Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/jupyterphysscilab/jupyter-instructortools
Tools for making JupyterPhysSciLab notebook templates for student handouts
https://github.com/jupyterphysscilab/jupyter-instructortools
educational-software educational-technology jupyter jupyter-notebook pandas plotting python
Last synced: 12 days ago
JSON representation
Tools for making JupyterPhysSciLab notebook templates for student handouts
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jupyterphysscilab/jupyter-instructortools
- Owner: JupyterPhysSciLab
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2020-03-20T00:24:46.000Z (almost 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-15T20:14:26.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-15T20:18:14.785Z (about 1 month ago)
- Topics: educational-software, educational-technology, jupyter, jupyter-notebook, pandas, plotting, python
- Language: TypeScript
- Size: 132 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: license-GPLV3.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# jupyter-instructortools
[Introduction](#introduction) |
[Usage](#usage) |
[Current Menu Items](#available-menu-items) |
[Typical workflow](#typical-workflow) | [Install](#install) |
[Issues or Comments](#issues-or-comments) |
[License](#this-software-is-distributed-under-the-gnu-v3-licensehttpsgnuorglicenses)
## Introduction
This adds a menu to Jupyter that automates some useful tasks an
instructor might want to do while building a notebook template for an
assignment. This is part of the
[Jupyter Physical Science Lab project](https://jupyterphysscilab.github.io/Documentation/),
but can be used independently of the rest of the project.
## Usage:
The menu that provides access to most of the tools is activated using the
"Activate menu" item in the "JPSL Instructor Tools" section of the Jupyter
Lab command palette (figure 1). By default it is inactive at the beginning
of a session.
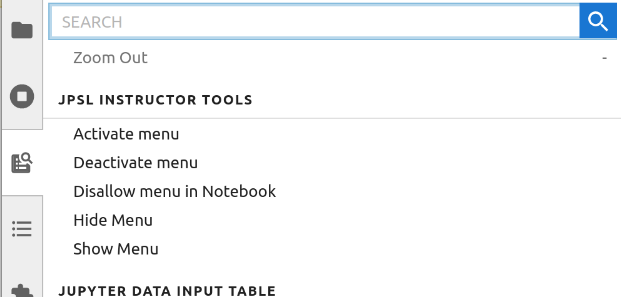
__Figure 1:__ Instructor Tool commands available in the Jupyter lab
command
palette.
The "Disallow menu in Notebook" option prevents the use of the Instructor
Tools menu with the _currently focused notebook_. This should only be done to
the final form of the notebook that will be distributed to students, because
it is very difficult to reverse.
### Available menu items
* Create a data input table.
* Table column and row labels can be locked once set.
* Number of rows and columns must be chosen on initial creation.
* Table will survive deletion of all cell output data.
* The code cell that creates the table is protected.
* Table creation code will work in a plain vanilla Jupyter install, but the
contents of the table cannot be edited.
* See the [jupyter-datainputtable](https://github.com/JupyterPhysSciLab/jupyter-datainputtable)
extension for more details.
* Add some highlight bars to a selected markdown cell. These can be removed by
deleting the associated`
`:
* A vertical cyan bracket at the left of the cell.
* A vertical red bracket at the left of the cell.
* A horizontal green start bar (fading down to beige). Useful for indicating
the beginning of an instruction block.
* A horizontal brown stop bar (fading down from beige to brown). Useful
for indicating the end of an instruction block.
* Protect/unprotect selected cells. Protected cells cannot be
edited or deleted by the user. This is a good way to prevent instructions
and example code from being damaged by students.
* Set/un-set selected cells as allowed to be hidden. This can be used to mark
cells to hide before producing a pdf to turn in.
* Set/un-set selected cells to collapse code before printing.
* Set/un-set selected cells to collapse code in JPSL.
* Temporarily highlight each kind of cell marked for hiding or code collapse.
* Temporarily completely hide (not collapse) code (all or just selected cells).
* Insert boilerplate instructions on initializing a
notebook into a selected markdown cell.
* Insert boilerplate instructions on preparing a pdf version of the notebook
to turn in with instructor selected parts hidden.
### Typical workflow
Work in a virtual environment that includes this tool plus all the tools
the students will have access to (see [Install](#install)).
1. Start the jupyter notebook server (from the command line use `jupyter
lab` or `jupyter notebook`).
1. Open a new notebook and activate the menu using the "Activate menu" item
in the "JPSL Instructor Tools" section of the Jupyter Lab command palette
(figure 1). By default it is inactive at the beginning of a session.
