Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/jketterl/csdr
A simple DSP library and command-line tool for Software Defined Radio.
https://github.com/jketterl/csdr
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
A simple DSP library and command-line tool for Software Defined Radio.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jketterl/csdr
- Owner: jketterl
- License: gpl-3.0
- Fork: true (ha7ilm/csdr)
- Created: 2019-06-01T15:49:37.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: develop
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-11T17:03:16.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-01T15:31:58.523Z (5 months ago)
- Language: C++
- Homepage:
- Size: 928 KB
- Stars: 46
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 20
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE-GPL
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
CSDR
====
`csdr` is a command line tool to carry out DSP tasks for Software Defined Radio.
It can be used to build simple signal processing flow graphs, right from the command line.
The included `libcsdr` library contains the DSP functions that `csdr` makes use of. It was designed to use auto-vectorization available in `gcc`.
Feel free to use it in your projects.
Most of the code is available under the permissive BSD license, with some optional parts under GPL. For additional details, see licensing.
`csdr` has already been used to build:
- AM, FM, SSB, CW and BPSK31 demodulators and waterfall display in [OpenWebRX](https://github.com/jketterl/openwebrx),
- AM, FM, SSB modulators in [qtcsdr](https://github.com/ha7ilm/qtcsdr) that can also be used standalone with [rpitx](https://github.com/ha7ilm/rpitx-app-note),
- a demodulator for FSK transmissions sent with the CC1111 wireless MCU, and also a standalone RTTY demodulator.
This animation shows the Gardner timing recovery algorithm in `csdr` locking on a baseband BPSK signal:
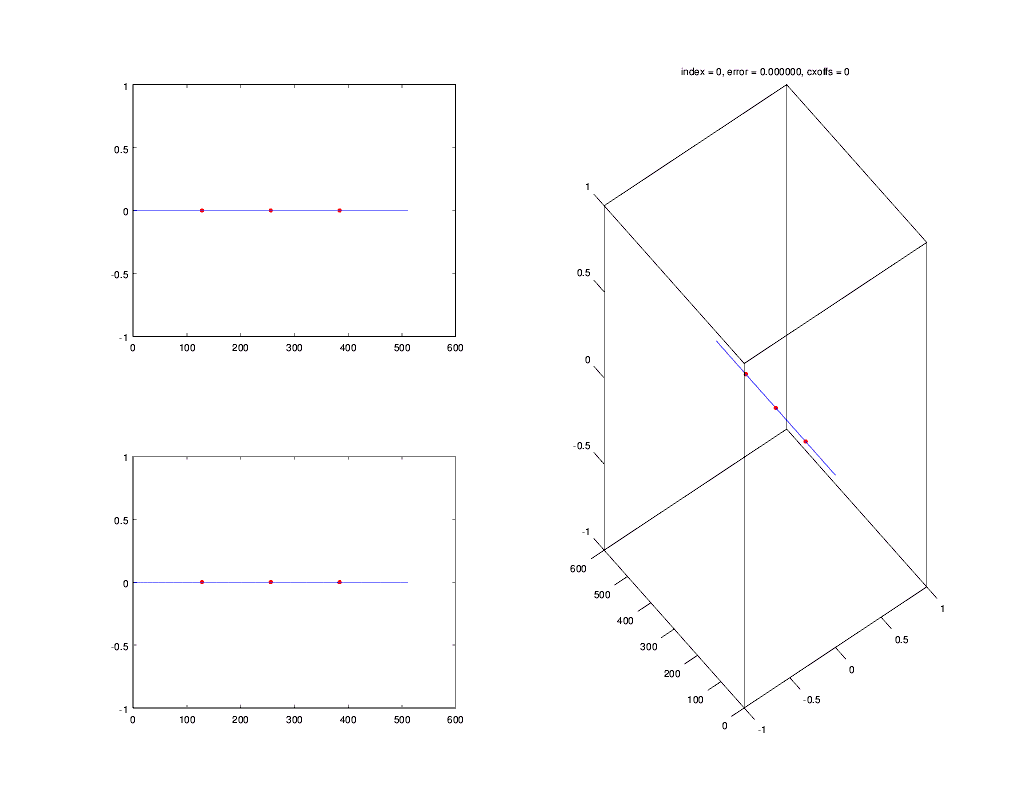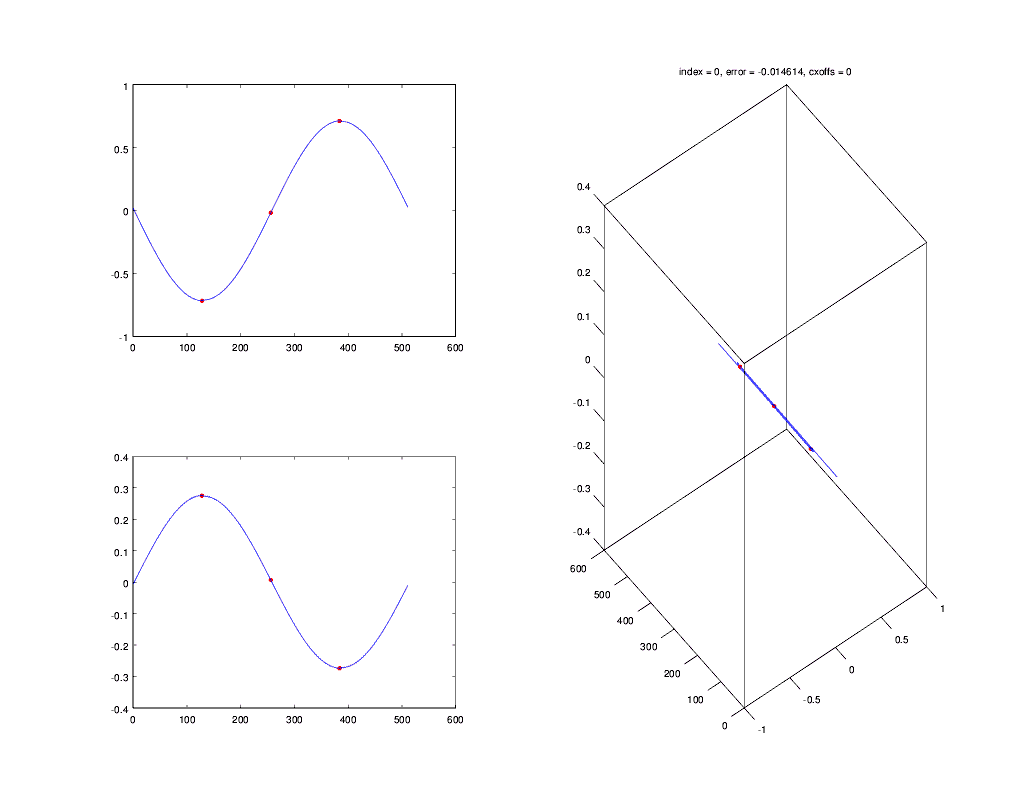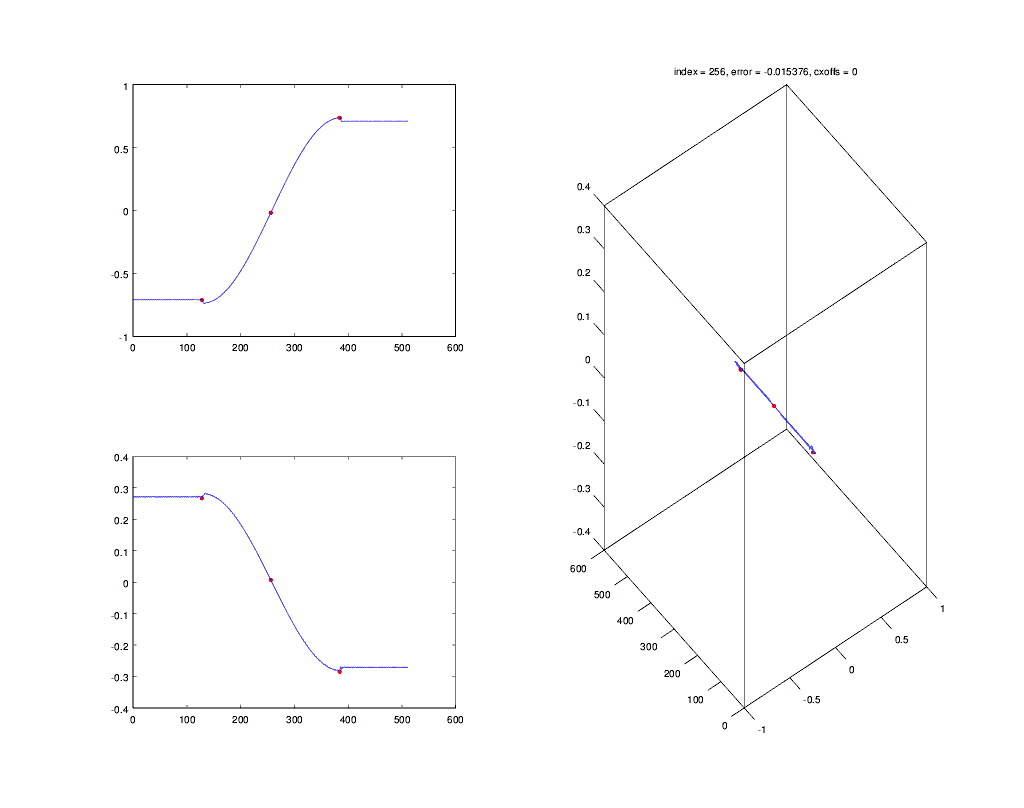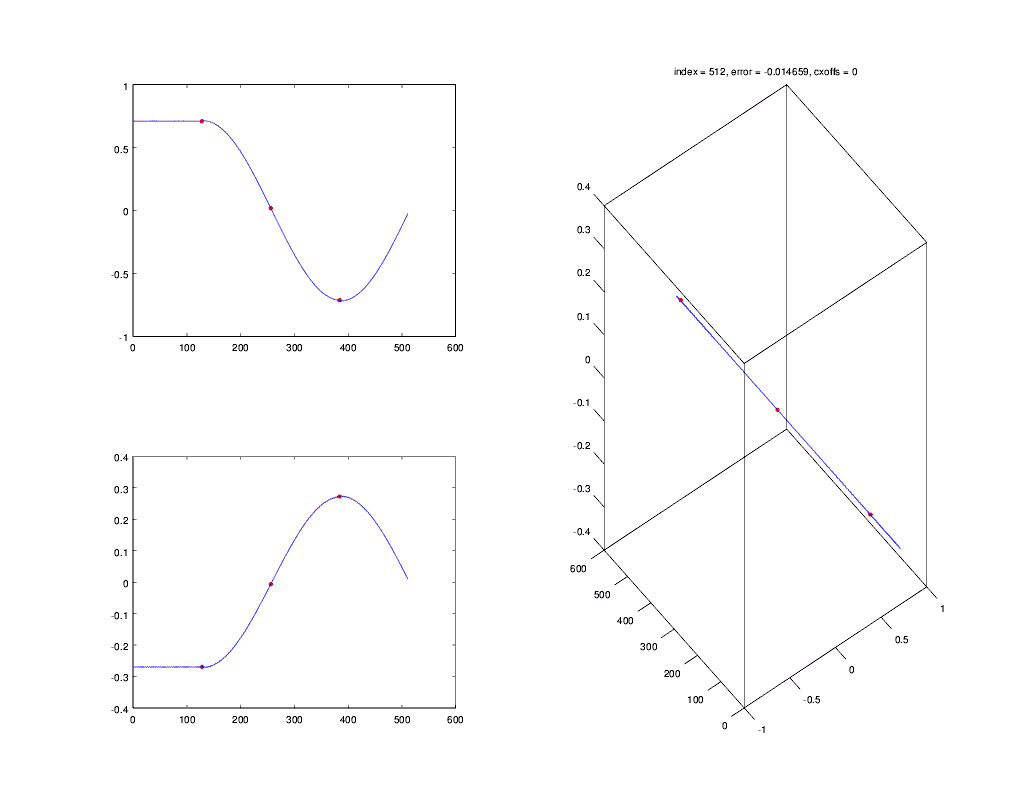
(The symbol is sampled at the left red dot. The algorithm moves the middle dot as close to the symbol transition center, as possible.)
