https://github.com/iiakshat/pca
https://github.com/iiakshat/pca
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/iiakshat/pca
- Owner: iiakshat
- Created: 2024-08-24T18:00:24.000Z (8 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-06T18:03:22.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-20T19:25:03.578Z (3 months ago)
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Size: 10.4 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# PCA
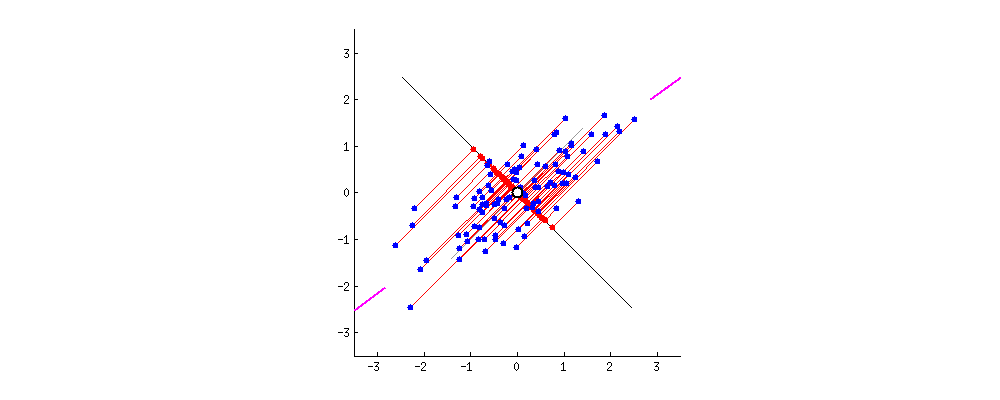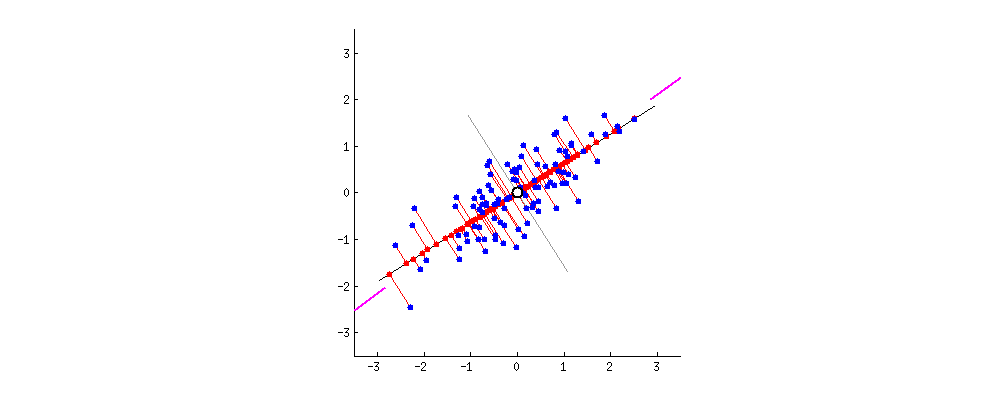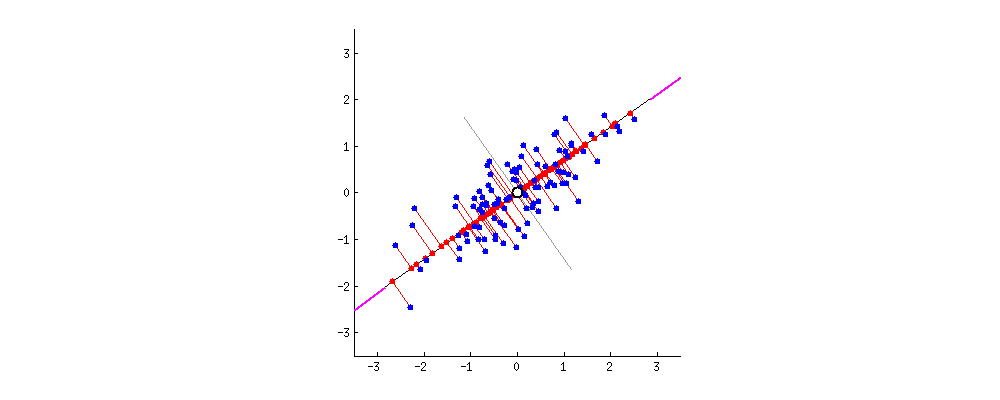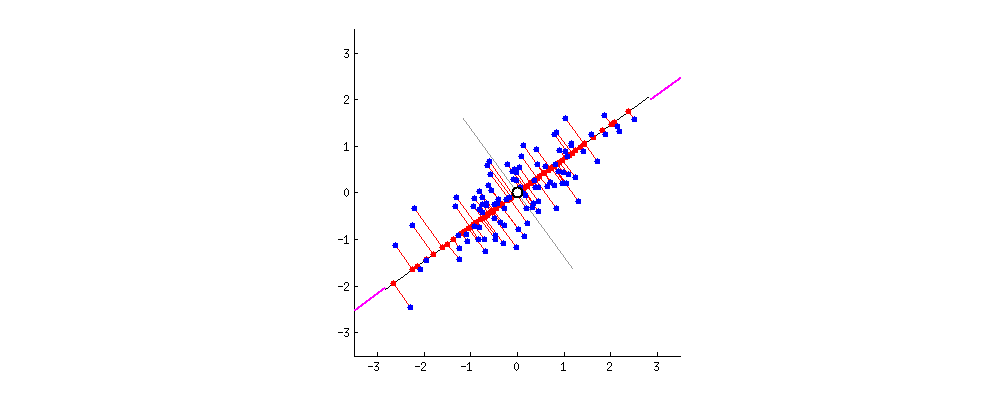
This repository contains a project on Principal Component Analysis (PCA) that consists of two Jupyter notebooks:
- `Implementation.ipynb` contains implementation of PCA from scratch.
