https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste
Haste: a fast, simple, and open RNN library
https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste
algorithm api cpp cuda deep-learning gru lstm machine-learning python pytorch rnn rnn-implementations rnn-layers tensorflow
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Haste: a fast, simple, and open RNN library
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste
- Owner: lmnt-com
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-01-29T18:42:44.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-07-18T01:29:25.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-28T20:08:33.494Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: algorithm, api, cpp, cuda, deep-learning, gru, lstm, machine-learning, python, pytorch, rnn, rnn-implementations, rnn-layers, tensorflow
- Language: C++
- Homepage:
- Size: 222 KB
- Stars: 330
- Watchers: 12
- Forks: 28
- Open Issues: 11
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
[](https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste/releases) [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1hzYhcyvbXYMAUwa3515BszSkhx1UUFSt) [](LICENSE)
**We're hiring!**
If you like what we're building here, [come join us at LMNT](https://explore.lmnt.com).
Haste is a CUDA implementation of fused RNN layers with built-in [DropConnect](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v28/wan13.html) and [Zoneout](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.01305) regularization. These layers are exposed through C++ and Python APIs for easy integration into your own projects or machine learning frameworks.
Which RNN types are supported?
- [GRU](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gated_recurrent_unit)
- [IndRNN](http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.04831)
- [LSTM](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Long_short-term_memory)
- [Layer Normalized GRU](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450)
- [Layer Normalized LSTM](https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450)
What's included in this project?
- a standalone C++ API (`libhaste`)
- a TensorFlow Python API (`haste_tf`)
- a PyTorch API (`haste_pytorch`)
- examples for writing your own custom C++ inference / training code using `libhaste`
- benchmarking programs to evaluate the performance of RNN implementations
For questions or feedback about Haste, please open an issue on GitHub or send us an email at [haste@lmnt.com](mailto:haste@lmnt.com).
## Install
Here's what you'll need to get started:
- a [CUDA Compute Capability](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-gpus) 3.7+ GPU (required)
- [CUDA Toolkit](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit) 10.0+ (required)
- [TensorFlow GPU](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/gpu) 1.14+ or 2.0+ for TensorFlow integration (optional)
- [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org) 1.3+ for PyTorch integration (optional)
- [Eigen 3](http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/) to build the C++ examples (optional)
- [cuDNN Developer Library](https://developer.nvidia.com/rdp/cudnn-archive) to build benchmarking programs (optional)
Once you have the prerequisites, you can install with pip or by building the source code.
### Using pip
```
pip install haste_pytorch
pip install haste_tf
```
### Building from source
```
make # Build everything
make haste # ;) Build C++ API
make haste_tf # Build TensorFlow API
make haste_pytorch # Build PyTorch API
make examples
make benchmarks
```
If you built the TensorFlow or PyTorch API, install it with `pip`:
```
pip install haste_tf-*.whl
pip install haste_pytorch-*.whl
```
If the CUDA Toolkit that you're building against is not in `/usr/local/cuda`, you must specify the
`$CUDA_HOME` environment variable before running make:
```
CUDA_HOME=/usr/local/cuda-10.2 make
```
## Performance
Our LSTM and GRU benchmarks indicate that Haste has the fastest publicly available implementation for nearly all problem sizes. The following charts show our LSTM results, but the GRU results are qualitatively similar.
