https://github.com/mbari-org/kelpcoverage
calculating kelp coverage from UAV imagery
https://github.com/mbari-org/kelpcoverage
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
calculating kelp coverage from UAV imagery
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mbari-org/kelpcoverage
- Owner: mbari-org
- License: mit
- Created: 2025-07-30T21:23:18.000Z (6 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-08-07T00:24:24.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-08-07T01:04:43.515Z (5 months ago)
- Language: Python
- Size: 22.1 MB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# KLP: Kelp Location Profiler Tool
[](https://pypi.org/project/kelp-coverage/)
**Version: 1.0**
`kelp-coverage` is a command-line package designed to analyze UAV imagery of the ocean to calculate the percentage of kelp coverage. It utilizes the Segment Anything Model (SAM) in combination with Sliced Aided Hyper-Inference (SAHI) to create high-resolution segmentations of kelp from water.

*Example of one UAV image.*
## Table of Contents
1. [How It Works](#how-it-works)
2. [Installation](#installation)
3. [Output Files and Directory Structure](#output-files-and-directory-structure)
4. [Examples](#examples)
5. [Command Reference](#command-reference)
## Installation
**Install from PyPI:**
Install the package directly from PyPI using [pip](https://pypi.org/project/kelp-coverage/). The MobileSAM model will be downloaded by default on the first run of the program.
```bash
pip install kelp-coverage
```
## How It Works
The core idea behind how the program works is by leveraging the segment anything model to mask out the background (water) within the image. Since most of the images will contain either kelp or water, by inversing the problem and instead creating a segmentation for where the water is within the image we can get a good estimate of the kelp coverage.
### 1. Median water pixel
The pipeline begins by sampling 50,000 pixels from each image within a site. It then calculates the median pixel value in CIELAB color space. This creates a unique "water pixel" value for each individual site which is crucial since water color can be incredibly varied.


