Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/jmcnamara/vba_extract-rs
Utility to extract a vbaProject.bin binary from an Excel xlsm macro file
https://github.com/jmcnamara/vba_extract-rs
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Utility to extract a vbaProject.bin binary from an Excel xlsm macro file
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jmcnamara/vba_extract-rs
- Owner: jmcnamara
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-07-15T23:03:51.000Z (4 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-21T20:29:05.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-21T22:44:59.865Z (3 months ago)
- Language: Rust
- Size: 11.7 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE_Apache2.0
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# vba_extract
The `vba_extract` command line application is a simple utility to extract a
`vbaProject.bin` binary from an Excel xlsm file for insertion into an
`rust_xlsxwriter` file.
If the macro is digitally signed the utility will also extract a
`vbaProjectSignature.bin` file.
See [Working with VBA Macros in
`rust_xlsxwriter`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/macros/index.html).
## Usage
```bash
Usage: vba_extract [OPTIONS]
Arguments:
Input Excel xlsm filename
Options:
-o, --output-macro-filename
Output vba macro filename
[default: vbaProject.bin]
-s, --output-sig-filename
Output vba signature filename (if present in the parent file)
[default: vbaProjectSignature.bin]
-h, --help
Print help (see a summary with '-h')
-V, --version
Print version
```
## Installation
```bash
cargo install vba_extract
```
## Adding VBA macros to a `rust_xlsxwriter` file
Once the `vbaProject.bin` file has been extracted it can be added to the
`rust_xlsxwriter` workbook using the
[`Workbook::add_vba_project()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/workbook/struct.Workbook.html#method.add_vba_project)
method:
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
#[allow(unused_variables)]
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
workbook.add_vba_project("examples/vbaProject.bin")?;
Ok(())
}
```
Here is a complete example which adds a macro file with a dialog. It also uses a
button, via [`Worksheet::insert_button()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/worksheet/struct.Worksheet.html#method.insert_button), to
trigger the macro:
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Button, Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
// Create a new Excel file object.
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
// Add the VBA macro file.
workbook.add_vba_project("examples/vbaProject.bin")?;
// Add a worksheet and some text.
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Widen the first column for clarity.
worksheet.set_column_width(0, 30)?;
worksheet.write(2, 0, "Press the button to say hello:")?;
// Add a button tied to a macro in the VBA project.
let button = Button::new()
.set_caption("Press Me")
.set_macro("say_hello")
.set_width(80)
.set_height(30);
worksheet.insert_button(2, 1, &button)?;
// Save the file to disk. Note the `.xlsm` extension. This is required by
// Excel or it raise a warning.
workbook.save("macros.xlsm")?;
Ok(())
}
```
The macro in this example is the following VBA code:
```basic
Sub say_hello()
MsgBox ("Hello from Rust!")
End Sub
```
Output file after running macro:
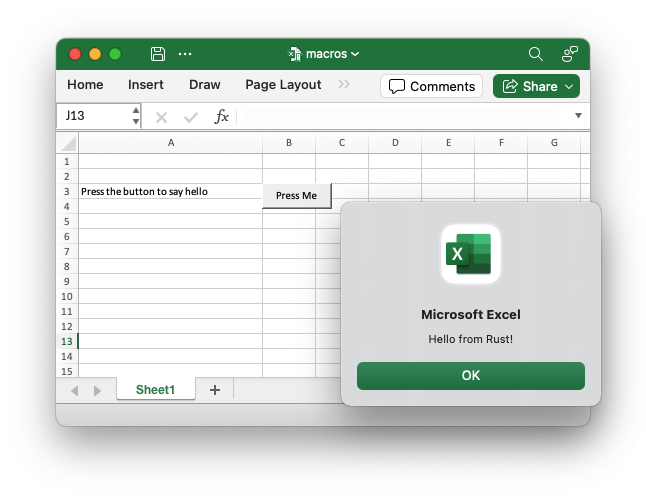
If the VBA file contains functions you can then refer to them in calculations
using [`Worksheet::write_formula()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/worksheet/struct.Worksheet.html#method.write_formula):
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
workbook.add_vba_project("examples/vbaProject.bin")?;
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
worksheet.write_formula(0, 0, "=MyMortgageCalc(200000, 25)")?;
// Note the `.xlsm` extension.
workbook.save("macros.xlsm")?;
Ok(())
}
```
**Note**: Excel files that contain functions and macros must use an `.xlsm`
extension or else Excel will complain and possibly not open the file.
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
#[allow(unused_variables)]
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
workbook.add_vba_project("examples/vbaProject.bin")?;
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Note the `.xlsm` extension.
workbook.save("macros.xlsm")?;
Ok(())
}
```
Here is the dialog that appears when a valid `xlsm` file is incorrectly given a
`xlsx` extension:
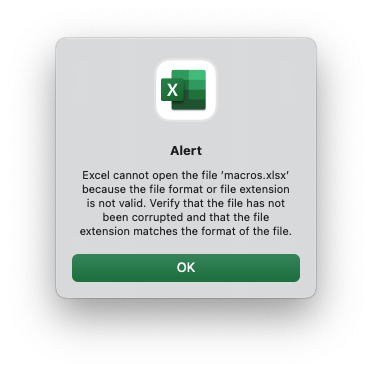
## Setting the VBA object names
VBA macros generally refer to workbook and worksheet objects via names such as
`ThisWorkbook` and `Sheet1`, `Sheet2` etc.
