https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug
Session manager and task runner for tmux. Start your development environment within one command.
https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug
go golang hacktoberfest tmux
Last synced: 27 days ago
JSON representation
Session manager and task runner for tmux. Start your development environment within one command.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug
- Owner: ivaaaan
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-12-20T13:04:19.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-09-26T08:56:34.000Z (about 2 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-09-27T03:47:03.659Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: go, golang, hacktoberfest, tmux
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 148 KB
- Stars: 779
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 30
- Open Issues: 13
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-tmux - smug
README
# Smug - tmux session manager
[](https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug/actions)
[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/ivaaaan/smug)
Inspired by [tmuxinator](https://github.com/tmuxinator/tmuxinator) and [tmuxp](https://github.com/tmux-python/tmuxp).
Smug automates your [tmux](https://github.com/tmux/tmux) workflow. You can create a single configuration file, and Smug will create all the required windows and panes from it.
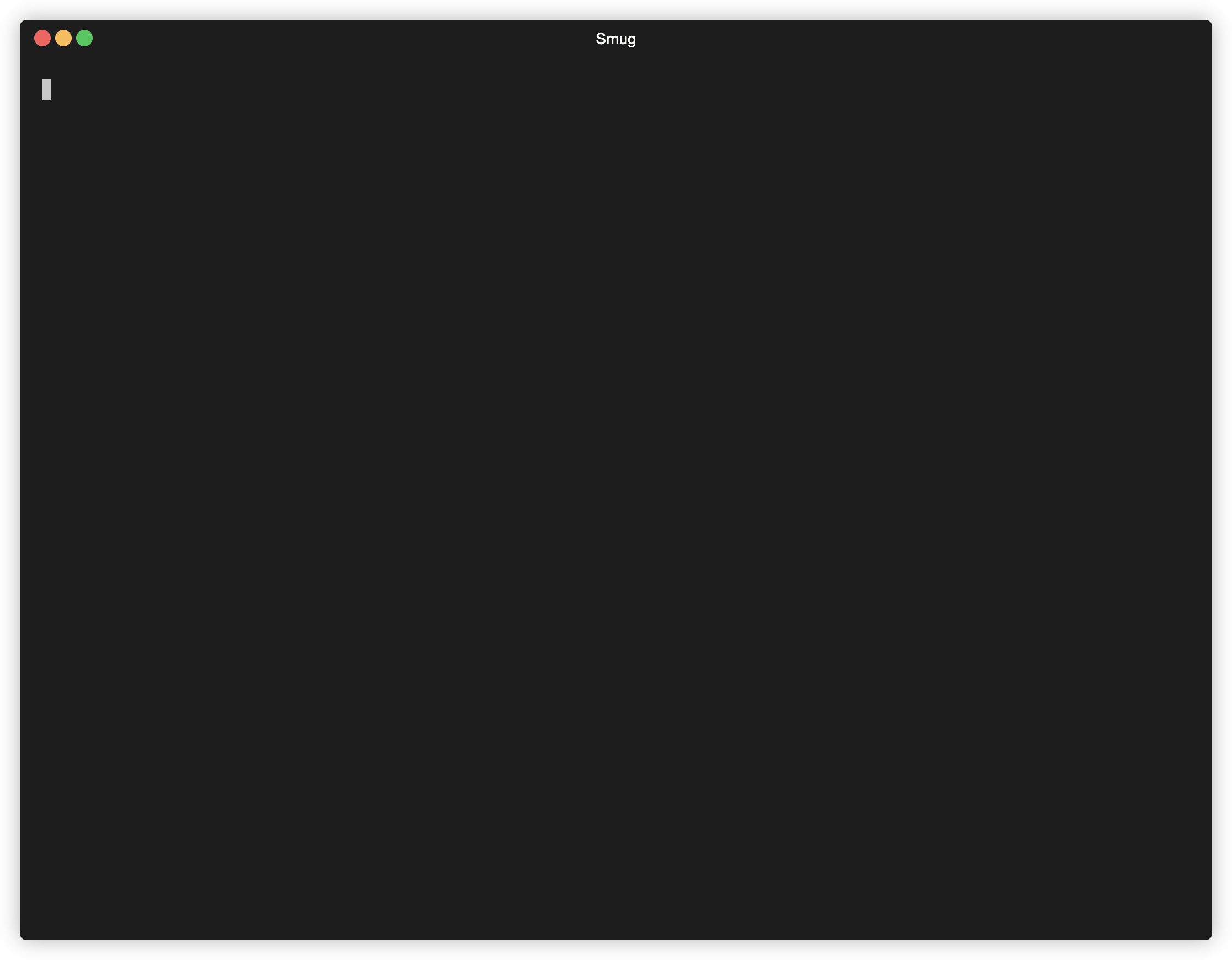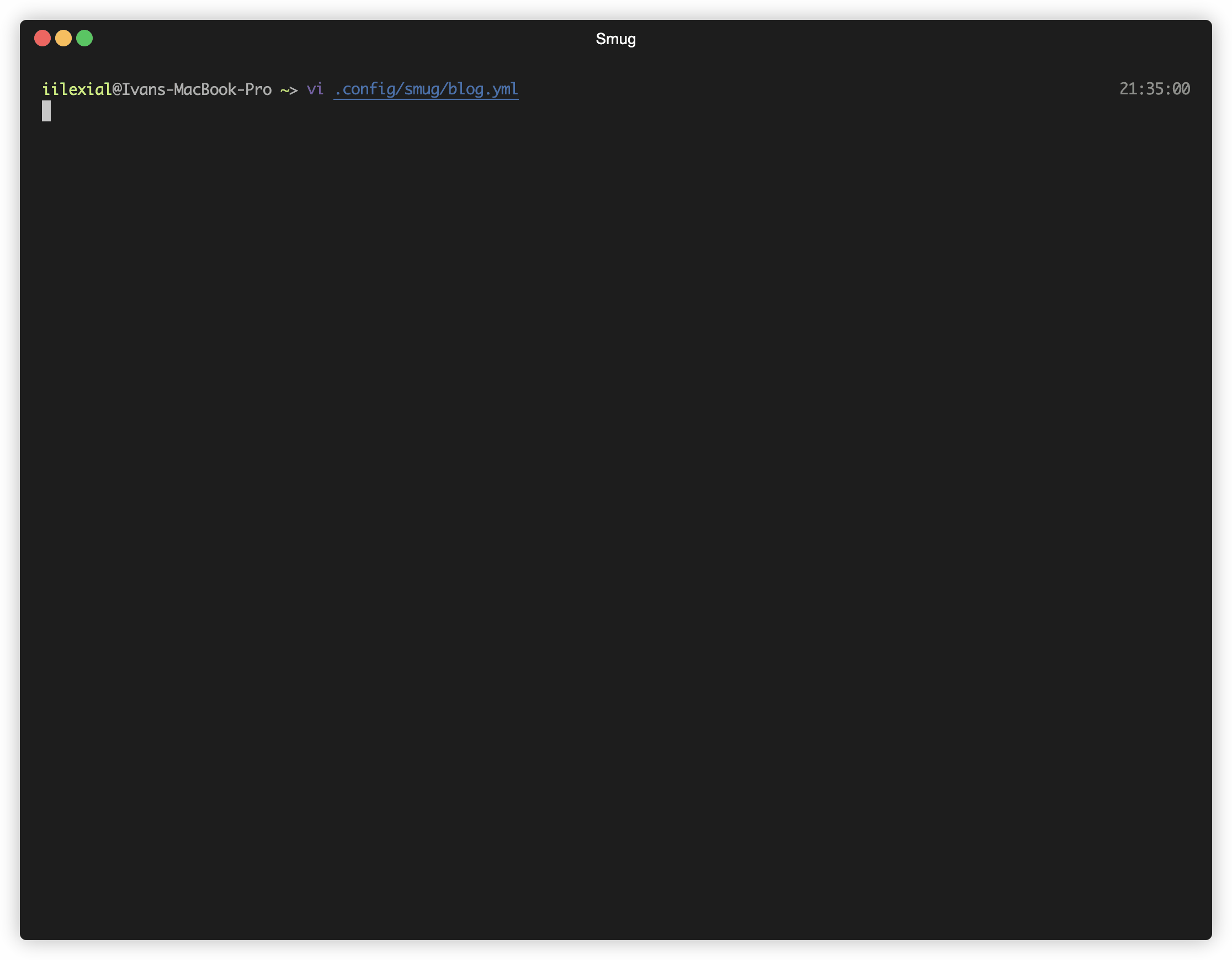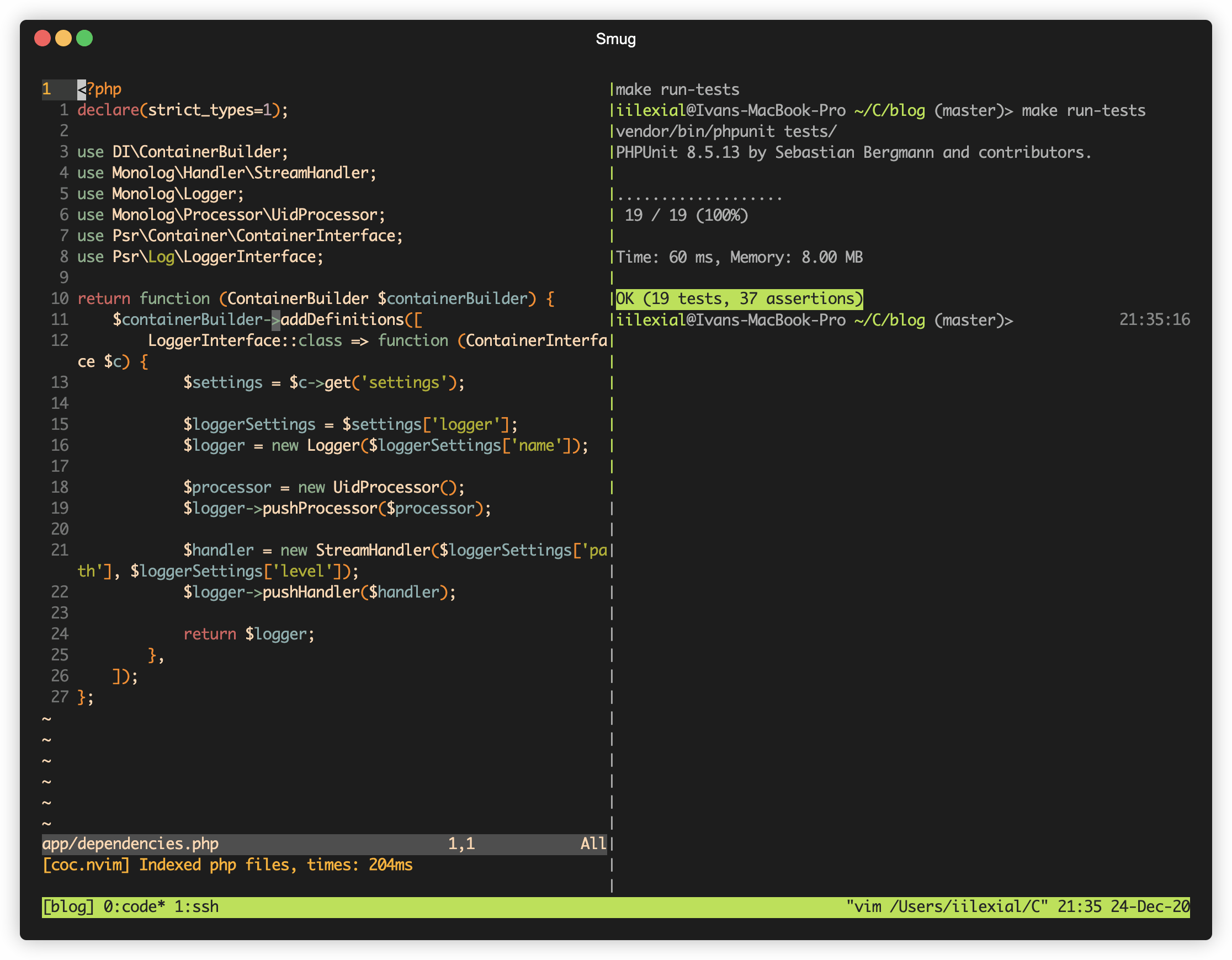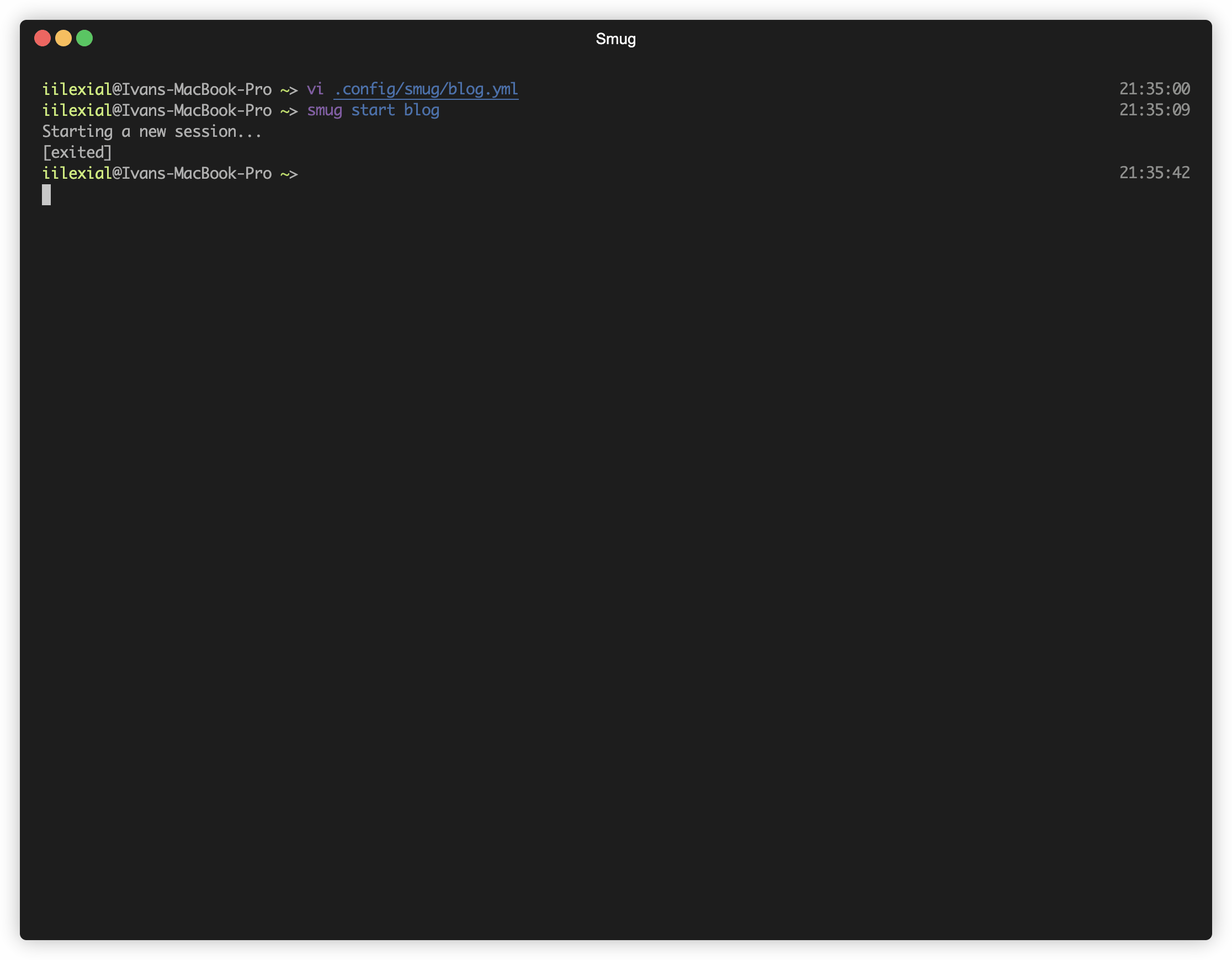
The configuration used in this GIF can be found [here](#example-2).
