https://github.com/interactivecomputergraphics/splishsplash
SPlisHSPlasH is an open-source library for the physically-based simulation of fluids.
https://github.com/interactivecomputergraphics/splishsplash
deformable-solids fluid-dynamics fluid-simulation fluids multiphase-flow simulation smoothed-particle-hydrodynamics sph sph-fluids viscous-fluids
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
SPlisHSPlasH is an open-source library for the physically-based simulation of fluids.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/interactivecomputergraphics/splishsplash
- Owner: InteractiveComputerGraphics
- License: mit
- Created: 2016-11-17T19:14:23.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-04T07:39:35.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-28T17:02:52.058Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: deformable-solids, fluid-dynamics, fluid-simulation, fluids, multiphase-flow, simulation, smoothed-particle-hydrodynamics, sph, sph-fluids, viscous-fluids
- Language: C++
- Homepage: https://splishsplash.physics-simulation.org/
- Size: 17.3 MB
- Stars: 1,687
- Watchers: 70
- Forks: 297
- Open Issues: 15
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: Changelog.txt
- License: LICENSE
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

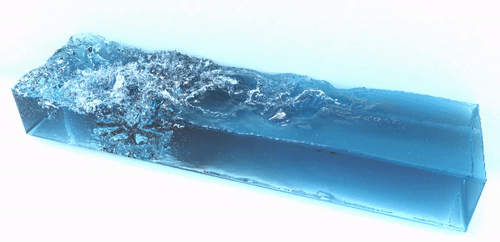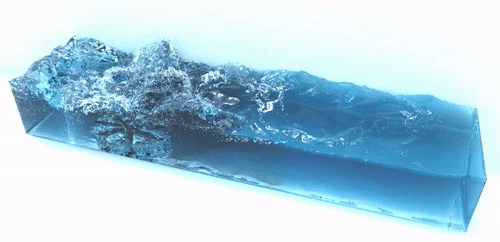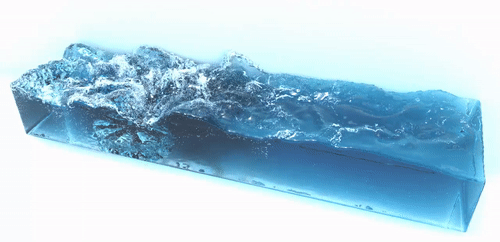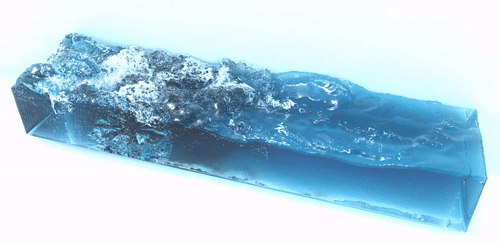
SPlisHSPlasH is an open-source library for the physically-based simulation of fluids. The simulation in this library is based on the Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) method which is a popular meshless Lagrangian approach to simulate complex fluid effects. The SPH formalism allows an efficient computation of a certain quantity of a fluid particle by considering only a finite set of neighboring particles. One of the most important research topics in the field of SPH methods is the simulation of incompressible fluids. SPlisHSPlasH implements current state-of-the-art pressure solvers (WCSPH, PCISPH, PBF, IISPH, DFSPH, PF) to simulate incompressibility. Moreover, the library provides different methods to simulate viscosity, surface tension and vorticity.
The library uses the following external libraries: [Eigen](http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/), [json](https://github.com/nlohmann/json/), [partio](https://github.com/wdas/partio/), [zlib](https://github.com/madler/zlib), [cxxopts](https://github.com/jarro2783/cxxopts), [tinyexpr](https://github.com/codeplea/tinyexpr), [toojpeg](https://github.com/stbrumme/toojpeg), [pybind](https://github.com/pybind/pybind11), [glfw](https://www.glfw.org/), [hapPLY](https://github.com/nmwsharp/happly), [nfd](https://github.com/btzy/nativefiledialog-extended), and [imgui](https://github.com/ocornut/imgui). All external dependencies are included.
