https://github.com/jzaragosa06/flask_server
https://github.com/jzaragosa06/flask_server
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/jzaragosa06/flask_server
- Owner: jzaragosa06
- Created: 2024-07-10T04:35:54.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: improved-decision-rule
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-07T10:44:59.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-07T11:39:26.766Z (11 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 372 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# API for Automated time series forecasting project
This is an http API that receives and process time series data and sends back the result. This API is built using Flask. This API was developed as a complement this [web application](https://github.com/jzaragosa06/forecast_web_app).
### API Functionality:
1. Forecast on univariate or multivariate time series data. If the data has a gap, the system inserts date in between these gaps and use forward fill method so that the each consecutive data points have equal interval.
2. Analyze the trend of time series data using Facebook's Prophet package.
3. Analyze for the seasonality of time series data using Facebook's Prophet package.
### End point
The following describe the routes to access the API functionality. Note that the time series data is passed in the request body. All the endpoint uses POST method. All endpoints require date index.
1. `/forecast-univariate` forecast a univariate time series data.
2. `/forecast-multivariate` forecast multivariate time series data. The last column is the target time series variable to forecast.
3. `/trend` analyzes for trend. This accepts univariate and multivariate time series data.
4. `/seasonality` analyzes for seasonality (i.e., recurring patterns). This accepts univariate and multivariate time series data. Only week and yearly seasonality is supported.
## About Univariate Time Series Forecasting
For univariate forecasting, we employ a **hybrid model** using **stacking regression**. The base models include:
- **Lasso** (`sklearn.linear_model.Lasso`)
- **ElasticNet** (`sklearn.linear_model.ElasticNet`)
- **DecisionTreeRegressor** (`sklearn.tree.DecisionTreeRegressor`)
The meta-model is:
- **Ridge Regression** (`sklearn.linear_model.Ridge`)
These models were selected based on research findings.