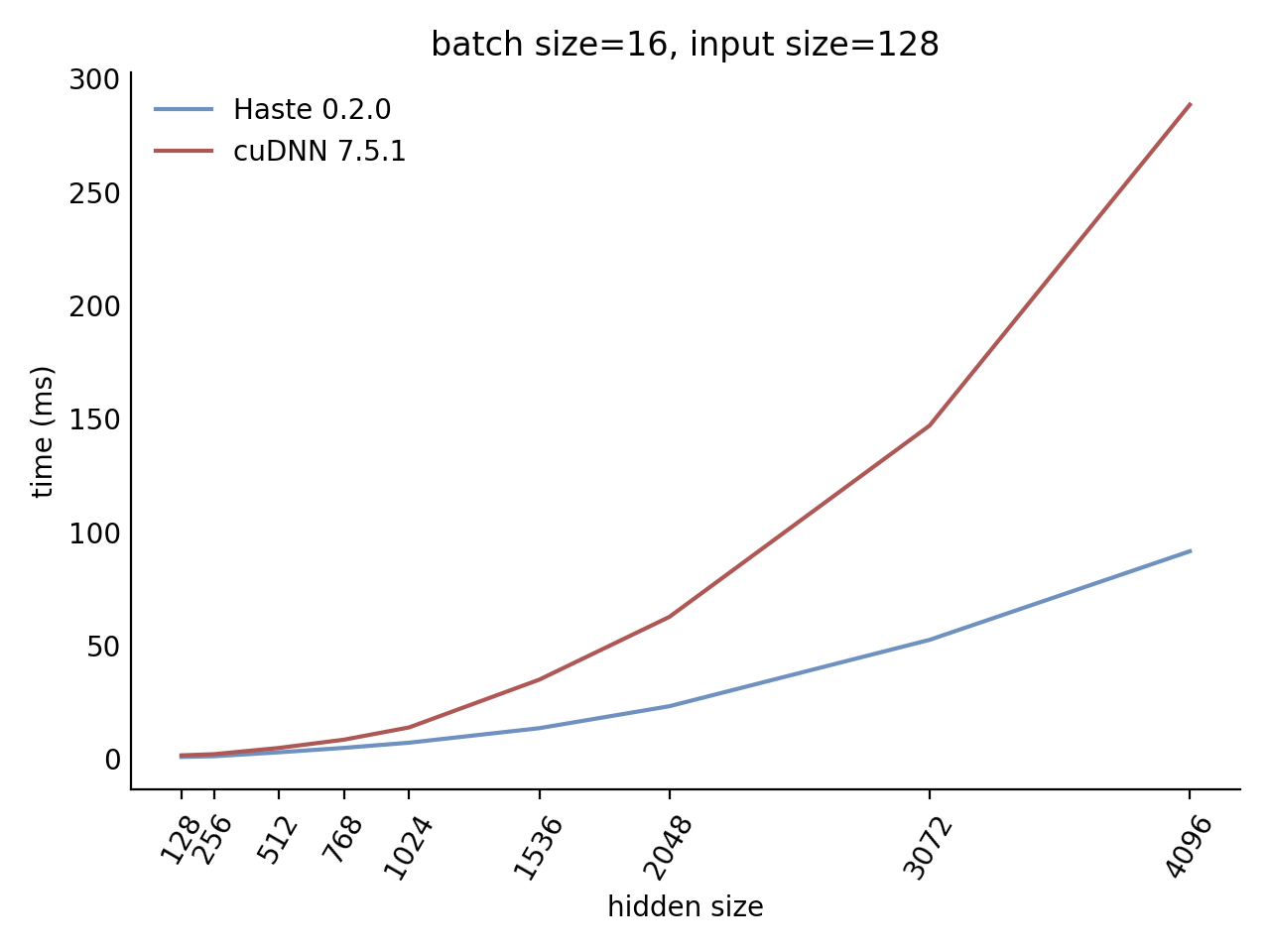
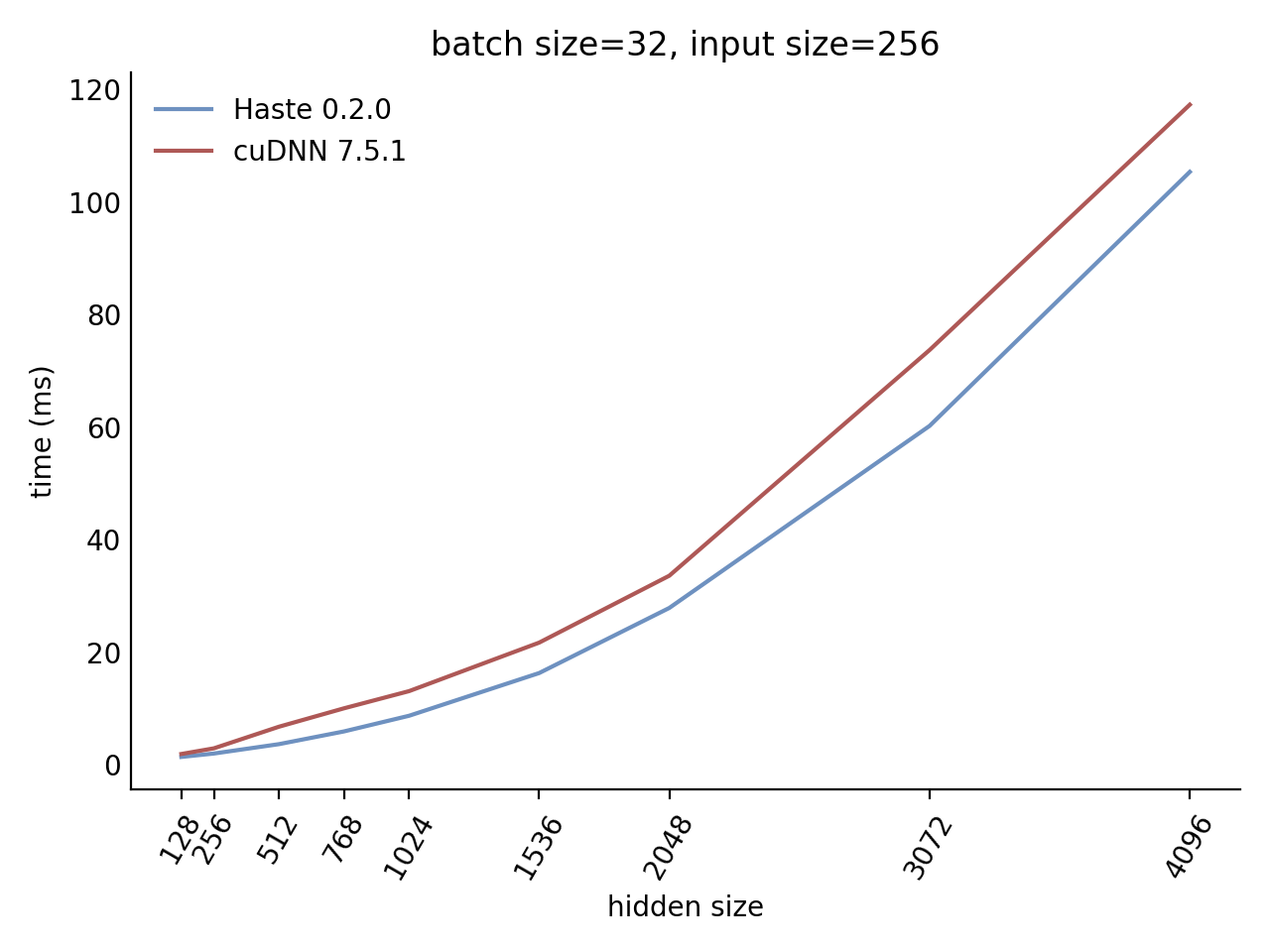
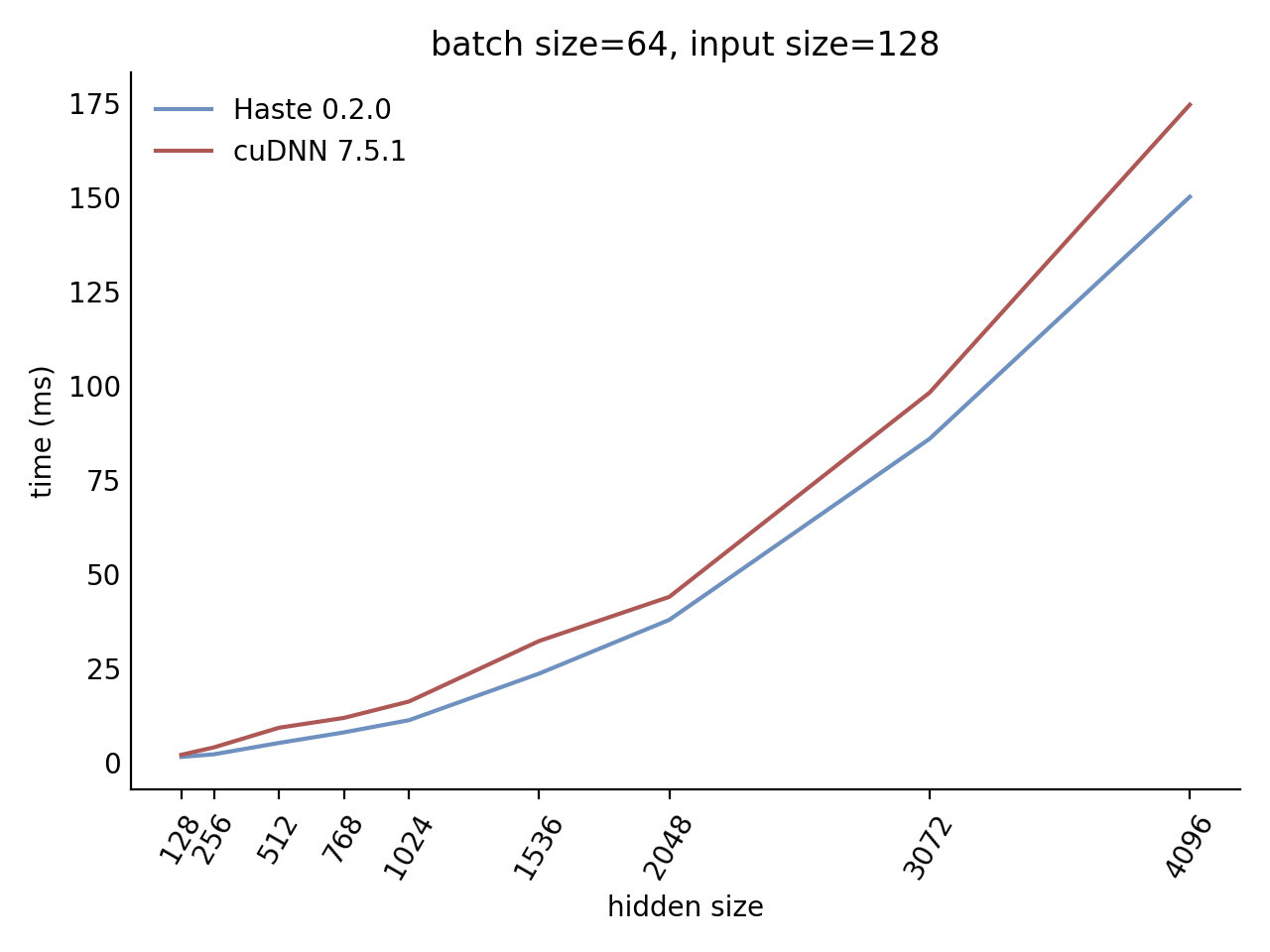

Here is our complete LSTM benchmark result grid:
[`N=1 C=64`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=1_c=64.png)
[`N=1 C=128`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=1_c=128.png)
[`N=1 C=256`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=1_c=256.png)
[`N=1 C=512`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=1_c=512.png)
[`N=32 C=64`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=32_c=64.png)
[`N=32 C=128`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=32_c=128.png)
[`N=32 C=256`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=32_c=256.png)
[`N=32 C=512`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=32_c=512.png)
