https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms
Polyglot Data Structures/Algorithms. Collection of classic computer science data-structures: LinkList, Queue/Stack, Binary Tree, Hashmap, Graph and the sorts: bubble, insertion, merge, quicksort. Whiteboarded and originally written in Python, then ported to Java, Node and Golang.
https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms
algorithms binary-search-tree computer-science data-structrues data-structures-algorithms data-structures-and-algorithms go golang graph-algorithms graphs hashtable java junit5 linked-list node node-js nodejs polyglot python whiteboards
Last synced: 21 days ago
JSON representation
Polyglot Data Structures/Algorithms. Collection of classic computer science data-structures: LinkList, Queue/Stack, Binary Tree, Hashmap, Graph and the sorts: bubble, insertion, merge, quicksort. Whiteboarded and originally written in Python, then ported to Java, Node and Golang.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms
- Owner: marvincolgin
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-07-08T21:11:11.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-12-30T18:43:46.000Z (almost 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-03-02T23:21:51.757Z (over 2 years ago)
- Topics: algorithms, binary-search-tree, computer-science, data-structrues, data-structures-algorithms, data-structures-and-algorithms, go, golang, graph-algorithms, graphs, hashtable, java, junit5, linked-list, node, node-js, nodejs, polyglot, python, whiteboards
- Language: Python
- Homepage: http://marvincolgin.com
- Size: 36.9 MB
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 15
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
**Algorithms and Data Structures**
*Written in Python, Golang, Node and Java*
Vin Colgin (Summer/Fall 2019)
https://github.com/marvincolgin
https://linkedin.com/in/mcolgin
**Table of Contents:**
* [Algorithms](#algorithms)
* [Bubble Sort](#bubble-sort)
* [Insertion Sort](#insertion-sort)
* [Merge Sort](#merge-sort)
* [Quick Sort](#quick-sort)
* [Data Structures](#data-structures)
* [Arrays](#arrays)
* [Reverse Elements](#reverse-elements)
* [Insert and Shift Array Elements](#insert-and-shift-array-elements)
* [Binary Search](#binary-search)
* [Singly Linked Lists](#singly-linked-lists)
* [Stack (LIFO)](#stack-lifo)
* [Balanced Brackets](#balanced-brackets)
* [Queue (FIFO)](#queue-fifo)
* [Queue: Animal Shelter](#queue-animal-shelter)
* [Binary Tree (BT)](#binary-tree-bt)
* [Breadth-first Traversal](#breadth-first-traversal)
* [Find the Maximum Value](#find-the-maximum-value)
* [FizzBuzzTree](#fizzbuzztree)
* [Tree Intersection](#tree-intersection)
* [Binary Search Tree (BST)](#binary-search-tree-bst)
* [Hash Table](#hash-table)
* [Repeated Words](#repeated-words)
* [Left Join](#left-join)
* [Graphs](#graphs)
* [Get Graph Edges](#get-graph-edges)
* [Depth-First Traversal](#depth-first-traversal)
# CI/CD
CircleCi for Tests:
[](https://circleci.com/gh/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms)
# Algorithms
## Bubble Sort
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/algorithms/bubble_sort)
```python
def bubble_sort(arr):
# BigO == n^2
```
---
## Insertion Sort
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/algorithms/insertion_sort)
```python
def insertion_sort(arr):
# BigO = O(2n)
```
---
## Merge Sort
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/algorithms/merge_sort)
```python
def merge_sort(arr):
# BigO (n log n)
# :: log n, as this is a divide algo
# :: n, as we need to merge the halfs back
def merge_split(arr):
# actual merge_sort function, without error handling
# :: recursivily called
def merge_array(arr, left, right):
# combine left and right sides
```
---
## Quick Sort
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/algorithms/quick_sort)
```python
def quick_sort(arr):
# BigO (n log n)
# :: log n, as this is a divide algo
# :: n, as we need to merge the halfs back
```
# Data Structures
## Arrays
In Python, arrays are dynamic lists of pointers to memory addresses, Big O Time == 0(1)
### Reverse Elements
Create a function, which reverses an array/linked-list, as passed via a parameter and pass the new array back as the `return()` for the function.
