Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/mean-average-precision-from-scratch
Mean Average Precision from Scratch using PyTorch
https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/mean-average-precision-from-scratch
mean-average-precision object-detection pytorch
Last synced: about 2 hours ago
JSON representation
Mean Average Precision from Scratch using PyTorch
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/mean-average-precision-from-scratch
- Owner: matin-ghorbani
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-08-18T13:19:29.000Z (about 1 month ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-18T13:33:28.000Z (about 1 month ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-09-22T06:02:16.515Z (5 days ago)
- Topics: mean-average-precision, object-detection, pytorch
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 5.86 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Mean Average Precision (mAP) for Object Detection
## Overview
Mean Average Precision (mAP) is a crucial metric used in evaluating object detection models. It provides a comprehensive measure of how well a model is performing by taking into account both the precision and recall of the predictions across different classes.
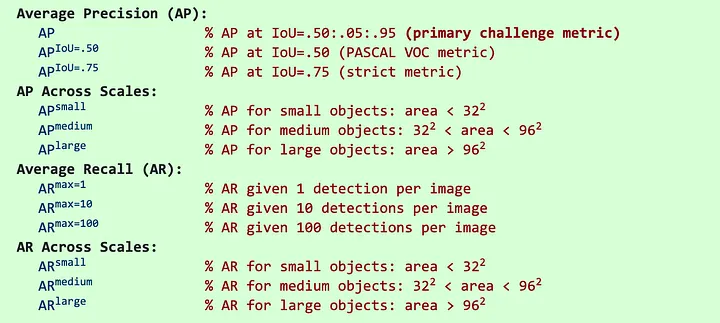
### What is Mean Average Precision (mAP)?
Mean Average Precision (mAP) is calculated by first computing the Average Precision (AP) for each class. AP is determined by the area under the precision-recall curve, which is plotted by varying the threshold for detection confidence. mAP is then obtained by taking the mean of the AP values across all classes.
In object detection, mAP not only evaluates the classification accuracy but also the localization accuracy, using the Intersection over Union (IoU) metric. IoU measures the overlap between the predicted bounding box and the ground truth bounding box. If the IoU exceeds a specified threshold (e.g., 0.5), the detection is considered a true positive.
#### Precision & Recall


### Use Cases
- **Object Detection Models**: mAP is widely used to evaluate models such as YOLO, SSD, and Faster R-CNN.
- **Benchmarking**: It serves as a standard metric for competitions like COCO and PASCAL VOC.
## Repository Structure
This repository contains the implementation of Mean Average Precision (mAP) from scratch, along with unit tests to verify its correctness. Below is a breakdown of the files:
### 1. `IoU.py`
This file contains the implementation of the Intersection over Union (IoU) function, which calculates the IoU between predicted and ground truth bounding boxes. The IoU is a crucial step in determining whether a prediction is a true positive.
For a detailed implementation of IoU, you can refer to the [IoU repository](https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/IoU-from-Scratch).
### 2. `mAP.py`
This file contains the core implementation of the Mean Average Precision (mAP) metric. The function `mean_average_precision` accepts predictions and ground truth boxes, calculates the AP for each class, and then returns the mean AP across all classes. Key steps include:
- Sorting detections by confidence score.
- Calculating true positives (TP) and false positives (FP) based on IoU.
- Computing cumulative precision and recall to generate the precision-recall curve.
- Calculating AP using the trapezoidal rule to integrate the precision-recall curve.
### 3. `mAP_tests.py`
This file contains unit tests for the `mean_average_precision` function using the `unittest` framework. It includes several test cases to validate the correctness of the mAP implementation under different scenarios, such as:
- All predictions being correct.
- A batch of predictions for multiple images.
- Cases where all predictions are incorrect or belong to the wrong class.
- Predictions with one inaccurate bounding box.
### Unit Tests in `mAP_tests.py`
The `mAP_tests.py` file contains unit tests to validate the correctness of the `mean_average_precision` function. These tests ensure that the implementation works correctly in different scenarios:
- **Test 1: All Predictions Correct for One Class (`test_all_correct_one_class`)**
- **Description**: This test checks the scenario where all predictions perfectly match the ground truth for a single class. The expected mAP should be 1, indicating perfect performance.
- **Test 2: All Predictions Correct for a Batch (`test_all_correct_batch`)**
- **Description**: This test evaluates the mAP when all predictions across multiple images are correct. It verifies the function's ability to handle batch predictions accurately. The expected mAP is 1.
- **Test 3: All Predictions Wrong Class (`test_all_wrong_class`)**
- **Description**: In this test, all predictions are made for the wrong class. The expected mAP should be 0, indicating no correct detections.
- **Test 4: One Inaccurate Bounding Box (`test_one_inaccurate_box`)**
- **Description**: This test introduces a scenario where one predicted bounding box is inaccurate. The mAP should reflect the impact of this inaccuracy.
- **Test 5: All Predictions Wrong Class (Duplicate) (`test_all_wrong_class`)**
- **Description**: This test is a duplicate of Test 3 and checks the scenario where all predictions belong to the wrong class, ensuring consistent results.
Each test uses assertions to compare the calculated mAP with the expected value, allowing a small epsilon for floating-point precision differences.