https://github.com/lovaslin/pybumphunter
Python implementation of the BumpHunter algorithm used by HEP community.
https://github.com/lovaslin/pybumphunter
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Python implementation of the BumpHunter algorithm used by HEP community.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/lovaslin/pybumphunter
- Owner: lovaslin
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2020-05-07T14:31:11.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-09-03T21:07:26.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-19T06:57:23.564Z (about 2 months ago)
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 2.7 MB
- Stars: 6
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 5
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# pyBumpHunter
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/lovaslin/pyBumpHunter/master)
[](https://github.com/lovaslin/pyBumpHunter/actions)
[](https://pypi.org/project/pyBumpHunter/)
## Important notice
***The project has been mooved to [sckit-hep](https://github.com/scikit-hep/pyBumpHunter).***
***For all future fork/clone, please usse the new link.***
This is a python version of the BumpHunter algorithm, see [arXiv:1101.0390, G. Choudalakis](https://arxiv.org/abs/1101.0390), designed to find localized excess (or deficit) of events in a 1D distribution.
The main BumpHunter function will scan a data distribution using variable-width window sizes and calculate the p-value of data with respect to a given background distribution in each window. The minimum p-value obtained from all windows is the local p-value. To cope with the "look-elsewhere effect" a global p-value is calculated by performing background-only pseudo-experiments.
The BumpHunter algorithm can also perform signal injection tests where more and more signal is injected in toy data until a given signal significance (global) is reached.
### Content
* pyBumpHunter : The pyBumpHunter package
* example/example.py : A little example script that use pyBumpHunter
* example/example.ipynb : A little example notebook that use pyBumpHunter
* example/results : Folder containing the outputs of example script
* testing : Folder containing the testing scripts (based on pytest)
* data/data.root : Toy data used in the examples and tests
* data/gen_data.C : Code used to generate the toy data with ROOT
### python dependancies
Requires python >= 3.5
pyBumpHunter depends on the following python libraries :
* numpy
* scipy
* matplotlib
