https://github.com/lexsi-labs/dlbacktrace
DL Backtrace is a new explainablity technique for deep learning models that works for any modality and model type.
https://github.com/lexsi-labs/dlbacktrace
deep-learning explainability xai
Last synced: 20 days ago
JSON representation
DL Backtrace is a new explainablity technique for deep learning models that works for any modality and model type.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/lexsi-labs/dlbacktrace
- Owner: Lexsi-Labs
- License: other
- Created: 2024-11-18T10:21:54.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: dlb_v2
- Last Pushed: 2026-01-13T11:17:46.000Z (about 1 month ago)
- Last Synced: 2026-01-16T20:12:08.863Z (27 days ago)
- Topics: deep-learning, explainability, xai
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://dlbacktrace.lexsi.ai/
- Size: 29.3 MB
- Stars: 20
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.md
- Support: docs/support/changelog.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

DLBacktrace: Model-Agnostic Explainability for Any Deep Learning Model
Making AI Transparent and Explainable — Developed by Lexsi Labs 🚀
---
## Overview
DLBacktrace is a model-agnostic explainability framework developed by *Lexsi Labs*. It provides comprehensive layerwise importance values (relevance scores) and model tracing capabilities across a wide range of model architectures — including Transformers, Large Language Models (LLMs), Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs), and more — as well as diverse task types such as Tabular, Vision, and Text. The framework is designed for robust and efficient execution on both CPU and GPU environments.
## Key Features
### Core Capabilities
- **🔍 Deep Model Interpretability:** Gain comprehensive insights into your AI models using advanced relevance propagation algorithms
- **🎯 Multi-Task Support:** Binary/Multi-class classification, object detection, segmentation, and text generation
- **🏗️ Architecture Agnostic:** Support for Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Transformer, and custom architectures including Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs)
- **⚡ High Performance:** Optimized execution engine with CUDA acceleration and deterministic tracing
- **🔧 Robust Operations:** Full support for negative indexing and complex tensor operations
- **📊 Comprehensive Tracing:** Layer-wise activation and relevance analysis with detailed execution tracking
- **🛡️ Production Ready:** Deterministic execution environment with comprehensive error handling
### Advanced Features
- **🚀 High-Level Pipeline Interface:** Simplified API for text/image classification and generation with automatic model loading and configuration
- **🎲 DLB Auto Sampler:** Advanced text generation with multiple decoding strategies — including greedy decoding, beam search (deterministic), and stochastic sampling methods such as temperature, top-k, and top-p — along with token-level relevance tracking
- **🧠 Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs) Support:** Built-in support for MoEs architectures (JetMoE, OLMoE, Qwen3-MoE, GPT-Oss) with expert-level relevance analysis
- **🌡️ Temperature Scaling:** Control generation diversity and model confidence with flexible temperature parameters
- **🔄 Enhanced Execution Engine:** Critical fixes for RoBERTa, LLaMA, and other transformer models
---
## ⚡ Performance Improvements in DLB v2
DLB v2 introduces **major architectural upgrades** to the explainability engine — resulting in *orders of magnitude faster performance* compared to v1.
> 📘 **Note:** All benchmarks below were conducted on the **LLaMA-3.2–3B model** using the MMLU dataset on an NVIDIA RTX 4090.
