https://github.com/imsky/pull-review
:white_check_mark: Assign pull request reviewers intelligently.
https://github.com/imsky/pull-review
github hacktoberfest hubot pull-requests review slack
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
:white_check_mark: Assign pull request reviewers intelligently.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/imsky/pull-review
- Owner: imsky
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-03-01T02:27:13.000Z (almost 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-03-02T12:20:06.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-14T10:50:44.955Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Topics: github, hacktoberfest, hubot, pull-requests, review, slack
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage: https://pull-review.herokuapp.com
- Size: 1.01 MB
- Stars: 205
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 17
- Open Issues: 34
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-monorepo - Pull Review - review.svg?style=social&label=Star) (开发流程工具 / Code reviews)
- awesome-ospo - pull-review - Assign pull request reviewers intelligently, inspired by mention-bot. (Code Reviews)
README
# Pull Review
[](https://gitlab.com/imsky/pull-review/commits/master) [](https://gitlab.com/imsky/pull-review/commits/master) [](https://www.npmjs.com/package/pull-review) [](https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/blob/master/LICENSE)
**Pull Review** assigns pull request reviewers [intelligently](#algorithm).
Pull Review looks through the changes in a pull request and assigns the most relevant reviewers, those who have made the largest and most recent contributions to the changed files. The number of reviewers assigned, along with other things, [can be configured](#configuration).
