https://github.com/jamsoft/JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs
Provides the ability to show various dialogs and child windows in a DI injectable application dialog service ready to plug into MVVM AvaloniaUI applications. The general idea is to make it as simple as possible to handle all the basics of using dialogs with as few assumptions as possible whilst also providing a feature rich experience.
https://github.com/jamsoft/JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs
avaloniaui c-sharp csharp dialog dotnet mvvm mvvm-architecture mvvm-pattern services window-manager windows wizard wizard-steps wizards
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Provides the ability to show various dialogs and child windows in a DI injectable application dialog service ready to plug into MVVM AvaloniaUI applications. The general idea is to make it as simple as possible to handle all the basics of using dialogs with as few assumptions as possible whilst also providing a feature rich experience.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jamsoft/JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs
- Owner: jamsoft
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-02-17T01:04:52.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-26T13:09:59.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-23T00:27:11.982Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: avaloniaui, c-sharp, csharp, dialog, dotnet, mvvm, mvvm-architecture, mvvm-pattern, services, window-manager, windows, wizard, wizard-steps, wizards
- Language: C#
- Homepage:
- Size: 389 KB
- Stars: 9
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-avalonia - JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs - An MVVM dialog service, allows custom views, file dialogs and includes a complete multistep Wizard Control. (Libraries & Extensions / Controls)
README
# Introduction
Provides the ability to show various dialogs, child windows, message boxes and Wizards in a DI injectable service ready to plug into MVVM AvaloniaUI applications.
The general idea is to make it as simple as possible to handle all the basics of using dialogs with as few assumptions as possible whilst also providing a feature rich experience.
More or less everything is replaceable, extendable & customisable.
## GitHub Pages Site


[](https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/jamsoft/jamsoft.avaloniaui.dialogs)
https://jamsoft.github.io/JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs/
## Installation
```shell
dotnet add package JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs --version 1.4.0
```
```shell
Install-Package JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs -Version 1.4.0