*Approach & Efficiency*
My initial approach was to utilize the `list.insert()` and `list.pop()` to rebuild the list in reverse order. However, my white boarding partner showed me a more pythonic method utilizing slices with a -1 stride.
*Solution*
Two solutions were used, one that utilizes a while() loop and is destructive on the inbound array. The second is "pythonic" and utilizes an index slice and a -1 stride.
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/blob/master/python/challenges/array_reverse/array_reverse.py)
```python
def reverse_array(orig):
def reverse_array2(orig):
```
---
### Insert and Shift Array Elements
Write a function which takes in an array and the value to be added. Without utilizing any of the built-in methods available to your language, return an array with the new value added at the middle index.
*Solution*
Create an index into the array where the value will be inserted, utilize slice and .append/.extend to construct a return array
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/blob/master/python/challenges/array_shift/array_shift.py)
```python
def insert_shift_array_sorted(arr, val):
def insert_shift_array(arr, val):
```
---
### Binary Search
Write a function which takes in an array and the value to be searched. Return -1 if the value is not found, otherwise return the index (0 based). Incoming array is sorted.
*Solution*
Divide and Conquer! Look at the middle element, is it the middle element? Return. If not, create a new middle from either the smaller side or larger side. Repeat.
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/blob/master/python/challenges/array_binary_search/array_binary_search.py)
```python
def array_binary_search(arr, val):
```
---
## Singly Linked Lists
Linked-Lists (singly) are dynamic data-structures which resembles a length of chain, where the entire length of chain is the list and the individual links of the chain are nodes. A singlarly linked list is only traversable in one direction, but utilizing a head element that points to the first node in the list, the second node in the list points to the next link in the chain, and finally the last element in the list points to "none"
Whiteboard
_*Insert()*_

_*KthFromEnd(): Iterative Approach*_

_*KthFromEnd(): Recursive Approach*_

_*MergeList()*_

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/linked_list)
```python
class LinkList()
def __init__(self):
# constructor
def toJSON(self):
# dump object to JSON and return as String
def insert(self, value):
# insert value at the head of the list
def includes(self, value):
# traverse list and determine if a value exists
# return bool
def count(self):
# count the number of nodes and return count
def append(value):
# adds a new node with the given value to the end of the list
# BigO == O(n)
def insertBefore(value, newVal):
# add a new node with the given newValue immediately before the first value node
# BigO == O(n)
def insertAfter(value, newVal):
# add a new node with the given newValue immediately after the first value node
# BigO == O(n)
class ListNode()
def __init__(self, value, next=None, prev=None):
# constructor
```
Golang
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/golang/src/linklist)
```golang
type LinkNode struct {
value interface{}
next *LinkNode
prev *LinkNode
}
func (node *LinkNode) Init(value interface{}) {
head *LinkNode
// @TODO: comparison_func func
}
type LinkList struct {
head *LinkNode
// @TODO: comparison_func func
}
func (list *LinkList) Init() {}
func (list *LinkList) toJSON() string {}
func (list *LinkList) toStr() string {}
func (list *LinkList) Insert(value interface{}) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) Includes(value interface{}) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) Get(value interface{}) interface{} {}
func (list *LinkList) Count() int {}
func (list *LinkList) Append(value interface{}) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) Remove(value interface{}) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) Peek() (bool, interface{}) {}
func (list *LinkList) InsertBefore(targetVal, newVal interface{}, afterInstead bool) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) InsertAfter(targetVal, newVal interface{}) bool {}
