https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline
Snakemake-like pipeline manager for reproducible Jupyter Notebooks
https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline
jupyter jupyter-notebook snakemake
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Snakemake-like pipeline manager for reproducible Jupyter Notebooks
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline
- Owner: krassowski
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-05-22T16:24:15.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-10-04T19:36:41.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-13T04:05:06.394Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: jupyter, jupyter-notebook, snakemake
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 421 KB
- Stars: 17
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 5
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# nbpipeline
[](https://travis-ci.org/krassowski/nbpipeline)
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/188075188)
Snakemake-like pipelines for Jupyter Notebooks, producing interactive pipeline reports like this:
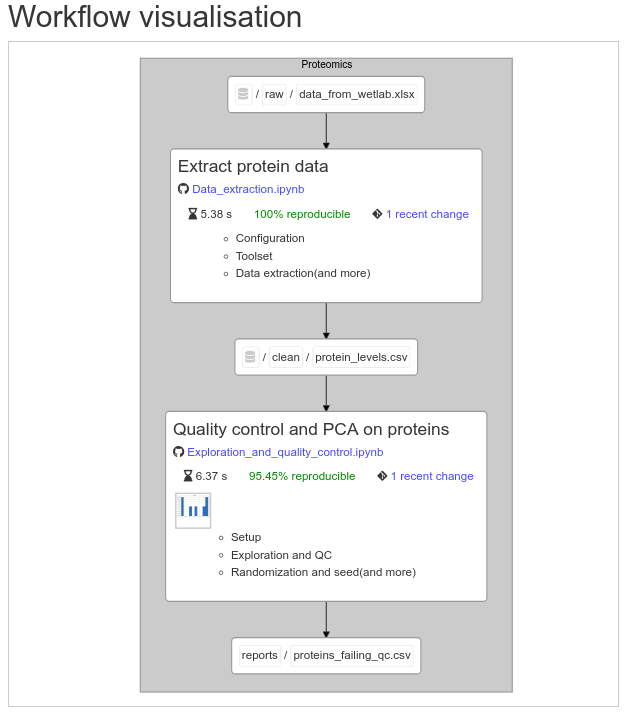
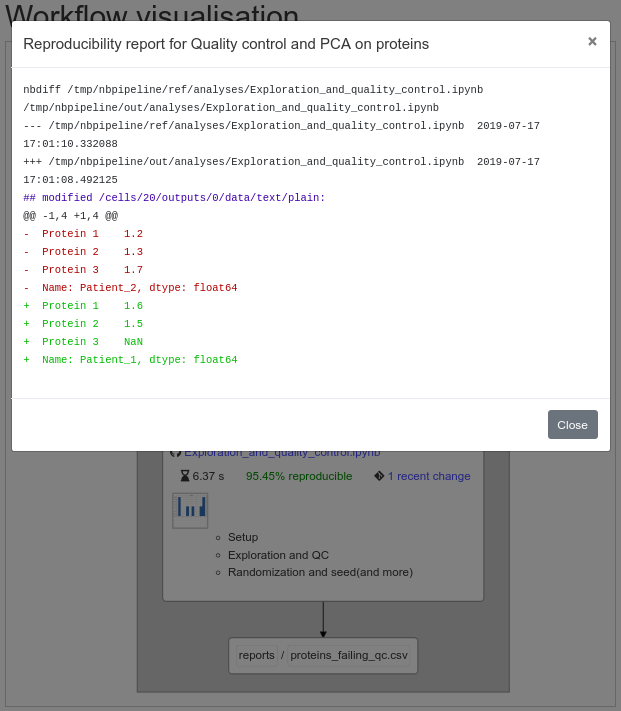
### Install & general remarks
These are still early days of this software so please bear in mind that it is not ready for production yet.
Note: for simplicity I assume that you are using a recent Ubuntu with git installed.