```python
base_estimators = [
("lasso", Lasso(random_state=123)),
("enr", ElasticNet(random_state=123)),
("dt", DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=123)),
]
meta_estimator = Ridge(random_state=123)
stacking_regressor = StackingRegressor(
estimators=base_estimators, final_estimator=meta_estimator
)
# Initialize the ForecasterAutoreg
forecaster = ForecasterAutoreg(
regressor=stacking_regressor,
lags=lag_value,
transformer_y=StandardScaler(),
transformer_exog=StandardScaler(),
)
```
The hybrid model which uses the stacking regression can be visualized using the diagram below:
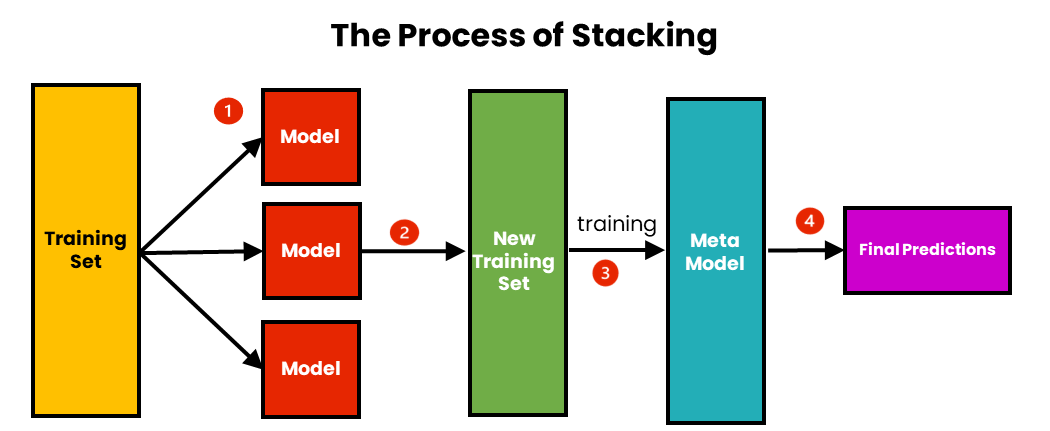
We used `skforecast` package to transform this model into a forecasting model. To optimize the hybrid model specific for a time series data, we perform a hyperparameter tuning using random search for the parameters of the models. We use `Mean Squared Error` as metric. The data are normalized using the StandardScaler from `sklearn.preprocessing`
```python
param_grid = {
"lasso__alpha": [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100],
"lasso__max_iter": [500, 1000, 1500],
"enr__alpha": [0.001, 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10.0],
"enr__l1_ratio": [0.1, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9, 1.0],
"dt__max_depth": [3, 5, 10, None],
"dt__min_samples_split": [2, 5, 10],
"dt__min_samples_leaf": [1, 2, 4],
"dt__max_features": [None, "sqrt", "log2"],
"final_estimator__alpha": [0.01, 0.1, 1, 10, 100],
"final_estimator__fit_intercept": [True, False],
"final_estimator__solver": ["auto", "svd", "cholesky", "lsqr", "saga"],
}
# Perform random search with verbose output
search_results = random_search_forecaster(
forecaster=forecaster,
y=df.iloc[:, 0], # Time series data
param_distributions=param_grid,
lags_grid=[3, 5, 7, 12, 14],
steps=10,
exog=exog,
n_iter=10,
metric="mean_squared_error",
initial_train_size=int(len(df) * 0.8),
fixed_train_size=False,
refit=True,
return_best=True,
random_state=123,
verbose=True,
)
```
To make the search more robust, we are performing backtesting on different split (i.e., by setting the refit parameter to True).
we started with the 80% of the training and 20% of the testing and incrementally increase the training set and reduce the testing set.