func (list *LinkList) KthFromEnd(k int) (bool, interface{}) {}
func (list *LinkList) MergeList(listA, listB LinkList) LinkList {}
```
Node
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/node/src/linklist)
```javascript
// LinkNode this is the internal object for individual link-nodes
class LinkNode {
constructor(value) {
}
// LinkList is the internal data-structure
class LinkList {
constructor() {}
toStr() {}
count() {}
peek() {}
append(value) {}
insert(value) {}
includes(value) {}
remove(value) {}
insertBefore(targetVal, newVal, afterInstead=false) {}
insertAfter(targetVal, newVal) {}
kthFromEnd(k) {}
mergeList(listA, listB) { }
```
Java
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/java/src/main/java/datastructs/LinkList.java)
```java
public class LinkList {
public class RetObj {}
public Node head;
private BiFunction comparisonFunc;
public void setComparisonFunc(BiFunction f) {}
public LinkList(BiFunction cf) {}
class Node {}
public void insert(String value) {}
public int count() {}
public Boolean includes(String value) {}
public RetObj peek() {}
public String toStr() {}
public Boolean append(String value) {}
public Boolean remove(String value) {}
public String get(String value) {}
private Boolean insertBeforeOrAfter(String targetVal, String newVal, Boolean afterInstead) {}
public Boolean insertBefore(String targetVal, String newVal) {}
public Boolean insertAfter(String targetVal, String newVal) {}
public void traverse(Consumer actionFunc) {}
public String kthFromEnd(int k) {}
public LinkList mergeList(LinkList listA, LinkList listB) {}
}
```
---
## Stack (LIFO)
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/stacks_and_queues)
```python
class Stack():
def push(val) -> bool:
def pop() -> str:
def peek() -> str:
```
Golang
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/golang/src/linklist)
```golang
type Stack struct {
_data linklist.LinkList
}
func (stack *Stack) Init() {}
func (stack *Stack) Count() int {}
func (stack *Stack) Pop() (bool, interface{}) {}
func (stack *Stack) Push(val interface{}) bool {}
func (stack *Stack) Peek() (bool, interface{}) {}
```
Node
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/node/src/stack)
```javascript
// Stack implementation of LIFO
class Stack {
constructor() {}
count() {}
pop() {}
push(val) {}
peek() {)
}
```
Java
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/java/src/main/java/datastructs/Stack.java)
```java
public class Stack {
private LinkList _data = null;
public Stack() {}
public int count() {}
public Boolean push(String val) {}
public String pop() {}
public LinkList.RetObj peek() {}
public String toStr() {}
}
```
---
### Balanced Brackets
Create a function, which takes in a string and tests it to make sure that any open brackets ('{','(','[') are balanced with their corresponding closing-brackets ('}',')',']').
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/multi_bracket_validation)
```python
def multi_bracket_validation(input : str) -> boolean:
```
---
## Queue (FIFO)
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python (queue)
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/stacks_and_queues)
```python
class Queue():
def enqueue(val) -> bool:
# Add a value to the queue
def dequeue(val) -> bool:
# Remove entry from queue with a given value
def peek() -> str:
# Get value from the head of the queue (without removing it)
```
Python (stack)
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/stacks_and_queues)
```python
class PseudoQueue(object):
def __init__(self):
# create Stack for internal data-struct
def count(self):
# pass through method to underlying data struct
# BigO == O(n)
def enqueue(self, val: str) -> bool:
# enqeue a value at the end queue
# BigO == O(1)
def dequeue(self) -> (str, bool):
# dequeue from head of queue
# BigO == O(n)
# Algo: use a second stack, as we need the bottom element on the first stack
# so we are going to unload the first stack, into a temp stack, in order to
# get at the bottom element of the first, then rebuild it from temp to first-stack
```
Node
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/node/src/queue)
```javascript
class Queue {
constructor() {}
count() {}
toStr() {}
enqueue(val) {}
dequeue(val) {}
