https://github.com/kubeflow-kale/kale
Kubeflow’s superfood for Data Scientists
https://github.com/kubeflow-kale/kale
jupyter-notebook kubeflow kubeflow-pipelines machine-learning
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Kubeflow’s superfood for Data Scientists
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/kubeflow-kale/kale
- Owner: kubeflow-kale
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2019-01-24T17:58:44.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-06T03:22:37.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-28T20:46:20.876Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: jupyter-notebook, kubeflow, kubeflow-pipelines, machine-learning
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://kubeflow-kale.github.io
- Size: 25.5 MB
- Stars: 633
- Watchers: 18
- Forks: 126
- Open Issues: 128
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-mlops - Kale - Aims at simplifying the Data Science experience of deploying Kubeflow Pipelines workflows. (Workflow Tools)
- awesome-kubeflow - Kale
- best-of-python - GitHub - 14% open · ⏱️ 06.11.2025): (Data Pipelines & Streaming)
README

---
KALE (Kubeflow Automated pipeLines Engine) is a project that aims at simplifying
the Data Science experience of deploying Kubeflow Pipelines workflows.
Kubeflow is a great platform for orchestrating complex workflows on top
Kubernetes and Kubeflow Pipeline provides the mean to create reusable components
that can be executed as part of workflows. The self-service nature of Kubeflow
make it extremely appealing for Data Science use, at it provides an easy access
to advanced distributed jobs orchestration, re-usability of components, Jupyter
Notebooks, rich UIs and more. Still, developing and maintaining Kubeflow
workflows can be hard for data scientists, who may not be experts in working
orchestration platforms and related SDKs. Additionally, data science often
involve processes of data exploration, iterative modelling and interactive
environments (mostly Jupyter notebook).
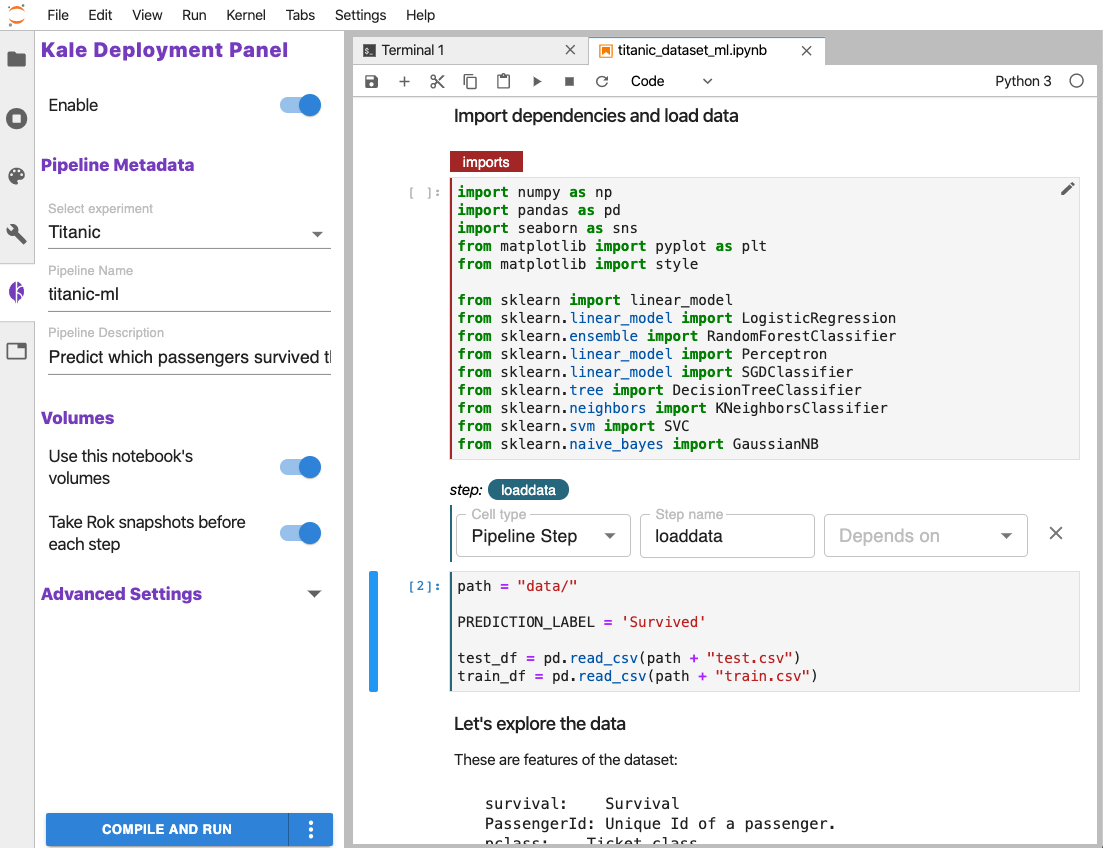
Kale bridges this gap by providing a simple UI to define Kubeflow Pipelines
workflows directly from you JupyterLab interface, without the need to change a
single line of code.