Installation
------------
The OpenWebRX project is hosting csdr packages in their repositories. Please click the respective link for [Debian](https://www.openwebrx.de/download/debian.php) or [Ubuntu](https://www.openwebrx.de/download/ubuntu.php).
How to compile from source
--------------------------
```
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
sudo ldconfig
```
The project was only tested on Linux. It has the following dependencies: `libfftw3-dev`, `libsamplerate-dev`
To run the examples, you will also need rtl_sdr from Osmocom, and the following packages (at least on Debian): `mplayer octave gnuplot gnuplot-x11`
If you compile `fftw3` from sources for use with `libcsdr`, you need to configure it with 32-bit float support and shared libaries enabled:
./configure --enable-float --enable-shared
(This is for `fftw3`, not `libcsdr`.)
Credits
-------
The library was written by Andras Retzler, HA7ILM <>.
I would like to say special thanks to Péter Horváth, PhD (HA5CQA) and János Selmeczi, PhD (HA5FT) for their continous help and support.
Usage by example
----------------
### Demodulate WFM
rtl_sdr -s 240000 -f 89500000 -g 20 - | csdr convert -i char -o float | csdr fmdemod | csdr fractionaldecimator 5 | csdr deemphasis --wfm 48000 50e-6 | csdr convert -i float -o s16 | mplayer -cache 1024 -quiet -rawaudio samplesize=2:channels=1:rate=48000 -demuxer rawaudio -
- Baseband I/Q signal is coming from an RTL-SDR USB dongle, with a center frequency of `-f 104300000` Hz, a sampling rate of `-s 240000` samples per second.
- The `rtl_sdr` tool outputs an unsigned 8-bit I/Q signal (one byte of I sample and one byte of Q coming after each other), but `libcsdr` DSP routines internally use floating point data type, so we convert the data stream of `unsigned char` to `float` by `csdr convert`.
- We want to listen one radio station at the frequency `-f 89500000` Hz (89.5 MHz).
- No other radio station is within the sampled bandwidth, so we send the signal directly to the demodulator. (This is an easy, but not perfect solution as the anti-aliasing filter at RTL-SDR DDC is too short.)
- After FM demodulation we decimate the signal by a factor of 5 to match the rate of the audio card (240000 / 5 = 48000).
- A de-emphasis filter is used, because pre-emphasis is applied at the transmitter to compensate noise at higher frequencies. The time constant for de-emphasis for FM broadcasting in Europe is 50 microseconds (hence the `50e-6`).
- Also, `mplayer` cannot play floating point audio, so we convert our signal to a stream of 16-bit integers.
### Demodulate WFM: advanced
rtl_sdr -s 2400000 -f 89300000 -g 20 - | csdr convert -i char -o float | csdr shift -0.085 | csdr firdecimate 10 0.05 | csdr fmdemod | csdr fractionaldecimator 5 | csdr deemphasis --wfm 48000 50e-6 | csdr convert -i float -o s16 | mplayer -cache 1024 -quiet -rawaudio samplesize=2:channels=1:rate=48000 -demuxer rawaudio -
- We want to listen to one radio station, but input signal contains multiple stations, and its bandwidth is too large for sending it directly to the FM demodulator.
- We shift the signal to the center frequency of the station we want to receive: `-0.085*2400000 = -204000`, so basically we will listen to the radio station centered at 89504000 Hz.
- We decimate the signal by a factor of 10. The transition bandwidth of the FIR filter used for decimation will be 10% of total bandwidth (as of parameter 0.05 is 10% of 0.5). Hamming window will be used for windowed FIR filter design.
Sample rates look like this:
2.4 Msps 240 ksps 48 ksps
I/Q source ------------> FIR decimation ------------> FM demod -> frac. decimation ---------> deemphasis -> sound card
The first parameter is the frequency in MHz, and the second optional parameter is the RTL-SDR tuner gain in dB.
