https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl
Kepler.gl is a powerful open source geospatial analysis tool for large-scale data sets.
https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl
data-visualization geospatial kepler mapbox visualization
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
Kepler.gl is a powerful open source geospatial analysis tool for large-scale data sets.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl
- Owner: keplergl
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-02-28T21:36:16.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-05-13T08:00:20.000Z (2 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-13T11:01:49.870Z (2 months ago)
- Topics: data-visualization, geospatial, kepler, mapbox, visualization
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: http://kepler.gl
- Size: 33.9 MB
- Stars: 10,758
- Watchers: 206
- Forks: 1,820
- Open Issues: 552
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: contributing/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- License: LICENSE
- Security: .github/SECURITY.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-robotic-tooling - kepler.gl - Kepler.gl is a powerful open source geospatial analysis tool for large-scale data sets. (Data Visualization and Mission Control / Command Line Interface)
- awesome-starts - keplergl/kepler.gl - Kepler.gl is a powerful open source geospatial analysis tool for large-scale data sets. (Jupyter Notebook)
- awesome-robotic-tooling - kepler.gl - Kepler.gl is a powerful open source geospatial analysis tool for large-scale data sets. (Interaction / Data Visualization and Mission Control)
README
kepler.gl | Website | Demo App | Docs
[ ](http://kepler.gl)
](http://kepler.gl)
[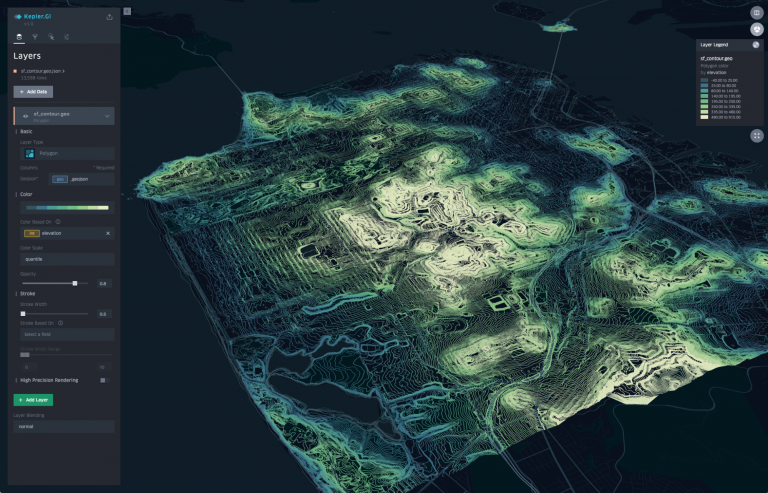 ](http://kepler.gl/#/demo)
](http://kepler.gl/#/demo)
[Kepler.gl][web] is a data-agnostic, high-performance web-based application for visual exploration of large-scale geolocation data sets. Built on top of [MapLibre GL](https://maplibre.org/) and [deck.gl](https://deck.gl/), kepler.gl can render millions of points representing thousands of trips and perform spatial aggregations on the fly.
Kepler.gl is also a React component that uses [Redux](https://redux.js.org/) to manage its state and data flow. It can be embedded into other React-Redux applications and is highly customizable. For information on how to embed kepler.gl in your app take a look at this step-by-step [tutorial](https://github.com/uber-archive/vis-academy/blob/master/src/docs/kepler.gl/0-setup.md) on vis.academy.
## Links
- [Website][web]
- [Demo][demo-app]
- [Examples][examples]
- [Get Started][get-started]
- [App User Guide][user-guide]
- [Jupyter Widget User Guide][user-guide-jupyter]
- [Tutorial][vis-academy]
- [Stack Overflow][stack]
- [Contribution Guidelines][contributing]
- [Api Reference][api-reference]
- [Roadmap][roadmap]
## Env
Use Node 18.18.2 or above, older node versions have not been supported/ tested.
For best results, use [nvm](https://github.com/creationix/nvm) `nvm install`.
## Install kepler.gl modules
Kepler.gl consists of different modules. Each module can be added to the project like this:
```sh
npm install --save @kepler.gl/components
// or
yarn add @kepler.gl/components
```
kepler.gl is built upon [mapbox][mapbox]. You will need a [Mapbox Access Token][mapbox-token] to use it.
If you don't use a module bundler, it's also fine. Kepler.gl npm package includes precompiled production UMD builds in the [umd folder](https://unpkg.com/kepler.gl/umd).
