https://github.com/jevonmao/permissionsswiftui
A SwiftUI package to beautifully display and handle permissions.
https://github.com/jevonmao/permissionsswiftui
coding developer github ios ios-swift learn-swift library macos package programming swift swiftpackage swiftui swiftui-learning ui-design ux
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
A SwiftUI package to beautifully display and handle permissions.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jevonmao/permissionsswiftui
- Owner: jevonmao
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-01-30T18:50:24.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-04-06T10:15:25.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-15T15:06:48.883Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: coding, developer, github, ios, ios-swift, learn-swift, library, macos, package, programming, swift, swiftpackage, swiftui, swiftui-learning, ui-design, ux
- Language: Swift
- Homepage: https://jevonmao.github.io/PermissionsSwiftUI/
- Size: 19.2 MB
- Stars: 1,507
- Watchers: 9
- Forks: 86
- Open Issues: 15
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

# PermissionsSwiftUI: A SwiftUI package to handle permissions







`PermissionsSwiftUI` displays and handles permissions in SwiftUI. It is largely inspired by [SPPermissions](https://github.com/varabeis/SPPermissions).
The UI is highly customizable and resembles an **Apple style**. If you like the project, please `star ★`.
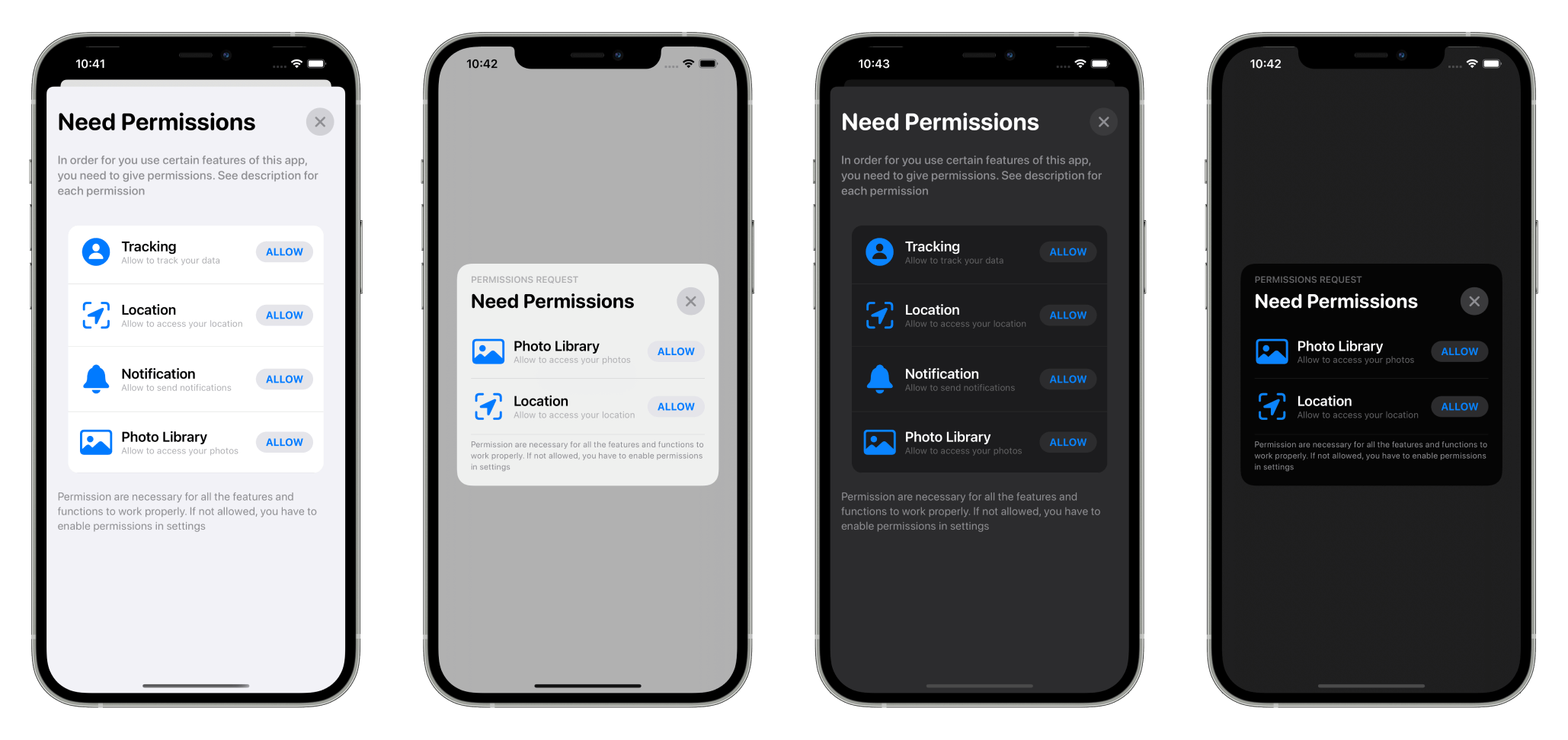
PermissionsSwiftUI looks equally gorgeous on both ☀️light and 🌑 dark mode.
