https://github.com/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci-libvrt
Example project showing how to run Vagrant on TravisCI using libvrt & KVM
https://github.com/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci-libvrt
kvm kvm-hypervisor libvirt travis travis-ci vagrant vagrant-libvirt
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
Example project showing how to run Vagrant on TravisCI using libvrt & KVM
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci-libvrt
- Owner: jonashackt
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-02-24T15:46:44.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-01-06T11:07:00.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-28T13:46:48.626Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: kvm, kvm-hypervisor, libvirt, travis, travis-ci, vagrant, vagrant-libvirt
- Homepage: https://stackoverflow.com/a/60615201/4964553
- Size: 22.5 KB
- Stars: 25
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# vagrant-travisci-libvrt
[](https://www.travis-ci.com/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci-libvrt)
Example project showing how to run Vagrant on TravisCI using libvrt & KVM
> If you're interested, here's also a setup using VirtualBox: https://github.com/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci __BUT__ I didn't get it to work. Maybe you have an idea?!
## Why Vagrant on a CI system?
I´d really want to test bigger Infrastructure-as-Code projects like https://github.com/jonashackt/kubernetes-the-ansible-way and therefore need Vagrant running on a CI system (I don´t want to setup or host the CI system myself).
And no, Docker-in-Docker won´t suffice here!
Well until today, I really thought that __there is no way to do it with TravisCI__ - just have a look into https://github.com/jonashackt/vagrant-ansible-on-appveyor ([and this so thread](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31828555/using-vagrant-on-cloud-ci-services)).
But then I came upon these GitHub issues in my beloved Molecule project: https://github.com/ansible-community/molecule-vagrant/issues/2#issuecomment-585616279 & especially https://github.com/ansible-community/molecule-vagrant/issues/8#issuecomment-589902704, which confused me right away.
Did you know [libvirt](https://libvirt.org/)??! I didn't, this thing is a crazy thing - [an API for all those virtualization providers out there](https://help.ubuntu.com/lts/serverguide/libvirt.html) (sounds like Vagrant, huh?!). And as the GitHub Issue comments state, it should be possible to use Vagrant with libvrt & KVM on TravisCI... Which would give us the following workflow for our tools:
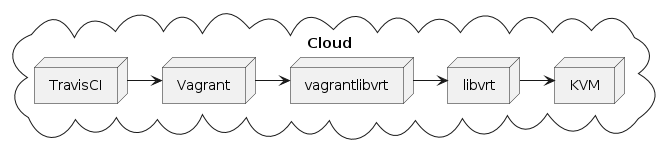
We also need an Vagrant-extension for libvirt, which is luckily already available: [the Vagrant libvirt Plugin](https://github.com/vagrant-libvirt/vagrant-libvirt)
__ONLY IF__ there are Vagrant Boxes that support both `libvrt` & `virtualbox` as a provider. And... there are! Just have a look at the `generic` boxes on the Vagrant Cloud: https://app.vagrantup.com/boxes/search?provider=libvirt&q=ubuntu+bionic&sort=downloads&utf8=%E2%9C%93, which are backed by https://roboxes.org
This would fulfil our request: in both cases a simple `vagrant up` based on the same [Vagrantfile](Vagrantfile) would work.
## Using vagrant-libvirt to run Vagrant with libvrt & KVM on TravisCI
First we need to configure the usual Travis [.travis.yml](.travis.yml) for our project:
```yaml
dist: bionic
language: python
install:
# Install libvrt & KVM (see https://github.com/alvistack/ansible-role-virtualbox/blob/master/.travis.yml)
- sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get install -y bridge-utils dnsmasq-base ebtables libvirt-bin libvirt-dev qemu-kvm qemu-utils ruby-dev
# Download Vagrant & Install Vagrant package
- sudo wget -nv https://releases.hashicorp.com/vagrant/2.2.7/vagrant_2.2.7_x86_64.deb
- sudo dpkg -i vagrant_2.2.7_x86_64.deb
# Vagrant correctly installed?
- vagrant --version
# Install vagrant-libvirt Vagrant plugin
- sudo vagrant plugin install vagrant-libvirt
```
Then we also need to install [vagrant-libvirt](https://github.com/vagrant-libvirt/vagrant-libvirt) on TravisCI.