You can add the script tag to your html file as it follows (latest version of Kepler.gl):
```html
```
or if you would like, you can load a specific version:
```html
```
## Develop kepler.gl
Take a look at the [development guide][developers] to develop kepler.gl locally.
## Basic Usage
Here are the basic steps to import kepler.gl into your app. You also take a look at the examples folder. Each example in the folder can be installed and run locally.
### 1. Mount reducer
Kepler.gl uses Redux to manage its internal state, along with [react-palm][react-palm] middleware to handle side effects.
You need to add `taskMiddleware` of `react-palm` to your store too. We are actively working on a solution where
`react-palm` will not be required, however it is still a very lightweight side effects management tool that is easier to test than react-thunk.
```js
import {createStore, combineReducers, applyMiddleware, compose} from 'redux';
import keplerGlReducer from '@kepler.gl/reducers';
import {enhanceReduxMiddleware} from '@kepler.gl/middleware';
const initialState = {};
const reducers = combineReducers({
// <-- mount kepler.gl reducer in your app
keplerGl: keplerGlReducer,
// Your other reducers here
app: appReducer
});
// using createStore
export default createStore(
reducer,
initialState,
applyMiddleware(
enhanceReduxMiddleware([
/* Add other middlewares here */
])
)
);
```
Or if use enhancer:
```js
// using enhancers
const initialState = {};
const middlewares = enhanceReduxMiddleware([
// Add other middlewares here
]);
const enhancers = [applyMiddleware(...middlewares)];
export default createStore(reducer, initialState, compose(...enhancers));
```
If you mount kepler.gl reducer in another address instead of `keplerGl`, or the kepler.gl reducer is not
mounted at root of your state, you will need to specify the path to it when you mount the component
with the `getState` prop.
Read more about [Reducers][reducers].
### 2. Mount Component
```js
import KeplerGl from '@kepler.gl/components';
const Map = props => (
);
```
### Props
| Prop Name | Type | Default Value | Description |
|-------------------------------|-------------|----------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| `id` | String | `map` | The unique identifier for the KeplerGl instance. Required when multiple KeplerGl instances exist. It maps to the state in the reducer (e.g. component with id `foo` can be found in`state.keplerGl.foo`). |
| `mapboxApiAccessToken` | String | `undefined` | API token for Mapbox, used for rendering base maps. Create a free token at [Mapbox](https://www.mapbox.com). |
| `getState` | Function | `state => state.keplerGl` | Function that specifies the path to the root KeplerGl state in the reducer. |
| `width` | Number | `800` | The width of the KeplerGl UI in pixels. |
| `height` | Number | `800` | The height of the KeplerGl UI in pixels. |
| `appName` | String | `Kepler.Gl` | The app name displayed in the side panel header. |
| `version` | String | `v1.0` | The version displayed in the side panel header. |
| `onSaveMap` | Function | `undefined` | A function called when the "Save Map URL" in side panel header is clicked. |
| `onViewStateChange` | Function | `undefined` | Triggered when the map viewport is updated. Receives `viewState` parameter with updated values like longitude, latitude, zoom, etc. |
| `getMapboxRef(mapbox, index)` | Function | `undefined` | Called when `KeplerGl` adds or removes a MapContainer with an inner Mapbox map. `mapbox` is a `MapRef` when added, or `null` when removed. `index` is `0` for the first map and `1` for the second map in a split view. |
| `actions` | Object | `{}` | Custom action creators to override the default KeplerGl action creators. Only use custom action when you want to modify action payload. |
| `mint` | Boolean | `true` | Determines whether to load a fresh empty state when mounted. When `false`, the state persists across remounts. Useful for modal use cases. |
| `theme` | Object/String| `null` | Set to `"dark"`, `"light"`, or `"base"`, or pass a theme object to customize KeplerGl’s style. |
| `mapboxApiUrl` | String | `https://api.mapbox.com` | The Mapbox API URL if you are using a custom Mapbox tile server. |
| `mapStylesReplaceDefault` | Boolean | `false` | Set to `true` to replace default map styles with custom ones. (see ```mapStyles``` prop) |
| `mapStyles` | Array | `[]` | An array of [custom map styles](#example-custom-map-style) for the map style selection panel. Styles replace the default ones if `mapStylesReplaceDefault` is `true`. |
| `initialUiState` | Object | `undefined` | The initial UI state applied to the `uiState` reducer. |
| `localeMessages` | Object | `undefined` | Used to modify or add new translations. Read more about [Localization][localization]. |
#### Example Custom Map Style
You can supply additional map styles to be displayed in [map style selection panel](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/blob/master/docs/user-guides/f-map-styles/1-base-map-styles.md). By default, additional map styles will be added to default map styles. If you pass `mapStylesReplaceDefault: true`, they will replace the default ones. kepler.gl will attempt to group layers of your style based on its `id` naming convention and use it to allow toggle visibility of [base map layers](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/blob/master/docs/user-guides/f-map-styles/2-map-layers.md). Supply your own `layerGroups` to override default for more accurate layer grouping.