You can use Pull Review through [GitHub comments](#github), from chat rooms in Slack/HipChat/etc. using [Hubot](#hubot), on the [command line](#cli), via [API](#api), or as a [Docker image](#docker).
## Installation
```
npm install pull-review
```
[](https://heroku.com/deploy?template=https://github.com/imsky/pull-review)
## Usage
First, add a `.pull-review` configuration file in your repository:
```yaml
version: 1
reviewers:
your_github_username: {}
```
In order to use Pull Review as a Hubot plugin or in server mode, you'll need a [GitHub token](https://github.com/settings/tokens). The token must have `repo`, `public_repo`, `read:user`, and `read:org` scopes.
For details on configuration options, check out the [configuration](#configuration) section.
### GitHub
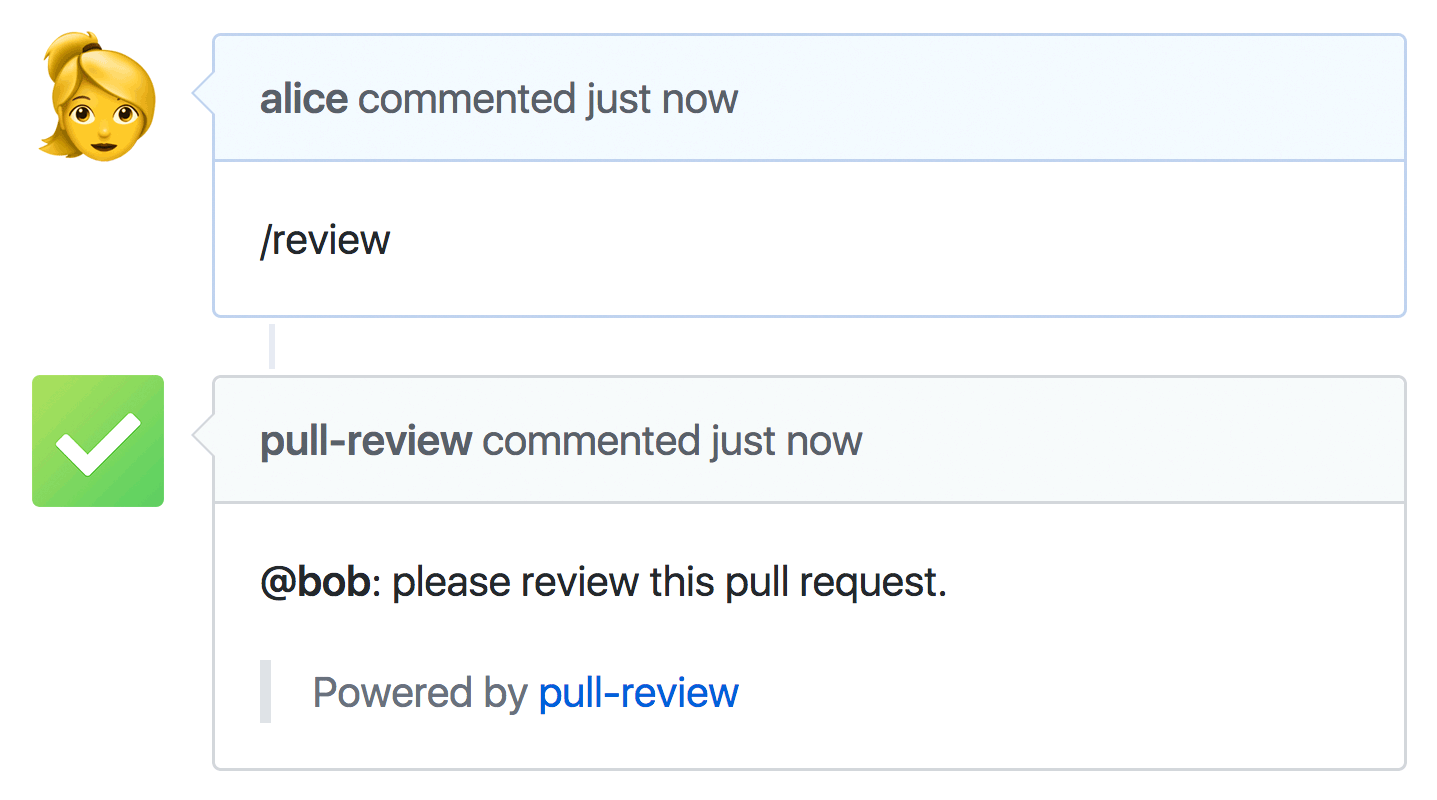
* In your GitHub repository, go to **Settings**→**Webhooks**
* Click **Add webhook**
* Set **Payload URL** to the Pull Review server URL ()
* Set **Content type** to `application/json`
* Choose **Let me select individual events**
* Pick the **Issue comment** event
* Click **Add webhook**
To assign reviewers on a pull request, post `/review`. To [run Pull Review again](#reviewing-again) post `/review again`.
> The public Pull Review server limits some configuration options. However, you can [run your own server](#server).
### Hubot
Add `pull-review` to your `external-scripts.json`:
```json
[
"pull-review"
]
```
Ensure [environment variables](#environment-variables) are set correctly.
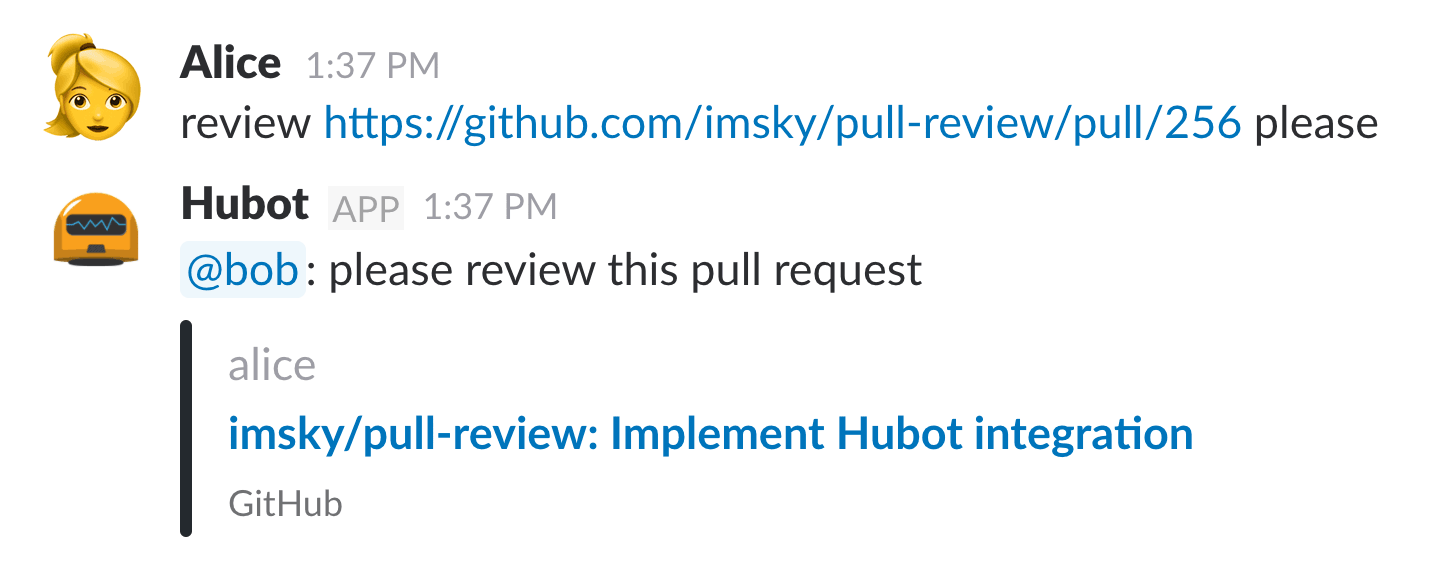
You can request review assignments like this:
```text
review https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1
```
You can [run Pull Review again](#reviewing-again) on a pull request like this:
```text
review https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1 again
```
To notify users on Slack, configuration must include a [reviewers](#reviewers) section.
