https://github.com/matthewfilipovich/torchoptics
Python library for differentiable wave optics simulations with PyTorch.
https://github.com/matthewfilipovich/torchoptics
computational-optics deep-learning differentiable-optics diffraction fourier-optics holography imaging inverse-design machine-learning microscopy optical-neural-network optics physics pytorch wave-optics
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Python library for differentiable wave optics simulations with PyTorch.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/matthewfilipovich/torchoptics
- Owner: MatthewFilipovich
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-11-27T22:32:02.000Z (10 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-04-11T16:49:39.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-12T04:53:09.454Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: computational-optics, deep-learning, differentiable-optics, diffraction, fourier-optics, holography, imaging, inverse-design, machine-learning, microscopy, optical-neural-network, optics, physics, pytorch, wave-optics
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://torchoptics.readthedocs.io
- Size: 37.2 MB
- Stars: 44
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

> TorchOptics is an open-source Python library for differentiable wave optics simulations with PyTorch.
[](https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics/actions/workflows/build.yml)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics)
[](https://torchoptics.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://pypi.org/project/torchoptics/)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
[](https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics/blob/main/LICENSE)
# Key Features
- 🌊 **Differentiable Wave Optics**: A comprehensive framework for modeling, analyzing, and designing optical systems using differentiable Fourier optics.
- 🔥 **Built on PyTorch**: Leverages PyTorch for GPU acceleration, batch processing, automatic differentiation, and efficient gradient-based optimization.
- 🛠️ **End-to-End Optimization**: Enables optimization of optical hardware and deep learning models within a unified, differentiable pipeline.
- 🔬 **Optical Elements**: Features standard optical elements like modulators, lenses, detectors, and polarizers.
- 🖼️ **Spatial Profiles**: Provides a wide range of spatial profiles, including Hermite-Gaussian and Laguerre-Gaussian beams.
- 🔆 **Polarization & Coherence**: Supports simulations of polarized light and optical fields with arbitrary spatial coherence.
Our research paper, available on [arXiv](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.18591), introduces the TorchOptics library and provides a comprehensive review of its features and applications.
## Documentation
Access the latest documentation at [torchoptics.readthedocs.io](https://torchoptics.readthedocs.io/).
## Installation
To install the latest **stable release** of TorchOptics from [PyPI](https://pypi.org/project/torchoptics/), run:
```sh
pip install torchoptics
```
For the latest **development version**, install directly from [GitHub](https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics):
```sh
git clone https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics
cd torchoptics
pip install -e '.[dev]'
```
This installs the library in editable mode, along with additional dependencies for development and testing.
## Usage
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics/blob/main/docs/source/_static/torchoptics_colab.ipynb)
This example demonstrates how to simulate a 4f imaging system using TorchOptics. The field at each focal plane along the z-axis is computed and visualized:
```python
import torch
import torchoptics
from torchoptics import Field, System
from torchoptics.elements import Lens
from torchoptics.profiles import checkerboard
# Set simulation properties
shape = 1000 # Number of grid points in each dimension
spacing = 10e-6 # Spacing between grid points (m)
wavelength = 700e-9 # Field wavelength (m)
focal_length = 200e-3 # Lens focal length (m)
tile_length = 400e-6 # Checkerboard tile length (m)
num_tiles = 15 # Number of tiles in each dimension
# Determine device
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# Configure default properties
torchoptics.set_default_spacing(spacing)
torchoptics.set_default_wavelength(wavelength)
# Initialize input field with checkerboard pattern
field_data = checkerboard(shape, tile_length, num_tiles)
input_field = Field(field_data).to(device)
# Define 4f optical system with two lenses
system = System(
Lens(shape, focal_length, z=1 * focal_length),
Lens(shape, focal_length, z=3 * focal_length),
).to(device)
# Measure field at focal planes along the z-axis
measurements = [
system.measure_at_z(input_field, z=i * focal_length)
for i in range(5)
]
# Visualize the measured intensity distributions
for i, measurement in enumerate(measurements):
measurement.visualize(title=f"z={i}f", vmax=1)
```
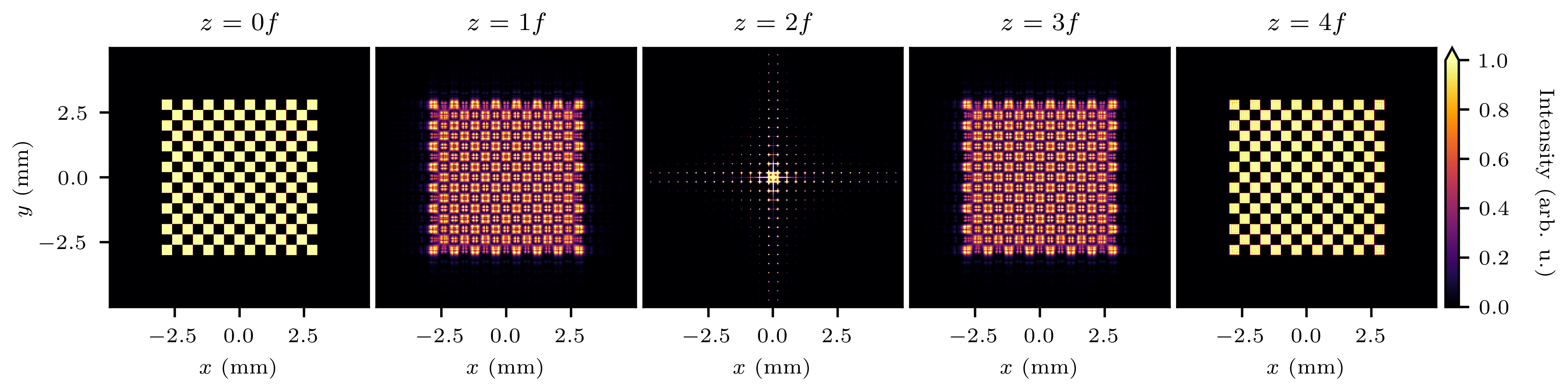
Intensity distributions at different focal planes in the 4f system.

Propagation of the intensity distribution.
_For more examples and detailed usage, please refer to the [documentation](https://torchoptics.readthedocs.io/)._
## Contributing
We welcome bug reports, questions, and feature suggestions to improve TorchOptics.
- **Found a bug or have a question?** Please [open an issue on GitHub](https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics/issues).
- **Want to contribute a new feature?** Follow these steps:
1. **Fork the repository**: Go to
2. **Create a feature branch**: `git checkout -b feature/fooBar`
3. **Commit your changes**: `git commit -am 'Add some fooBar'`
4. **Push to the branch**: `git push origin feature/fooBar`
5. **Submit a Pull Request**: Open a Pull Request on GitHub
## Citing TorchOptics
If you use TorchOptics in your research, please cite our paper:
> M.J. Filipovich and A.I. Lvovsky, _TorchOptics: An open-source Python library for differentiable Fourier optics simulations_, arXiv preprint [arXiv:2411.18591](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.18591) (2024).
## License
TorchOptics is distributed under the MIT License. See the [LICENSE](https://github.com/MatthewFilipovich/torchoptics/blob/main/LICENSE) file for more details.