Read more about Kale and how it works in this Medium post:
[Automating Jupyter Notebook Deployments to Kubeflow Pipelines with Kale](https://medium.com/kubeflow/automating-jupyter-notebook-deployments-to-kubeflow-pipelines-with-kale-a4ede38bea1f)
## Getting started
Install the Kale backend from PyPI and the JupyterLab extension. You can find a
set of curated Notebooks in the
[examples repository](https://github.com/kubeflow-kale/examples)
```bash
# install kale
pip install kubeflow-kale
# install jupyter lab
pip install "jupyterlab>=2.0.0,<3.0.0"
# install the extension
jupyter labextension install kubeflow-kale-labextension
# verify extension status
jupyter labextension list
# run
jupyter lab
```
To build images to be used as a NotebookServer in Kubeflow, refer to the
Dockerfile in the `docker` folder.
### FAQ
Head over to [FAQ](FAQ.md) to read about some known issues and some of the
limitations imposed by the Kale data marshalling model.
## Resources
- Kale introduction [blog post](https://medium.com/kubeflow/automating-jupyter-notebook-deployments-to-kubeflow-pipelines-with-kale-a4ede38bea1f)
- Codelabs showcasing Kale working in MiniKF with Arrikto's [Rok](https://www.arrikto.com/):
- [From Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines](https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/cloud-kubeflow-minikf-kale/#0)
- [From Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines with HP Tuning](https://arrik.to/demowfhp)
- KubeCon NA Tutorial 2019: [From Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines: An End-to-End Data Science Workflow](https://kccncna19.sched.com/event/Uaeq/tutorial-from-notebook-to-kubeflow-pipelines-an-end-to-end-data-science-workflow-michelle-casbon-google-stefano-fioravanzo-fondazione-bruno-kessler-ilias-katsakioris-arrikto?iframe=no&w=100%&sidebar=yes&bg=no)
/ [video](http://youtube.com/watch?v=C9rJzTzVzvQ)
- CNCF Webinar 2020: [From Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines with MiniKF & Kale](https://www.cncf.io/webinars/from-notebook-to-kubeflow-pipelines-with-minikf-kale/)
/ [video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1fX9ZFWkvvs)
- KubeCon EU Tutorial 2020: [From Notebook to Kubeflow Pipelines with HP Tuning: A Data Science Journey](https://kccnceu20.sched.com/event/ZerG/tutorial-from-notebook-to-kubeflow-pipelines-with-hp-tuning-a-data-science-journey-stefano-fioravanzo-ilias-katsakioris-arrikto)
/ [video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QK0NxhyADpM)
## Contribute
#### Backend
Create a new Python virtual environment with `Python >= 3.6`. Then:
```bash
cd backend/
pip install -e .[dev]
# run tests
pytest -x -vv
```
#### Labextension
The JupyterLab Python package comes with its own yarn wrapper, called `jlpm`.
While using the previously installed venv, install JupyterLab by running:
```bash
pip install "jupyterlab>=2.0.0,<3.0.0"
```
You can then run the following to install the Kale extension:
```bash
cd labextension/
# install dependencies from package.lock
jlpm install
# build extension
jlpm run build
# list installed jp extensions
jlpm labextension list
# install Kale extension
jlpm labextension install .
# for development:
# build and watch
jlpm run watch
# in another shell, run JupyterLab in watch mode
jupyter lab --no-browser --watch
```
#### Git Hooks
This repository uses
[husky](https://github.com/typicode/husky)
to set up git hooks.
For `husky` to function properly, you need to have `yarn` installed and in your
`PATH`. The reason that is required is that `husky` is installed via
`jlpm install` and `jlpm` is a `yarn` wrapper. (Similarly, if it was installed
using the `npm` package manager, then `npm` would have to be in `PATH`.)
Currently installed git hooks:
- `pre-commit`: Run a prettier check on staged files, using
[pretty-quick](https://github.com/azz/pretty-quick)