https://github.com/johnsusek/FlowStack
A grid layout view for SwiftUI
https://github.com/johnsusek/FlowStack
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
A grid layout view for SwiftUI
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/johnsusek/FlowStack
- Owner: johnsusek
- Archived: true
- Created: 2019-06-26T02:52:19.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-07-22T21:26:24.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-01T20:58:53.638Z (8 months ago)
- Language: Swift
- Size: 10.7 KB
- Stars: 152
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-swiftui-libraries - FlowStack - A grid layout view for SwiftUI (Grid / Content)
- awesome-swiftui - FlowStack is a grid layout component
- fucking-about-SwiftUI - FlowStack
README
## Update July 2020 - latest SwiftUI now has built-in components to do this, which should be used instead.
# FlowStack
FlowStack is a SwiftUI component for laying out content in a grid.
## Requirements
Xcode 11 beta on MacOS 10.14 or 10.15
## Installation
In Xcode, choose File -> Swift Packages -> Add Package Dependency and enter [this repo's URL](https://github.com/johnsusek/FlowStack).
## Usage
### FlowStack(*columns*, *numItems*, *alignment*) { *index*, *colWidth* in }
- columns (Int)
- The number of columns to display.
- numItems (Int)
- The total count of items you will be displaying.
- alignment (HorizontalAlignment?)
- Default: .leading
The alignment of any trailing columns in the last row.
#### Callback parameters
- index (Int)
- The index of the item currently being processed.
- colWidth (CGFloat)
- The computed width of the column currently being processed.
## Examples
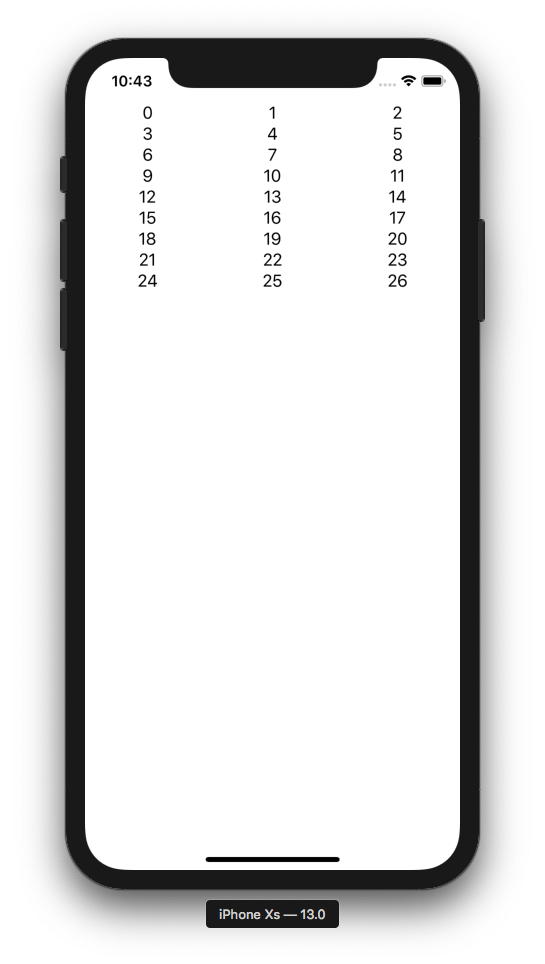
### 1) Simple
The simplest possible example:
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Text(" \(index) ").frame(width: colWidth)
}
```
You should always add `.frame(width: colWidth)` to the immediate child of `FlowStack`.
