Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/lightingghost/chemopt
Optimizing Chemical Reactions with Deep Reinforcement Learning
https://github.com/lightingghost/chemopt
Last synced: 11 days ago
JSON representation
Optimizing Chemical Reactions with Deep Reinforcement Learning
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/lightingghost/chemopt
- Owner: lightingghost
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-12-29T23:04:37.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-03-03T19:07:44.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-02T15:06:14.329Z (4 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 63.5 KB
- Stars: 112
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 41
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Optimizing Chemical Reactions with Deep Reinforcement Learning
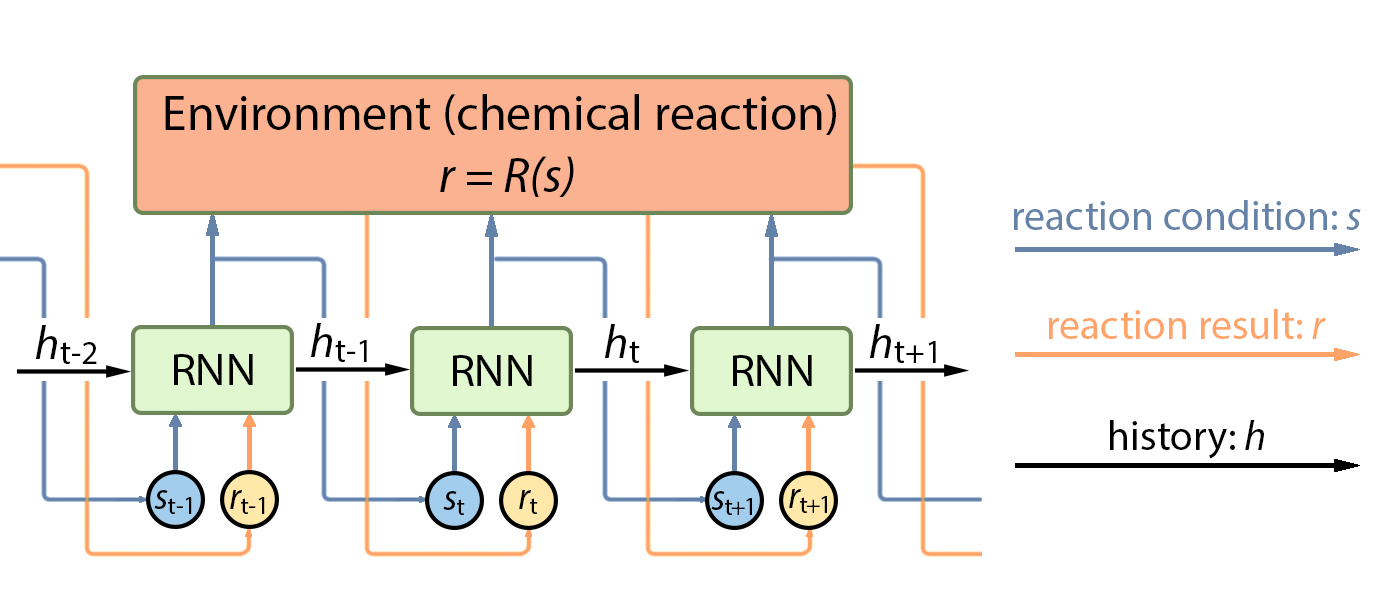
Zhenpeng Zhou, Xiaocheng Li, Richard N. Zare
The tensorflow implementation of the [paper](http://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00492)
# Abstract
Deep reinforcement learning was employed to optimize chemical reactions. Our model iteratively records the results of a chemical reaction and chooses new experimental conditions to improve the reaction outcome. This model outperformed a state-of-the-art blackbox optimization algorithm by using 71% fewer steps on both simulations and real reactions. Furthermore, we introduced an efficient exploration strategy by drawing the reaction conditions from certain probability distributions, which resulted in an improvement on regret from 0.062 to 0.039 compared with a deterministic policy. Combining the efficient exploration policy with accelerated microdroplet reactions, optimal reaction conditions were determined in 30 min for the four reactions considered, and a better understanding of the factors that control microdroplet reactions was reached. Moreover, our model showed a better performance after training on reactions with similar or even dissimilar underlying mechanisms, which demonstrates its learning ability.
# Getting Started
edit the hyperparameters in `config.json` and execute
```python
python lets_start.py
```
# Use
after training, execute
```python
python realreaction.py
```
to access the interactive interface for optimizing a real reaction.
# Implementation references
We wish to thank the authors of the following projects for inspiration.
- [Learning to Learn by Gradient Descent by Gradient Descent](https://github.com/deepmind/learning-to-learn)