## prevent errors like The home directory you specified is not accessible
You may experience some strange errors like `The home directory you specified is not accessible`:
```
$ vagrant up --provider=libvirt
Vagrant failed to initialize at a very early stage:
The home directory you specified is not accessible. The home
directory that Vagrant uses must be both readable and writable.
You specified: /home/travis/.vagrant.d
The command "vagrant up --provider=libvirt" exited with 1.
```
or `Permission denied @ rb_sysopen - /home/travis/.vagrant.d/data/machine-index/index.lock (Errno::EACCES)`:
```
$ vagrant up --provider=libvirt
/opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/machine_index.rb:321:in `initialize': Permission denied @ rb_sysopen - /home/travis/.vagrant.d/data/machine-index/index.lock (Errno::EACCES)
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/machine_index.rb:321:in `open'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/machine_index.rb:321:in `with_index_lock'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/machine_index.rb:52:in `initialize'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/environment.rb:723:in `new'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/environment.rb:723:in `machine_index'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/environment.rb:206:in `block in action_runner'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/action/runner.rb:34:in `run'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/environment.rb:525:in `hook'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/lib/vagrant/environment.rb:774:in `unload'
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/bin/vagrant:185:in `ensure in '
from /opt/vagrant/embedded/gems/2.2.7/gems/vagrant-2.2.7/bin/vagrant:185:in `'
The command "vagrant up --provider=libvirt" exited with 1.
```
The simplest solution here is to always use `sudo` prefixing our `vagrant` commands (although [this stackoverflow answer](https://stackoverflow.com/a/29438084/4964553) tells us not to do so).
## Finally testdrive the Vagrant installation
Now we should be able to add a `vagrant up` to the `script` section to our [.travis.yml](.travis.yml). __But be sure__ to add the ` --provider=libvirt` to the command! Otherwise Vagrant won't pick up `libvrt` as it's virtualization provider ([as stated in the docs](https://github.com/vagrant-libvirt/vagrant-libvirt#start-vm9)):
```yaml
script:
- sudo vagrant up --provider=libvirt
- sudo vagrant ssh -c "echo 'hello world!'"
```
## polishing: cache vagrant boxes
To speed up our future builds, we should try to cache the big Vagrant boxes throughout our builds. [The Travis docs state](https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/caching/#arbitrary-directories), that we only need to add the following to our [.travis.yml](.travis.yml):
```yaml
cache:
directories:
- /home/travis/.vagrant.d/boxes
```
Don't simple use `.vagrant.d/boxes` here, since Vagrant will place it's boxes inside `/home/travis/.vagrant.d/boxes` - and not inside `$TRAVIS_BUILD_DIR/.vagrant.d/boxes` which expands to `/home/travis/build/jonashackt/vagrant-travisci/.vagrant.d/boxes`.
## prevent Error while creating domain: Error saving the server: Call to virDomainDefineXML failed: invalid argument: could not find capabilities for domaintype=kvm
If we don't have a look into our [Vagrantfile](Vagrantfile) beforehand, we may run into the following error:
```
$ sudo vagrant up --provider=libvirt
Bringing machine 'ubuntu' up with 'libvirt' provider...
==> ubuntu: Box 'generic/ubuntu1804' could not be found. Attempting to find and install...
ubuntu: Box Provider: libvirt
ubuntu: Box Version: >= 0
==> ubuntu: Loading metadata for box 'generic/ubuntu1804'
ubuntu: URL: https://vagrantcloud.com/generic/ubuntu1804
==> ubuntu: Adding box 'generic/ubuntu1804' (v2.0.6) for provider: libvirt
ubuntu: Downloading: https://vagrantcloud.com/generic/boxes/ubuntu1804/versions/2.0.6/providers/libvirt.box
ubuntu: Download redirected to host: vagrantcloud-files-production.s3.amazonaws.com
==> ubuntu: Successfully added box 'generic/ubuntu1804' (v2.0.6) for 'libvirt'!
==> ubuntu: Uploading base box image as volume into libvirt storage...
==> ubuntu: Creating image (snapshot of base box volume).
==> ubuntu: Creating domain with the following settings...