## 🧭 Navigation
- [Installation](#-installation)
- [Quickstart](#-quickstart)
Usage
- [Usage](#-usage)
- [Customize Permission Texts](#customize-permission-texts)
- [Customize header texts](#customize-header-texts)
- [`onAppear` and `onDisappear` Override](#onappear-and-ondisappear-override)
- [Auto Check Authorization](#auto-check-authorization)
- [Auto Dismiss](#auto-dismiss)
- [Customize Colors](#customize-colors)
- [Restrict Dismissal](#restrict-dismissal)
- [Configuring Health Permissions](#configuring-health-permissions)
- [Cheatsheet](#-cheatsheat)
- [Supported Permissions](#-supported-permissions)
- [Contribute](#-contribute)
Additional Information
- [Additional Information](#additional-information)
- [Acknowledgement](#acknowledgement)
- [License](#license)
## 🖥️ Installation
### Requirements
* iOS 11 (SwiftUI require iOS 13.0) or iPadOS 13
* Xcode 12 and Swift 5.3
* tvOS support coming soon
* No MacOS, and WatchOS support for now
### Install
#### Swift Package Manager (Recommended)
You can install PermissionsSwiftUI into your Xcode project via SPM.
To learn more about SPM, click [here](https://swift.org/package-manager/)
1. In Xcode 12, open your project and navigate to **File** → **Swift Packages** → **Add Package Dependency...**
For Xcode 13, navigate to **Files** → **Add Package**
2. Paste the repository URL (`https://github.com/jevonmao/PermissionsSwiftUI`) and click **Next**.
3. For **Version**, verify it's **Up to next major**.
4. Click **Next** and ONLY SELECT PERMISSIONS NEEDED else Apple will reject your app
(You don't need to add CorePermissionsSwiftUI or PermissionsSwiftUI)

5. Click **Finish**
6. You are all set, thank you for using PermissionsSwiftUI!
#### Cocoapods (Deprecated)
You can also install PermissionsSwiftUI with Cocoapods. Add `pod 'PermissionsSwiftUI'` in your podfile:
```Ruby
platform :ios, '14.0'
target 'test abstract' do
use_frameworks!
pod 'PermissionsSwiftUI'
end
```
## 🚀 Quickstart
> Before you start, please `star ★` this repository. Your star is my biggest motivation to pull all-nighters and maintain this open-source project.
### ⚠️ v1.4.0 Migration Guide
`v1.4` is here! If you encounter any issues, please check out the [migration guide](https://github.com/jevonmao/PermissionsSwiftUI/wiki/Migrating-to-v1.4.0) designed to help developers resolve any deprecations and API updates.
### Modal Style
To use PermissionsSwiftUI, simply add the `JMModal` modifier to any view:
```Swift
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, for: [.locationAlways, .photo, .microphone])`
```
Pass in a `Binding` to show the modal view, and add whatever permissions you want to show. For example:
```Swift
struct ContentView: View {
@State var showModal = false
var body: some View {
Button(action: {
showModal=true
}, label: {
Text("Ask user for permissions")
})
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, for: [.locationAlways, .photo, .microphone])
}
}
```
### Alert Style

The alert style is equally gorgeous, and allows for more versatile use. It is recommended when you have less than 3 permissions.
To show a permission pop up alert, use:
```Swift
.JMAlert(showModal: $showModal, for: [.locationAlways, .photo])
```
Similar to the previous `JMPermissions`, you need to pass in a `Binding` to show the view, and add whatever permissions you want to show.
To quickly glance at all of PermissionsSwiftUI's customization and configurations, check out the [cheatsheet](#cheatsheat)!