peek() {}
```
Golang
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/golang/src/queue)
```golang
// Queue implementation of LIFO
type Queue struct {
_data linklist.LinkList
}
// Init inistantiate the stuct
func (queue *Queue) Init() {}
// Count the number of items in linklist
func (queue *Queue) Count() int {}
// ToStr return the Queue as a String
func (queue *Queue) ToStr() string {}
// Enqueue to add a value to the queue
func (queue *Queue) Enqueue(val interface{}) bool {}
// Dequeue to remove a specific value from the Qeueue
func (queue *Queue) Dequeue(val interface{}) bool {}
// Peek at the front value in the Queue
func (queue *Queue) Peek() (bool, interface{}) {}
```
Java
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/java/src/main/java/datastructs/Queue.java)
```java
public class Queue {
private LinkList _data = null;
public Queue() {}
public int count() {}
public Boolean enqueue(String val) {}
public Boolean dequeue(String val) {}
public LinkList.RetObj peek() {}
public String toStr() {}
}
```
---
### Queue: Animal Shelter
create a class called AnimalShelter which holds only dogs/cats. The shelter operates as first-in / first-out
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/fifo_animal_shelter)
```python
class AnimalType(IntEnum):
class Animal(object):
def __init__(self, animaltype : AnimalType):
# create internal data structs
def serialize(self):
# return json for obj
def Factory(jsonstr : str): # -> Animal
# create Animal class Dog|Cat for Json
class Cat(Animal):
def __init__(self):
# create internal data structs
class Dog(Animal):
def __init__(self):
# create internal data structs
class AnimalShelter():
def __init__(self):
# create internal data structs
def enqueue(self, animal : Animal):
# add animal to shelter
def dequeue(self, pref : AnimalType=None) -> Animal:
# grab animal that has been in queue the longest, optionally provide parameter
```
---
## Binary Tree (BT)
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/tree)
```python
class TraverseMethod(IntEnum):
# enum class for traversal and processing order
class Node:
# class for nodes within Tree
def __init__(self, value):
# constructor for creating Node
class BinaryTree:
def __init__(self):
# constructor for creating BinaryTree
def traverse(self, method : TraverseMethod, action_func):
# visit each node in atree, using a specified method and call action_func() for each node
def _visit(node):
# recusive function for visiting each node
def returnAsArr(self, method : TraverseMethod):
# return the enter tree as an array using a specified method
```
Node
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/node/src/tree)
```javascript
// enum class for traversal and processing order
var TraverseMethod = {
PRE_ORDER: 1,
IN_ORDER: 2,
POST_ORDER: 3
}
// enum class for comparisons, gt, lt and equal
var ComparisonSign = {
LESS: 1,
GREATER: 2,
EQUAL: 3
}
// class for nodes within Tree
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value
this.left = null
this.right = null
}
}
// BinaryTree Implementation
class BinaryTree {
constructor() {}
traverse(method, action_func) { }
returnAsArr(method) {}
}
class BinarySearchTree extends BinaryTree {
constructor(comparison_func=null) { }
comparison_func_default(val1, val2, CS) {}
add(new_value) {}
contains(target_value) {}
}
```
---
### Breadth-first Traversal
Breadth first traversal method which takes a Binary Tree as its unique input.
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/tree)
```python
def breadth_first(tree, action_func):
```
---
### Find the Maximum Value
Function called find_maximum_value which takes binary tree as its only input
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/find_maximum_binary_tree)
```python
def find_max(tree : BinaryTree) -> (bool,int):
```
---
### FizzBuzzTree
Write a function called FizzBuzzTree which takes a tree as an argument.
Determine weather or not the value of each node is divisible by 3, 5 or both, and change the value of each of the nodes:
- [x] value is divisible by 3, replace the value with "Fizz"
- [x] value is divisible by 5, replace the value with "Buzz"
- [x] value is divisible by 3 and 5, replace the value with "FizzBuzz"
- [x] Return the tree with its new values.
