- { key: node-role.kubernetes.io/control-plane, operator: DoesNotExist }
serviceAccountName: system-upgrade-controller
prepare:
# Defaults to the same "resolved" tag that is used for the `upgrade` container, NOT `latest`
image: rancher/k3s-upgrade
args: ["prepare", "k3s-server"]
upgrade:
image: rancher/k3s-upgrade
```
### Update Cilium
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values cilium cilium/cilium -n kube-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/cilium/cilium
# Chart Values: https://github.com/cilium/cilium/blob/main/install/kubernetes/cilium/values.yaml
# Hetzner networking configuration: https://github.com/hetznercloud/hcloud-cloud-controller-manager/blob/main/docs/deploy_with_networks.md
# See also kube-hetzner configuration of cilium: https://github.com/kube-hetzner/terraform-hcloud-kube-hetzner
# MTU: 1450
masquerade: true
bpf:
masquerade: true
endpointRoutes:
enabled: true
k8s:
requireIPv4PodCIDR: true
# Native routing saves one layer of packet encapsulation
routingMode: native
# WARNING: IP address ranges need to be in line with the cluster configuration
ipv4NativeRoutingCIDR: 10.0.0.0/8
ipam:
mode: kubernetes
operator:
clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList: 10.244.0.0/16
operator:
replicas: 2
kubeProxyReplacement: true
nodePort:
enabled: true
loadBalancer:
acceleration: native
hubble:
enabled: true
# Enable, if needed. By default it isn't needed
# egressGateway:
# enabled: true
# HAproxy runs on every node to provide HA access to control plane nodes
k8sServiceHost: 127.0.0.1
k8sServicePort: 16443
```
### Update Hetzner Cloud Controller Manager (CCM)
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add hcloud https://charts.hetzner.cloud
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values hcloud-ccm hcloud/hcloud-cloud-controller-manager -n kube-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://github.com/hetznercloud/hcloud-cloud-controller-manager/tree/main/chart
# WARNING: needs to be in line with the cluster configuration
networking:
enabled: true
clusterCIDR: 10.244.0.0/16
additionalTolerations:
# INFO: this taint occurred but isn't coveryd by default .. and caused the
# whole cluster to not start properly
- key: node.kubernetes.io/not-ready
value: NoSchedule
```
### Update Hetzner Cloud Storage Interface (CSI)
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add hcloud https://charts.hetzner.cloud
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values hcloud-csi hcloud/hcloud-csi -n kube-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://github.com/hetznercloud/csi-driver/tree/main/chart
storageClasses:
- name: hcloud-volumes-retain
defaultStorageClass: true
reclaimPolicy: Retain
- name: hcloud-volumes-delete
defaultStorageClass: false
reclaimPolicy: Delete
```
### Update Kured
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add kubereboot https://kubereboot.github.io/charts
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values kured kubereboot/kured -n kube-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/kured/kured
configuration:
timeZone: Europe/Berlin
startTime: 1am
endTime: 5am
rebootDays:
- mo
- tu
- we
- th
- fr
- sa
- su
tolerations:
- key: CriticalAddonsOnly
operator: Exists
```
### Update Metrics Server
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add metrics-server https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/metrics-server/
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values metrics-server metrics-server/metrics-server -n kube-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://artifacthub.io/packages/helm/metrics-server/metrics-server
```
### Update System Upgrade Controller
- Available versions:
- Update instructions:
```bash
helm repo add rancher https://charts.rancher.io
helm repo update
helm upgrade --reuse-values system-upgrade-controller rancher/system-upgrade-controller -n cattle-system --version ''
```
`values.yaml`:
```yaml
# Documentation: https://github.com/rancher/system-upgrade-controller
# Documentation: https://github.com/rancher/charts/tree/release-v2.8/charts/system-upgrade-controller
systemUpgradeJobTTLSecondsAfterFinish: 86400 # retain jobs for 1 day for inspection purposes
```
## Deletion
After applying the Terraform plan you'll see several output variables like the
load balancer's, control plane's, and node pools' IP addresses.
```bash
terraform destroy -force
```
Be sure to clean up any CSI created Block Storage Volumes, and CCM created
LoadBalancers that you no longer require.