If the imported macro uses other names you can set them using the
[`Workbook::set_vba_name()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/workbook/struct.Workbook.html#method.set_vba_name)
and
[`Worksheet::set_vba_name()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/worksheet/struct.Worksheet.html#method.set_vba_name)
methods as follows.
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
workbook.add_vba_project("examples/vbaProject.bin")?;
workbook.set_vba_name("MyWorkbook")?;
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
worksheet.set_vba_name("MySheet1")?;
// Note the `.xlsm` extension.
workbook.save("macros.xlsm")?;
Ok(())
}
```
**Note**: If you are using a non-English version of Excel you need to pay
particular attention to the workbook/worksheet naming that your version of Excel
uses and add the correct VBA names. You can find the names that are used in the
VBA editor:
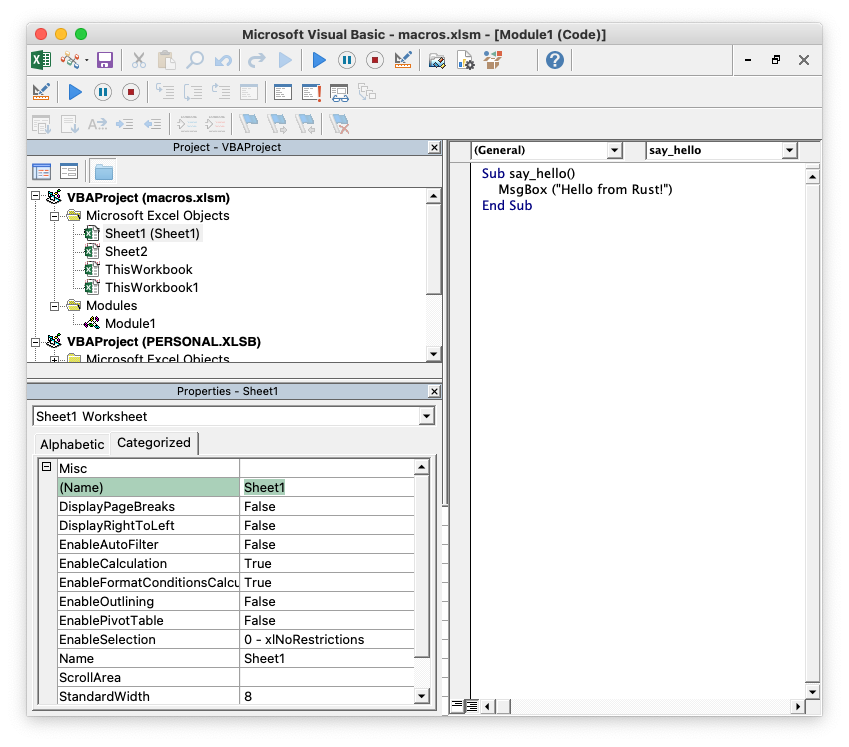
You can also find them by unzipping the `xlsm` file and grepping the component
XML files. The following shows how to do that using system `unzip` and libxml's
[xmllint](http://xmlsoft.org/xmllint.html) to format the XML for clarity
```bash
$ unzip myfile.xlsm -d myfile
$ xmllint --format `find myfile -name "*.xml" | xargs` | grep "Pr.*codeName"
```
## Adding a VBA macro signature file to an `rust_xlsxwriter` file
VBA macros can be signed in Excel to allow for further control over execution.
The signature part is added to the `xlsm` file in another binary called `vbaProjectSignature.bin`.
The `vba_extract` utility will extract the `vbaProject.bin` and
`vbaProjectSignature.bin` files from an `xlsm` file with signed macros.
These files can be added to a `rust_xlsxwriter` file using the
[`Workbook::add_vba_project_with_signature()`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/workbook/struct.Workbook.html#method.add_vba_project_with_signature)
method:
```rust
use rust_xlsxwriter::{Workbook, XlsxError};
#[allow(unused_variables)]
fn main() -> Result<(), XlsxError> {
let mut workbook = Workbook::new();
workbook.add_vba_project_with_signature(
"examples/vbaProject.bin",
"examples/vbaProjectSignature.bin",
)?;
let worksheet = workbook.add_worksheet();
// Note the `.xlsm` extension.
workbook.save("macros.xlsm")?;
Ok(())
}
```
## What to do if it doesn't work
The `rust_xlsxwriter` test suite contains several tests to ensure that this
feature works and there is a working example shown above. However, there is no
guarantee that it will work in all cases. Some trial and error may be required
and some knowledge of VBA will certainly help. If things don't work out here are
some things to try:
1. Start with a simple macro file, ensure that it works, and then add
complexity.
2. Check the code names that macros use to refer to the workbook and worksheets
(see the previous section above). In general VBA uses a code name of
`ThisWorkbook` to refer to the current workbook and the sheet name (such as
`Sheet1`) to refer to the worksheets. These are the defaults used by
`rust_xlsxwriter`. If the macro uses other names, or the macro was extracted
from an non-English language version of Excel, then you can specify these
using the workbook and worksheet `set_vba_name` methods.
## See also
See [Working with VBA Macros in
`rust_xlsxwriter`](https://docs.rs/rust_xlsxwriter/latest/rust_xlsxwriter/macros/index.html).