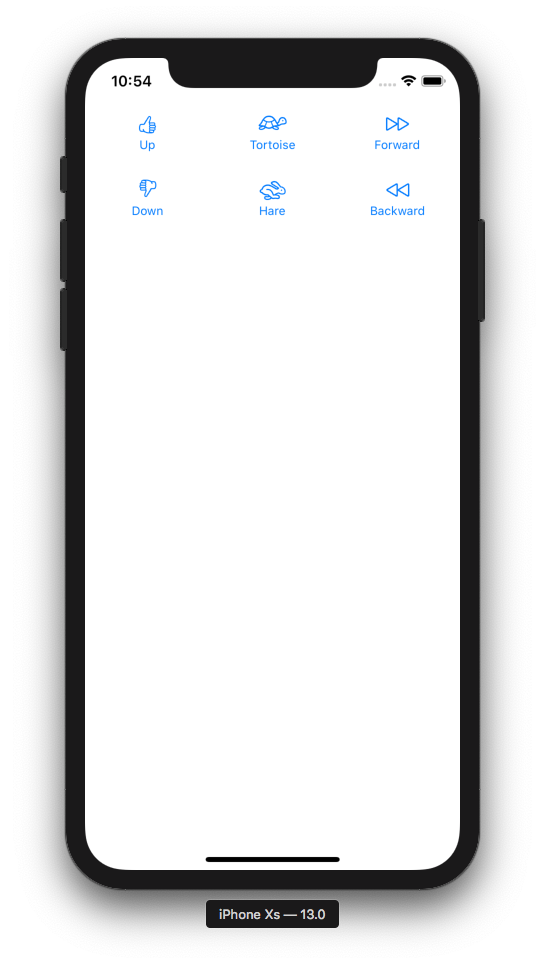
### 2) Displaying Data
```swift
struct Item {
var image: String
var label: String
}
let items = [
Item(image: "hand.thumbsup", label: "Up"),
Item(image: "tortoise", label: "Tortoise"),
Item(image: "forward", label: "Forward"),
Item(image: "hand.thumbsdown", label: "Down"),
Item(image: "hare", label: "Hare"),
Item(image: "backward", label: "Backward")
]
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: items.count, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Button(action: { print("Tap \(index)!") }) {
Image(systemName: items[index].image)
Text(items[index].label).font(Font.caption)
}
.padding()
.frame(width: colWidth)
}
```
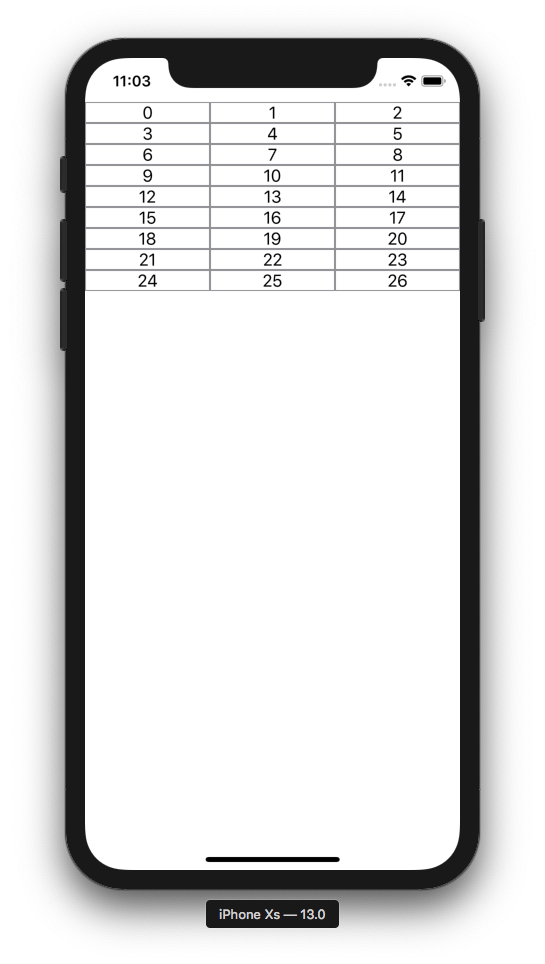
### Padding/Borders/Actions
Let's draw a border on our cells to visualize some concepts:
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Text(" \(index) ").frame(width: colWidth).border(Color.gray)
}
```
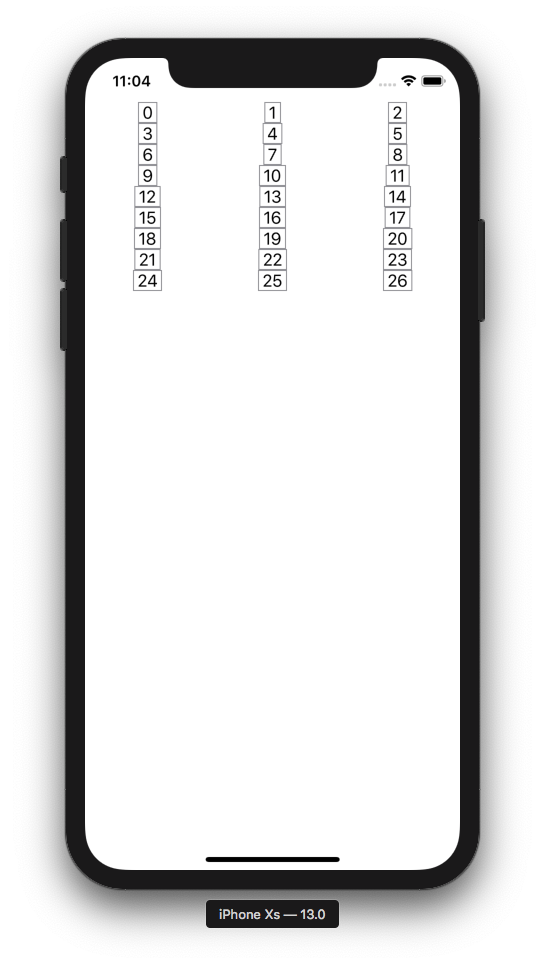
Now let's swap the `.frame` and `.border` order and note what happens. This demonstrates the **order of operations is important when chaining layout modifiers**.
