Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/joaohf/nifi_s2s
NiFi Site-to-Site Erlang client implementation
https://github.com/joaohf/nifi_s2s
beam dataflow elixir erlang flowfiles nifi
Last synced: 29 days ago
JSON representation
NiFi Site-to-Site Erlang client implementation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/joaohf/nifi_s2s
- Owner: joaohf
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-06-24T20:21:47.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-06-24T20:48:25.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-17T17:49:29.808Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: beam, dataflow, elixir, erlang, flowfiles, nifi
- Language: Erlang
- Homepage:
- Size: 108 KB
- Stars: 2
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# nifi_s2s
nifi_s2s is an Erlang implementation of NiFi Site-to-Site flowfile transfer protocol.
If you are not aware about what does NiFi mean, please take a look in the official [Apache NiFi project](https://nifi.apache.org).
This library only makes sense if you need to transfer data from and to NiFi node or cluster.
## Overview
[Apache NiFi](https://nifi.apache.org) is a tool aim to automate the flow of data between systems. The tool brings valuable features that allows moving data around secondary systems.
[NiFi Site to Site Protocol](https://nifi.apache.org/docs/nifi-docs/html/user-guide.html#site-to-site) is a native NiFi protocol which can be used in order to transfer flowfiles between systems.
The intention of this application library (nifi_s2s) is to provide a site-to-site Erlang client implementation where flowfiles can be transferred or received.
The figure below shows a common use case where a device transfers data to a central NiFi node:
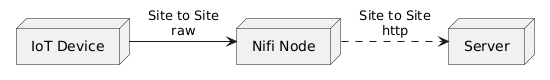
Currently, there are a few NiFi Site-to-Site implementations, none targeting BEAM VM. The most important are:
* [Java](https://github.com/apache/nifi/tree/master/nifi-commons/nifi-site-to-site-client/src/main/java/org/apache/nifi/remote/client)
* [C++](https://github.com/apache/nifi-minifi-cpp/tree/master/libminifi/src/sitetosite)
* [C](https://github.com/apache/nifi-minifi-cpp/tree/master/nanofi/src/sitetosite)All of the above implementations are from NiFi official project.
This application library provides an Erlang site-to-site client which could be used to connect and send data to and from NiFi nodes or clusters.
The figure below shows a typical NiFi flowfile which there are three processors:
* receiving flowfiles using a port
* writing each flowfiles to file
* sending each flowfile to remote port
## Design
This library follows the common site-to-site protocol sequence as described in [NiFi System Administrator’s Guide](https://nifi.apache.org/docs/nifi-docs/html/administration-guide.html#site-to-site-protocol-sequence).
There are two state machines which encapsulates all the site-to-site protocol:
* `nifi_s2s_raw_protocol_statem`: in charge of controlling the initial connection to NiFi instance and also establishing the Peer connection
* `nifi_s2s_transaction_statem`: responsible for creating and control the transaction state when sending or receiving flowfiles.The main user level interface is implemented by the module `nifi_s2s`. The rest of the code are just about help functions and encode/decode helpers.
## How to use
This client exports to main functions to transfer and receive flowfiles.
The follow example show how to create a client which uses the raw protocol and transfer
a flowfile to a Peer (that is a NiFi node):```
S2SConfig = #{hostname => "localhost",
port => 8080,
transport_protocol => raw,
local_network_interface => "lo0",
port_id => ?config(input_port, Config)},{ok, Pid} = nifi_s2s:create_client(S2SConfig),
Content = <<"Test Nifi Content">>,
Attributes = #{ <<"TEST1">> => <<"Test">>},Flowfiles = nifi_flowfile:add(Attributes, Content, nifi_flowfile:new())
ok = nifi_s2s:transfer_flowfiles(Pid, Flowfiles),
ok = nifi_s2s:close(Pid).
```Now, in order to receive flowfiles from the remote Peer:
```
{ok, _Flowfiles} = nifi_s2s:receive_flowfiles(Pid).
```## Build
```
rebar3 compile
```## Test
In order to run unit tests:
```
rebar3 eunit
```However, to run integration tests the approach is to have a running NiFi instance on the developer machine and import the template `samples/Input_and_Output_Flowfiles.xml`. Having it imported and started is necessary when running integration tests. After that, run:
```
rebar3 ct
```## TODO
- [x] Sending and receiving flowfiles
- [] Add internal metrics
- [] Add SSL context
- [] Add suport to compress flowfile
- [] Add http protocol
- [] Improve the state machine and use push and pop callbacks from statem
- [] Improve test code coverage to get edge cases
- [] Add supervisor tree
- [] Implement peer work checks and reconnect to the less busy peer
- [] Add Peer list persistent file
- [] Add async receive and transfer flowfiles API## License
[MIT](https://spdx.org/licenses/MIT.html)