https://github.com/meyerls/pc-skeletor
Skeletonization of 3D Point Clouds
https://github.com/meyerls/pc-skeletor
3d-skeleton laplacian lbc pointcloud python s-lbc skeleton-extraction skeletonization
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Skeletonization of 3D Point Clouds
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/meyerls/pc-skeletor
- Owner: meyerls
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-11-18T15:08:58.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-14T08:32:54.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-29T09:20:45.260Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: 3d-skeleton, laplacian, lbc, pointcloud, python, s-lbc, skeleton-extraction, skeletonization
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 70.2 MB
- Stars: 150
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 18
- Open Issues: 13
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: Readme.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# PC Skeletor - Point Cloud Skeletonization 
**PC Skeletor** is a Python library for extracting a curved skeleton from 3d point clouds using
[Laplacian-Based Contraction](https://taiya.github.io/pubs/cao2010cloudcontr.pdf) and
[Semantic Laplacian-Based Contraction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.04708).
## Abstract
Basic Laplacian-based contraction (LBC) is prone to mal-contraction in cases where
there is a significant disparity in diameter between trunk and branches. In such cases fine structures experience
an over-contraction and leading to a distortion of their topological characteristics. In addition, LBC shows a
topologically incorrect tree skeleton for trunk structures that have holes in the point cloud.In order to address
these topological artifacts, we introduce semantic Laplacian-based contraction (S-LBC). It integrates semantic
information of the point cloud into the contraction algorithm to overcome these artifacts.
Laplacian-Based Contraction (LBC)

Semantic LBC (S-LBC)

## ⚡️ Quick Start
### Installation
First install [Python](https://www.python.org/downloads/) Version 3.8 or higher. The python package can be installed
via [PyPi](https://pypi.org/project/pc-skeletor/) using pip.
````sh
pip install pc-skeletor
````
### Installation from Source
````sh
git clone https://github.com/meyerls/pc-skeletor.git
cd pc-skeletor
pip install --upgrade pip setuptools
pip install -r requirements.txt
pip install -e .
````