## 🛠️ Usage
### Customize Permission Texts
To customize permission texts, use the modifier `setPermissionComponent()`
For example, you can change title, description, and image icon:
```Swift
.setPermissionComponent(for: .camera,
image: AnyView(Image(systemName: "camera.fill")),
title: "Camcorder",
description: "App needs to record videos")
```
and the result:

Or only change 1 of title and description:
```Swift
setPermissionComponent(for: .tracking, title: "Trackers")
```
```Swift
setPermissionComponent(for: .tracking, description: "Tracking description")
```
**Note:**
* The parameters you don't provide will show the default text
* Add the `setPermissionComponent` modifier on your root level view, after `JMPermissions` modifier
The `image` parameter accepts **AnyView**, so feel free to use [SF Symbols](https://developer.apple.com/design/human-interface-guidelines/sf-symbols/overview/) or your custom asset:
```Swift
.setPermissionComponent(for: .camera,
image: AnyView(Image("Your-cool-image"))
```
Even full SwiftUI views will work😱:
```Swift
.setPermissionComponent(for: .camera,
image: AnyView(YourCoolView())
```
You can use custom text and icons for all the supported permissions, with a single line of code.
### Customize Header Texts
To customize the header title, use the modifier `changeHeaderTo`:
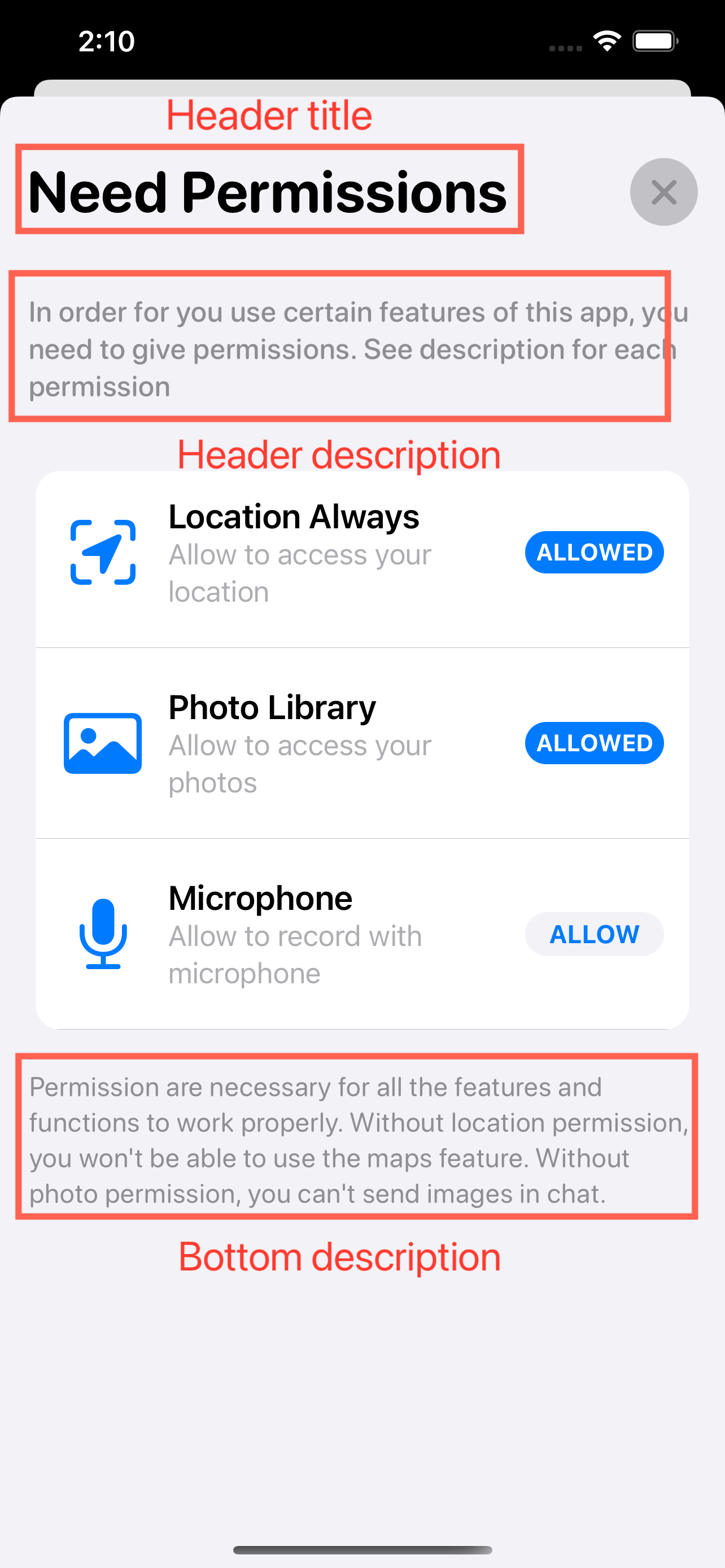
```Swift
.JMPermissions(showModal: $showModal, for: [.camera, .location, .calendar])
.changeHeaderTo("App Permissions")
```
To customize the header description, use the modifier `changeHeaderDescriptionTo`:
```Swift
.JMPermissions(showModal: $showModal, for: [.camera, .location, .photo])
.changeHeaderDescriptionTo("Instagram need certain permissions in order for all the features to work.")