```
```xml
```
```shell
paket add JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs --version 1.4.0
```
### Tested On
- Windows 10 & 11
- MacOS Sonoma 14.5
- Pop!_OS 22.04
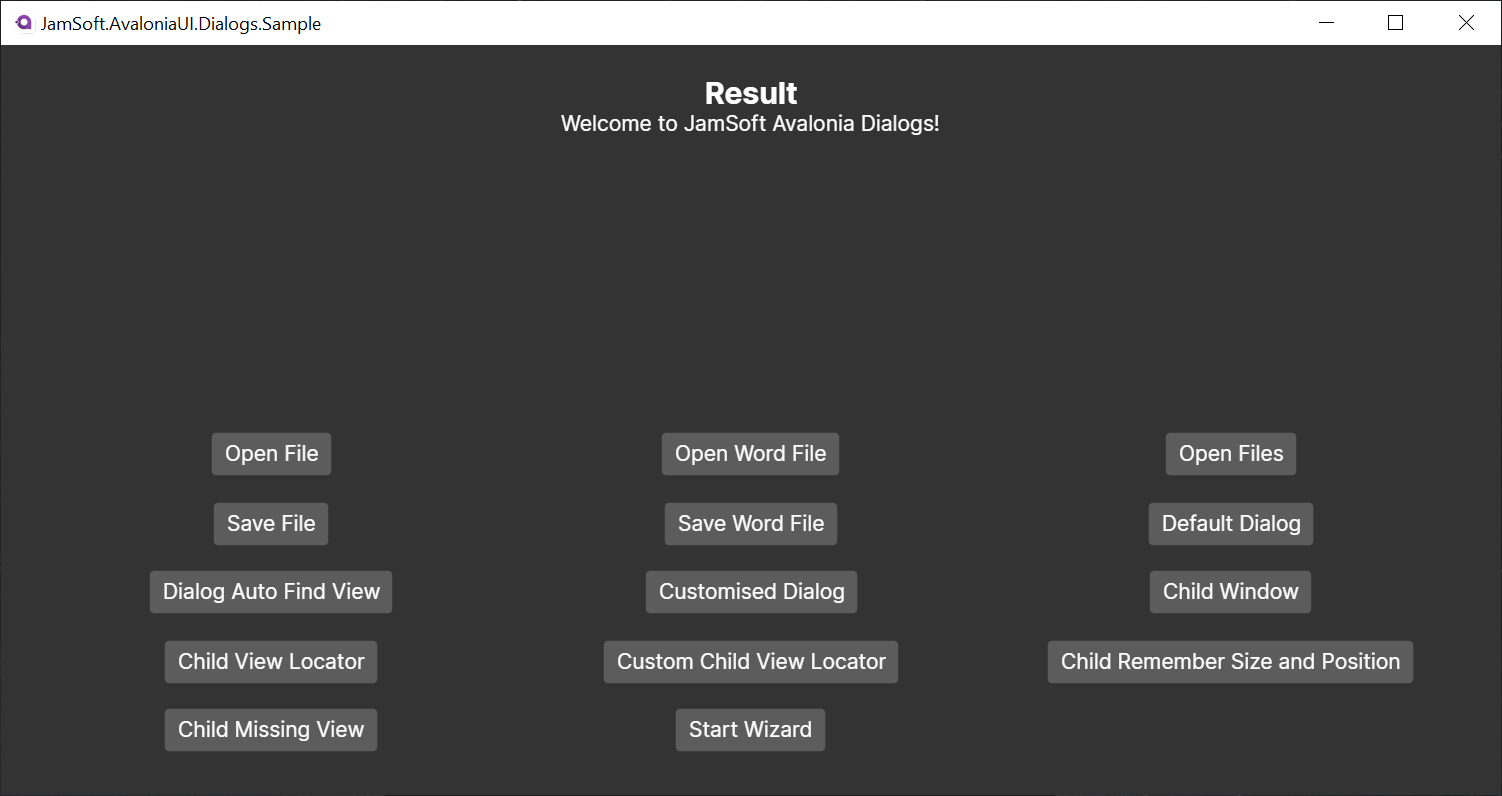
## Sample Application
The sample application demonstrates how to use the library in a real-world scenario. It shows how to use the dialog service to open files, save files, show message boxes, show dialogs and child windows. It also demonstrates how to use the wizard control along with saving and restoring window sizes and positions.
## Import Styles
### All Defaults
```xml
```
### Individual Style Files
```xml
```
### Custom Window Styling
Since we are using plain old `Window` objects, basic styling properties like `Background` colors will be inherited from your own applications default `Window` style, such as:
```xml
<Setter Property="Background" Value="#333333" />
```
The same is true for your default button styles and basic text and font settings so theming things should be little more than plugging in the library and starting to use it.
## Creating Service Instances
#### Dialog Service
```csharp
IDialogService dialogService = DialogServiceFactory.Create(new DialogServiceConfiguration({
ApplicationName = "Dialog Sample App",
UseApplicationNameInTitle = true,
ViewsAssemblyName = Assembly.GetExecutingAssembly().GetName().Name
});
```
#### MessageBox Service
```csharp
IMessageBoxService msgboxService = DialogServiceFactory.CreateMessageBoxService();
```
## Registration Example Using Splat DI
#### Registering the Services - Program.cs
```csharp
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
RegisterDependencies();
BuildAvaloniaApp()
.StartWithClassicDesktopLifetime(args);
}
private static void RegisterDependencies() =>
BootStrapper.Register(Locator.CurrentMutable, Locator.Current);
```
#### Registering the Services - Bootstrapper.cs
```csharp
public class BootStrapper
{
public static void Register(IMutableDependencyResolver services, IReadonlyDependencyResolver resolver)
{
services.RegisterLazySingleton(() => DialogServiceFactory.Create(new DialogServiceConfiguration
{
ApplicationName = "Dialog Sample App",
UseApplicationNameInTitle = true,
ViewsAssemblyName = "JamSoft.AvaloniaUI.Dialogs.Sample"
}));
services.RegisterLazySingleton(DialogServiceFactory.CreateMessageBoxService);
services.Register(() => new MainWindowViewModel(resolver.GetService()!, resolver.GetService()!));
services.Register(() => new MyDialogViewModel());
services.Register(() => new MyChildViewModel());
}
}
```
# Usage
## Resolving Services
Now that we have this setup and registered, we can make use of the service from view models like this. First, add it as a constructor parameter.