Furthermore we use our own libraries:
- [PositionBasedDynamics](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/PositionBasedDynamics/) to simulate dynamic rigid bodies
- [Discregrid](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/Discregrid) to detect collisions between rigid bodies
- [CompactNSearch](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/CompactNSearch) to perform the neighborhood search
- [cuNSearch](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/cuNSearch) to perform the neighborhood search on the GPU
- [GenericParameters](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/GenericParameters) to handle generic parameters
SPlisHSPlasH can export the particle data in the partio and vtk format. If you want to import partio files in Maya or Blender, try out our plugins:
- [Blender Sequence Loader](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/blender-sequence-loader)
- [MayaPartioTools](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/MayaPartioTools)
**Author**: [Jan Bender](https://animation.rwth-aachen.de/person/1/)
## License
The SPlisHSPlasH library code is licensed under the MIT license. See [LICENSE](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH/blob/master/LICENSE) for details.
External dependencies are covered by separate licensing terms.
See the [extern](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH/tree/master/extern) folder for the code and respective licensing terms of each dependency.
## Documentation
* [Documentation](https://splishsplash.readthedocs.io)
* [SPH tutorial](https://interactivecomputergraphics.github.io/SPH-Tutorial)
## Forum
On our [GitHub discussions](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH/discussions) page you can ask questions, discuss about simulation topics, and share ideas.
## Build Instructions
This project is based on [CMake](https://cmake.org/). Simply generate project, Makefiles, etc. using [CMake](https://cmake.org/) and compile the project with a compiler of your choice that supports C++11. The code was tested with the following configurations:
- Windows 10 64-bit, CMake 3.18.3, Visual Studio 2019
- Debian 11.5 64-bit, CMake 3.18.4, GCC 10.2.1.
Note: Please use a 64-bit target on a 64-bit operating system. 32-bit builds on a 64-bit OS are not supported.
## Python Installation Instruction
For Windows and Linux targets there exists prebuilt python wheel files which can be installed using
```
pip install pysplishsplash
```
These are available for Python versions 3.6-3.10. See also here: [pySPlisHSPlasH](https://pypi.org/project/pySPlisHSPlasH/).
If you do not meet these conditions please refer to the build instructions and to the python binding
[Getting started guide](https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH/blob/master/doc/py_getting_started.md).
The command line simulator is available by running one of the following
```
splash
splash --help
```
## Features
SPlisHSPlasH implements:
* an open-source SPH fluid simulation (2D & 3D)
* neighborhood search on CPU or GPU
* supports vectorization using AVX
* Python binding (thanks to Stefan Jeske)
* supports embedded Python scripts
* several implicit pressure solvers (WCSPH, PCISPH, PBF, IISPH, DFSPH, PF)
* explicit and implicit viscosity methods
* current surface tension approaches
* different vorticity methods
* computation of drag forces
* support for multi-phase simulations
* simulation of deformable solids
* rigid-fluid coupling with static and dynamic bodies
* two-way coupling with deformable solids
* XSPH velocity filter
* fluid emitters
* scripted animation fields
* a json-based scene file importer
* automatic surface sampling
* a tool for volume sampling of closed geometries
* a tool to generate spray, foam and bubble particles in a postprocessing step
* a tool to skin a visual mesh to the moving particles of an elastic solid in a postprocessing step
* partio file export of all particle data
* VTK file export of all particle data (enables the data import in ParaView)
* rigid body export
* a Maya plugin to model and generate scene files
* a ParaView plugin to import particle data
A list of all implemented simulation methods can be found here:
[https://splishsplash.physics-simulation.org/features](https://splishsplash.physics-simulation.org/features/)
## Screenshots & Videos
[https://splishsplash.physics-simulation.org/gallery](https://splishsplash.physics-simulation.org/gallery/)
## Citation
To cite SPlisHSPlasH you can use this BibTeX entry:
```bibtex
@software{SPlisHSPlasH_Library,
author = {Bender, Jan and others},
license = {MIT},
title = {{SPlisHSPlasH Library}},
url = {https://github.com/InteractiveComputerGraphics/SPlisHSPlasH},
}
```