Each `mapStyles` should has the following properties:
- `id` (String, required) unique string that should **not** be one of these reserved `dark` `light` `muted`. `muted_night`
- `label` (String, required) name to be displayed in map style selection panel
- `url` (String, required) mapbox style url or a url pointing to the map style json object written in [Mapbox GL Style Spec](https://docs.mapbox.com/mapbox-gl-js/style-spec/).
- `icon` (String, optional) image icon of the style, it can be a url, or an [image data url](https://flaviocopes.com/data-urls/#how-does-a-data-url-look)
- `layerGroups` (Array, optional)
```js
const mapStyles = [
{
id: 'my_dark_map',
label: 'Dark Streets 9',
url: 'mapbox://styles/mapbox/dark-v9',
icon: `${apiHost}/styles/v1/mapbox/dark-v9/static/-122.3391,37.7922,9.19,0,0/400x300?access_token=${accessToken}&logo=false&attribution=false`,
layerGroups: [
{
slug: 'label',
filter: ({id}) => id.match(/(?=(label|place-|poi-))/),
defaultVisibility: true
},
{
slug: '3d building',
filter: () => false,
defaultVisibility: false
}
]
}
];
```
### 3. Dispatch custom actions to `keplerGl` reducer.
One advantage of using the reducer over React component state to handle keplerGl state is the flexibility
to customize its behavior. If you only have one `KeplerGl` instance in your app or never intend to dispatch actions to KeplerGl from outside the component itself,
you don’t need to worry about forwarding dispatch and can move on to the next section. But life is full of customizations, and we want to make yours as enjoyable as possible.
There are multiple ways to dispatch actions to a specific `KeplerGl` instance.
- In the root reducer, with reducer updaters.
Each action is mapped to a reducer updater in kepler.gl. You can import the reducer updater corresponding to a specific action, and call it with the previous state and action payload to get the updated state.
e.g. `updateVisDataUpdater` is the updater for `ActionTypes.UPDATE_VIS_DATA` (take a look at each reducer `reducers/vis-state.js` for action to updater mapping).
Here is an example how you can listen to an app action `QUERY_SUCCESS` and call `updateVisDataUpdater` to load data into Kepler.Gl.
```js
import {keplerGlReducer, visStateUpdaters} from '@kepler.gl/reducers';
// Root Reducer
const reducers = combineReducers({
keplerGl: keplerGlReducer,
app: appReducer
});
const composedReducer = (state, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'QUERY_SUCCESS':
return {
...state,
keplerGl: {
...state.keplerGl,
// 'map' is the id of the keplerGl instance
map: {
...state.keplerGl.map,
visState: visStateUpdaters.updateVisDataUpdater(state.keplerGl.map.visState, {
datasets: action.payload
})
}
}
};
}
return reducers(state, action);
};
export default composedReducer;
```
Read more about [using updaters to modify kepler.gl state][using-updaters]
- Using redux `connect`
You can add a dispatch function to your component that dispatches actions to a specific `keplerGl` component,
using connect.