---
### 📊 Benchmark Summary
| Metric | DLB v1 | DLB v2 | Improvement |
|:-------|:-------|:-------|:-------------|
| ⏱️ **Explainability Time** | 250–30,000 s (grows exponentially) | 🕒 12–18 s (nearly constant) | 🔥 **20× → 1400× faster** depending on sequence length |
| 🚀 **Throughput** | ~0.01–0.03 tokens/s | 🧩 3–75 tokens/s | ⚡ **100× → 2500× higher** |
| 📈 **Scalability** | Time increases ~8× every doubling | Grows slowly with input size | ✅ **Stable & linear-like scaling** |
---
### 📈 Performance Graphs
| Metric | Comparison Plot |
|:--------|:----------------|
| 🕒 **Total Time vs Sequence Length** | 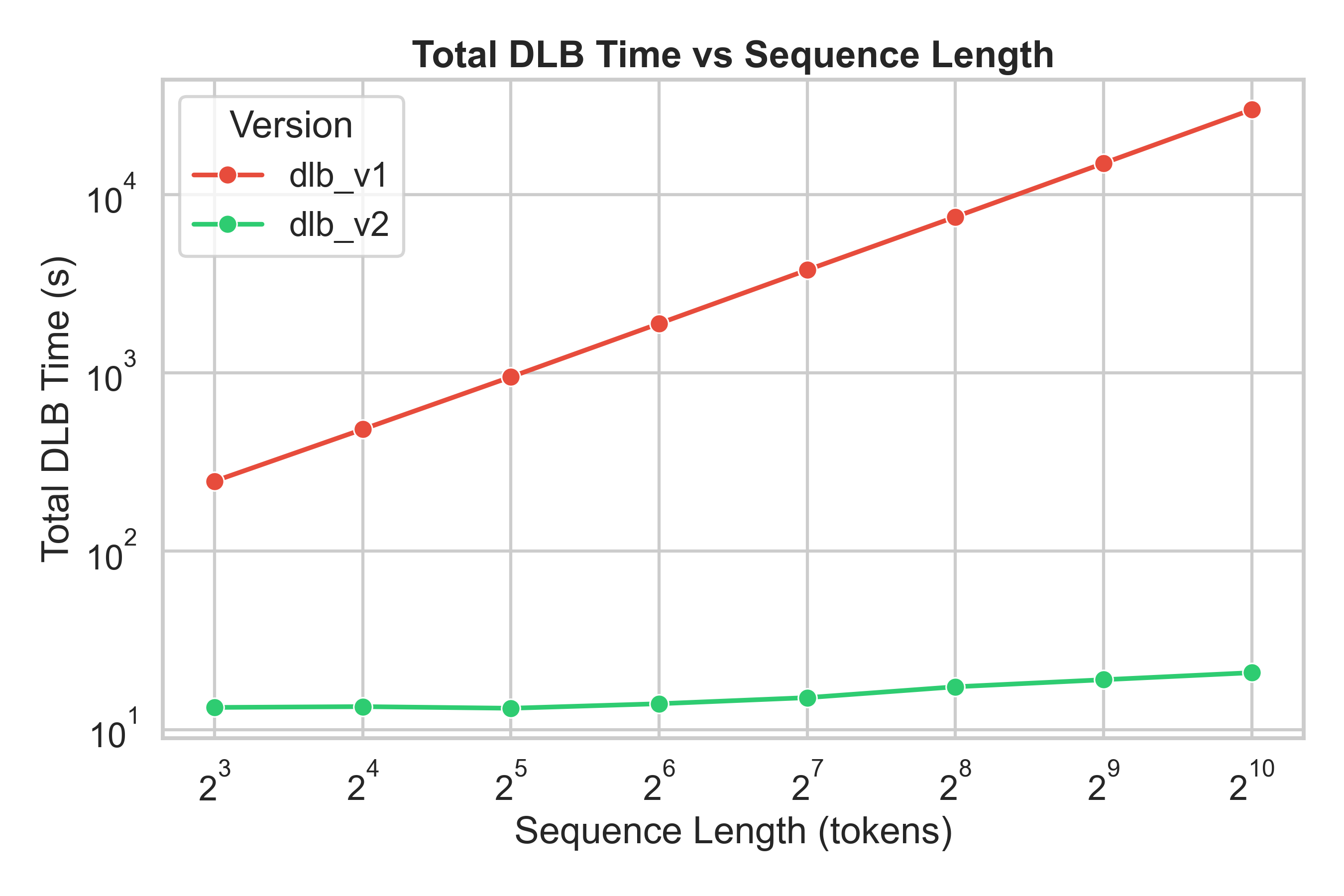 |
|
| 🚀 **Token Throughput** | 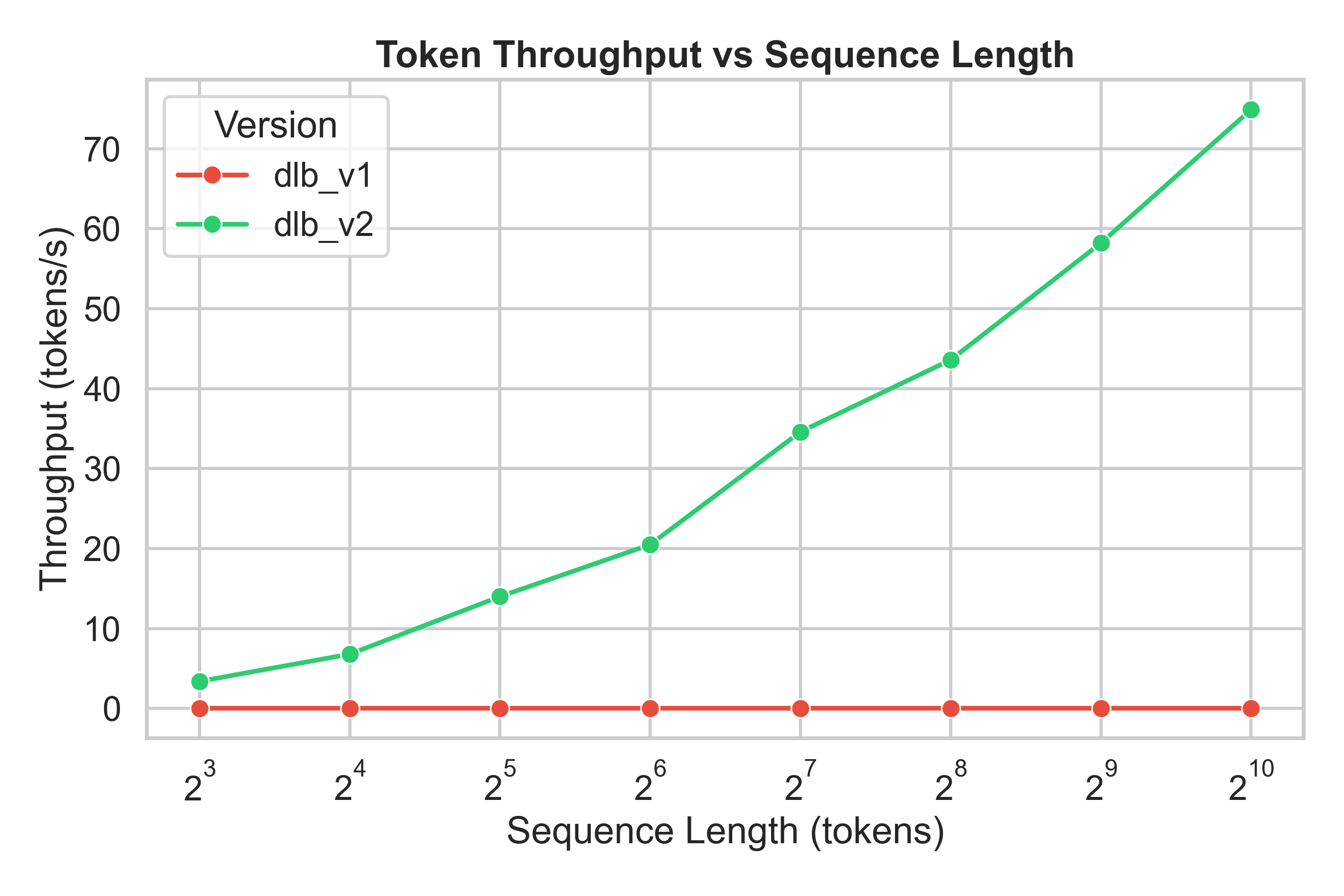 |
|
| ⚙️ **Speedup (v2 / v1)** | 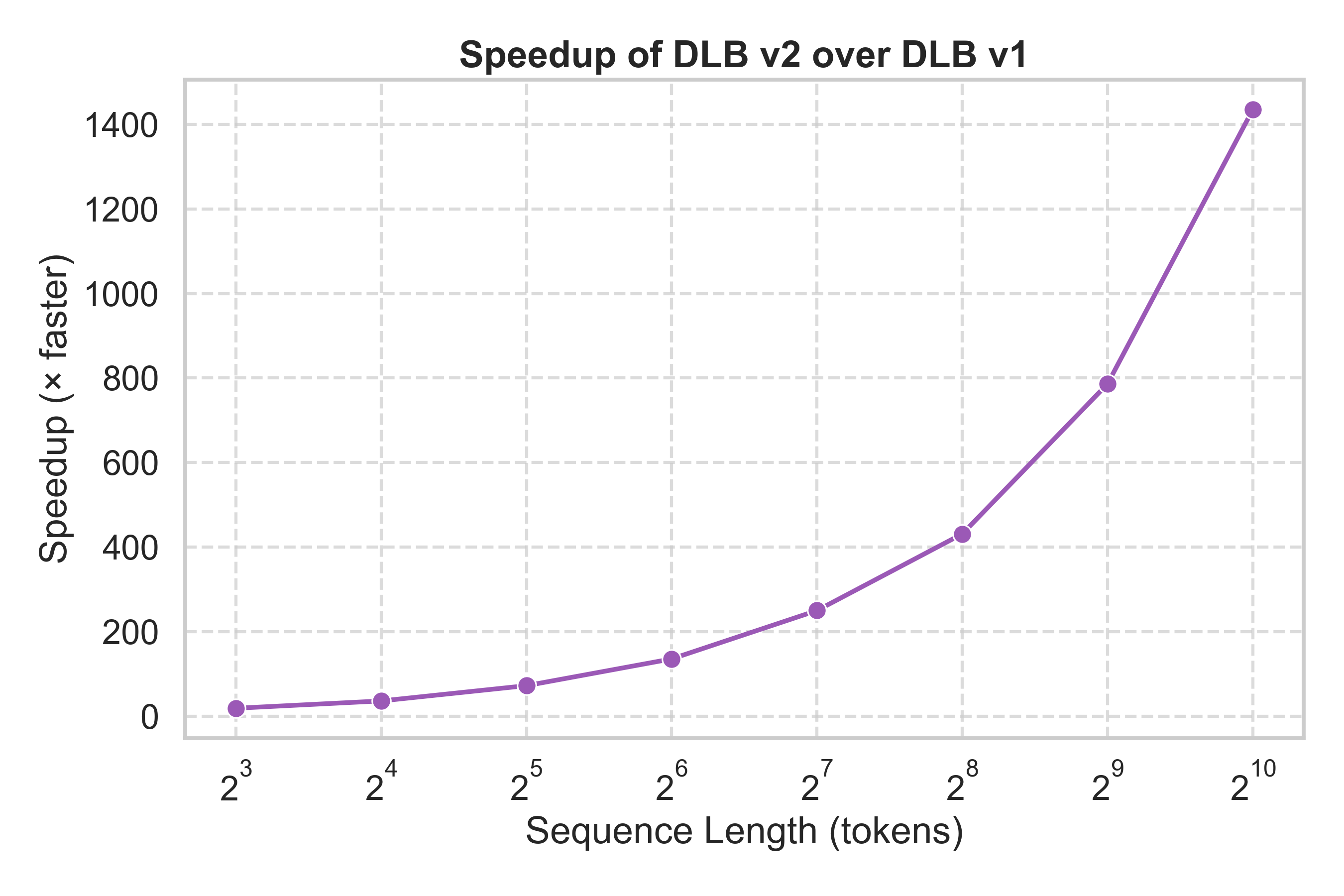 |
|
---
> 💡 **DLB v2** provides **consistent low latency** and achieves **20×–1400× speedup** over DLB v1 as sequence length increases.
## Installation
### From Source (Recommended)
```bash
pip install torch==2.6.0 torchvision==0.21.0 torchaudio==2.6.0 --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu126
pip install dl-backtrace
```
### Requirements
- Python 3.8+
- PyTorch 2.6+ (with CUDA 12.6 support recommended)
- Additional dependencies: transformers, matplotlib, seaborn, graphviz, joblib, zstandard
See `requirements.txt` for the complete list of dependencies.
### Hugging Face Setup
For accessing models from Hugging Face Hub (required for BERT, RoBERTa, LLaMA, etc.):
```bash
# Install Hugging Face CLI
pip install huggingface_hub
# Login to Hugging Face (required for gated models)
huggingface-cli login
```
You'll need a Hugging Face account and access token. Get your token from [https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens](https://huggingface.co/settings/tokens).