```bash
pip install nbpipeline
```
Graphiz is required for static SVG plots:
```bash
sudo apt-get install graphviz libgraphviz-dev graphviz-dev
```
#### Development install
To install the latest development version you may use:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline
cd nbpipeline
pip install -r requirements.txt
ln -s $(pwd)/bin/nbpipeline-dev ~/bin/nbpipeline
```
### Quickstart
Create `pipeline.py` file with list of rules for your pipeline. For example:
```python
from nbpipeline.rules import NotebookRule
NotebookRule(
'Extract protein data', # a nice name for the step
input={'protein_data_path': 'data/raw/data_from_wetlab.xlsx'},
output={'output_path': 'data/clean/protein_levels.csv'},
notebook='analyses/Data_extraction.ipynb',
group='Proteomics' # this is optional
)
NotebookRule(
'Quality control and PCA on proteins',
input={'protein_levels_path': 'data/clean/protein_levels.csv'},
output={'qc_report_path': 'reports/proteins_failing_qc.csv'},
notebook='analyses/Exploration_and_quality_control.ipynb',
group='Proteomics'
)
```
the keys of the input and output variables should correspond to variables in one of the first cells
in the corresponding notebook, which should be tagged as "parameters". It can be done easily in JupyterLab:
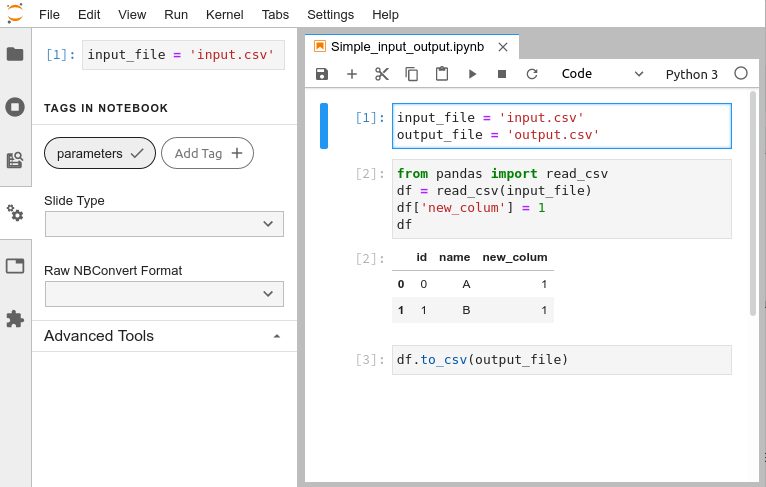
If you forget to add them, a warning will be displayed.
Alternativaly, you can create a dedicated cell for input paths definitions and tag it "inputs" and a separate one for output paths definitions, tagging it "outputs", which allows to omit input and output keywords when creating a `NotebookRule`. However, only simple variable definitions will be deduced (parsing uses regular expressions to avoid potential dangers of `eval`).
For more details, please see the example [pipeline](https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline/blob/master/examples/pipeline.py) and [notebooks](https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline/tree/master/examples/analyses) in the [examples](https://github.com/krassowski/nbpipeline/tree/master/examples) directory.
#### Run the pipeline:
```bash
nbpipeline
```
On any consecutive run the notebooks which did not change will not be run again.
To disable this cache, use `--disable_cache` switch.
To generate an interactive diagram of the rules graph, together with reproducibility report add `-i` switch:
```bash
nbpipeline -i
```
The software defaults to `google-chrome` for graph visualization display, which can be changed with a CLI option.
If you named your definition files differently (e.g. `my_rules.py` instead of `pipeline.py`), use:
```bash
nbpipeline --definitions_file my_rules.py
```
To display all command line options use:
```bash
nbpipeline -h
```
#### Troubleshooting
If you see `ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'name_of_your_local_module'`, you may need to enforce the path, running nbpipeline with:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=/path/to/the/parent/of/local/module:$PYTHONPATH nbpipeline
```
Oftentimes the path is the same as the current directory, so the following command may work:
```bash
PYTHONPATH=$(pwd):$PYTHONPATH nbpipeline
```