```js
// component
import KeplerGl from '@kepler.gl/components';
// action and forward dispatcher
import {toggleFullScreen, forwardTo} from '@kepler.gl/actions';
import {connect} from 'react-redux';
const MapContainer = props => (
props.keplerGlDispatch(toggleFullScreen())}/>
)
const mapStateToProps = state => state
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch, props) => ({
dispatch,
keplerGlDispatch: forwardTo(‘foo’, dispatch)
});
export default connect(
mapStateToProps,
mapDispatchToProps
)(MapContainer);
```
- Wrap action payload
You can also simply wrap an action into a forward action with the `wrapTo` helper
```js
// component
import KeplerGl from '@kepler.gl/components';
// action and forward dispatcher
import {toggleFullScreen, wrapTo} from '@kepler.gl/actions';
// create a function to wrapper action payload to 'foo'
const wrapToMap = wrapTo('foo');
const MapContainer = ({dispatch}) => (
dispatch(wrapToMap(toggleFullScreen())} />
);
```
Read more about [forward dispatching actions][forward-actions]
### 4. Customize style.
Kepler.gl implements css styling using [Styled-Components](https://www.styled-components.com/). By using said framework Kepler.gl offers the ability to customize its style/theme using the following approaches:
- Passing a Theme prop
- Styled-Components ThemeProvider
The available properties to customize are listed here [theme](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/blob/master/src/styles/base.js).
[Custom theme example](https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/tree/master/examples/custom-theme).
#### Passing a Theme prop.
You can customize Kepler.gl theme by passing a **theme** props to Kepler.gl react component as it follows:
```javascript
const white = '#ffffff';
const customTheme = {
sidePanelBg: white,
titleTextColor: '#000000',
sidePanelHeaderBg: '#f7f7F7',
subtextColorActive: '#2473bd'
};
return (
);
```
As you can see the customTheme object defines certain properties which will override Kepler.gl default style rules.
#### Styled-Components Theme Provider.
In order to customize Kepler.gl theme using [ThemeProvider](https://www.styled-components.com/docs/api#themeprovider) you can simply wrap Kepler.gl using ThemeProvider as it follows:
```javascript
import {ThemeProvider} from 'styled-components';
const white = '#ffffff';
const customTheme = {
sidePanelBg: white,
titleTextColor: '#000000',
sidePanelHeaderBg: '#f7f7F7',
subtextColorActive: '#2473bd'
};
return (
);
```
### 5. Render Custom UI components.
Everyone wants the flexibility to render custom kepler.gl components. Kepler.gl has a dependency injection system that allow you to inject
components to KeplerGl replacing existing ones. All you need to do is to create a component factory for the one you want to replace, import the original component factory
and call `injectComponents` at the root component of your app where `KeplerGl` is mounted.
Take a look at `examples/demo-app/src/app.js` and see how it renders a custom side panel header in kepler.gl
```javascript
import {injectComponents, PanelHeaderFactory} from '@kepler.gl/components';
// define custom header
const CustomHeader = () =>
My kepler.gl app;
const myCustomHeaderFactory = () => CustomHeader;
// Inject custom header into Kepler.gl, replacing default
const KeplerGl = injectComponents([[PanelHeaderFactory, myCustomHeaderFactory]]);
// render KeplerGl, it will render your custom header instead of the default
const MapContainer = () => (
);
```
Using `withState` helper to add reducer state and actions to customized component as additional props.
```js
import {withState, injectComponents, PanelHeaderFactory} from '@kepler.gl/components';
import {visStateLens} from '@kepler.gl/reducers';
// custom action wrap to mounted instance
const addTodo = text =>
wrapTo('map', {
type: 'ADD_TODO',
text
});
// define custom header
const CustomHeader = ({visState, addTodo}) => (
addTodo('hello')}>{`${
Object.keys(visState.datasets).length
} dataset loaded`}
);
// now CustomHeader will receive `visState` and `addTodo` as additional props.
const myCustomHeaderFactory = () =>
withState(
// keplerGl state lenses
[visStateLens],
// customMapStateToProps
headerStateToProps,
// actions
{addTodo}
)(CustomHeader);
```
Read more about [replacing UI component][replace-ui-component]
### 6. How to add data to map
To interact with a kepler.gl instance and add new data to it, you can dispatch the **`addDataToMap`** action from anywhere inside your app. It adds a dataset or multiple datasets to a kepler.gl instance and updates the full configuration (mapState, mapStyle, visState).
#### Parameters
- `data` **[Object][40]** **\*required**
- `datasets` **([Array][41]<[Object][40]> | [Object][40])** **\*required** datasets can be a dataset or an array of datasets
Each dataset object needs to have `info` and `data` property.
- `datasets.info` **[Object][40]** \-info of a dataset
- `datasets.info.id` **[string][42]** id of this dataset. If config is defined, `id` should matches the `dataId` in config.