```csharp
private readonly IDialogService _dialogService;
private readonly IMessageBoxService _messageBoxService;
public MainWindowViewModel(IDialogService dialogService, IMessageBoxService messageBoxService)
{
_dialogService = dialogService;
_messageBoxService = messageBoxService;
}
...
```
# Usage - Message Boxes
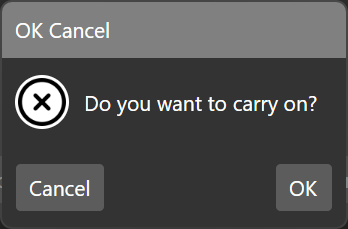
The message box implementation closely follows the .NET/Forms/WPF `MessageBox` class. It provides a simple way to show message boxes with various button configurations and icons.
## Result Object
The `Show` method returns a `MsgBoxResult` object which contains the button result that was clicked by the user. This can be used to determine the action to take in your application.
If the checkbox is also used, by providing text for the `CheckBox` message in the `Show` call, the result can be checked in the returned `MsgBoxResult` object.
```csharp
public sealed class MsgBoxResult
{
public MsgBoxButtonResult ButtonResult { get; }
public bool CheckBoxResult { get; }
private MsgBoxResult(bool checkBoxResult, MsgBoxButtonResult buttonResult)
{
CheckBoxResult = checkBoxResult;
ButtonResult = buttonResult;
}
public static MsgBoxResult CreateResult(bool checkBoxChecked, MsgBoxButtonResult buttonResult) => new(checkBoxChecked, buttonResult);
}
```
## Show Message Box
```csharp
var msgbResult = await _messageBoxService.Show("OK Cancel", "Do you want to carry on?", MsgBoxButton.OkCancel, MsgBoxImage.Question);
```
You can also pass a view model instance to the `Show` method to customise the message box using the default provided `MsgBoxViewModel` class.
```csharp
var viewModel = new MsgBoxViewModel("Yes No With Icon", "Do you want to carry on?", MsgBoxButton.YesNo, MsgBoxImage.Warning);
var btnResult = await _messageBoxService.Show(viewModel);
```
You can also use any custom view model class by implementing the `IMessageBoxViewModel` interface.
```csharp
public class MyCustomMsgBoxViewModel : IMsgBoxViewModel
{
}
var myCustomMsgBoxViewModel = new MyCustomMsgBoxViewModel();
...
var btnResult = await _messageBoxService.Show(myCustomMsgBoxViewModel);
```
### Custom Icons
```csharp
var viewModel = new MsgBoxViewModel("Yes No With Icon", "Do you want to carry on?", MsgBoxButton.YesNo, MsgBoxImage.Custom);
viewModel.Icon = new Bitmap("myicon.png");
var result = await _messageBoxService.Show(viewModel);
```
### Changing Icon Background Color
```xml
<Setter Property="Fill" Value="Red"/>
```
### Custom Button Text
```csharp
var result = await _messageBoxService.Show("German Yes No Cancel", "Möchten Sie weitermachen?",
MsgBoxButton.YesNoCancel,
MsgBoxImage.Question, "Nein", "Ja", "Abbrechen");
```
### Show Message Box With Checkbox

```csharp
var msgBoxResult = await _messageBoxService.Show("OK Cancel With Checkbox", "Do you want to carry on?", MsgBoxButton.OkCancel, MsgBoxImage.Error, checkBoxText:"Don't ask me again");
msgBoxResult.ButtonResult;
msgBoxResult.CheckBoxResult;
```
# File Paths
### Open Any File
```csharp
string path = await _dialogService.OpenFile("Open Any File");
```
### Open A Specific File Type
```csharp
string path = await _dialogService.OpenFile("Open Word File", new List
{
new("Word Files")
{
Patterns = new List { "*.docx", "*.doc" },
AppleUniformTypeIdentifiers = new List { "com.microsoft.word.doc", "org.openxmlformats.wordprocessingml.document" },
MimeTypes = new List { "application/msword", "application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.wordprocessingml.document" }
}
});
```
You can also make use of the built in `CommonFilters` helper class.