### Basic Usage
The following code performs the skeletonization algorithm on a downloaded point cloud example. It also generates an
animation that includes the original point cloud and the resulting skeleton, which is exported as a gif.
#### Download Example Dataset
````python
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
from pc_skeletor import Dataset
downloader = Dataset()
trunk_pcd_path, branch_pcd_path = downloader.download_semantic_tree_dataset()
pcd_trunk = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(trunk_pcd_path)
pcd_branch = o3d.io.read_point_cloud(branch_pcd_path)
pcd = pcd_trunk + pcd_branch
````
#### Laplacian-Based Contraction (LBC)
````python
from pc_skeletor import LBC
lbc = LBC(point_cloud=pcd,
down_sample=0.008)
lbc.extract_skeleton()
lbc.extract_topology()
# Debug/Visualization
lbc.visualize()
lbc.export_results('./output')
lbc.animate(init_rot=np.asarray([[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0]]),
steps=300,
output='./output')
````
#### Semantic Laplacian-Based Contraction (S-LBC)
````python
from pc_skeletor import SLBC
s_lbc = SLBC(point_cloud={'trunk': pcd_trunk, 'branches': pcd_branch},
semantic_weighting=30,
down_sample=0.008,
debug=True)
s_lbc.extract_skeleton()
s_lbc.extract_topology()
# Debug/Visualization
s_lbc.visualize()