## Troubleshooting
### Gateway
Ensure gateway is set up correctly: `./ssh-node gateway`
#### Verify packet masquerading is set up properly
```bash
iptables -L -t nat
# Expected output:
# Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
# target prot opt source destination
#
# Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT)
# target prot opt source destination
#
# Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT)
# target prot opt source destination
#
# Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT)
# target prot opt source destination
# MASQUERADE all -- 10.0.1.0/24 anywhere
```
#### Verify firewall is set up properly
```bash
ufw status
# Expected output:
# Status: active
#
# To Action From
# -- ------ ----
# 22,6443/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
# 22,6443/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
#
# Anywhere on eth0 ALLOW FWD Anywhere on enp7s0
# Anywhere (v6) on eth0 ALLOW FWD Anywhere (v6) on enp7s0
```
### Nodes
#### Inspect local firewall settings
```bash
ufw status
```
#### Verify correctness of date/timezone and locale
```bash
date
echo $LANG
```
#### Inspect cloud-init logs
```bash
# Retrieve status
cloud-init status
# Verify configuration
cloud-init schema --system
# Collect logs for inspection
cloud-init collect-logs
tar xvzf cloud-init.tar.gz
# Inspect cloud-init.log for error messages
# Quickly find runcmd
find /var/lib/cloud/instances -name runcmd
sh -ex PATH_TO_RUNCMD
```
### Cluster
Ensure cluster is set up correctly: `./ssh-node cluster`
#### Verify default route
```bash
ip r s
# Expected output:
# default via 10.0.0.1 dev enp7s0 proto static onlink <-- this is the important line
# 10.0.0.0/8 via 10.0.0.1 dev enp7s0 proto dhcp src 10.0.1.2 metric 1024
# 10.0.0.1 dev enp7s0 proto dhcp scope link src 10.0.1.2 metric 1024
# 169.254.169.254 via 10.0.0.1 dev enp7s0 proto dhcp src 10.0.1.2 metric 1024
```
#### Verify connectivity to the Internet
```bash
ping 1.1.1.1
# Expected output:
# PING 1.1.1.1 (1.1.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
# 64 bytes from 1.1.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=53 time=4.60 ms
# 64 bytes from 1.1.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=53 time=6.82 ms
# ...
```
#### Verify name resolution
```bash
host k3s.io
# Expected output:
# k3s.io has address 185.199.108.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.110.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.111.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.109.153
# ...
```
#### Verify cluster status
```bash
k3s kubectl get nodes
# Expected output:
# k3s.io has address 185.199.108.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.110.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.111.153
# k3s.io has address 185.199.109.153
# ...
```
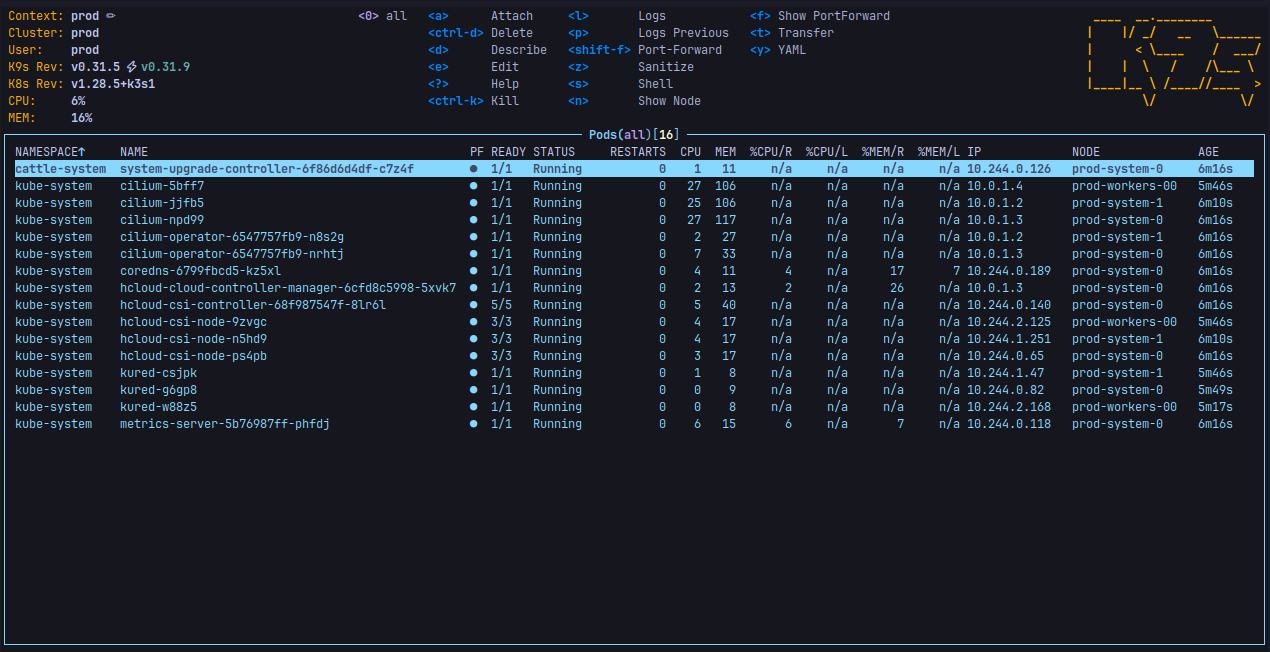
#### Verify Cilium Networking Status
This command only works after installing the
[cilium cli](https://github.com/cilium/cilium-cli).