### Demodulate NFM
rtl_sdr -s 2400000 -f 145000000 -g 20 - | csdr convert -i char -o float | csdr shift `python -c "print(float(145000000-145350000)/2400000)"` | csdr firdecimate 50 0.005 | csdr fmdemod | csdr limit | csdr deemphasis --nfm 48000 | csdr agc | csdr convert -i float -o s16 | mplayer -cache 1024 -quiet -rawaudio samplesize=2:channels=1:rate=48000 -demuxer rawaudio -
- Note that the decimation factor is higher (we want to select a ~25 kHz channel).
- Also there is a python hack to calculate the relative shift offset. The real receiver frequency is `145350000` Hz.
- The de-emphasis filter is a fixed FIR filter that has a passband of 400-4000 Hz, also with a roll-off of -20 dB/decade.
### Demodulate AM
rtl_sdr -s 2400000 -f 145000000 -g 20 - | csdr convert -i char -o float | csdr shift `python -c "print(float(145000000-144400000)/2400000)"` | csdr firdecimate 50 0.005 | csdr amdemod | csdr dcblock | csdr agc | csdr limit | csdr convert -i float -o s16 | mplayer -cache 1024 -quiet -rawaudio samplesize=2:channels=1:rate=48000 -demuxer rawaudio -
- `amdemod` is used as demodulator.
- `agc` should be used for AM and SSB.
### Demodulate SSB
rtl_sdr -s 2400000 -f 145000000 -g 20 - | csdr convert -i char -o float | csdr shift `python -c "print(float(145000000-144400000)/2400000)"` | csdr firdecimate 50 0.005 | csdr bandpass --fft --low 0 --high 0.1 0.05 | csdr realpart | csdr agc | csdr limit | csdr convert -i float -o s16 | mplayer -cache 1024 -quiet -rawaudio samplesize=2:channels=1:rate=48000 -demuxer rawaudio -
- It is a modified Weaver-demodulator. The complex FIR filter removes the lower sideband and lets only the upper pass (USB). If you want to demodulate LSB, change `bandpass --low 0 --high 0.1` to `bandpass --low -0.1 --high 0`.
Usage
-----
Some basic concepts on using *libcsdr*:
### Data types
`csdr convert` can convert a real/complex stream from one data format to another, to interface it with other SDR tools and the sound card.
You can use `csdr convert` on complex streams, too, as they are only interleaved values (I,Q,I,Q,I,Q... coming after each other).
### csdr commands
`csdr` should be considered as a reference implementation on using `libcsdr`. For additional details on how to use the library, check `csdr.cpp`.
Regarding `csdr`, the first command-line parameter is the name of a function, others are the parameters for the given function. Compulsory parameters are noted as ``, optional parameters are noted as `[parameter]`.
All commands also provide a short help text and information about their mandatory and optional parameters when called with the `--help` argument.
Optional parameters have safe defaults, you can query the `--help` text to see what they are.
----
### realpart
Syntax:
csdr realpart
It takes the real part of the complex signal, and throws away the imaginary part.
----
### limit
Syntax:
csdr limit [max_amplitude]
The input signal amplitude will not be let out of the `-max_amplitude ... max_amplitude` range.
----
### gain
Syntax:
csdr gain
It multiplies all samples by `gain`.
----
### shift
Syntax:
csdr shift
It shifts the signal in the frequency domain by `rate`.
`rate` is a floating point number between -0.5 and 0.5.
`rate` is relative to the sampling rate.
Internally, this function uses trigonometric addition formulas to generate sine and cosine.
----
### dcblock
Syntax:
csdr dcblock
This is a DC blocking IIR filter.
----
### fmdemod
Syntax:
csdr fmdemod
It is an FM demodulator that is based on the quadri-correlator method, and it can be effectively auto-vectorized, so it should be faster.
----
### deemphasis
Syntax:
csdr deemphasis [--wfm|--nfm] [tau]
When used in `--wfm` mode, it performs de-emphasis with the given RC time constant `tau`.