- `MNIST.ipynb` contains implementation of PCA using `scikit-learn` on Mnist Dataset.
# What is PCA?
**Principal Component Analysis (PCA)** is a dimensionality reduction technique commonly used in data analysis and machine learning. The main objective of PCA is to reduce the dimensionality of a dataset while retaining as much variance (information) as possible.
## How PCA Works
1. **Standardization**: Since PCA is affected by the scale of variables, the dataset is standardized by subtracting the mean and dividing by the standard deviation.
2. **Covariance Matrix**: After standardization, a covariance matrix is computed to understand the relationships between the variables.
3. **Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors**: PCA calculates the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of the covariance matrix. Eigenvectors determine the directions (principal components) along which the data varies the most, while eigenvalues represent the magnitude of the variance along each principal component.
4. **Projection**: The original dataset is projected onto a new set of axes (principal components), reducing the dimensionality of the data by keeping only the components with the largest eigenvalues (those that explain the most variance).
## Key Benefits of PCA
- **Dimensionality Reduction**: PCA helps to reduce the number of features in a dataset while preserving the important information, making computations more efficient.
- **Visualization**: PCA can reduce data to 2 or 3 dimensions, making it easier to visualize.
- **Noise Reduction**: By focusing on components with the highest variance, PCA can reduce the influence of noise and irrelevant features.
## When to Use PCA
- When you have a large number of features and want to reduce complexity without losing significant information.
- When you want to eliminate multicollinearity among features.
- When you need to visualize high-dimensional data in 2D or 3D space.
## Example Use Case
PCA is often used in image processing, such as in the **MNIST digit classification problem**. Here, PCA can reduce the number of pixels (features) in the dataset while retaining the essential information for classifying handwritten digits.
1. **Implementation Notebook**: A PCA implementation from scratch.
2. **MNIST Notebook**: A practical example of using PCA via the scikit-learn library to classify the MNIST dataset.
## Project Overview
This project aims to demonstrate the theory and application of PCA. It provides two distinct notebooks:
- **PCA from scratch**: This notebook shows how PCA works internally by coding it from the ground up without relying on external libraries.
- **PCA on the MNIST dataset**: This notebook demonstrates how PCA can be used to reduce dimensionality in real-world applications, utilizing scikit-learn to classify digits from the MNIST dataset.
## Notebooks
### 1. PCA Implementation from Scratch
This notebook walks through the process of implementing PCA using Python from scratch. It covers:
- Theoretical foundation of PCA
- Standardizing the dataset
- Calculating covariance matrix
- Computing eigenvalues and eigenvectors
- Projecting the dataset onto new principal components
### 2. PCA on MNIST Dataset
This notebook uses PCA as a dimensionality reduction technique on the MNIST dataset, followed by classification using a machine learning model. It leverages the scikit-learn library for:
- PCA implementation
- Loading and preprocessing the MNIST dataset
- Reducing the feature space using PCA
- Training a classifier (e.g., Logistic Regression) on the reduced data
### Requirements
Make sure you have the following libraries installed:
`numpy`
`pandas`
`matplotlib`
`scikit-learn`
### Usage
* Open the implementation.ipynb notebook to explore how PCA works under the hood.
* Open the mnist.ipynb notebook to see PCA in action on the MNIST dataset using scikit-learn.
### Project Structure
```graphql
PCA/
│
├── Implementation.ipynb # PCA from scratch implementation
├── MNIST.ipynb # PCA with scikit-learn on the MNIST dataset
├── digits.csv # For training
└── README.md # Project readme file
```
### Contributing
If you have any suggestions or improvements, feel free to fork the repository and open a pull request.