*Example of how UAV images from the same site but at different times can be different. UAV image on the right was taken on 2025/06/18 and image on the left was taken on 2025/04/04 at the Seymour survey site*
### 2. Slicing and Segmentation
Slicing the image serves two purposes.
1. since the model was trained on 1024x1024 images, reducing the image to the native size of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) helps it better detect objects
2. by slicing the image, the amount of space the kelp takes increases, thus making it easier for the model to detect it as an object and not a part of the background
The tool first slices the image into smaller overlapping tiles. For each slice, the pipeline uses the calibrated water color to find pixels that are a close match. These water-colored pixels are used as **seed points** for the SAM model and are used to generate slice segmentations. This process also utilizes a hierarchical two-pass system (coarse and fine) to ensure both large bodies of water and small gaps are accurately captured.
*utilizing a hierarchical two-pass approach is optional but recommended for more accurate results*
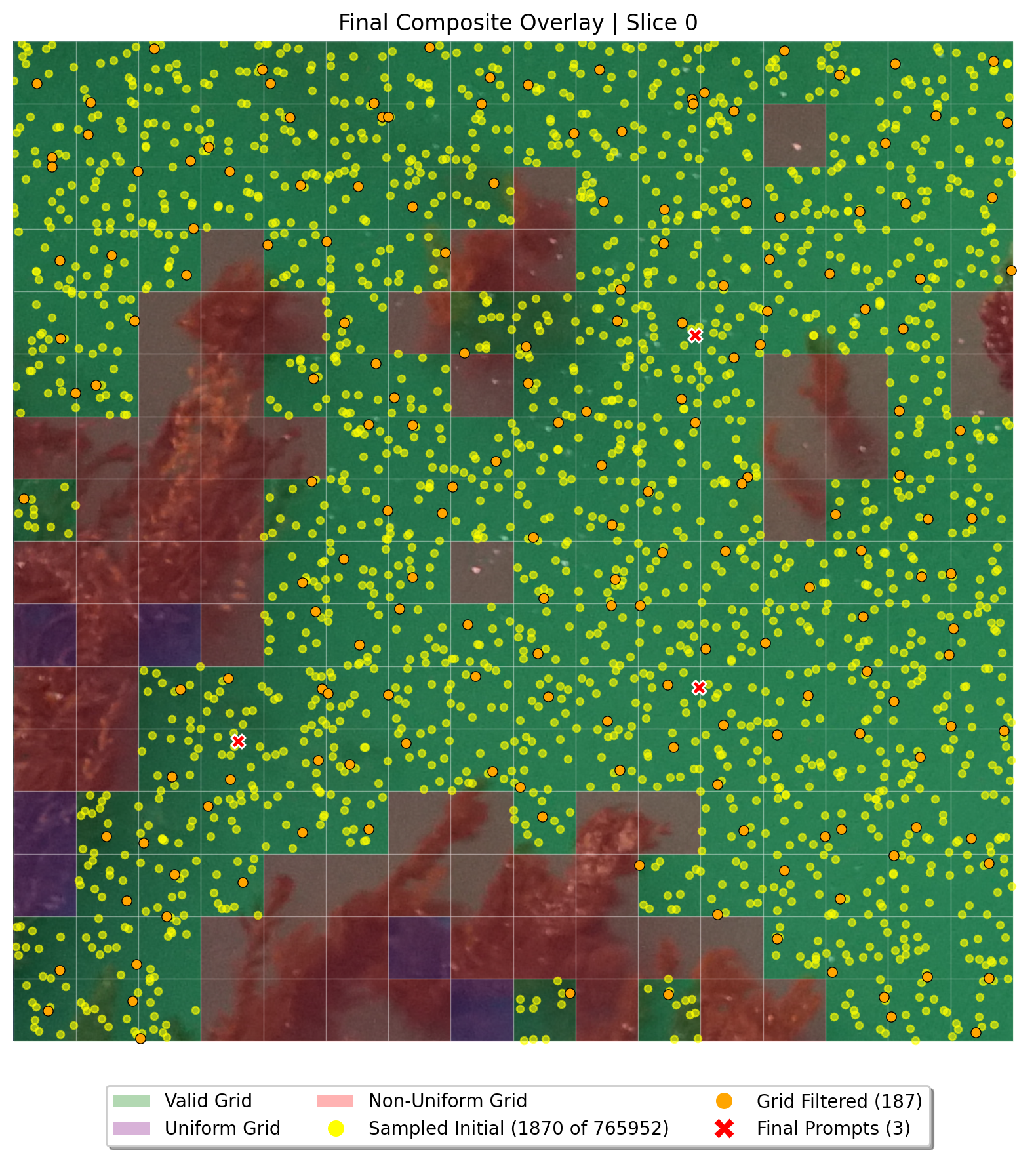
*Debug image showcasing the point selection.*
### 3. Merging and Reconstruction
After all slices are processed they are merged and inverted to create a full resolution kelp segmentation mask.
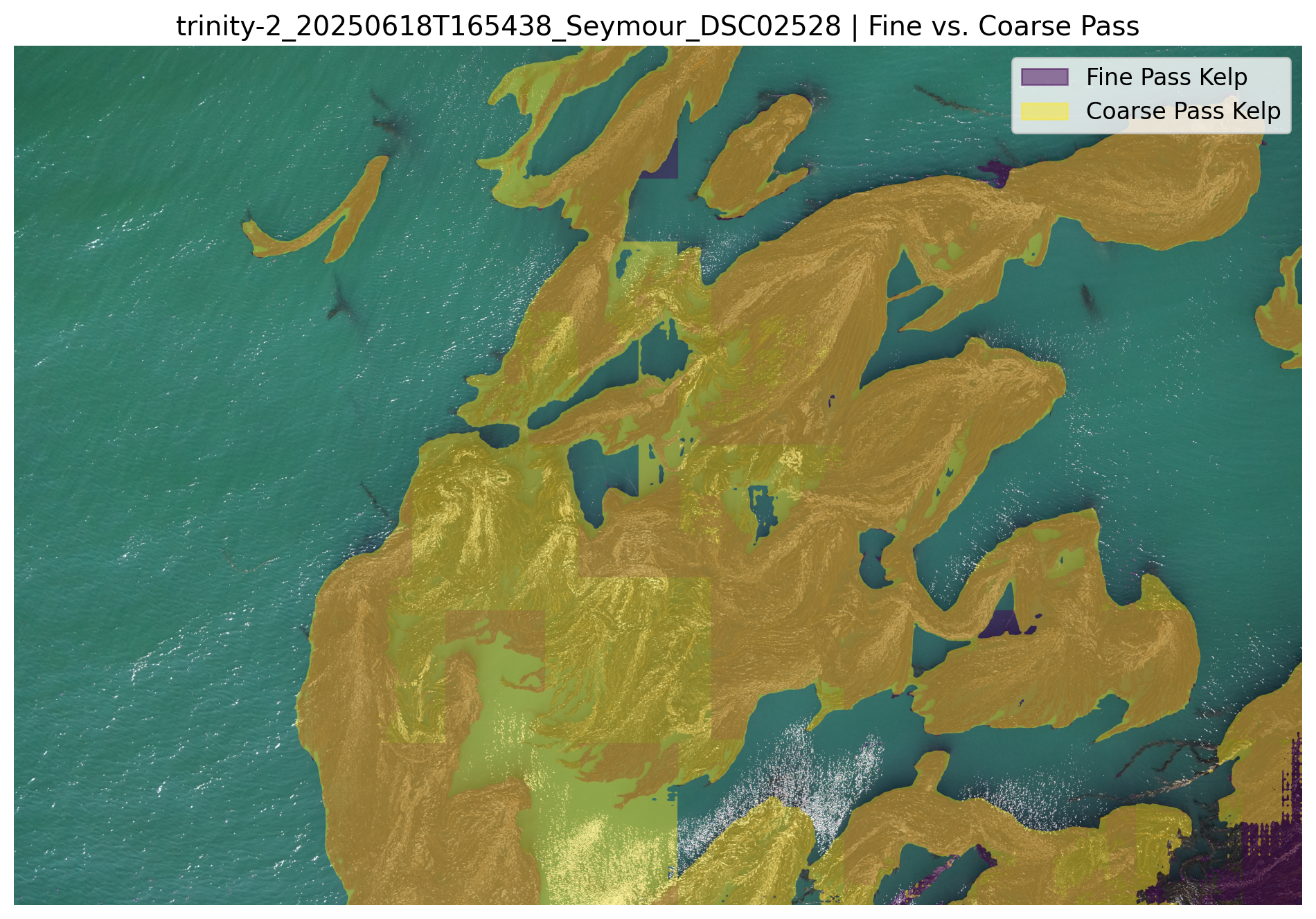
*The two masks generated from the fine and coarse model...*
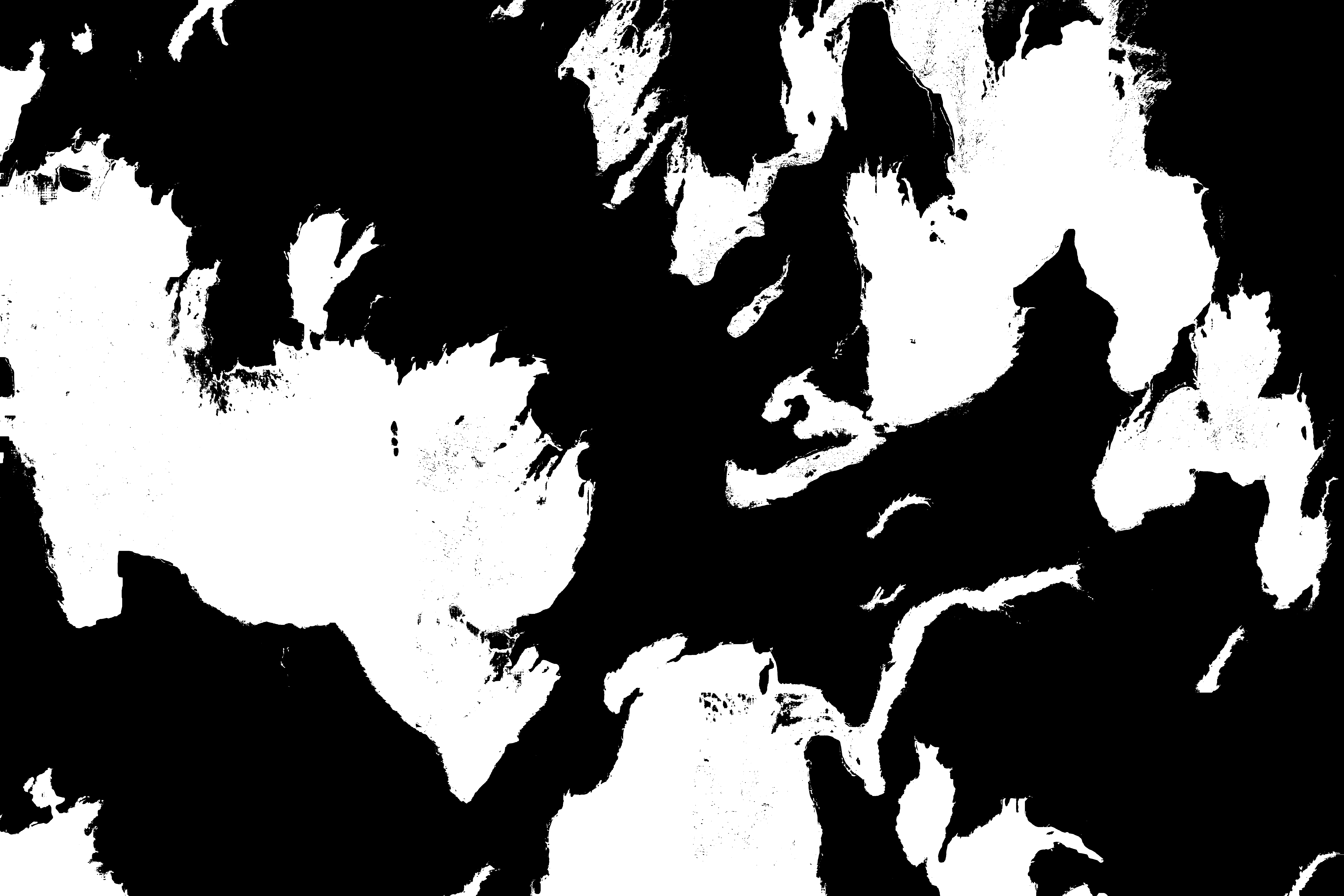

*..The final joined kelp mask...*
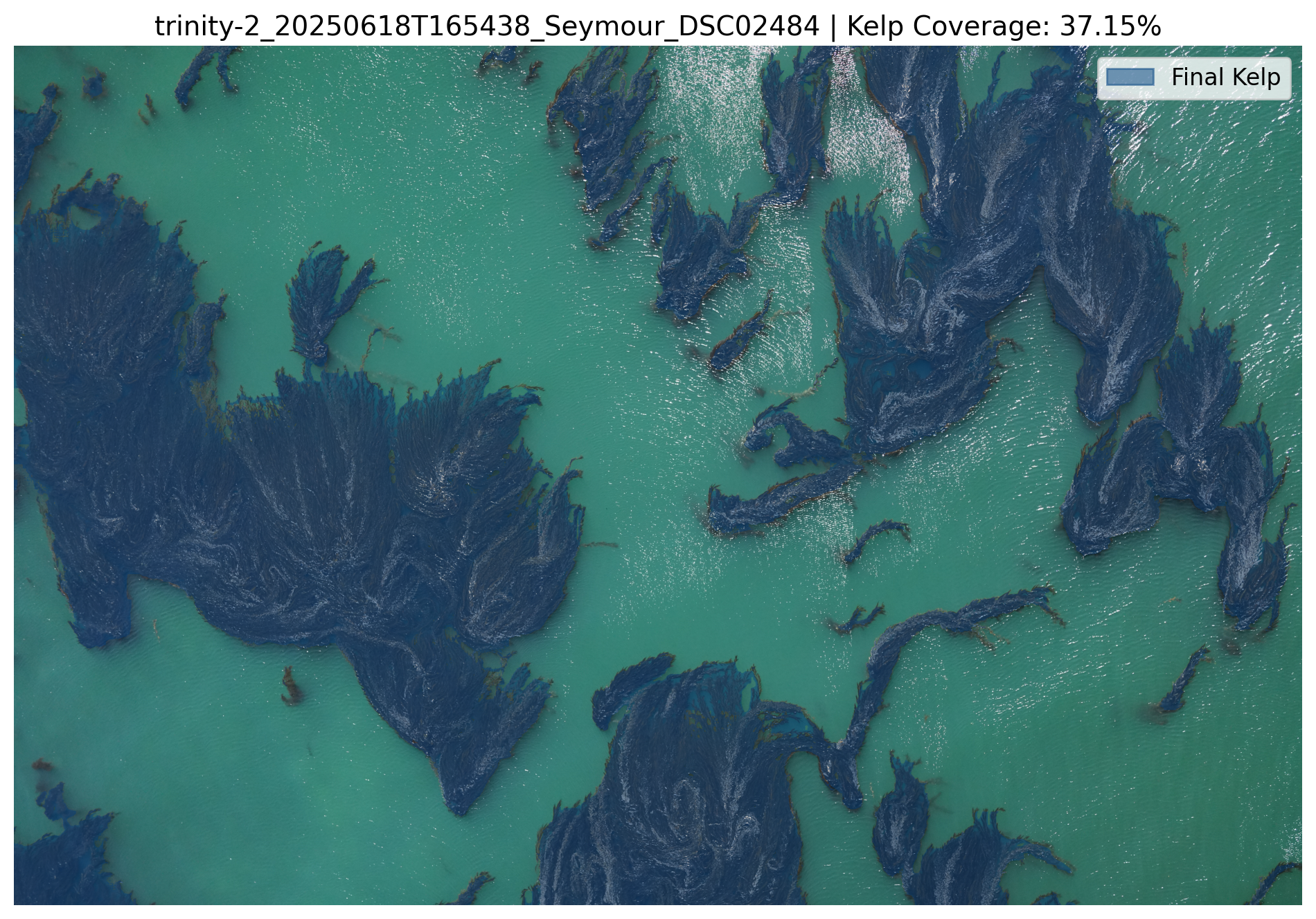

*...and overlay visualizations which are saved in the run-specific output folder.*
## Output Files and Directory Structure
The tool organizes all outputs into a `results/` directory. Each analysis run is stored in a subdirectory named with a unique hash of the run parameters, ensuring that results from different settings don't overwrite each other.
```text
results/
├── debug/
│ └── trinity-2..._slice_0_thresh20_stage1_grid_validation.png
│ └── trinity-2..._slice_0_thresh20_stage2_point_selection.png
│ └── ... (more debug images)
├── heatmap/
│ └── 20241220T190455_heatmap.png
├── trinity-2_20241220T190455/
│ └── 89bb41f9/
│ ├── results.json
│ ├── masks/
│ │ └── trinity-2..._kelp_mask.png
│ └── visualizations/
│ └── trinity-2..._overlay.png
│ └── ... (more viz images)
└── pixel_values.csv
```
### `results.json`
This is the main output file, containing the command used, all run parameters, and a list of results for each processed image, including its name, ID, geolocation, and the final calculated kelp coverage percentage.
```json
{
"command": "kelp-coverage analyze --site trinity-2_20241220T190455...",
"run_args": {
"command": "analyze",
"hierarchical": true,
"slice_size": 1024,
"hierarchical_slice_size": 4096,
"threshold": 20,
"use_erosion_merge": true,
"use_color_validation": true,
"...": "..."
},
"results": [
{
"image_name": "trinity-2_20241220T190455_NewBrighton_DSC01634.JPG",
"image_id": 162986,
"latitude": 36.97335830004439,
"longitude": -121.94042791898332,
"coverage_percentage": 0.0
},
"..."