## Quick Start
### PyTorch Models (Recommended)
```python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from dl_backtrace.pytorch_backtrace import DLBacktrace
# Define your model
class MyModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(10, 1)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
# Initialize model and DLBacktrace
model = MyModel()
x = torch.randn(1, 10) # Example input
# Create DLBacktrace instance
dlb = DLBacktrace(
model=model,
input_for_graph=(x,),
device='cuda', # 'cpu',
verbose=False
)
# Get layer-wise outputs
node_io = dlb.predict(x)
# Calculate relevance propagation
relevance = dlb.evaluation(
mode="default",
multiplier=100.0,
task="binary-classification"
)
```
## Advanced Features
### 🚀 High-Level Pipeline Interface
Simplified API for common ML tasks with automatic model loading and configuration:
```python
from dl_backtrace.pytorch_backtrace import DLBacktrace
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
# Load model and tokenizer
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("textattack/bert-base-uncased-SST-2")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("textattack/bert-base-uncased-SST-2")
# Prepare input
text = "This movie is fantastic!"
tokens = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids = tokens["input_ids"]
attention_mask = tokens["attention_mask"]
# Initialize DLBacktrace
dlb = DLBacktrace(
model,
(input_ids, attention_mask),
device='cuda', # or 'cpu'
verbose=False
)
# Run text classification with run_task() - ONE CALL!
results = dlb.run_task(
task="text-classification", # or "auto" for automatic detection
inputs={'input_ids': input_ids, 'attention_mask': attention_mask},
debug=False
)
# Access predictions and relevance
predictions = results['predictions']
relevance = results['relevance']
print(f"Predicted class: {predictions.argmax(axis=-1)}")
print(f"Token relevance shape: {relevance['input_ids'].shape}")
```
### 🎲 DLB Auto Sampler
Advanced text generation with multiple sampling strategies and token-level relevance tracking:
```python
from dl_backtrace.pytorch_backtrace.dlbacktrace.core.dlb_auto_sampler import DLBAutoSampler
sampler = DLBAutoSampler(model, tokenizer)
# Greedy sampling
output = sampler.generate("Prompt", strategy="greedy", max_length=50)
# Top-k and Top-p sampling
output = sampler.generate("Prompt", strategy="top_k", top_k=50, temperature=0.8)
output = sampler.generate("Prompt", strategy="top_p", top_p=0.9, temperature=0.8)
# Beam search
output = sampler.generate("Prompt", strategy="beam_search", num_beams=5)
# Access token-level relevance
print(output['relevance_scores'])
```
### 🧠 Mixture-of-Experts (MoEs) Support
Built-in support for MoE architectures with expert-level relevance analysis:
```python
from dl_backtrace.moe_pytorch_backtrace import Backtrace
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
# Load MoE model (GPT-OSS, JetMoE, OLMoE, Qwen3-MoE)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai/gpt-oss-20b")
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai/gpt-oss-20b")
# Initialize MoE Backtrace
bt = Backtrace(
model=model,
model_type='gpt_oss', # or 'jetmoe', 'olmoe', 'qwen'
device='cpu' # or 'cuda'
)
# Prepare input
prompt = "What is the capital of France?"
tokens = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
input_ids = tokens["input_ids"]
attention_mask = tokens["attention_mask"]
# Run generation with run_task() - ONE CALL!
results = bt.run_task(
task="generation",
inputs={'input_ids': input_ids, 'attention_mask': attention_mask},
tokenizer=tokenizer,
max_new_tokens=10,
return_relevance=True,
return_scores=True,
debug=False
)
# Access generated text and relevance
generated_text = tokenizer.decode(results['generated_ids'][0], skip_special_tokens=True)
print(f"Generated: {generated_text}")
# Get expert-level relevance
expert_relevance = bt.all_layer_expert_relevance
print(f"Expert routing across {len(expert_relevance)} layers")
```
### 🌡️ Temperature Scaling
Control generation diversity and model confidence:
```python
from dl_backtrace.pytorch_backtrace.dlbacktrace import DLBacktrace
dlb = DLBacktrace(model, input_for_graph=(input_tensor,))
# Apply temperature scaling for generation
output = dlb.generate_with_temperature(
input_ids,
temperature=0.7, # Lower = more focused, Higher = more diverse
max_length=100
)
```
### ⚡ Execution Engines
DLBacktrace provides optimized execution engines:
#### ExecutionEngineNoCache
- **Memory-efficient**: Runs entirely in RAM for faster execution