==> ubuntu: -- Name: molecule-ansible-docker-aws_ubuntu
==> ubuntu: -- Domain type: kvm
==> ubuntu: -- Cpus: 2
==> ubuntu: -- Feature: acpi
==> ubuntu: -- Feature: apic
==> ubuntu: -- Feature: pae
==> ubuntu: -- Memory: 2048M
==> ubuntu: -- Management MAC:
==> ubuntu: -- Loader:
==> ubuntu: -- Nvram:
==> ubuntu: -- Base box: generic/ubuntu1804
==> ubuntu: -- Storage pool: default
==> ubuntu: -- Image: /var/lib/libvirt/images/molecule-ansible-docker-aws_ubuntu.img (32G)
==> ubuntu: -- Volume Cache: default
==> ubuntu: -- Kernel:
==> ubuntu: -- Initrd:
==> ubuntu: -- Graphics Type: vnc
==> ubuntu: -- Graphics Port: -1
==> ubuntu: -- Graphics IP: 127.0.0.1
==> ubuntu: -- Graphics Password: Not defined
==> ubuntu: -- Video Type: cirrus
==> ubuntu: -- Video VRAM: 256
==> ubuntu: -- Sound Type:
==> ubuntu: -- Keymap: en-us
==> ubuntu: -- TPM Path:
==> ubuntu: -- INPUT: type=mouse, bus=ps2
Error while creating domain: Error saving the server: Call to virDomainDefineXML failed: invalid argument: could not find capabilities for domaintype=kvm
The command "sudo vagrant up --provider=libvirt" exited with 1.
```
To prevent this, we need to use at least Ubuntu `bionic` as our Travis build system. Therefore we should configure it inside our [.travis.yml](.travis.yml):
```yaml
---
dist: bionic
...
```
# Optional: Install libvirt locally
You may also want to use libvirt locally. Therefore [we need to install libvirt and QEMU/KVM according to the docs](https://github.com/vagrant-libvirt/vagrant-libvirt#installation).
On Mac OS we can [simply use `homebrew` like this post describes](https://lunar.computer/posts/vagrant-libvirt-macos/):
```shell script
brew install libiconv gcc libvirt
```
Then run the libvirt service with
```
brew services start libvirt
```
Now we should be able to install the [vagrant-libvirt plugin](https://github.com/vagrant-libvirt/vagrant-libvirt#installation), but with some additions (cause otherwise we'll run into errors like `extconf.rb:73:in '': libvirt library not found in default locations (RuntimeError)`):
First, check the ruby version Vagrant uses with:
```
$ /opt/vagrant/embedded/bin/ruby --version
ruby 2.4.4p296 (2018-03-28 revision 63013) [x86_64-darwin13]
```
For me this is `2.4.4`, so insert the version and run:
```
$ CONFIGURE_ARGS='with-ldflags=-L/opt/vagrant/embedded/lib with-libvirt-include=/usr/local/include/libvirt with-libvirt-lib=/usr/local/lib' \
GEM_HOME=~/.vagrant.d/gems/2.4.4 \
GEM_PATH=$GEM_HOME:/opt/vagrant/embedded/gems \
PATH=/opt/vagrant/embedded/bin:$PATH \
vagrant plugin install vagrant-libvirt
```
This should install `libvirt` successfully:
```
Installing the 'vagrant-libvirt' plugin. This can take a few minutes...
Building native extensions. This could take a while...
Fetching: fog-libvirt-0.7.0.gem (100%)
Fetching: vagrant-libvirt-0.0.45.gem (100%)
Installed the plugin 'vagrant-libvirt (0.0.45)'!
```
Now we should be able to fire up our Molecule Vagrant test based on `libvirt`:
```
pipenv run molecule --debug create --scenario-name vagrant-libvirt-ubuntu
```
Final problem: https://discourse.brew.sh/t/failed-to-connect-socket-to-var-run-libvirt-libvirt-sock-no-such-file-or-directory/1297
As simple `vagrant up` with libirt doesn't work right now:
```
vagrant up --provider=libvirt
Bringing machine 'ubuntu' up with 'libvirt' provider...
Error while connecting to libvirt: Error making a connection to libvirt URI qemu:///system?no_verify=1&keyfile=/Users/jonashecht/.ssh/id_rsa&socket=/var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock:
Call to virConnectOpen failed: Socket-Erstellung zu '/var/run/libvirt/libvirt-sock' fehlgeschlagen: No such file or directory
```