## Installation
### Download from the releases page
Download the latest version of Smug from the [releases page](https://github.com/ivaaaan/smug/releases) and then run:
```bash
mkdir smug && tar -xzf smug_0.1.0_Darwin_x86_64.tar.gz -C ./smug && sudo mv smug/smug /usr/local/bin && rm -rf smug
```
Don't forget to replace `smug_0.1.0_Darwin_x86_64.tar.gz` with the archive that you've downloaded.
### Go (recommended)
#### Prerequisite Tools
- [Git](https://git-scm.com/)
- [Go (we test it with the last 2 major versions)](https://golang.org/dl/)
#### Fetch from GitHub
The easiest way is to clone Smug from GitHub and install it using `go-cli`:
```bash
go install github.com/ivaaaan/smug@latest
```
### macOS
On macOS, you can install Smug using [MacPorts](https://www.macports.org) or [Homebrew](https://brew.sh).
#### Homebrew
```bash
brew install smug
```
#### MacPorts
```bash
sudo port selfupdate
sudo port install smug
```
### Linux
#### Arch
There's [AUR](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/smug) with smug.
```bash
git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/smug.git
cd smug
makepkg -si
```
## Usage
```
smug [] [-f, --file ] [-w, --windows ]... [-a, --attach] [-d, --debug]
```
### Options:
```
-f, --file A custom path to a config file
-w, --windows List of windows to start. If session exists, those windows will be attached to current session.
-a, --attach Force switch client for a session
-i, --inside-current-session Create all windows inside current session
-d, --debug Print all commands to ~/.config/smug/smug.log
--detach Detach session. The same as `-d` flag in the tmux
```
### Custom settings
You can pass custom settings into your configuration file. Use `${variable_name}` syntax in your config and then pass key-value args:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project variable_name=value
```
### Examples
To create a new project, or edit an existing one in the `$EDITOR`:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug new project
xyz@localhost:~$ smug edit project
```
To start/stop a project and all windows, run:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop project
```
Also, smug has aliases to the most of the commands:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug project # the same as "smug start project"
xyz@localhost:~$ smug st project # the same as "smug stop project"
xyz@localhost:~$ smug p ses # the same as "smug print ses"
```
When you already have a running session, and you want only to create some windows from the configuration file, you can do something like this:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project:window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project:window1,window2
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project -w window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start project -w window1 -w window2
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop project:window1
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop project -w window1 -w window2
```
Also, you are not obliged to put your files in the `~/.config/smug` directory. You can use a custom path in the `-f` flag:
```console
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start -f ./project.yml
xyz@localhost:~$ smug stop -f ./project.yml
xyz@localhost:~$ smug start -f ./project.yml -w window1 -w window2
```
## Configuration
Configuration files can stored in the `~/.config/smug` directory in the `YAML` format, e.g `~/.config/smug/your_project.yml`.
You may also create a file named `.smug.yml` in the current working directory, which will be used by default.
### Examples
#### Example 1
```yaml
session: blog
root: ~/Developer/blog
before_start:
- docker-compose -f my-microservices/docker-compose.yml up -d # my-microservices/docker-compose.yml is a relative to `root`
env:
FOO: BAR
stop:
- docker stop $(docker ps -q)
windows:
- name: code
root: blog # a relative path to root
manual: true # you can start this window only manually, using the -w arg
layout: main-vertical
commands:
- docker-compose start
panes:
- type: horizontal
root: .
commands:
- docker-compose exec php /bin/sh
- clear
- name: infrastructure
root: ~/Developer/blog/my-microservices
layout: tiled
panes:
- type: horizontal
root: .
commands:
- docker-compose up -d
- docker-compose exec php /bin/sh
- clear
```
#### Example 2
```yaml
session: blog
root: ~/Code/blog
before_start:
- docker-compose up -d
stop:
- docker-compose stop
windows:
- name: code
selected: true # Selects this window at the start of the session
layout: main-horizontal
commands:
- $EDITOR app/dependencies.php
panes:
- type: horizontal
commands:
- make run-tests
- name: ssh
commands:
- ssh -i ~/keys/blog.pem ubuntu@127.0.0.1
```