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Text(" \(index) ").border(Color.gray).frame(width: colWidth)
}
```
Now let's swap the order back and add some padding:
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Text(" \(index) ").padding().frame(width: colWidth).border(Color.gray)
}
```
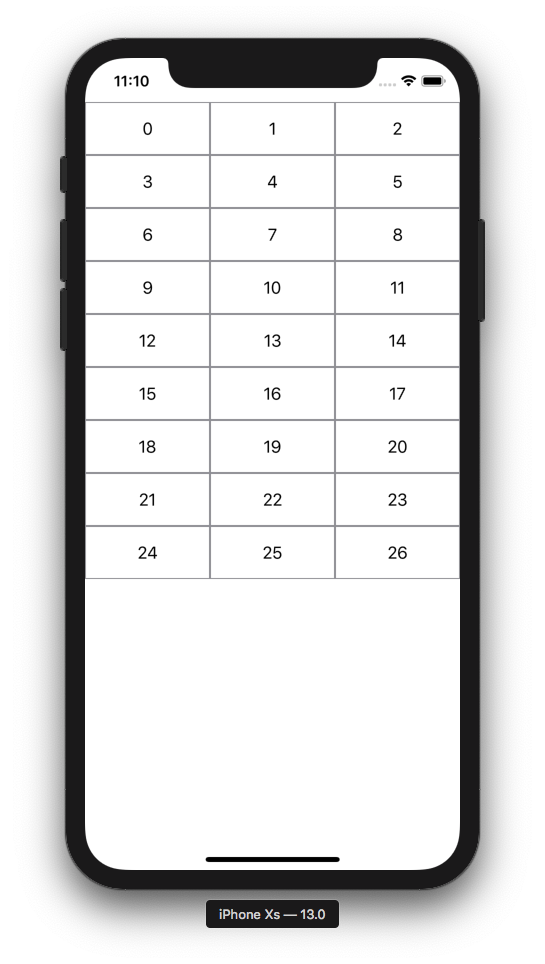
To add actions, you can of course **just put buttons in your cells** like example #2. But there is also a way to detect a tap on the entire cell. Note we add a background to detect taps in the empty areas outside the text.
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
Text(" \(index) ")
.padding()
.frame(width: colWidth)
.border(Color.gray)
.background(Color.white)
.tapAction {
print("Tap!")
}
}
```
### Example with images
Here's an example with images. LoadableImageView is from [here](https://github.com/schmidyy/SwiftUI-ListFetching/blob/23c1d5d4b506236e0a7a34a2aa5f991edd4091f4/Views.swift).
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 3, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
VStack {
LoadableImageView(with: "https://cataas.com/cat?type=sq?foo")
.padding()
.frame(width: colWidth, height: colWidth)
.tapAction { print("Meow!") }
Text(" \(index) ")
}
.padding()
.frame(width: colWidth)
.border(Color.gray)
.background(Color.white)
.tapAction {
print("Tap!")
}
}
```

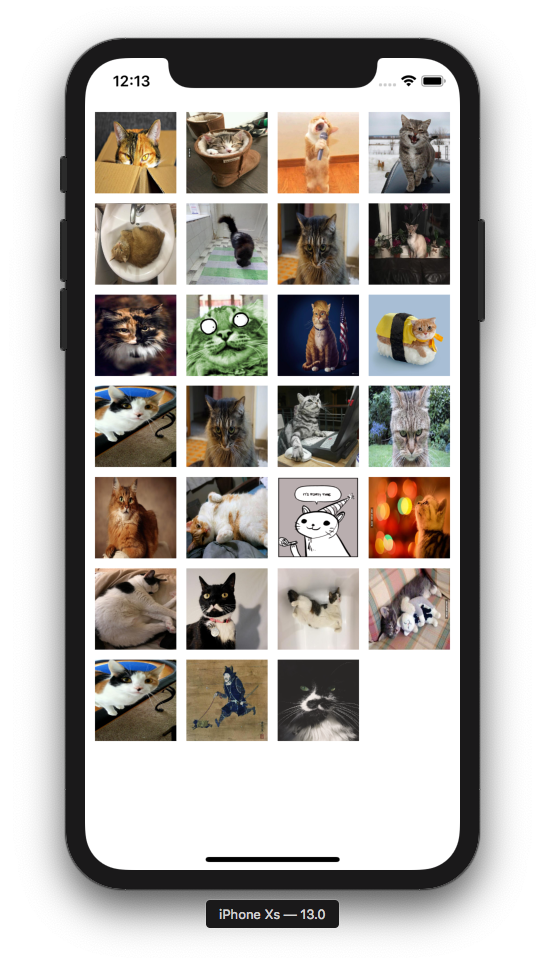
### Evenly spaced grid
```swift
FlowStack(columns: 4, numItems: 27, alignment: .leading) { index, colWidth in
LoadableImageView(with: "https://cataas.com/cat?type=sq?rando")
.padding(5)
.frame(width: colWidth, height: colWidth)
}.padding(5)
```
## Feedback
Please file a github issue if you're having trouble or spot a bug.