]
}
```
### Geospatial Heatmap
You can also generate a georeferenced heatmap to get a spatial overview of kelp density across a site.
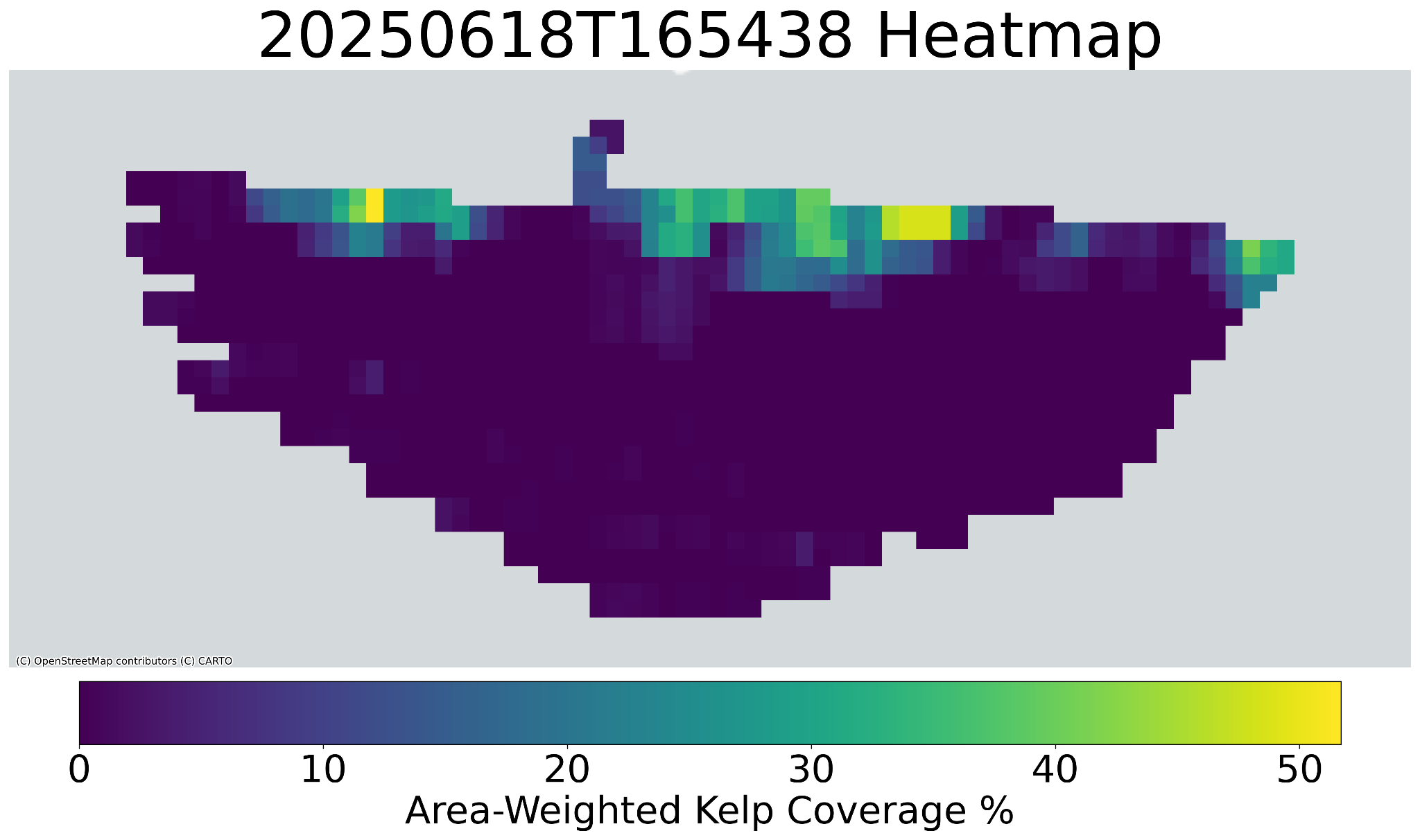
*Heatmaps are saved in the `results/heatmap/` directory.*
## Examples
**Standard Workflow:**
1. **Setup:** Download 5 images per site from a csv containing Tator metadata.
