https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl
Framework to easily develop robotics Reinforcement Learning tasks using Gazebo and stable-baselines-3.
https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
Framework to easily develop robotics Reinforcement Learning tasks using Gazebo and stable-baselines-3.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl
- Owner: jmfajardod
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-08-14T21:52:46.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-05T15:16:46.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-05T16:28:06.820Z (9 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 3.66 MB
- Stars: 112
- Watchers: 41
- Forks: 33
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-legged-locomotion-learning - [FRobs_RL - baselines-3.  (Code / Quadrupeds)
README
# FRobs_RL: A Flexible Robotics Reinforcement Learning Library
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/jmfajardod/frobs_rl/context:python)
[](https://frobs-rl.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
## Description
FRobs_RL is a flexible robotics reinforcement learning (RL) library. It is primarly designed to be used in robotics applications using the [ROS](https://www.ros.org) framework. It is written in Python and uses libraries based on the [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) framework to handle the machine learning. The library uses [Gymnasium](https://gymnasium.farama.org/index.html) to create and handle the RL environments, [stable-baselines3](https://stable-baselines3.readthedocs.io/en/master/) to provide state-of-the-art RL algorithms, [Gazebo](http://gazebosim.org) to simulate the physical environments, and [XTerm](https://invisible-island.net/xterm/) to display and launch many of the ROS nodes and processes in a lightweight terminal.
FRobs_RL has the following goals:
- Provide a framework to easily train and deploy RL algorithms in robotics applications using the ROS middleware.
- Provide a framework to easily create RL enviroments for any type of task.
- Provide a framework to easily use, test or create state-of-the-art RL algorithms in robotics applications.
# Documentation
Documentation is available at: [frobs-rl.readthedocs.io](https://frobs-rl.readthedocs.io/en/latest)
# Installation Instructions
FRobs_RL has been tested in ROS [Noetic](https://wiki.ros.org/noetic), although it should work in previous versions of ROS like [Melodic](https://wiki.ros.org/melodic) or [Kinetic](https://wiki.ros.org/Kinetic) with minimal changes. Although it is recommended that the user has previous knowledge of the ROS ecosystem, and has a working ROS distribution environment, in the following instructions an example of the installation of ROS will be provided, especially for the Noetic distribution.
## ROS Installation
To install ROS Noetic, the user can go to the official website [ROS Melodic ](http://wiki.ros.org/noetic/Installation) installation and follow the instructions. Below are the suggested commands to install ROS Noetic on a Ubuntu 20.04 Focal machine.
```sh
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu $(lsb_release -sc) main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
sudo apt install curl
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ros/rosdistro/master/ros.asc | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ros-noetic-desktop-full
echo "source /opt/ros/noetic/setup.bash" >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrc
sudo apt install python3-rosdep python3-rosinstall python3-rosinstall-generator python3-wstool build-essential
sudo apt install python3-rosdep
sudo rosdep init
rosdep update
```
## Catkin tools and XTerm
We recommend [catkin-tools](https://catkin-tools.readthedocs.io/en/latest/installing.html) to build your ROS workspace:
```sh
sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.ros.org/ros/ubuntu `lsb_release -sc` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ros-latest.list'
wget http://packages.ros.org/ros.key -O - | sudo apt-key add -
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-catkin-tools
```
As `XTerm` is widely used in the library to execute some processes in a lightweith terminal, if the user does not already has XTerm it can be installed with the command:
```sh
sudo apt install xterm
```
The library requieres Moveit! to run, to install it just run:
```shell
sudo apt install ros-noetic-moveit
```
## Workspace creation and library compilation
To use the library it is necessary to download and compile the library package. To create a new ROS workspace called `rl_ws` and compile the `frobs_rl` package, one can use the following commands:
```sh
cd ~
mkdir -p rl_ws/src
cd rl_ws
git clone https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl src/frobs_rl -b main
rosdep install -y --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro ${ROS_DISTRO}
catkin config --extend /opt/ros/${ROS_DISTRO}
catkin build
source devel/setup.bash
```
## Python dependencies
As the library is based in the [Gymnasium](https://gymnasium.farama.org/index.html) and [stable-baselines3](https://github.com/DLR-RM/stable-baselines3) libraries, one must install these libraries along with PyTorch and TensorBoard. To go to the `frobs_rl` package and install these dependencies execute the following commands.
Note that the following commands will try to install a PyTorch version without GPU support, as it is written in the dependencies of stable-baselines3, if your computer supports GPUs, you can install the GPU version of PyTorch by following the instructions on the [PyTorch website](https://pytorch.org).