```
To customize the bottom description, use the modifier `changeBottomDescriptionTo`:
```Swift
.JMPermissions(showModal: $showModal, for: [.camera, .location, .photo])
.changeBottomDescriptionTo("If not allowed, you have to enable permissions in settings")
```
### `onAppear` and `onDisappear` Override
You might find it incredibly useful to execute your code, or perform some update action when a PermissionsSwiftUI view appears and disappears.
You can perform some action when PermissionsSwiftUI view appears or disappears by:
```Swift
.JMPermissions(showModal: $showModal, for: [.locationAlways, .photo, .microphone], onAppear: {}, onDisappear: {})
```
The `onAppear` and `onDisappear` **closure parameters will be executed** everytime PermissionsSwiftUI view **appears and disappears.**
The same view modifier closure for state changes are available for the `JMAlert` modifier:
```Swift
.JMAlert(showModal: $showModal,
for: [.locationAlways, .photo],
onAppear: {print("Appeared")},
onDisappear: {print("Disappeared")})
```
### Auto Check Authorization
PermissionsSwiftUI by default will automatically check for authorization status. It will only show permissions that are currently `notDetermined` status. (the iOS system prevents developers from asking for denied permissions. Allowed permissions will also be ignored by PermissionsSwiftUI). If all permissions are allowed or denied, PermissionsSwiftUI will not show the modal or alert at all.
To set auto check authorization, use the `autoCheckAuthorization` parameter:
```Swift
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, for: [.camera], autoCheckAuthorization: false)
```
same applies for JMAlert
```Swift
.JMAlert(showModal: $showModal, for: [.camera], autoCheckAuthorization: false)
```
### Auto Dismiss
PermissionsSwiftUI by default will not have any auto dismiss behavior. You can override this behavior to make it automatically dismiss the modal or alert after the user allows the last permission item. (All permissions must be ALLOWED, if any is DENIED, it will not auto dismiss).
```Swift
.JMModal(... autoDismiss: Bool) -> some View
```
Pass in `true` or `false` to select whether to automatically dismiss the view.
### Customize Colors
Using PermissionSwiftUI's capabilities, developers and designers can customize all the UI colors with incredible flexibility. You can fully configure all color at all states with your custom colors.
To easily change the accent color:
```Swift
.setAccentColor(to: Color(.sRGB, red: 56/255, green: 173/255,
blue: 169/255, opacity: 1))
```
To change the primary (default Apple blue) and tertiary (default Apple red) colors:
```Swift
.setAccentColor(toPrimary: Color(.sRGB, red: 56/255, green: 173/255,
blue: 169/255, opacity: 1),
toTertiary: Color(.systemPink))
```

> ⚠️ `.setAccentColor()` and `.setAllowButtonColor()` should never be used at the same time.
To unleash the full customization of all button colors under all states, you need to pass in the `AllButtonColors` struct:
```Swift
.setAllowButtonColor(to: .init(buttonIdle: ButtonColor(foregroundColor: Color,
backgroundColor: Color),
buttonAllowed: ButtonColor(foregroundColor: Color,
backgroundColor: Color),
buttonDenied: ButtonColor(foregroundColor: Color,
backgroundColor: Color)))
```
For more information regarding the above method, reference the [official documentation](https://jevonmao.github.io/PermissionsSwiftUI/Structs/AllButtonColors.html).
### Restrict Dismissal
PermissionsSwiftUI will by default, prevent the user from dismissing the modal and alert before all permissions have been interacted with. This means if the user has not explicitly denied or allowed EVERY permission shown, they will not be able to dismiss the PermissionsSwiftUI view. This restricts dismissal behavior can be overridden by the `var restrictModalDismissal: Bool` or `var restrictAlertDismissal: Bool` properties.
To disable the default restrict dismiss behavior:
```Swift
.JMModal(showModal: $show, for permissions: [.camera], restrictDismissal: false)
```
You can also configure with the model:
```Swift
let model: PermissionStore = {
var model = PermissionStore()
model.permissions = [.camera]
model.restrictModalDismissal = false
model.restrictAlertDismissal = false
return model
}
......