Different parts of the world use different pre-emphasis filters for FM broadcasting: In Europe, `tau` should be chosen as `50e-6`, and in the USA, `tau` should be `75e-6`.
When used in `--nfm` mode, it uses fixed filters so it works only on predefined sample rates. See the file `src/lib/predefined.h` for the available rates and information on how to add others.
### amdemod_cf
Syntax:
csdr amdemod
It is an AM demodulator that uses `sqrt`. On some architectures `sqrt` can be directly calculated by dedicated CPU instructions, but on others it may be slower.
### firdecimate
Syntax:
csdr firdecimate [transition_bw] [--window=hamming]
It is a decimator that keeps one sample out of `decimation_factor` samples.
To avoid aliasing, it runs a filter on the signal and removes spectral components above `0.5 × nyquist_frequency × decimation_factor` from the input signal.
----
### fractionaldecimator
Syntax:
csdr fractionaldecimator [--format=(complex|float)] [--numpoly=12] [--transition=0.0e] [--window=hamming] [--prefilter]
It can decimate by a floating point ratio.
It uses Lagrange interpolation, where `numpoly` (12 by default) input samples are taken into consideration while calculating one output sample.
This function is available for both complex and real data, `--format` to switch. Possible arguments: `complex` and `float`.
It can filter the signal with an anti-aliasing FIR filter before applying the Lagrange interpolation. This filter is inactive by default, but can be activated by:
* passing only the `transition`, or both the `transition` and the `window` parameters of the filter,
* using the `--prefilter` switch to switch this filter on with the default parameters.
----
### bandpass
Syntax:
csdr bandpass <--low=low_cut> <--high=high_cut> [--window=hamming]
It performs a bandpass FIR filter on complex samples, using FFT and the overlap-add method.
`low_cut` and `high_cut` both may be between -0.5 and 0.5, and are proportional to the sampling frequency.
----
### agc
Syntax:
csdr agc [--format=(complex|float|s16)] [--profile=(slow|fast)] [--hangtime=t] [--reference=r] [--attack=a] [--decay=d] [--max=m] [--initial=i]
It is an automatic gain control function.
This command can process different sample formats, use `--format` to switch. Available formats: `complex`, `float` and `s16`.
`--profile` switches between the two sets of default values for "fast" and "slow" agc. You can still override them
with the arguments below for fine-tuning.
If no arguments are given, the agc will run with the defaults of the "fast" profile:
```
hang_time = 200
reference = 0.800000
attack_rate = 0.100000
decay_rate = 0.001000
max_gain = 65536.000000
initial_gain = 1.000000
```
All arguments below take a number as a parameter:
- `--hangtime` is the number of samples to wait before starting to increase the gain after a peak.
- `--reference` is the reference level for the AGC. It tries to keep the amplitude of the output signal close to that.
- `--attack` is the rate of decreasing the signal level if it gets higher than it used to be before.
- `--decay` is the rate of increasing the signal level if it gets lower than it used to be before.
- AGC won't increase the gain over `--max`.
- `--initial` sets an initial gain value (best guess)
Its default parameters work best for an audio signal sampled at 48000 Hz.
----
### fft
Syntax:
csdr fft [--window=hamming]
It performs an FFT on the first `fft_size` samples out of `every_n_samples`, thus skipping `every_n_samples - fft_size` samples in the input.
----
### logpower
Syntax:
csdr logpower [--add_db=0]
Calculates `10*log10(i^2+q^2)+add_db` for the input complex samples. It is useful for drawing power spectrum graphs.
----
### adpcm
Syntax:
csdr adpcm <--encode|--decode> [--sync]
Encodes or decodes an ADPCM audio stream. An ADPCM audio stream uses only 25% of the bandwidth compared to the original.
Can optionally embed proprietary synchronization frames with `--sync` (used in OpenWebRX).
----
### fftadpcm
Syntax:
csdr fftadpcm
Encodes the FFT output vectors of `fft_size`. It should be used on the data output from `csdr logpower`.