[`N=64 C=64`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=64_c=64.png)
[`N=64 C=128`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=64_c=128.png)
[`N=64 C=256`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=64_c=256.png)
[`N=64 C=512`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=64_c=512.png)
[`N=128 C=64`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=128_c=64.png)
[`N=128 C=128`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=128_c=128.png)
[`N=128 C=256`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=128_c=256.png)
[`N=128 C=512`](https://lmnt.com/assets/haste/benchmark/report_n=128_c=512.png)
## Documentation
### TensorFlow API
```python
import haste_tf as haste
gru_layer = haste.GRU(num_units=256, direction='bidirectional', zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
indrnn_layer = haste.IndRNN(num_units=256, direction='bidirectional', zoneout=0.1)
lstm_layer = haste.LSTM(num_units=256, direction='bidirectional', zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
norm_gru_layer = haste.LayerNormGRU(num_units=256, direction='bidirectional', zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
norm_lstm_layer = haste.LayerNormLSTM(num_units=256, direction='bidirectional', zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
# `x` is a tensor with shape [N,T,C]
x = tf.random.normal([5, 25, 128])
y, state = gru_layer(x, training=True)
y, state = indrnn_layer(x, training=True)
y, state = lstm_layer(x, training=True)
y, state = norm_gru_layer(x, training=True)
y, state = norm_lstm_layer(x, training=True)
```
The TensorFlow Python API is documented in [`docs/tf/haste_tf.md`](docs/tf/haste_tf.md).