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, forModel: model)
```
### Configuring Health Permissions
Unlike all the other permissions, the configuration for health permission is a little different. Because Apple requires developers to explicitly set read and write types, PermissionsSwiftUI greatly simplifies the process.
#### `HKAccess`
The structure HKAccess is required when initializing health permission’s enum associated values. It encapsulates the read and write type permissions for the health permission.
To set read and write health types (`activeEnergyBurned` is used as example here):
```Swift
let healthTypes = Set([HKSampleType.quantityType(forIdentifier: .activeEnergyBurned)!])
.JMModal(showModal: $show, for: [.health(categories: .init(readAndWrite: healthTypes))])
//Same exact syntax for JMAlert styles
.JMAlert(showModal: $show, for: [.health(categories: .init(readAndWrite: healthTypes))])
```
To set read or write individually:
```Swift
let readTypes = Set([HKSampleType.quantityType(forIdentifier: .activeEnergyBurned)!])
let writeTypes = Set([HKSampleType.quantityType(forIdentifier: .appleStandTime)!])
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, for: [.health(categories: .init(read: readTypes, write: writeTypes))])
```
You may also set only read or write type:
```Swift
let readTypes = Set([HKSampleType.quantityType(forIdentifier: .activeEnergyBurned)!])
.JMModal(showModal: $showModal, for: [.health(categories: .init(read: readTypes))])
```
## 📖 Cheatsheet
### Modifiers
**Customize overall accent color:**
```Swift
setAccentColor(to:)
setAccentColor(toPrimary:toTertiary:)
```
**Customize title:**
```Swift
changeHeaderTo(_:)
```
**Customize top description:**
```Swift
changeHeaderDescriptionTo(_:)
```
**Customize bottom description:**
```Swift
changeBottomDescriptionTo(_:)
```
**Customize each permission's displayed text & image:**
```Swift
setPermissionComponent(for:image:title:description:)
setPermissionComponent(for:title:)
setPermissionComponent(for:description:)
```
**Customize `allow` button's colors:**
```Swift
setAllowButtonColor(to:)
```
**Automatically dismiss after last**
```Swift
autoDismiss: Bool
```
### Parameters of `JMModal` and `JMAlert`
**Check authorization before showing modal or alert**
```Swift
autoCheckAuthorization: Bool
```
**Prevent dismissing before all permissions interacted**
```Swift
restrictDismissal: Bool
```
**Do something right before view appear**
```Swift
onAppear: () -> Void
```
**Do something right before view disappear**
```Swift
onDisappear: (() -> Void
```
## 🧰 Supported Permissions
Here is a list of all the permissions PermissionsSwiftUI supports. Yup, even the newest `tracking` permission for iOS 14 so you can stay on top of your game. All permissions in PermissionsSwiftUI come with a default name, description, and a stunning Apple native SF Symbols icon.
Support for FaceID permission is work in progress and coming soon! If you don't find a permission you need, open an issue. Even better, build it yourself and open a pull request, you can follow [this](docs/New_Permission_Guide.md) step-by-step guide on adding new permissions.

## 💪 Contribute
Contributions are welcome here for coders and non-coders alike. No matter what your skill level is, you can for certain contribute to PermissionSwiftUI's open source community. Please read [contributing.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) before starting, and if you are looking to contributing a new type of iOS permission, be sure to read this step-by-step [guide](docs/New_Permission_Guide.md).
**If you encounter ANY issue, have ANY concerns, or ANY comments, please do NOT hesitate to let me know. Open a discussion, issue, or email me.** As a developer, I feel you when you don't understand something in the codebase. I try to comment and document as best as I can, but if you happen to encounter any issues, I will be happy to assist in any way I can.
## Additional Information
### Acknowledgement
SPPermissions is in large a SwiftUI remake of the famous Swift library **[SPPermissions](https://github.com/varabeis/SPPermissions)** by @verabeis. SPPermissions was initially created in 2017, and today on GitHub has over 4000 stars. PermissionsSwiftUI aims to deliver a just as beautiful and powerful library in SwiftUI. If you `star ★` my project PermissionsSwiftUI, be sure to check out the original project SPPermissions where I borrowed the UI Design, some parts of README.md page, and important source code references along the way.
### License
PermissionsSwiftUI is created by Jingwen (Jevon) Mao and licensed under the [MIT License](https://jingwen-mao.mit-license.org)