- **Enhanced Operations**: Supports 100+ PyTorch operations with robust error handling
- **Recent Improvements**: Critical fixes for transformer models (RoBERTa, LLaMA, BERT)
### 🛡️ Deterministic Execution Environment
DLBacktrace automatically sets up a deterministic environment for consistent results:
- ✅ CUDA memory management and synchronization
- ✅ Deterministic algorithms and cuDNN settings
- ✅ Random seed control and environment variables
- ✅ Warning suppression for cleaner output
### 🔧 Robust Tensor Operations
Full support for PyTorch's negative indexing and complex operations:
- ✅ `transpose(-1, -2)`, `permute([-1, -2, 0])`
- ✅ `unsqueeze(-1)`, `squeeze(-1)`
- ✅ `slice(dim=-1, ...)`, `cat(tensors, dim=-1)`
- ✅ `index_select(dim=-1, ...)`
### Evaluation Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Values |
|--------------|-------------|--------|
| `mode` | Evaluation algorithm mode | `default`, `contrastive` |
| `multiplier` | Starting relevance at output layer | Float (default: 100.0) |
| `scaler` | Relevance scaling factor | Float (default: 1.0) |
| `thresholding` | Pixel selection threshold for segmentation | Float (default: 0.5) |
| `task` | Model task type | `binary-classification`, `multi-class classification` |
## Example Notebooks
| Name | Task | Colab Link | HTML Link |
|-------------|-------------|-------------------------------| -------------------------------|
| Custom Tabular Model | Binary Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/13N2sfAxA_7GJsZ7VAKS5WIOg6GusQghI?usp=sharing)| [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1_5DZWIe0Q5eB4CtVhkbO4zTCRbe6yW5D/view?usp=sharing) |
| VGG Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1LxSazvy1Y2i0Ho1Qw7K905aNmvh66GzR?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1AO7cBJ9o6-Xtaqnall8HWG9ZccwtY-QZ/view?usp=sharing) |
| ResNet Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1O8Is0X-IrKxXzgJeR1Xxy21OOR-UGfm7?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1tU573KFG2HPwM0bhFnGSueSc1uYm1ZCb/view?usp=sharing) |
| ViT Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1B1xN5w51-tRnHyycbHV6lxi0tKxONnoS?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1E59Jlsv-v65V4qRL1q0xb0f5gmIsgPeg/view?usp=sharing) |
| DenseNet Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1TspNRXd-qf81iZepUpU_TrUokZynynbu?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1B-6YwaA97ZVk693bQVukRZjVmZeaJt5Z/view?usp=sharing) |
| EfficientNet Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Xv9ghxp0OXcfYOseoq37KiJbz-UkLvWq?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/19sl0_U9VZbFooX21osmKj35lwHNI6_uz/view?usp=sharing) |
| MobileNet Model | Multi-Class Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12D6NgYTf4Gud3BXLRfnUK1m5-RLZY6dv?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Bi01z-_9Gejy7_eA7MsA6-fk9JTRfOQs/view?usp=sharing) |
| BERT-Base Model | Sentiment Classification | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1eBAQ8TToJUs6EN4-md08cjfZUmAArX0s?usp=drive_link) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/11YmWQ4KtztAk8TEIwFU3kajtM-VLc2O_/view?usp=sharing) |
| LLaMA-3.2-1B Model | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1eZUK-PwI6iZeKnfcQHxIXO7xo8wYDEek?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1QJMWMcxD5ifS8ygoySXgFo9OxhXZTgVY/view?usp=sharing) |
| Qwen-3-0.6B Model | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1nJsxk7HPhiZ1DUIXn0eOnu0yjye-WOQT?usp=drive_link) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1yBqe34IExmfD-YYZF_U3wuOK8JiEBDM2/view?usp=sharing) |
| JetMoE | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1MKxR60Mf1F_TNMuE31T3GRWHFPTm5IhP?usp=drive_link) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1z39LZVa88YCFKgQPTXKgZIVoav7t1PBH/view?usp=sharing) |
| OLMoE | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e13QAFw4A8jKhZVb1jh-C_16A2u1vZIH?usp=drive_link) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1cHByb9EcR-7k2BAL-HmbprNS5oiL2k8q/view?usp=sharing) |
| Qwen-3-MoE | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1ja26JGNt22rOMT0HCyjOMASXxfnMpkm8?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1Upk1l-SnDGT_Mw3Bm6mNmdAVWWYpyW-S/view?usp=sharing) |
| GPT-Oss | Text Generation | [Colab Link](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1zZXTOV4NOrauNDXjjYB8rausbBGoLYtX?usp=sharing) | [HTML Version](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1zs_XyjqmKiT-W3YEqFFTqEKL7z0N_bXq/view?usp=sharing) |
For more detailed examples and use cases, check out our documentation.