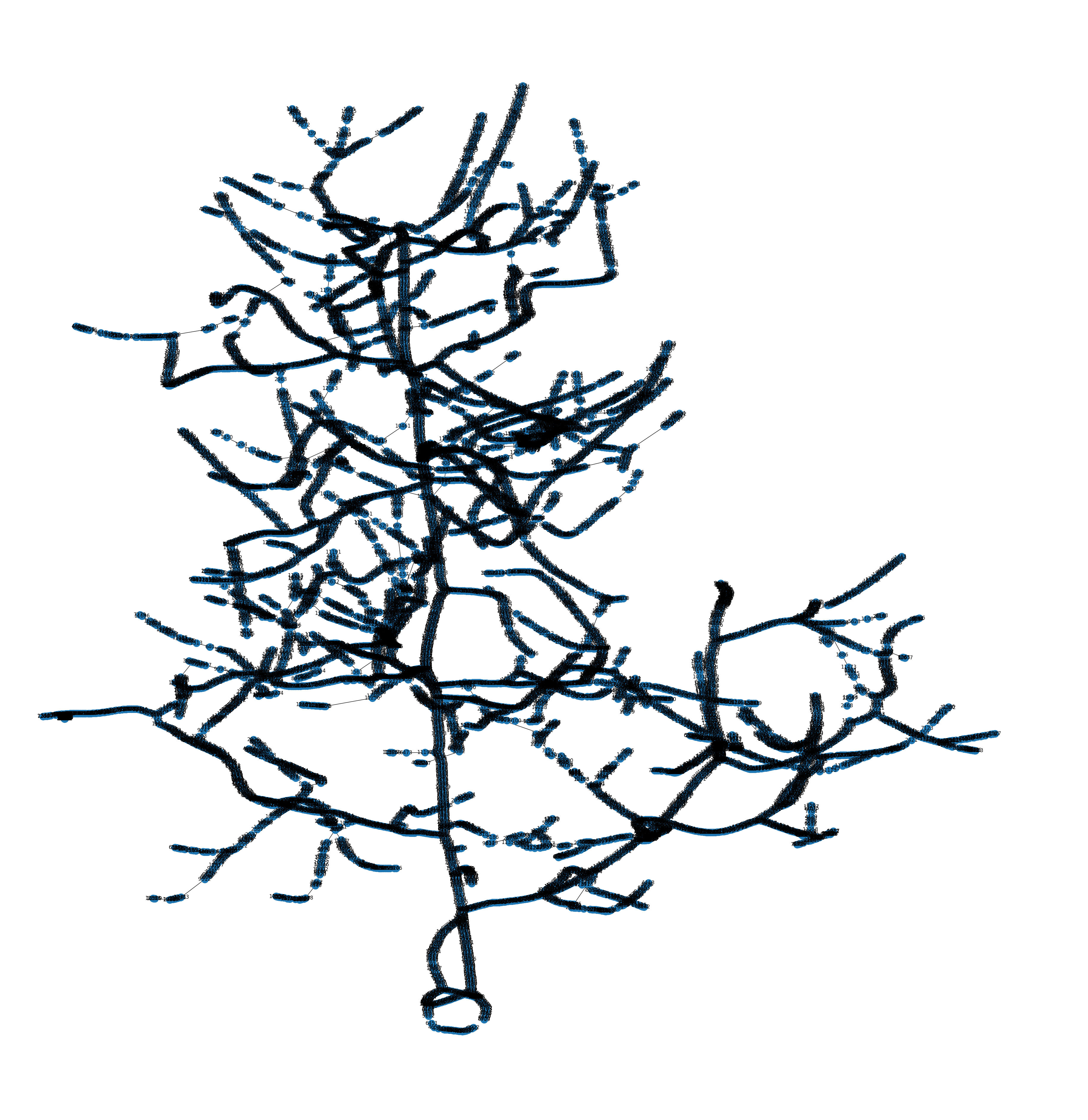
s_lbc.show_graph(s_lbc.skeleton_graph)
s_lbc.show_graph(s_lbc.topology_graph)
s_lbc.export_results('./output')
s_lbc.animate(init_rot=np.asarray([[1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0]]), steps=300, output='./output')
````
#### Output
Skeleton
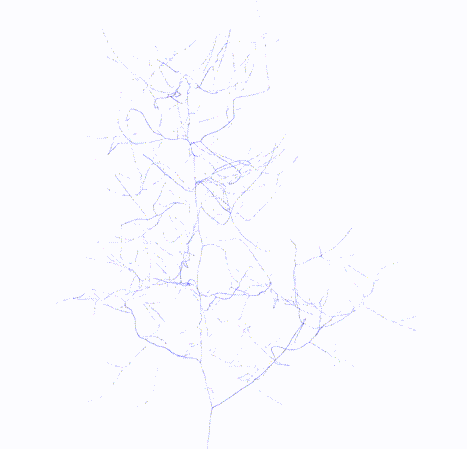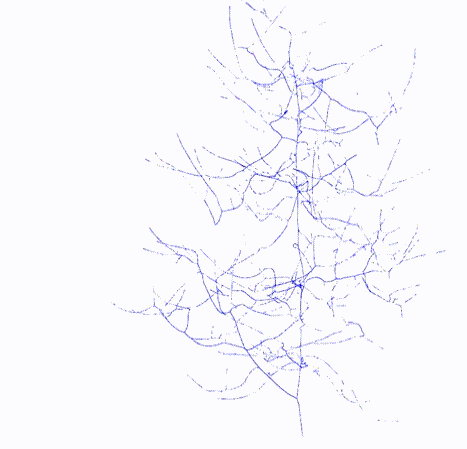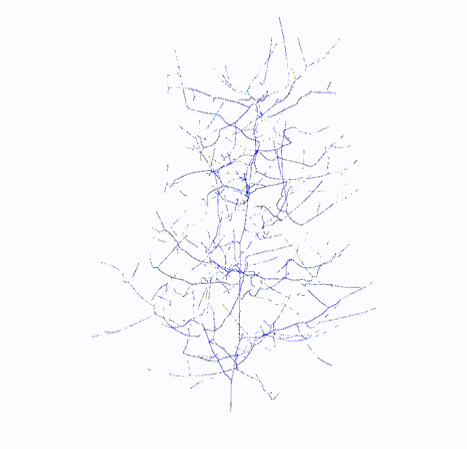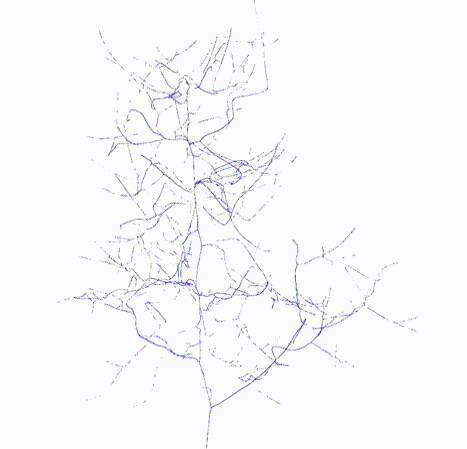
Topology
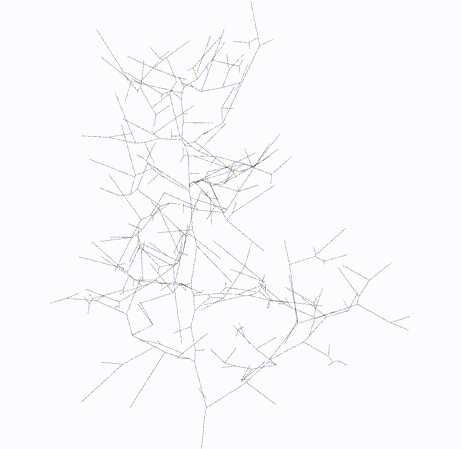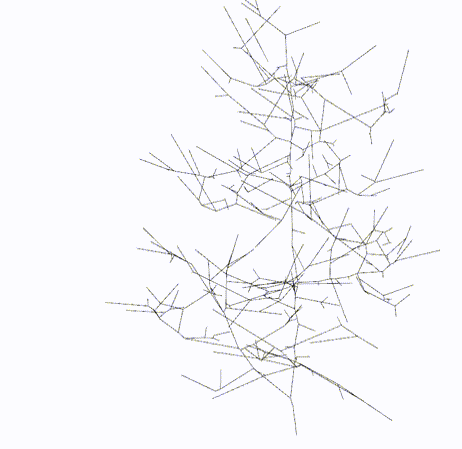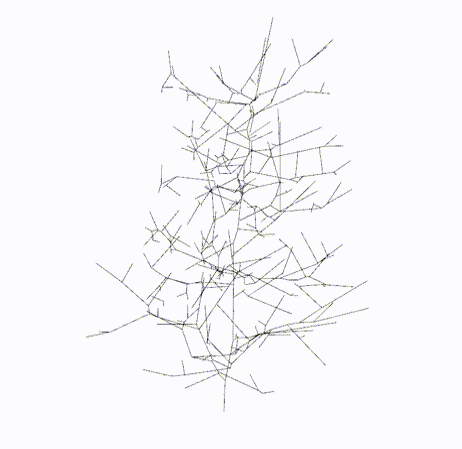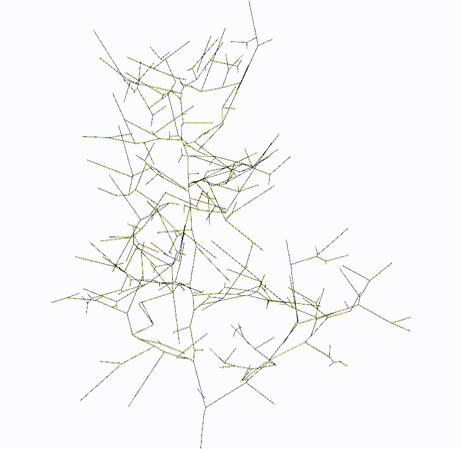
Skeletal Graph
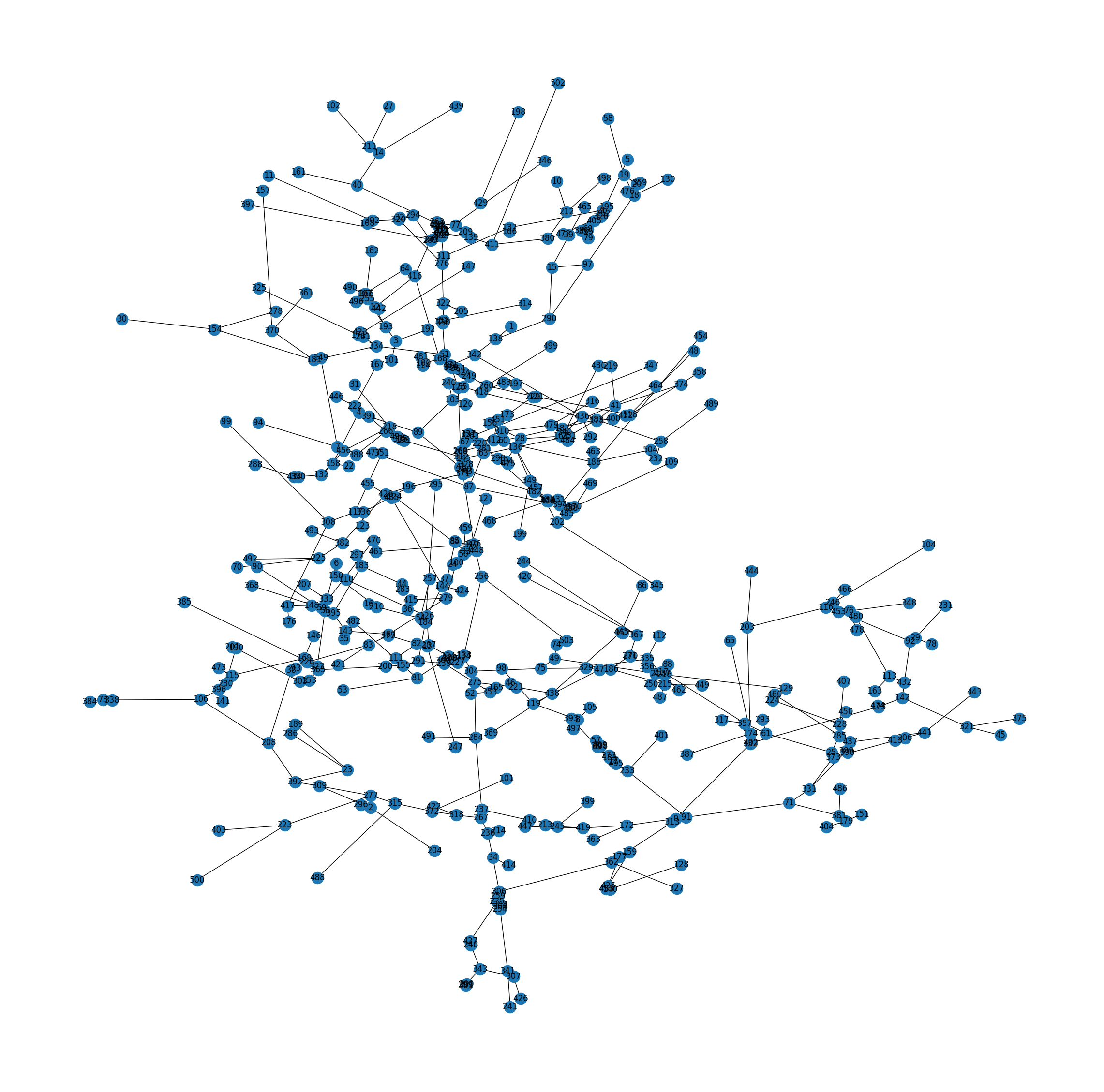

Topology Graph
````python
lbc.contracted_point_cloud: o3d.geometry.PointCloud
lbc.skeleton: o3d.geometry.PointCloud
lbc.skeleton_graph: networkx.nx
lbc.topology: o3d.geometry.LineSet
lbc.topology_graph: networkx.nx
````
## Ω Parametrization
### Laplacian-Based Contraction
Laplacian-Based Contraction is a method based on contraction of point clouds to extract curve skeletons by iteratively
contracting the point cloud. This method is robust to missing data and noise. Additionally no prior knowledge on the
topology of the object has to be made.