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/fizz_buzz_tree)
```python
def fizzBuzzTree(tree: BinaryTree) -> BinaryTree:
# traverse tree, value = value%3==0 ? 'Fizz, value = value%5==0 ? 'Buzz' (set value to 'FizzBuzz' if both conditions met)
```
---
### Tree Intersection
tree_intersection(): given two binary-trees, return an array containing shared values
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/tree_intersection)
```python
def tree_intersection(tree1, tree2: BinaryTree) -> list:
# return an array with all the values in both tree1 and tree2
# BigO Time==O(2n) Space==0(1.3n) 30% for hashtable
# assumption: No Duplicates within Trees
```
---
## Binary Search Tree (BST)
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/tree)
```python
class BinarySearchTree(BinaryTree):
# class for binary-search-tree
def add(self, new_value):
# adds new value to the tree
def _find_and_insert(node):
# recursive method for evaluating a node and calling itself depending on the value
def contains(self, target_value) -> bool:
# accepts a value, and returns a boolean indicating whether or not the value is in the tree at least once.
def _visit(node):
# recursive function for isiting each node
```
---
## Hash Table
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/hashtable)
```python
class HashTable():
def __init__(self, hashtableSize = 1024):
# create with hashTableSize
def _makePayload(self, name, value):
# return dict of name/value pair
def _makeHash(self, name) -> int:
# create a hash based on the name to be added to hashtable
# this is a silly hash, as it's just for experiment and
# gives us the ability to easily create collisions. Live
# code should use something more sophisticated
def _getHashIndex(self, hash: int) -> int:
# get the index into the hash-table for a given hash value
def _hashtable_compare_func(self, payload1, payload2) -> bool:
# func passed to LinkList compare
def add(self, name, value):
# accepts name/value pair and adds them to the hashtable
# if there are collisions, then they will be handled
# by using a linked-list
def get(self, name):
# returns value in hashtable for a given name
# if the value is not found, and exception will be raised
def contains(self, name) -> bool:
# returns true|false if the name is in the hashtable
```
---
### Repeated Words
repeated_words(): search the longstr for complete words, return the first word that has more than one occurrence
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/repeated_word)
```python
def repeated_word(longstr: str) -> str:
# search the longstr for complete words
# return the first word that has more than
# one occurrence
# BigO Time==O(n) Space==O(n*1.3)
```
---
### Left Join
left_join(): given two hash-tables, return a list of all items from the first h1 and the value that exists in h2, if no value exists return None
- [x] LEFT JOINs two hashmaps into a single data structure.
- [x] 1st param is hashmap with words and synonyms
- [x] 2nd param is hashmap with words and antonyms
- [x] Combine the key and corresponding values (if they exist) into a new data structure according to LEFT JOIN logic.
- [X] Code Styling: PEP8
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/left_join)
```python
def left_join(h1, h2: HashTable) -> list:
# perform a left-join on h1 against h2
# - returns a list of dict:{word,syntonym,antonym)
# - BigO time==O(n) space==0(n)
# - worst: time==O(3n)
```
---
## Graphs
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/datastructs/graph)
```python
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, value: Any):
class Edge:
def __init__(self, vertex: Vertex, weight=0):
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
def __len__(self) -> int:
def add_vertex(self, value) -> Vertex:
def add_edge(self, vert1: Vertex, vert2: Vertex, weight=0.0):
def get_neighbors(self, vertex: Vertex) -> List[Edge]:
def get_vertexes(self) -> Optional[List[Vertex]]:
def breadth_first(self, root, action_func):
```
---
### Get Graph Edges
Overall: Identify if a given path exists through the Graph where path is a given list of values
Use Case: Given a complete Graph data-structure, containing a variety of Vertexes/Edges containing city-names and costs, (Flight Routes) and a list of cities (Flight Plan), return True|False if the flight-plan can be performed and the cost.
Whiteboard

*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/tree/master/python/challenges/get_edges)
```python
def get_edges(graph: Graph, path_ro: List) -> Tuple[bool, float]:
# identify if a given path exists through the Graph
# where path is a given list of values
# @path_ro will be treated as read-only
# BigO time==O(V+P*E) .. where p is len(path_ro)
# BigO space==O(1)
```
---
### Depth-First Traversal
- [x] breadth first traversal method which takes a Binary Tree as its unique input.