```csharp
string path = await _dialogService.OpenFile("Open Word File", new List
{
CommonFilters.WordFilter
});
```
### Open Multiple Files
```csharp
string[] paths = await _dialogService.OpenFiles("Open Multiple Files");
```
### Save Any Path
```csharp
string path = await _dialogService.SaveFile("Save Any File");
```
### Save To Your Custom File Type
```csharp
string path = await _dialogService.SaveFile("Save New MyApp Project", new List
{
new()
{
Name = "MyApp Project",
Patterns = new List { "*.myappext" },
AppleUniformTypeIdentifiers = new List { "com.myorgname.myappext" },
}
});
```
# Usage - Dialogs
There are two base view model classes already baked in for ease of use of the library. These are provided as defaults and a starting point. Create a suitable view model and inherit from either `DialogViewModel` or `ChildWindowViewModel` as base class.
## Show Dialog

```csharp
_dialogService.ShowDialog(Locator.Current.GetService(), DialogCallback);
private void DialogCallback(MyDialogViewModel obj)
{
Message = obj.DialogMessage;
}
```
### Custom Button Text
```csharp
private void ShowCustomizedDialogCommandExecuted()
{
var vm = Locator.Current.GetService();
vm.AcceptCommandText = "Accept";
vm.CancelCommandText = "Oh No!";
_dialogService.ShowDialog(vm, DialogCallback);
}
```
### Alternate Views
```csharp
private void ShowCustomizedDialogCommandExecuted()
{
var vm = Locator.Current.GetService();
vm.AcceptCommandText = "Accept";
vm.CancelCommandText = "Oh No!";
_dialogService.ShowDialog(new MyAlternateDialogView(), vm, DialogCallback);
}
```
### Default Key Mapping
The dialog buttons are also associated with their keyboard inputs.
```xml
```
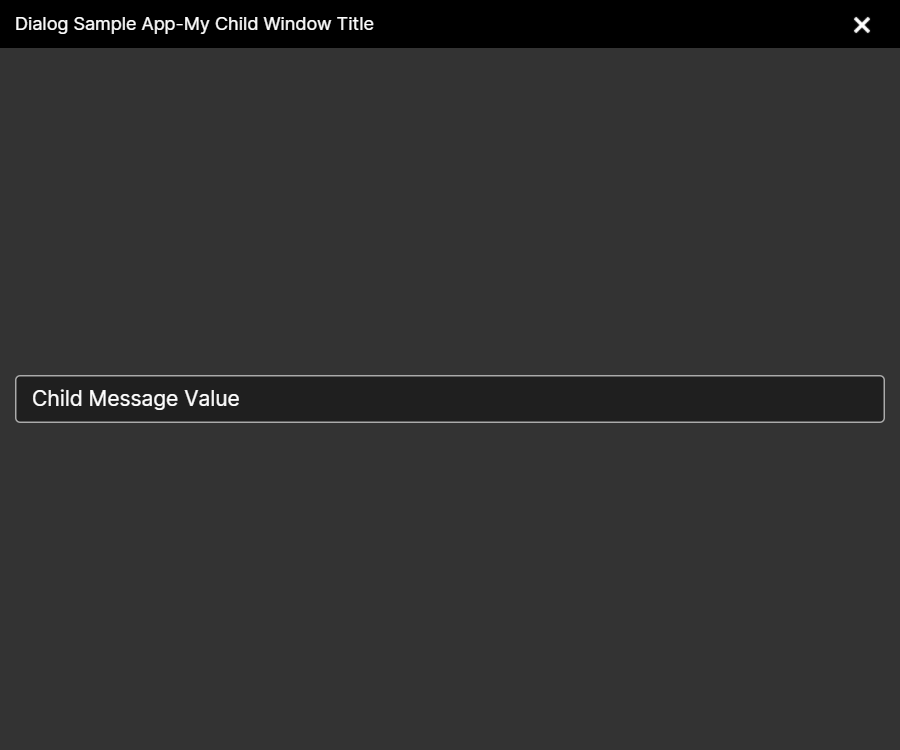
## Show Child Window
```csharp
private void ShowChildWindowCommandExecuted()
{
var vm = Locator.Current.GetService();
// these values could be stored in user settings and loaded at runtime etc.
vm.RequestedLeft = 50;
vm.RequestedTop = 50;
vm.RequestedHeight = 600;
vm.RequestedWidth = 800;
vm.ChildMessage = "Child Message Value";
