Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/non-max-suppression-from-scratch
Non Max Suppression from Scratch using PyTorch
https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/non-max-suppression-from-scratch
nms non-max-suppression object-detection pytorch
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Non Max Suppression from Scratch using PyTorch
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/non-max-suppression-from-scratch
- Owner: matin-ghorbani
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-08-18T12:21:56.000Z (3 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-18T12:35:16.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-09-22T06:02:17.324Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: nms, non-max-suppression, object-detection, pytorch
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 4.88 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Non-Max Suppression (NMS) for Object Detection
## Overview
This repository implements Non-Max Suppression (NMS) from scratch in Python, a key technique used in object detection tasks to filter and refine bounding boxes. NMS is essential for improving the accuracy and efficiency of object detection models by eliminating redundant and overlapping predictions.

## What is Non-Max Suppression?
Non-Max Suppression is an algorithm used in object detection to remove overlapping bounding boxes that correspond to the same object. When a model predicts multiple boxes for the same object, NMS selects the box with the highest confidence score and suppresses the others if their Intersection over Union (IoU) exceeds a certain threshold. This ensures that the final output contains only the most relevant bounding boxes, preventing multiple detections of the same object.
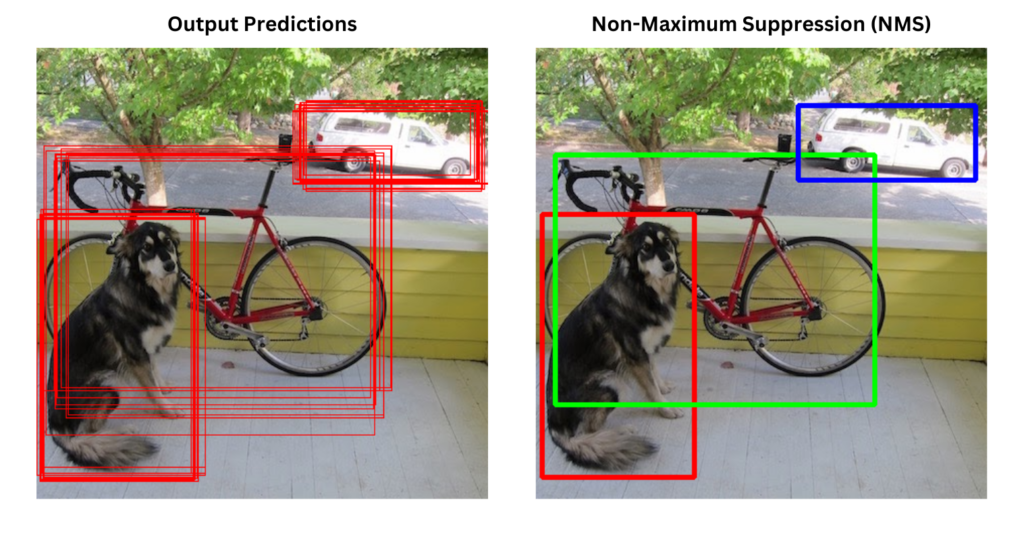
### Use Cases of Non-Max Suppression
- **Object Detection**: NMS is commonly used in object detection algorithms like YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and SSD to filter out redundant bounding boxes.
- **Face Detection**: In face detection tasks, NMS helps in selecting the most accurate bounding box for each face detected in an image.
- **Pedestrian Detection**: Similar to face detection, NMS is used in pedestrian detection to accurately localize each individual in crowded environments.
## Repository Structure
This repository contains the following files:
### 1. `IoU.py`
This file contains the implementation of the Intersection over Union (IoU) calculation. IoU is a measure of the overlap between two bounding boxes and is crucial in the Non-Max Suppression process to determine which boxes should be suppressed.
For more details on the IoU implementation, please visit the [IoU Repository](https://github.com/matin-ghorbani/IoU-from-Scratch).
### 2. `nms.py`
This file implements the Non-Max Suppression algorithm. The function `non_max_suppression` takes a list of bounding box predictions and filters out overlapping boxes based on their IoU and confidence scores. The function:
- Accepts bounding boxes, a probability threshold, and an IoU threshold.
- Filters out boxes with low confidence scores.
- Iteratively selects the box with the highest confidence score and suppresses other overlapping boxes.
- Returns the final set of bounding boxes after suppression.
### 3. `nms_tests.py`
This file contains unit tests for the `non_max_suppression` function using the `unittest` framework. The tests validate the correctness of the NMS implementation by checking various scenarios:
- Removing boxes based on IoU.
- Keeping boxes from different classes.
- Handling cases where both IoU and class conditions affect suppression.
These tests ensure that the NMS function behaves as expected under different conditions.
## Running the Code
1. **Prerequisites**: Ensure you have Python and PyTorch installed.
run this command to install PyTorch
```bash
pip install torch
```
2. **Run the Tests**: To verify the implementation, navigate to the directory containing the files and run the tests using:
```bash
python nms_tests.py
```
## Explanation of the Tests in `nms_tests.py`
The `nms_tests.py` file contains unit tests to verify the correctness of the Non-Max Suppression (NMS) implementation. These tests are designed using the `unittest` framework, with each test case targeting a specific behavior of the `non_max_suppression` function.
#### 1. `test_remove_on_iou`
- **Purpose**: This test checks whether the NMS implementation correctly removes overlapping bounding boxes based on the IoU threshold.
- **Test Input**: The `self.t1_boxes` list contains multiple bounding boxes for the same class, with varying levels of overlap.
- **Expected Output**: The function should retain only those boxes that do not exceed the specified IoU threshold when compared to the box with the highest confidence score.
- **Significance**: This test ensures that the function effectively suppresses boxes that have a high degree of overlap, keeping only the most relevant one.
#### 2. `test_keep_on_class`
- **Purpose**: This test checks whether the NMS function properly retains boxes of different classes, even if they overlap.
- **Test Input**: The `self.t2_boxes` list contains boxes from different classes with some overlap.
- **Expected Output**: The function should keep boxes that belong to different classes, regardless of their IoU values.
- **Significance**: This test verifies that NMS is class-aware and does not suppress boxes from different classes, ensuring that all distinct objects are detected.
#### 3. `test_remove_on_iou_and_class`
- **Purpose**: This test verifies that the NMS function correctly removes overlapping boxes when both IoU and class conditions apply.
- **Test Input**: The `self.t3_boxes` list contains overlapping boxes where both IoU and class conditions must be considered.
- **Expected Output**: The function should suppress overlapping boxes only if they belong to the same class and exceed the IoU threshold.
- **Significance**: This test checks the combined effect of IoU and class in the suppression logic, ensuring that the function handles both criteria properly.
#### 4. `test_keep_on_iou`
- **Purpose**: This test checks if the NMS implementation retains boxes that do not exceed a higher IoU threshold, even if they belong to the same class.
- **Test Input**: The `self.t4_boxes` list contains bounding boxes with varying degrees of overlap, but with a higher IoU threshold.
- **Expected Output**: The function should keep boxes that do not exceed the higher IoU threshold, even if they belong to the same class.
- **Significance**: This test ensures that the IoU threshold is correctly applied and that the function does not overly suppress boxes that have lower overlap.