### PyTorch API
```python
import torch
import haste_pytorch as haste
gru_layer = haste.GRU(input_size=128, hidden_size=256, zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
indrnn_layer = haste.IndRNN(input_size=128, hidden_size=256, zoneout=0.1)
lstm_layer = haste.LSTM(input_size=128, hidden_size=256, zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
norm_gru_layer = haste.LayerNormGRU(input_size=128, hidden_size=256, zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
norm_lstm_layer = haste.LayerNormLSTM(input_size=128, hidden_size=256, zoneout=0.1, dropout=0.05)
gru_layer.cuda()
indrnn_layer.cuda()
lstm_layer.cuda()
norm_gru_layer.cuda()
norm_lstm_layer.cuda()
# `x` is a CUDA tensor with shape [T,N,C]
x = torch.rand([25, 5, 128]).cuda()
y, state = gru_layer(x)
y, state = indrnn_layer(x)
y, state = lstm_layer(x)
y, state = norm_gru_layer(x)
y, state = norm_lstm_layer(x)
```
The PyTorch API is documented in [`docs/pytorch/haste_pytorch.md`](docs/pytorch/haste_pytorch.md).
### C++ API
The C++ API is documented in [`lib/haste/*.h`](lib/haste/) and there are code samples in [`examples/`](examples/).
## Code layout
- [`benchmarks/`](benchmarks): programs to evaluate performance of RNN implementations
- [`docs/tf/`](docs/tf): API reference documentation for `haste_tf`
- [`docs/pytorch/`](docs/pytorch): API reference documentation for `haste_pytorch`
- [`examples/`](examples): examples for writing your own C++ inference / training code using `libhaste`
- [`frameworks/tf/`](frameworks/tf): TensorFlow Python API and custom op code
- [`frameworks/pytorch/`](frameworks/pytorch): PyTorch API and custom op code
- [`lib/`](lib): CUDA kernels and C++ API
- [`validation/`](validation): scripts to validate output and gradients of RNN layers
## Implementation notes
- the GRU implementation is based on `1406.1078v1` (same as cuDNN) rather than `1406.1078v3`
- Zoneout on LSTM cells is applied to the hidden state only, and not the cell state
- the layer normalized LSTM implementation uses [these equations](https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste/issues/1)
## References
1. Hochreiter, S., & Schmidhuber, J. (1997). Long Short-Term Memory. _Neural Computation_, _9_(8), 1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
1. Cho, K., van Merrienboer, B., Gulcehre, C., Bahdanau, D., Bougares, F., Schwenk, H., & Bengio, Y. (2014). Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder-Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. _arXiv:1406.1078 [cs, stat]_. http://arxiv.org/abs/1406.1078.
1. Wan, L., Zeiler, M., Zhang, S., Cun, Y. L., & Fergus, R. (2013). Regularization of Neural Networks using DropConnect. In _International Conference on Machine Learning_ (pp. 1058–1066). Presented at the International Conference on Machine Learning. http://proceedings.mlr.press/v28/wan13.html.
1. Krueger, D., Maharaj, T., Kramár, J., Pezeshki, M., Ballas, N., Ke, N. R., et al. (2017). Zoneout: Regularizing RNNs by Randomly Preserving Hidden Activations. _arXiv:1606.01305 [cs]_. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.01305.
1. Ba, J., Kiros, J.R., & Hinton, G.E. (2016). Layer Normalization. _arXiv:1607.06450 [cs, stat]_. https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450.
1. Li, S., Li, W., Cook, C., Zhu, C., & Gao, Y. (2018). Independently Recurrent Neural Network (IndRNN): Building A Longer and Deeper RNN. _arXiv:1803.04831 [cs]_. http://arxiv.org/abs/1803.04831.
## Citing this work
To cite this work, please use the following BibTeX entry:
```
@misc{haste2020,
title = {Haste: a fast, simple, and open RNN library},
author = {Sharvil Nanavati},
year = 2020,
month = "Jan",
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/lmnt-com/haste/}},
}
```
## License
[Apache 2.0](LICENSE)