Pull Review also adds a pull request preview, for private and public repos.
### CLI
```bash
npm install --global pull-review
pull-review https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1
pull-review --help
Usage: pull-review [options]
Options:
-V, --version output the version number
-r, --retry-review Retry review
-d, --dry-run Do not assign or notify reviewers
-t, --github-token GitHub token to use
-c, --config-path Pull Review configuration path in repo
-h, --help output usage information
```
### API
```js
var PullReview = require('pull-review');
PullReview({
pullRequestURL: 'https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1',
// run Pull Review on a pull request, unassigning current reviewers first
retryReview: true,
// run Pull Review on a pull request, but do not assign or notify reviewers
dryRun: true,
// run Pull Review with a specific GitHub token
githubToken: 'PULL_REVIEW_GITHUB_TOKEN'
// run Pull Review with a custom Pull Review configuration
config: {version: 1},
// specify a different repo location for the Pull Review configuration
pullReviewConfigPath: 'config/.pull-review'
});
```
### Docker
The Docker image can be used in [CLI](#cli) mode or in [server](#server) mode.
```bash
# get the Pull Review image
docker pull ghcr.io/imsky/pull-review
# run Pull Review on a pull request
docker run -it -e PULL_REVIEW_GITHUB_TOKEN ghcr.io/imsky/pull-review https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1
# run Pull Review with a specific GitHub token
docker run -it ghcr.io/imsky/pull-review https://github.com/imsky/pull-review/pull/1 --github-token PULL_REVIEW_GITHUB_TOKEN
```
### Server
You can run your own Pull Review server [on Heroku](https://heroku.com/deploy?template=https://github.com/imsky/pull-review) or another host.
Ensure [environment variables](#environment-variables) are set correctly.
Start the server with `npm start` or by [running `pull-review`](#cli) with no arguments.
The port is 8080 by default, but can be changed using the `PORT` environment variable.
## Configuration
Configuration for Pull Review is a YAML/JSON file named `.pull-review` at the root of the repo.
Check out [.pull-review](.pull-review) for a documented example of a config file.
#### max_files
Maximum number of files to evaluate in order to assign reviewers. Set to 0 for no maximum.
Default: 5
#### min_reviewers
Minimum number of reviewers to assign.
Default: 1
#### max_reviewers
Maximum number of reviewers to assign.
Default: 2
#### max_files_per_reviewer
Maximum number of files per reviewer. If the number of files is over this limit, more reviewers will be assigned up to the [maximum number of reviewers](#max_reviewers). Set to 0 for no maximum.
Default: 0
#### max_lines_per_reviewer
Maximum number of lines changed across added and modified files per reviewer. If the number of lines is over this limit, more reviewers will be assigned up to the [maximum number of reviewers](#max_reviewers). If `max_files_per_reviewer` and `max_lines_per_reviewer` are set, the assignment with the fewest reviewers will be used. Set to 0 for no maximum.
Default: 0
#### assign_min_reviewers_randomly
If the [minimum number of reviewers](#min_reviewers) isn't found, assign reviewers using [path fallbacks](review_path_fallbacks) and/or at random.
Default: true
#### min_authors_of_changed_files
If the pull request changes code with fewer authors than this minimum, replace already assigned reviewers with a random reviewer. This option helps prevent "review loops" where only a few authors review an area of code.
Default: 0
#### min_percent_authorship_for_extra_reviewer
If the assigned reviewer has greater percentage authorship of the changed files than this minimum, an extra reviewer will be assigned. This is helpful for files with many authors and one author with majority authorship, making them the default reviewer for those files. Set to 0 to disable.
Default: 0
#### min_lines_changed_for_extra_reviewer
When using [min_authors_of_changed_files](#min_authors_of_changed_files) or [min_percent_authorship_for_extra_reviewer](#min_percent_authorship_for_extra_reviewer), a small pull request can warrant an extra reviewer if there aren't enough distinct authors of the changed code. However, small pull requests usually don't need more than one reviewer. This option can be used to ensure that an extra reviewer is assigned for pull requests that change at least a minimum of lines of code.
Default: 0
#### require_notification
Require a user to be listed in the [reviewers](#reviewers) section in order to be assigned as a reviewer.
Default: true
#### use_review_requests
Use [review requests](https://help.github.com/articles/about-pull-request-reviews/) instead of [assignees](https://help.github.com/articles/assigning-issues-and-pull-requests-to-other-github-users/) to assign reviewers to pull requests.