### [pyBumpHunter wiki](https://github.com/lovaslin/pyBumpHunter/wiki)
### Examples
The examples provided in example.py and test.ipynb require the [uproot](https://github.com/scikit-hep/uproot) package in order to read the data from a [ROOT software](https://root.cern.ch/) file.
The data provided in the example consists of three histograms: a steeply falling 'background' distribution in a [0,20] x-axis range, a 'signal' gaussian shape centered on a value of 5.5, and a 'data' distribution sampled from background and signal distributions, with a signal fraction of 0.15%. The data file is produced by running gen_data.C in ROOT.
In order to run the example script, simply type `python3 example.py` in a terminal.
You can also open the example notebook with jupyter or binder.
* Bump hunting:
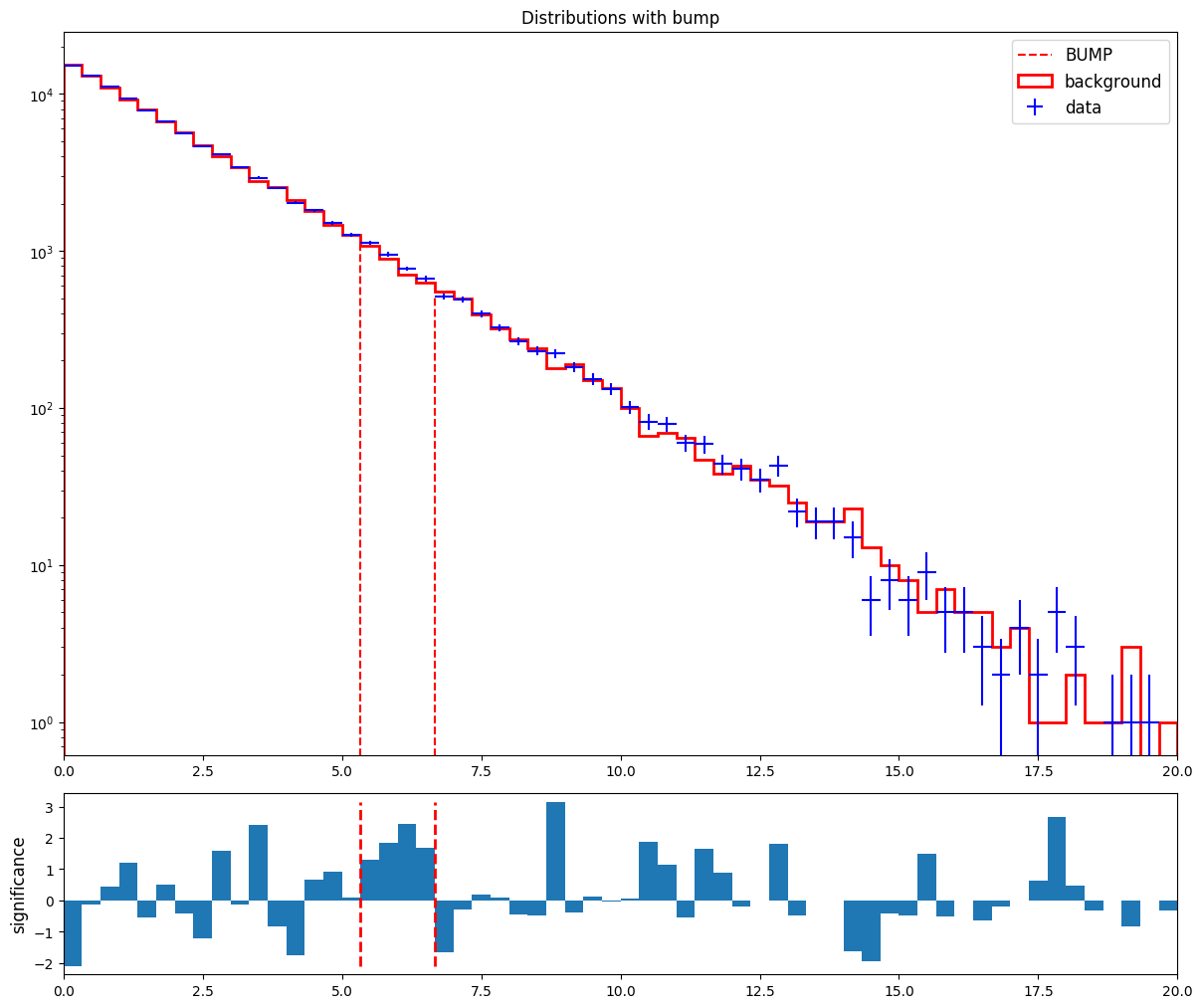
* Tomography scan:
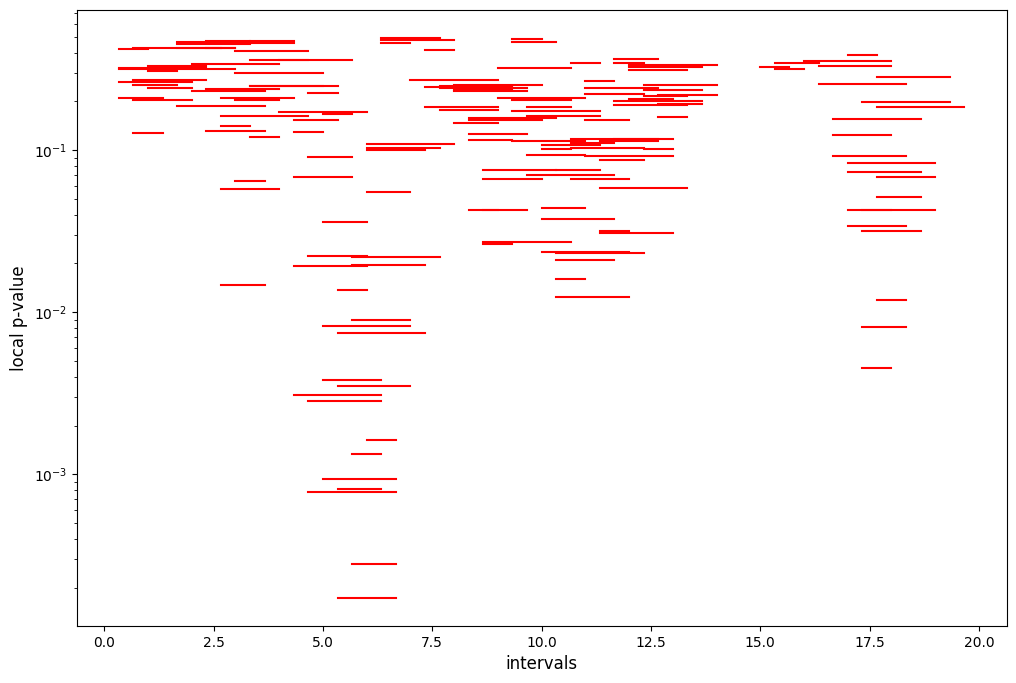
* Test statistics and global p-value:
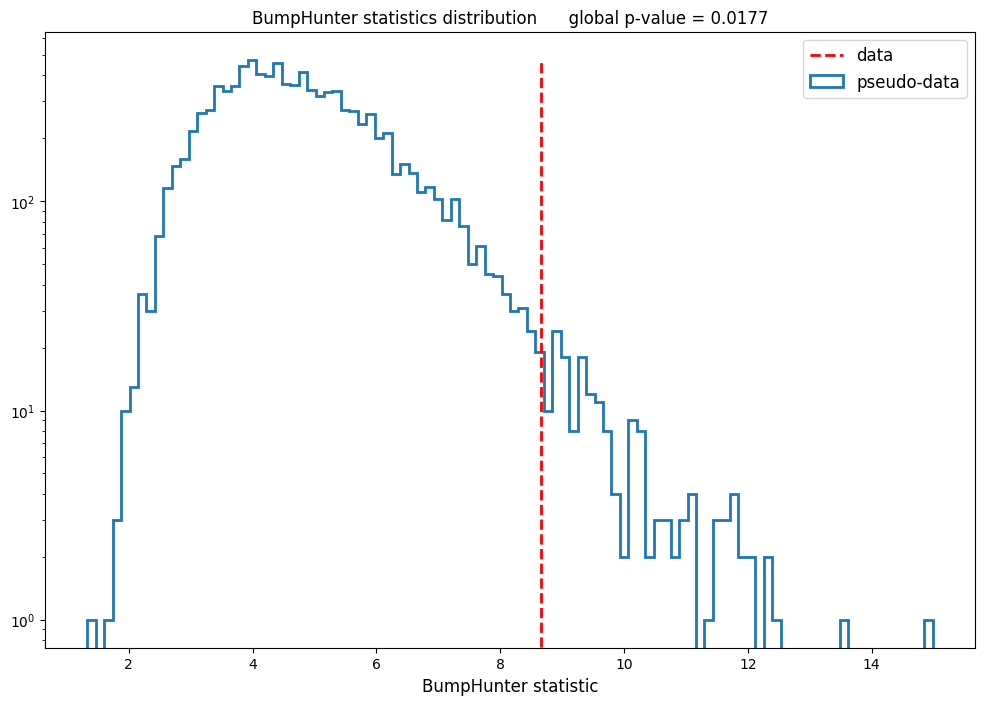
See the [wiki](https://github.com/lovaslin/pyBumpHunter/wiki) for a detailed overview of all the features offered by pyBumpHunter.
### To do list
* Run BH on 2D histograms
### Authors and contributors
Louis Vaslin (main developper), Julien Donini
Thanks to Samuel Calvet for his help in cross-checking and validating pyBumpHunter against the (internal) C++ version of BumpHunter developped by the [ATLAS collaboration](https://atlas.cern/).