## Supported Layers
### PyTorch
**Core Operations:**
- [x] **Linear (Fully Connected) Layer**
- [x] **Convolutional Layer** (Conv2D)
- [x] **Reshape & Flatten Layers**
- [x] **Pooling Layers** (AdaptiveAvgPool2d, MaxPool2d, AvgPool2d, AdaptiveMaxPool2d)
- [x] **1D Pooling Layers** (AvgPool1d, MaxPool1d, AdaptiveAvgPool1d, AdaptiveMaxPool1d)
- [x] **Concatenate & Add Layers**
- [x] **LSTM Layer**
- [x] **Dropout Layer**
- [x] **Embedding Layer**
**Advanced Operations:**
- [x] **Tensor Manipulation** (transpose, permute, unsqueeze, squeeze, slice, cat, index_select)
- [x] **Negative Indexing Support** (all operations support PyTorch's negative indexing)
- [x] **Layer Normalization**
- [x] **Batch Normalization**
- [x] **View & Reshape Operations**
## Testing & Validation
### Supported Models
DLBacktrace has been extensively tested with:
- **Vision Models**: ResNet, VGG, DenseNet, EfficientNet, MobileNet, ViT
- **NLP Models**: BERT, ALBERT, RoBERTa, DistilBERT, ELECTRA, XLNet, LLaMA-3.2, Qwen
- **MoE Models**: JetMoE, OLMoE (Open Language Model with Experts), Qwen3-MoE, GPT-OSS
- **Tasks**: Classification, Object Detection, Segmentation, Text Generation, Expert-Level Analysis
## Getting Started
If you're new to DLBacktrace:
1. **📖 Read the Documentation**: [https://dlbacktrace.lexsi.ai/](https://dlbacktrace.lexsi.ai/)
2. **🚀 Try the Quick Start**: See examples above for PyTorch models
3. **💻 Explore Notebooks**: Check out our comprehensive example notebooks for various use cases
4. **🧪 Run Tests**: Validate your installation with the benchmark scripts
For advanced features like the Pipeline Interface, Auto Sampler, MoE models, and Temperature Scaling, refer to the full documentation.
## Contributing
We welcome contributions from the community! Please follow our contribution guidelines and submit pull requests for any improvements.
## License
This project is licensed under a custom License - see the [LICENSE](LICENSE.md) file for details.
## Recent Updates & New Features
### Latest Release (2025)
**New Features:**
- 🚀 **High-Level Pipeline Interface**: Simplified API for text/image classification and generation
- 🎲 **DLB Auto Sampler**: Advanced text generation with multiple sampling strategies
- 🧠 **MoE Model Support**: Built-in support for Mixture of Experts architectures (JetMoE, OLMoE, Qwen3-MoE, GPT-OSS)
- 🌡️ **Temperature Scaling**: Flexible control over generation diversity and model confidence
**Critical Fixes & Improvements:**
- 🔧 Enhanced execution engine with robust handling of complex tensor operations
- ⚡ Deterministic environment setup for consistent, reproducible results
- 🛡️ Comprehensive error handling for production use
- 🚨 Critical fixes for transformer models (RoBERTa, LLaMA, BERT)
- 🧠 Smart attention detection for bidirectional vs causal attention
- 💾 Memory optimization and improved OOM error handling
## Contact
For any inquiries, support, or collaboration opportunities:
- **Email**: [support@lexsi.ai](mailto:support@lexsi.ai)
- **Website**: [https://lexsi.ai/](https://lexsi.ai/)
- **GitHub Issues**: [https://github.com/Lexsi-Labs/DLBacktrace/issues](https://github.com/Lexsi-Labs/DLBacktrace/issues)
- **Documentation**: [https://dlbacktrace.lexsi.ai/](https://dlbacktrace.lexsi.ai/)
## Citations
```
@misc{sankarapu2024dlbacktracemodelagnosticexplainability,
title={DLBacktrace: A Model Agnostic Explainability for any Deep Learning Models},
author={Vinay Kumar Sankarapu and Chintan Chitroda and Yashwardhan Rathore and Neeraj Kumar Singh and Pratinav Seth},
year={2024},
eprint={2411.12643},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.LG},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.12643},
}
```
---
DLBacktrace — Bridging Performance and Explainability 🔍
Lexsi Labs | support@lexsi.ai