- [cilium cli](https://www.klarmobil.de/)
```bash
cilium status
# Expected output:
# /¯¯\
# /¯¯\__/¯¯\ Cilium: OK
# \__/¯¯\__/ Operator: OK
# /¯¯\__/¯¯\ Envoy DaemonSet: disabled (using embedded mode)
# \__/¯¯\__/ Hubble Relay: disabled
# \__/ ClusterMesh: disabled
#
# Deployment cilium-operator Desired: 1, Ready: 1/1, Available: 1/1
# DaemonSet cilium Desired: 3, Ready: 3/3, Available: 3/3
# Containers: cilium Running: 3
# cilium-operator Running: 1
# Cluster Pods: 9/9 managed by Cilium
# Helm chart version: 1.14.5
# Image versions cilium quay.io/cilium/cilium:v1.14.5@sha256:d3b287029755b6a47dee01420e2ea469469f1b174a2089c10af7e5e9289ef05b: 3
# cilium-operator quay.io/cilium/operator-generic:v1.14.5@sha256:303f9076bdc73b3fc32aaedee64a14f6f44c8bb08ee9e3956d443021103ebe7a: 1
```
#### Verify k3s Cluster Configuration
This command only works out of the box on the first node of the control plane
node pool with the `cluster_can_init` setting.
```bash
k3s check-config
# Expected output:
# ...
# STATUS: pass
```
#### Inspect cluster status and logs
```bash
systemctl status k3s.service
journalctl -u k3s.service
```
## Related Documentation
- [Cilium](https://docs.cilium.io/)
- [Cloud-init](https://cloudinit.readthedocs.io/)
- [Hetzner API](https://docs.hetzner.cloud/)
- [Hetzner Cloud Platform](https://docs.hetzner.com/cloud)
- [Terraform Module Registry](https://registry.terraform.io/)
- [Terraform](https://www.terraform.io/docs/)
## Similar Projects
- [hcloud-kube-hetzner](https://github.com/kube-hetzner/terraform-hcloud-kube-hetzner)
very popular k3s stack based on openSUSE MicroOS.
- [hcloud-k3s](https://github.com/cicdteam/terraform-hcloud-k3s) Original
project that this project has been forked from.
- [hetzner-cloud-k3s](https://github.com/vitobotta/hetzner-cloud-k3s) A fully
functional, super cheap Kubernetes cluster in Hetzner Cloud in 1m30s or less
- Not terraform-based.
- Scripts that make it easy to manage a cluster.
- [hetzner-k3s](https://github.com/vitobotta/hetzner-k3s/) A CLI tool to create
and manage Kubernetes clusters in Hetzner Cloud using the lightweight
distribution k3s by Rancher. Successor of
[hetzner-cloud-k3s](https://github.com/vitobotta/hetzner-cloud-k3s).
- Not terraform-based.
- [k-andy](https://github.com/StarpTech/k-andy) Zero friction Kubernetes stack
on Hetzner Cloud.
- Terraform-based stack.
- Distributed across multiple Hetzner sites and data centers.
- Support for multiple control-plane servers.
- [terraform-hcloud-kube-hetzner](https://github.com/kube-hetzner/terraform-hcloud-kube-hetzner).
Optimized and Maintenance-free Kubernetes on Hetzner Cloud in one command!
## Special Thanks
- The initiators of and contributors to this project for getting the k3s cluster
running via terraform.
- And to God for providing and enabling me to do my share of this work. Solo Deo
Gloria.