Default: false
#### reviewers
A map of maps, with the main keys being the GitHub usernames of users, and the child keys providing application-specific contact information. Example:
```yaml
reviewers:
alice:
slack: ajones
bob: {}
charlie: "Charlie Smith"
```
When Pull Review sends its notification, it'll notify `@alice` on GitHub and `@ajones` on Slack.
Specifically for Slack, using real names instead of usernames (as in the example above for `charlie`) is recommended since Slack is [phasing out support for `@username` mentions](https://api.slack.com/changelog/2017-09-the-one-about-usernames).
If non-GitHub notification handles are not available/required, an empty object can be specified (as it is for `bob` in the example above). This will notify `@bob` on GitHub, and will work with the [`require_notification`](#require_notification) configuration option.
Currently only Slack user mapping is supported - for other chat networks like HipChat or IRC, Pull Review will mention the GitHub usernames instead.
#### review_blacklist
A list of usernames to never notify. This is useful to exclude machine users and users who are on vacation or otherwise unavailable for reviews.
#### review_path_assignments
A map of lists, where the keys are [minimatch](https://github.com/isaacs/minimatch) (glob) patterns, and the lists include the users to assign. **Note:** order is important. Example:
```yaml
review_path_assignments:
web/server/**:
- bob
```
When a file in `web/server` is found, `bob` will be assigned before other reviewers.
#### review_path_fallbacks
A map of lists, where the keys are [minimatch](https://github.com/isaacs/minimatch) (glob) patterns, and the lists include the users to assign. **Note:** order is important. Example:
```yaml
review_path_fallbacks:
web/ui/**:
- alice
```
When a file whose path begins with `web/ui` is found, `alice` will be assigned if more reviewers are required.
#### file_blacklist
An array of [minimatch](https://github.com/isaacs/minimatch) (glob) patterns that should be filtered out when retrieving files for a pull request. Blacklisted files will not be considered in Git blame processing, in [fallback path processing](#review_path_fallbacks), or in [max files per reviewer](#max_files_per_reviewer) or [max lines per reviewer](#max_lines_per_reviewer) calculations. Example:
```yaml
file_blacklist:
- web/ui/*.js
```
#### label_whitelist
An array of pull request labels that are required for pull request review.
#### label_blacklist
An array of pull request labels that are forbidden from pull request review.
#### notification_channels
An array of channels to use for review notifications. The default channels are `chat` (the same chat channel that Hubot uses, e.g. Slack) and `github` (a comment on the pull request).
To disable notifications, use an empty array:
```yaml
notification_channels: []
```
### Environment variables
* `PULL_REVIEW_GITHUB_TOKEN`: GitHub token used to fetch pull request information.
* `PULL_REVIEW_CONFIG_PATH`: location of the config file in the pull request repo (default is `.pull-review`).
* `PULL_REVIEW_CONFIG`: Pull Review configuration override in JSON/YAML format.
* `PULL_REVIEW_REQUIRED_ROOMS`: whitelist of Hubot chat rooms for Pull Review requests (e.g. `dev,ops`).
## Reviewing again
Sometimes it may be useful to run Pull Review again on a pull request, whether it's because the assigned reviewers are not available to review the PR or because another set of reviewers is necessary. You can run Pull Review again in the following ways:
* [GitHub](#github): `/review again`
* [Hubot](#hubot): `review ... again`
* [CLI](#cli): `--retry-review` or `-r`
* [API](#api): `retryReview: true`
When running Pull Review again, current reviewers are un-assigned, and the next best set of reviewers is assigned instead. Keep in mind that if Pull Review runs twice on a pull request, the original reviewers will be assigned again.
## Algorithm
Pull Review was partly inspired by [mention-bot](https://github.com/facebook/mention-bot), however its algorithm is a bit different.
* Get all modified files for a pull request and take the [top files](#max_files) with most changes
* Get information on which author changed what lines in these files using [Git blame](https://git-scm.com/docs/git-blame) data, filtering out older data
* Assign [authors who have precedence for particular paths](#review_path_assignments)
* Assign authors who have made the most changes in the top modified files
* If there are [not enough reviewers](#min_reviewers), assign more reviewers from [path fallback rules](#review_path_fallbacks)
* If there are still not enough reviewers, assign at random from a list of [all reviewers](#reviewers)
Limits can be set on [files per reviewer](#max_files_per_reviewer) and [lines of code per reviewer](#max_lines_per_reviewer). This helps by adding reviewers as needed.
## Support
Pull Review supports Node.js 8+.
## License
[MIT](http://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
## Credits
Made by [Ivan Malopinsky](http://imsky.co).