The contraction is computed by iteratively solving the linear system
```math
\begin{bmatrix}
\mathbf{W_L} \mathbf{L}\\
\mathbf{W_H}
\end{bmatrix} \mathbf{P}^{'} =
\begin{bmatrix}
\mathbf{0}\\
\mathbf{W_H} \mathbf{P}
\end{bmatrix}
```
obtained from [Kin-Chung Au et al.](http://graphics.csie.ncku.edu.tw/Skeleton/skeleton-paperfinal.pdf)
$\mathbf{L}$ is the $n \times n$
[Laplacian Matrix](http://rodolphe-vaillant.fr/entry/101/definition-laplacian-matrix-for-triangle-meshes)
with cotangent weights. The Laplacian of a point cloud (Laplace-Beltrami Operator) can be used to compute the [mean
curvature Vector](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~kmcrane/Projects/DDG/paper.pdf)(p. 88 & p. 100). $\mathbf{P}$ is the original
point cloud, $\mathbf{P}^{'}$ a contracted point cloud and $\mathbf{W_L}$ and $\mathbf{W_H}$ are diagonal weight
matrices balancing the contraction and attraction forces. During the contraction the point clouds get thinner and
thinner until the solution converges. Afterwards the contracted point cloud aka. skeleton is sampled using
farthest-point method.
To archive good contraction result and avoid over- and under-contraction it is necessary to initialize and update the
weights $\mathbf{W_L}$ and $\mathbf{W_H}$. Therefore the initial values and the maximum values for both diagonal
weighting matrices have to adjusted to archive good results.
#### Semantic Laplacian-Based Contraction
Semantic Laplacian-Based Contraction is based on Laplacian-based contraction and simply adds semantic knowledge to the
skeletonization algorithm.
```math
\begin{bmatrix}
\mathbf{S} \circ \mathbf{W_L} \mathbf{L}\\
\mathbf{W_H}
\end{bmatrix} \mathbf{P}^{'} =
\begin{bmatrix}
\mathbf{0}\\
\mathbf{W_H} \mathbf{P}
\end{bmatrix}
```
Standard LBC is prone to mal-contraction in cases where there is a significant disparity in
diameter between trunk and branches. In such cases fine structures experience an over- contraction and leading to a
distortion of their topological characteristics. In order to address these topological artifacts, we introduce semantic
Laplacian-based contraction (S-LBC). For more information please refer to the [[Paper](https://google.de)].
## 📖 Literature and Code used for implementation
#### Laplacian based contraction
Our implementation
of [Point Cloud Skeletons via Laplacian-Based Contraction](https://taiya.github.io/pubs/cao2010cloudcontr.pdf) is a
python reimplementation of the original [Matlab code](https://github.com/taiya/cloudcontr).
#### Robust Laplacian for Point Clouds
Computation of the discrete laplacian operator
via [Nonmanifold Laplace](http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~kmcrane/Projects/NonmanifoldLaplace/NonmanifoldLaplace.pdf) can be
found in the [robust-laplacians-py](https://github.com/nmwsharp/robust-laplacians-py) repository.
#### Minimum Spanning Tree
The Minimum Spanning Tree is computed via [Mistree](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1910.08562.pdf) a
open-source implementation which can be found [here](https://github.com/knaidoo29/mistree).
## :interrobang: Troubleshooting
For Windows users, there might be issues installing the `mistree` library via `python -m pip install mistree` command.
If you get an error message that the Fortran compiler cannot be found, please try the following:
- Download and install this suite of compilation tools: http://www.equation.com/servlet/equation.cmd?fa=fortran
- Add the `bin` folder in the installation directory to your `PATH` environment variable
- After restarting your terminal and now trying to install `mistree` this should work now.
- However, upon importing the library you might face an issue with missing DLL files. You simply need to copy or move
them within the `mistree` installation directory, as explained
here: https://github.com/knaidoo29/mistree/issues/14#issuecomment-1275022276
- Now the PC-Skeletor should be running on your Windows machine.
## :heavy_exclamation_mark: Limitation / Improvements
- [ ] Implement [Point2Skeleton](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2012.00230.pdf)
- [ ] Implement [L1-Medial Skeleton](https://www.cs.sfu.ca/~haoz/pubs/huang_sig13_l1skel.pdf)
- [ ] Test code
- [ ] Improve graph representation
# 📖 Citation
Please cite this [[Paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.04708)] if this work helps you with your research:
```
@misc{meyer2023cherrypicker,
title={CherryPicker: Semantic Skeletonization and Topological Reconstruction of Cherry Trees},
author={Lukas Meyer and Andreas Gilson and Oliver Scholz and Marc Stamminger},
year={2023},
eprint={2304.04708},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.CV}
}
```