1. Build the exercise including instructions, examples, tables (use the menu)
and imports.
1. Collect all the necessary imports into a code cell that will be the
first code cell in the worksheet. You may want introductory material
before this cell.
1. Use the menu to protect any cells you do not want students to
accidentally alter.
1. Use the menu to tag cells so they can be hidden. This allows students to
print a compressed version of the notebook for grading. Consider hiding
most of the instructions.
1. Restart the kernel and clear all cell outputs. Delete or emtpy any cells
that have things you want the students to be filling in.
1. Save the notebook and make a duplicate of it. Continue working with the
duplicate.
1. Work through the notebook as if you were a student, make adjustments as
you go. Iterate restarting the kernel, clearing the cell outputs, saving,
duplicating and working though until satisfied.
1. Save the final version of the worksheet. Duplicate it.
1. Open the duplicate worksheet. Make sure all the appropriate cell data is
cleared. Then select "Disallow menu in Notebook" item in the "JPSL
Instructor Tools" section of the Jupyter Lab command palette (figure 1).
This will deactivate the menu and block students from easily
reinstalling it. Save the notebook and distribute this copy to students.
## Requirements
* JupyterLab >= 4.0.0
* notebook >= 7.0.0
* jupyter-datainputtable >=0.8.0
## Install
Installation using pip into a virtual environment is recommended. My
favorite way to manage virtual environments is using
[pipenv](https://pipenv.pypa.io/en/latest/). You should also consider
[venv](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html) which is part of the
standard Python library and [hatch](https://hatch.pypa.io/latest/) for
development.
__Option 1__: Recommended, as this will install all of the Jupyter Physical
Science Lab packages an Instructor might need. Use the
[JPSLInstructor pseudo package](https://github.com/JupyterPhysSciLab/JPSLInstructor).
```bash
pip install JPSLInstructor
```
__Option 2__: Install just this package and its minimal requirements. You
may want to do this if you are just making worksheets, do not need live
data acquisition or want to use a very specific set of packages.
```bash
pip install jupyter_instructortools
```
## Contributing
### Development install
Note: You will need NodeJS to build the extension package.
The `jlpm` command is JupyterLab's pinned version of
[yarn](https://yarnpkg.com/) that is installed with JupyterLab. You may use
`yarn` or `npm` in lieu of `jlpm` below.
```bash
# Clone the repo to your local environment
# Change directory to the jupyter_datainputtable directory
# Install package in development mode
pip install -e "."
# Link your development version of the extension with JupyterLab
jupyter labextension develop . --overwrite
# Rebuild extension Typescript source after making changes
jlpm build
```
You can watch the source directory and run JupyterLab at the same time in different terminals to watch for changes in the extension's source and automatically rebuild the extension.
```bash
# Watch the source directory in one terminal, automatically rebuilding when needed
jlpm watch
# Run JupyterLab in another terminal
jupyter lab
```
With the watch command running, every saved change will immediately be built locally and available in your running JupyterLab. Refresh JupyterLab to load the change in your browser (you may need to wait several seconds for the extension to be rebuilt).
By default, the `jlpm build` command generates the source maps for this extension to make it easier to debug using the browser dev tools. To also generate source maps for the JupyterLab core extensions, you can run the following command:
```bash
jupyter lab build --minimize=False
```
### Development uninstall
```bash
pip uninstall jupyter_instructortools
```
In development mode, you will also need to remove the symlink created by `jupyter labextension develop`
command. To find its location, you can run `jupyter labextension list` to figure out where the `labextensions`
folder is located. Then you can remove the symlink named
`jupyter-instructortools` within that folder.
### Testing the extension (currently incomplete)
#### Frontend tests
This extension is using [Jest](https://jestjs.io/) for JavaScript code testing.
To execute them, execute:
```sh
jlpm
jlpm test
```
#### Integration tests
This extension uses [Playwright](https://playwright.dev/docs/intro) for the integration tests (aka user level tests).
More precisely, the JupyterLab helper [Galata](https://github.com/jupyterlab/jupyterlab/tree/master/galata) is used to handle testing the extension in JupyterLab.
More information are provided within the [ui-tests](./ui-tests/README.md) README.
### Packaging the extension
See [RELEASE](RELEASE.md)
## Issues or comments
Issues or bugs should be reported via the project's [issues pages](https://github.com/JupyterPhysSciLab/jupyter-instructortools/issues).
Copyright - Jonathan Gutow, 2020 - 2024.