- [x] print every node encountered
Whiteboard
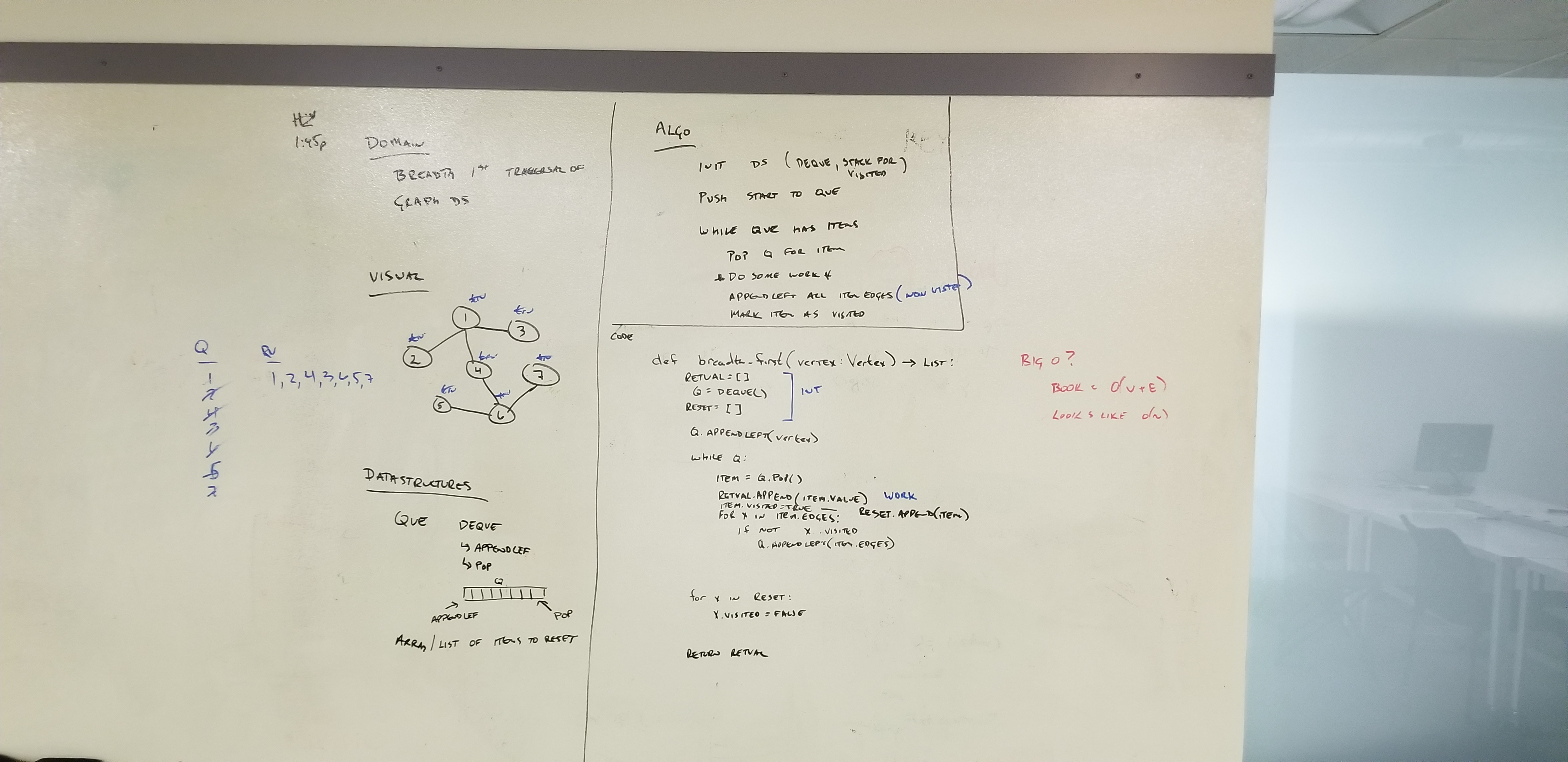
*Source Code:*
Python
Source: [Github](https://github.com/marvincolgin/data-structures-and-algorithms/blob/master/python/datastructs/graph/graph.py#L93)
```python
def depth_first_recursive(self, root: Vertex, action_func: Any) -> None:
def depth_first(self, root: Vertex, action_func: Any) -> None:
```