vm.ChildWindowTitle = "My Child Window Title";
_dialogService.ShowChildWindow(vm, model =>
{
Message = $"Child Closed - {model.ChildMessage}";
});
}
```
The child windows are draggable and also update these properties in real-time. This means that your application can easily restore child window positions between application runs by storing these values.
## Show Child Window - Alternate View Parameter
```csharp
private void ShowChildWindowCommandExecuted()
{
var vm = Locator.Current.GetService();
...
_dialogService.ShowChildWindow(new MyAlternateChildView(), vm, model =>
{
Message = $"Child Closed - {model.ChildMessage}";
});
}
```
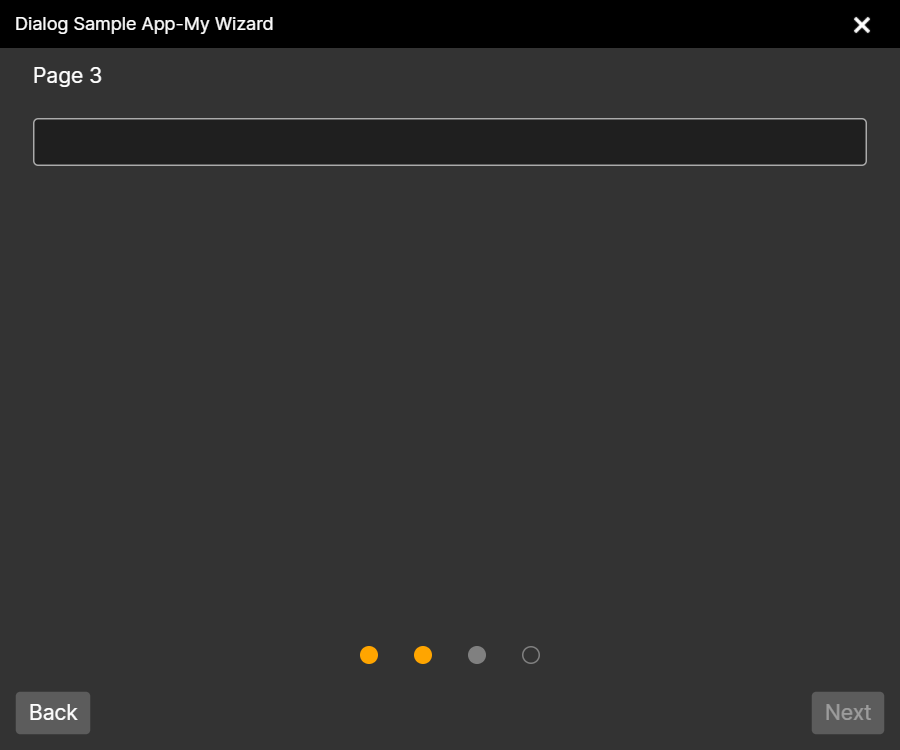
## Wizard Control
The library also has a wizard control allowing multiple page dialogs. You can define a wizard like this:
```csharp
private void WizardViewCommandExecuted()
{
var vm = Locator.Current.GetService();
vm.RequestedLeft = MyUserSettings.Instance.Left;
vm.RequestedTop = MyUserSettings.Instance.Top;
vm.RequestedHeight = MyUserSettings.Instance.Height;
vm.RequestedWidth = MyUserSettings.Instance.Width;
vm.ChildWindowTitle = "My Wizard";
_dialogService.StartWizard(vm, model =>
{
Message = $"Wizard Closed - {model.GetType()}";
});
}
```
```xml
Page 1
Page 2
Page 3
Final Step
```
The `WizardStep` defines a bindable property called `StepComplete` which you can bind in your view model to control step validation and navigation. It also makes use of the `ChildWindow` so inherits the position awareness should you want that functionality.
# Saving & Restoring Window Positions
First you need a mechanism to store positions as set by the user moving things around.
```csharp
public class MyUserSettings : SettingsBase
{
public double Left { get; set; } = 50;
public double Top { get; set; } = 50;
public double Height { get; set; } = 600;
public double Width { get; set; } = 800;
}
```
`SettingsBase` can be found in the JamSoft.Helpers package https://github.com/jamsoft/JamSoft.Helpers
Nuget - https://www.nuget.org/packages/JamSoft.Helpers