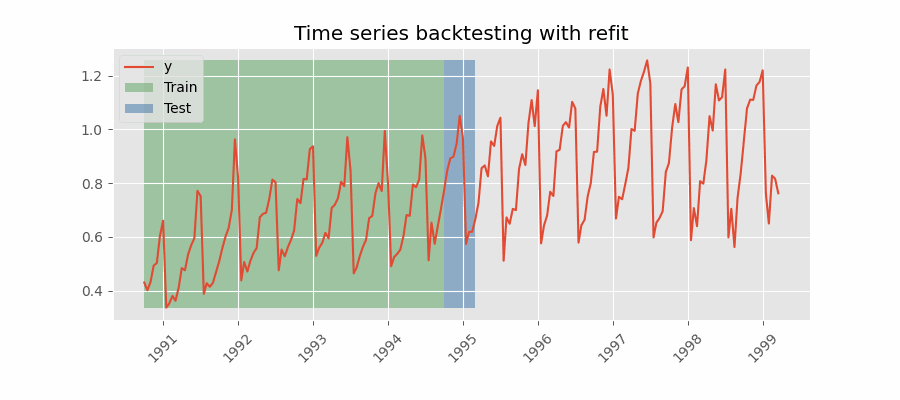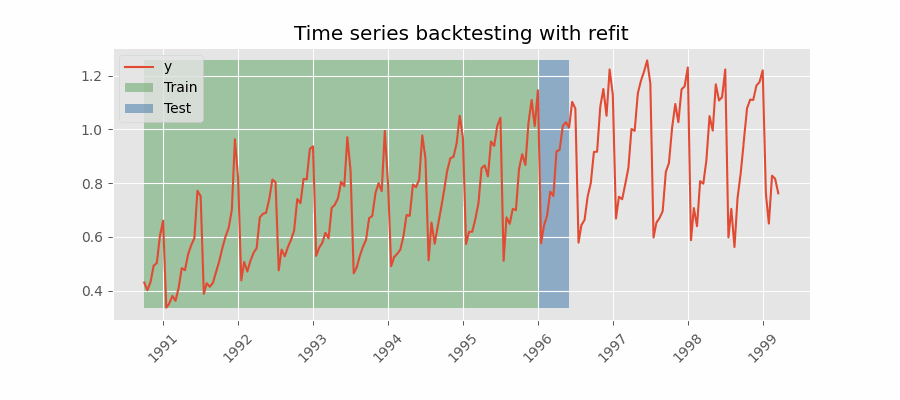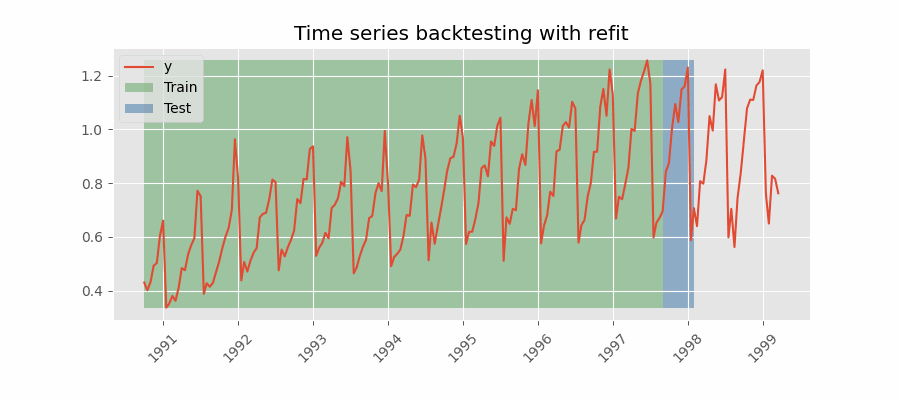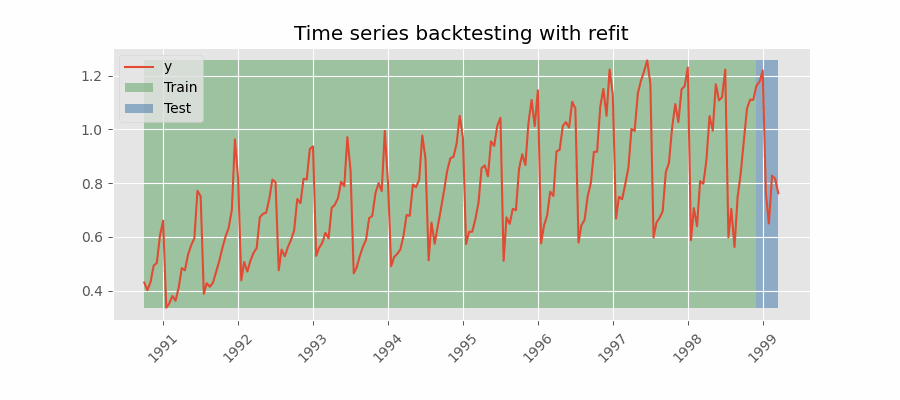
The result of this random search is a model with the lowest error.
we Then use this model to forecast the future values of the time series.
## About Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
For this we are using DecisionTreeRegressor from sklearn.tree. This decision is based on the result of our findings in our research/capstone.
```python
forecaster = ForecasterAutoregMultiVariate(
regressor=DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=123),
level=df.columns[-1],
lags=lag_value,
steps=10,
transformer_series=StandardScaler(),
transformer_exog=StandardScaler(),
)
```
The decision tree can be visualized using the diagram below:

We used `skforecast` package to transform this model into a forecasting model. To optimize the hybrid model specific for a time series data, we perform a hyperparameter tuning using random search for the parameters of the models. We use `Mean Squared Error` as metric.The data are normalized using the StandardScaler from `sklearn.preprocessing`
```python
param_grid = {
"max_depth": [3, 5, 10, None], # Depth of the tree
"min_samples_split": [2, 5, 10], # Minimum samples to split a node
"min_samples_leaf": [1, 2, 4], # Minimum samples per leaf
"max_features": [
None,
"sqrt",
"log2",
], # Number of features to consider for split
}
# Perform random search to find the best hyperparameters
results_random_search = random_search_forecaster_multivariate(
forecaster=forecaster,
series=df, # The column of time series data
param_distributions=param_grid,
lags_grid=[3, 5, 7, 12, 14],
steps=10,
exog=exog,
n_iter=10,
metric="mean_squared_error",
initial_train_size=int(len(df) * 0.8),
refit=True, # this will perform a backtesting on different split, where the model refit every increase in training size.
fixed_train_size=False,
return_best=True, # Return the best parameter set
random_state=123,
)
```
To make the search more robust, we are performing backtesting on different split (i.e., by setting the refit parameter to True).
we started with the 80% of the training and 20% of the testing and incrementally increase the training set and reduce the testing set.

The result of this random search is a model with the lowest error.
we Then use this model to forecast the future values of the time series.