- `datasets.info.label` **[string][42]** A display name of this dataset
- `datasets.data` **[Object][40]** **\*required** The data object, in a tabular format with 2 properties `fields` and `rows`
- `datasets.data.fields` **[Array][41]<[Object][40]>** **\*required** Array of fields,
- `datasets.data.fields.name` **[string][42]** **\*required** Name of the field,
- `datasets.data.rows` **[Array][41]<[Array][41]>** **\*required** Array of rows, in a tabular format with `fields` and `rows`
- `options` **[Object][40]**
- `options.centerMap` **[boolean][43]** `default: true` if `centerMap` is set to `true` kepler.gl will place the map view within the data points boundaries
- `options.readOnly` **[boolean][43]** `default: false` if `readOnly` is set to `true`
the left setting panel will be hidden
- `options.keepExistingConfig` **[boolean][43]** `default: false` whether to keep exiting map config, including layers, filters and splitMaps.
- `config` **[Object][40]** this object will contain the full kepler.gl instance configuration {mapState, mapStyle, visState}
Kepler.gl provides an easy API `KeplerGlSchema.getConfigToSave` to generate a json blob of the current kepler instance configuration.
#### Examples
```javascript
// app.js
import {addDataToMap} from '@kepler.gl/actions';
const sampleTripData = {
fields: [
{name: 'tpep_pickup_datetime', format: 'YYYY-M-D H:m:s', type: 'timestamp'},
{name: 'pickup_longitude', format: '', type: 'real'},
{name: 'pickup_latitude', format: '', type: 'real'}
],
rows: [
['2015-01-15 19:05:39 +00:00', -73.99389648, 40.75011063],
['2015-01-15 19:05:39 +00:00', -73.97642517, 40.73981094],
['2015-01-15 19:05:40 +00:00', -73.96870422, 40.75424576]
]
};
const sampleConfig = {
visState: {
filters: [
{
id: 'me',
dataId: 'test_trip_data',
name: 'tpep_pickup_datetime',
type: 'timeRange',
view: 'enlarged'
}
]
}
};
this.props.dispatch(
addDataToMap({
datasets: {
info: {
label: 'Sample Taxi Trips in New York City',
id: 'test_trip_data'
},
data: sampleTripData
},
option: {
centerMap: true,
readOnly: false
},
config: sampleConfig
})
);
```
Read more about [addDataToMap](./docs/api-reference/actions/actions.md#adddatatomap) and [Saving and loading maps with schema manager][saving-loading-w-schema].
[contributing]: contributing/README.md
[demo-app]: http://kepler.gl/#/demo
[github]: https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl
[github-pr]: https://help.github.com/articles/creating-a-pull-request/
[mapbox]: https://www.mapbox.com
[mapbox-token]: https://www.mapbox.com/help/define-access-token/
[developers]: contributing/DEVELOPERS.md
[examples]: https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/tree/master/examples
[react-palm]: https://github.com/btford/react-palm
[roadmap]: https://github.com/keplergl/kepler.gl/wiki/Kepler.gl-2019-Roadmap
[stack]: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/kepler.gl
[web]: http://www.kepler.gl/
[vis-academy]: http://vis.academy/#/kepler.gl/
[user-guide]: docs/user-guides/README.md
[user-guide-jupyter]: docs/keplergl-jupyter/README.md
[api-reference]: docs/api-reference/README.md
[get-started]: ./docs/api-reference/get-started.md
[reducers]: docs/api-reference/reducers/README.md
[components]: docs/api-reference/components/README.md
[custom-theme]: docs/api-reference/custom-theme/README.md
[reducers]: docs/api-reference/reducers/README.md
[actions-updaters]: docs/api-reference/actions/README.md
[processors]: docs/api-reference/processors/README.md
[schemas]: docs/api-reference/schemas/README.md
[using-updaters]: ./docs/api-reference/advanced-usages/using-updaters.md
[custom-map-styles]: ./docs/api-reference/advanced-usages/custom-map-styles.md
[forward-actions]: ./docs/api-reference/advanced-usages/forward-actions.md
[replace-ui-component]: ./docs/api-reference/advanced-usages/replace-ui-component.md
[saving-loading-w-schema]: ./docs/api-reference/advanced-usages/saving-loading-w-schema.md
[localization]: ./docs/api-reference/localization/README.md
[40]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object
[41]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Array
[42]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/String
[43]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Boolean
[44]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Number
[45]: https://developer.mozilla.org/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Statements/function