Then in your view model you can listen for the `RequestCloseDialog` event and respond accordingly by storing the settings in the `OnRequestCloseDialog` method.
```csharp
public class MyChildWindowViewModel : ChildWindowViewModel
{
private string? _childMessage;
public MyChildWindowViewModel()
{
RequestCloseDialog += OnRequestCloseDialog;
}
public string? ChildMessage
{
get => _childMessage;
set => RaiseAndSetIfChanged(ref _childMessage, value);
}
private void OnRequestCloseDialog(object? sender, RequestCloseDialogEventArgs e)
{
MyUserSettings.Instance.Top = RequestedTop;
MyUserSettings.Instance.Left = RequestedLeft;
MyUserSettings.Instance.Width = RequestedWidth;
MyUserSettings.Instance.Height = RequestedHeight;
RequestCloseDialog -= OnRequestCloseDialog;
}
}
```
The next time this view model is requested by the user you can then restore these values.
```csharp
vm.RequestedLeft = MyUserSettings.Instance.Left;
vm.RequestedTop = MyUserSettings.Instance.Top;
vm.RequestedHeight = MyUserSettings.Instance.Height;
vm.RequestedWidth = MyUserSettings.Instance.Width;
vm.ChildWindowTitle = "My Custom Child Window Title";
_dialogService.ShowChildWindow(vm, model =>
{
Message = $"Child Remember Position Closed - {model.GetType()}";
});
```
See the Sample Application for a complete implementation example and further guidance.
## Application Styles
You can easily target elements of the dialogs via their names and types, such as:
```xml
<Setter Property="Background" Value="#c42b1c" />
<Setter Property="Height" Value="32"/>
<Setter Property="Background" Value="#000000"/>
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="12"/>
<Setter Property="VerticalAlignment" Value="Center" />
<Setter Property="Margin" Value="10,0"/>
<Setter Property="Fill" Value="DeepPink" />
<Setter Property="StrokeThickness" Value="0" />
<Setter Property="IsVisible" Value="False" />
```
#### Known Issues
Window sizes and positions on Linux not always accurate due to window manager differences. Under investigation.