```bash
kelp-coverage setup \
--tator-csv all_sites_metadata.csv \
--tator-token \
--images 5
```
2. **Analysis:** Run analysis on a single site.
```bash
kelp-coverage analyze \
--site "trinity-2_20241220T190455" \
--tator-csv all_sites_metadata.csv \
--hierarchical \
--generate-overlay
```
4. **Debug a problematic image:**
```bash
kelp-coverage debug-slice \
--site "trinity-2_20241220T190455" \
--image-path "/content/images/trinity-2_20241220T190455/trinity-2_20241220T190455_NewBrighton_DSC01645.JPG" \
--slice-index 42 \
--visualize-stages \
--heatmap
```
5. **Create a heatmap from results:**
```bash
kelp-coverage heatmap --coverage-data "/content/results/trinity-2_20241220T190455/4005f6fd/results.json" --show-points
## Command Reference
### `setup`
Downloads images via Tator and computes representative water pixel values for each site.
```bash
kelp-coverage setup --tator-csv --tator-token [options]
```
**Arguments:**
* `--tator-csv `: **(Required)** Path to the image CSV file.
* `--tator-token `: **(Required)** API token for Tator.
* `--images `: Number of images to download per site. -1 for all images (default).
* `--start-idx ` / `--end-idx `: Optional start/end index from the CSV to process.
* `--visualize`: Display histograms of the LAB color channels for each site.
---
### `analyze`
Run the kelp segmentation analysis.
```bash
kelp-coverage analyze --site --tator-csv [options]
```
**Key Arguments:**
* `--site `: Specify a single site to process. Processes all sites if omitted.
* `--tator-csv `: **(Required)** Path to the CSV to link results with metadata.
* `--images `: A comma-separated list of specific image filenames to process.
* `--count `: Number of images to randomly select and process from each site. -1 for all (default).
* `--coverage-only`: Only compute and save coverage values (fastest).
* `--overwrite`: Overwrite existing results for a site.
* `--verbose, -v`: Verbose output.
**Hierarchical Method:**
* `--hierarchical / --no-hierarchical`: Use a two-pass hierarchical method (default: enabled).
* `--hierarchical-slice-size `: Slice size for the coarse pass (default: 4096).
* `--use-erosion-merge / --no-use-erosion-merge`: Use erosion on the coarse mask (default: enabled).
* `--use-color-validation / --no-use-color-validation`: Use color validation to merge masks (default: enabled).
**Visualization:**
* `--generate-overlay`: Generate a transparent overlay of the kelp mask on the original image.
* `--generate-slice-viz`: Generate a grid visualization of all slices.
* `--generate-erosion-viz`: Generate a visualization of the erosion merge effect.
* `--generate-merge-viz`: Generate a heatmap visualization of the disagreement area during mask merging.
* `--generate-component-viz`: Generate a visualization of the fine and coarse masks overlayed.
---
### `debug-slice`
Debug the program on a particular slice(s).
```bash
kelp-coverage debug-slice --image-path --slice-index --site [options]
```
**Arguments:**
* `--image-path `: **(Required)** One or more full paths to images to debug.
* `--slice-index `: **(Required)** One or more slice indices to debug.
* `--site `: **(Required)** Site name.
* `--heatmap`: Generate threshold visualization of color distances.
* `--visualize-stages`: Visualize the point filtering pipeline step-by-step.
---
### `heatmap`
Generates a spatial heatmap from a resulting json file.
```bash
kelp-coverage heatmap --coverage-data [options]
```
**Arguments:**
* `--coverage-data `: **(Required)** Path to the results.json file from an analysis run.
* `--output `: Path to save the output heatmap image.
* `--grid-size `: Size of heatmap grid cells (default: 30).
* `--show-grid-values`: Show numerical coverage values on the grid cells.
* `--show-points`: Show the location of data points on the map.
* `--show-point-labels`: Show labels for the data points.