```sh
roscd frobs_rl # Only works the setup.bash has been sourced
sudo apt install pip
python3 -m pip install -r requirements.txt
```
## Testing the library
To try the library using some example environments, the user needs to download the [resources package](https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl_resources) in the workspace src folder and compile it. The followings command can be used to do that:
```sh
cd ~
cd rl_ws/src
git clone https://github.com/jmfajardod/frobs_rl_resources -b main
cd ..
rosdep install -y --from-paths src --ignore-src --rosdistro ${ROS_DISTRO}
catkin build
source devel/setup.bash
```
Next to test the library, the user can use the following command to begin the training of a new agent for a reacher environment with a ABB IRB 120 robot:
```sh
rosrun abb_irb120_reacher train.py
```
Or the following command to begin the training of a new agent for a mobile robot environment with a Kobuki robot:
```sh
rosrun kobuki_maze_rl train.py
```
For both examples, the user can use use TensoBoard to visualize the training process. To do that go to the logs folder of either the `abb_irb120_reacher` or `kobuki_maze_rl` package and execute the following command:
```sh
tensorboard serve --logdir_spec=td3_logs:./td3/TD3_New/
```
This will open a web browser in the localhost:6006 port, where the user can see the training process logs located in the `TD3_New` folder, as configured in the `train.py` and `td3.yaml` files.
If some error occurs when launching the ROS Nodes, make sure that the `train.py` are executables using the `ll` and `chmod a+x train.py` commands.
## Official video
In the following video all FRobs_RL capabilies are shown. Training in virtual environments, Gazebo simulations, ROS integration and Deployment on real hardware.
[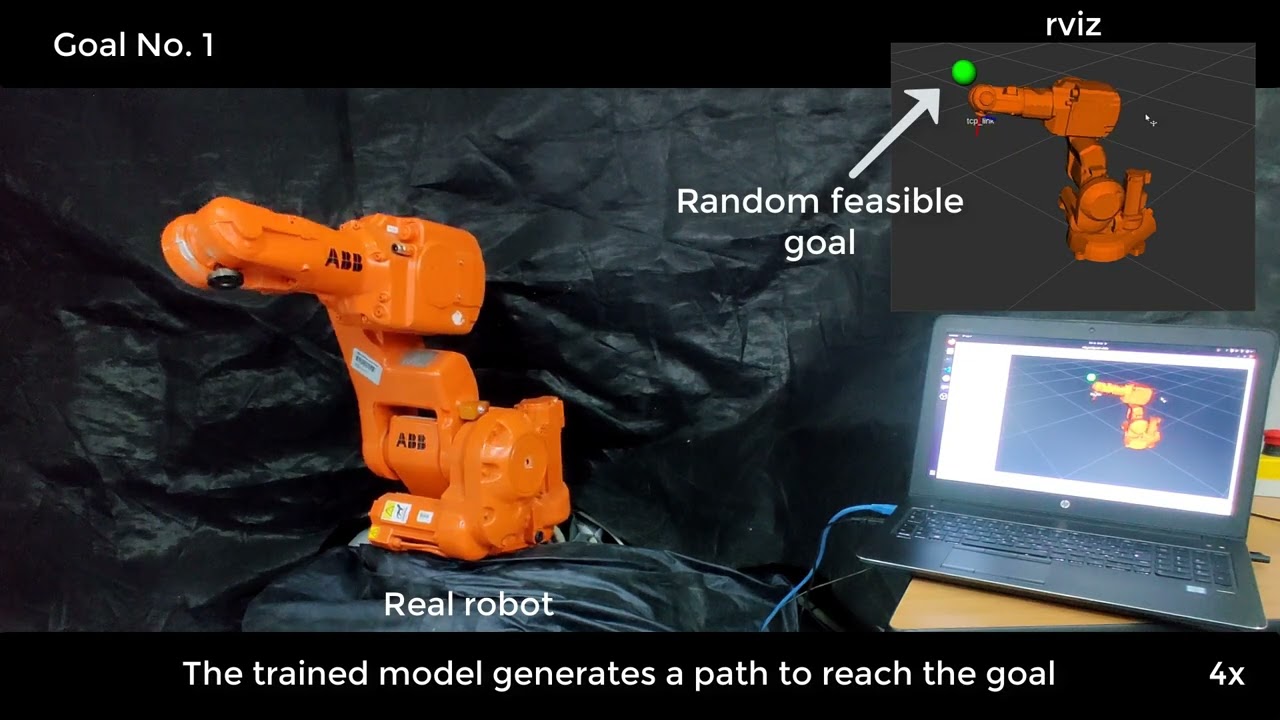](https://youtu.be/x6QIPuHeOSo)