Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/joao-lucas-de-oliveira-lima/chatting-with-lol-champions
A full-stack application developed during Santander Dev Week 2024 on the DIO platform, implementing a chat system with integration and interactivity themed around League of Legends champions.
https://github.com/joao-lucas-de-oliveira-lima/chatting-with-lol-champions
chat league-of-legends llm-integration
Last synced: 1 day ago
JSON representation
A full-stack application developed during Santander Dev Week 2024 on the DIO platform, implementing a chat system with integration and interactivity themed around League of Legends champions.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/joao-lucas-de-oliveira-lima/chatting-with-lol-champions
- Owner: Joao-Lucas-de-Oliveira-Lima
- Created: 2024-11-06T00:15:45.000Z (3 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-27T02:33:01.000Z (12 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-27T03:23:42.470Z (12 days ago)
- Topics: chat, league-of-legends, llm-integration
- Homepage:
- Size: 11.7 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# System Description
This application was developed during the [Santander Dev Week 2024](https://github.com/digitalinnovationone/santander-dev-week-2024) by the DIO platform.
The application allows users to select a champion from League of Legends, ask a question, and receive a response from a Chat Completion model that impersonates the selected champion.
# Front-end
This front-end was built using the [Horizontal Timeline](https://codepen.io/davidbiek/pen/BaWYWME) theme to display League of Legends champions in a carousel format.
# Running the Application
To run the application, simply open the `index.html` file located in the project root directory.
# Back-end
## About the API
REST API developed with Java Spring. This API enables users to engage in interactive
conversations with League of Legends champions, using a large language model (LLM)
integrated through an external service.
# Installation Guide
## 1. Running the Application with Docker Compose
### Prerequisites
- [Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/)
### Steps
#### 1. Obtain an API Key for the Chat Completion Service
The API connects to the Llama3-8b-8192 model provided by Groq Cloud. To acquire an API key,
follow [these instructions](https://console.groq.com/keys) and add the key to the `GROQ_CLOUD_API_KEY`
environment variable in the `docker-compose.yaml` file.
#### 2. Starting Containers
Run the following command to start the containers:
```bash
docker-compose up -d
```
## 2. Running the Application with Maven
### Prerequisites
- [Docker Desktop](https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/)
- [Java 21](https://www.oracle.com/br/java/technologies/downloads/#java21)
### Steps
#### 1. Start the PostgreSQL Database Container
```bash
docker-compose up db -d
```
#### 2. Create application-dev.properties
The `application.properties` file is configured to run the Spring `dev` profile by default.
To enable this, create a file named `application-dev.properties` in `src/main/resources` with the
following settings:
```properties
server.port=8080
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:postgresql://localhost:3003/lol
spring.datasource.username=postgres
spring.datasource.password=1234
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.postgresql.Driver
spring.jpa.open-in-view=false
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=none
groq-cloud.base-url=https://api.groq.com/openai
# Replace this with your API key
groq-cloud.api-key=your_api_key
```
>Note: Make sure to obtain an API key as shown [here](#1-obtain-an-api-key-for-the-chat-completion-service)
> and assign it to `groq-cloud.api-key`. The database settings above are provided for example purposes.
> If you choose to modify them, ensure that the database settings in `docker-compose.yaml` are updated accordingly.
#### 3. Run the Application
In the project root directory, run:
```bash
./mvnw clean install -DskipTests
./mvnw spring-boot:run
```
## Architecture
The project follows the Clean Architecture principles, as illustrated below.
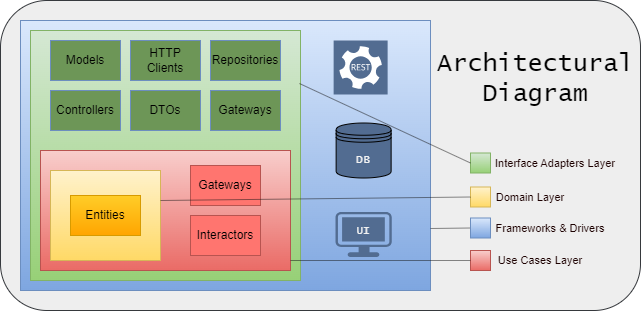
It includes five main directories:
- `application`: Contains use cases and interfaces for accessing resources such as databases and HTTP clients.
- `domain`: Defines system entities and business-rule exceptions.
- `infrastructure` Implements the application layer's gateways, providing access to database
- repositories, HTTP client interfaces, controllers, DTOs, framework-specific exceptions,
- and other Spring resources.
- `configuration` Holds configuration files with dependency injection beans.
- `shared` Contains utility classes accessible across multiple layers.
# Tests
Run the following commands in the terminal, from the application root directory:
- For unit tests:
```bash
./mvnw test
```
- For integration tests:
```bash
./mvnw verify -Pfailsafe
```
>Note: Ensure Docker is running, as the application uses TestContainers to create a PostgreSQL database
> in Docker for each integration test class.
# Documentation
## API Endpoints Preview
```text
GET /champions - Retrieve a list of champions.
POST /champions/ask/{id} - Ask a question to a specific champion by ID and retrieve the champion's response.
```
## OpenAPI Documentation
- To view the full API documentation, including endpoints and data schemas, open the Swagger UI at:
`/swagger-ui/index.html`
- For API documentation in JSON format suitable for tools like Postman, Insomnia, and other API clients, go to: `/v3/api-docs`.