It resets the ADPCM encoder at the beginning of every vector, and to compensate it, `COMPRESS_FFT_PAD_N` samples are added at beginning (these equal to the first relevant sample).
----
### fftswap
Syntax:
csdr fftswap
It exchanges the first and second part of the FFT vector, to prepare it for the waterfall/spectrum display. It should operate on the data output from `csdr logpower`.
----
### squelch
Syntax:
csdr squelch --fifo --outfifo
This is a controllable squelch, which reads the squelch level input from `` and writes the power level output to ``. Both input and output are in the format of `%g\n`. While calculating the power level, it takes only every `` sample into consideration. It writes the S-meter value for every `` buffer to ``. If the squelch level is set to 0, it it forces the squelch to be open. If the squelch is closed, it will stop outputting data.
----
### logaveragepower
Syntax:
csdr logaveragepower [--add=0]
It works like `csdr logpower`, but it calculates the average of every `avgnumber` FFTs.
----
### varicodedecode
Syntax:
csdr varicodedecode
It expects symbols encoded as 0x00 and 0x01 bytes on the input, and extracts Varicode characters from them.
----
### timingrecovery
Syntax:
csdr timingrecovery [--algorithm=gardner] [loop_gain] [max_error] [--add_q]
It implements non-data aided timing recovery (Gardner and early-late gate algorithms).
[More information](http://openwebrx.org/msc-thesis.pdf#page=34) (section 4.4 from page 34)
----
### dbpskdecoder
Syntax:
csdr dbpskdecode
It implements a differential BPSK demodulator, with the following data flow:
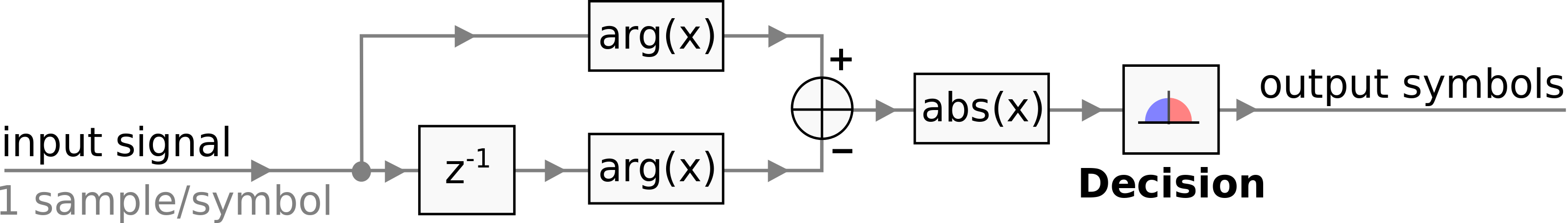
The output is 0x00 or 0x01.
----
#### Control via pipes
Some parameters can be changed while the `csdr` process is running. To achieve this, some `csdr` functions have special parameters. You have to supply a fifo previously created by the `mkfifo` command. Processing will only start after the first control command has been received by `csdr` over the FIFO.
csdr shift --fifo
By writing to the given FIFO file with the syntax below, you can control the shift rate:
\n
E.g. you can send `-0.3\n`
Processing will only start after the first control command has been received by `csdr` over the FIFO.
csdr bandpass --fifo [--window=hamming]
By writing to the given FIFO file with the syntax below, you can control the shift rate:
\n
E.g. you can send `-0.05 0.02\n`
#### Testbench
`csdr` was tested with GNU Radio Companion flowgraphs. These flowgraphs are available under the directory `grc_tests`, and they require the gr-ha5kfu set of blocks for GNU Radio.
## nmux
The repo also contains a command line tool called `nmux`, which is a TCP stream multiplexer. It reads data from the standard input, and sends it to each client connected through TCP sockets. Available command line options are:
* `--port (-p), --address (-a):` TCP port and address to listen.
* `--bufsize (-b), --bufcnt (-n)`: Internal buffer size and count.
* `--help (-h)`: Show help message.
`nmux` was originally written for use in OpenWebRX.
## Licensing
The code in this library is under mixed license, with parts being provided under BSD and other parts under GPL license. Please see the individual files for details.